Learninsta presents the core concepts of Microbiology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Protein Metabolism
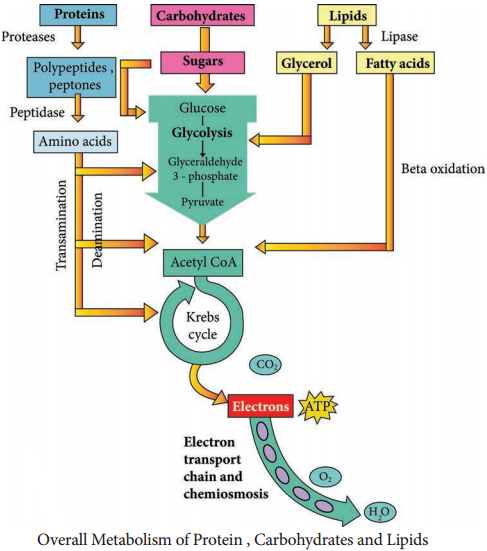
Many microbes use protein as their source of carbon and energy. Pathogenic microorganisms secrete protease enzyme that hydrolyze proteins and polypeptides to amino acids which are then transported into the cell and catabolized.
Protease (Peptidase or proteinase) helps in proteolysis (Figure 4.8). These proteolytic enzymes break the long chains of proteins into peptides and eventually into amino acids. The enzymes are classified based on the sites at which they catalyse the cleavage of proteins as exopeptidase and endopeptidase.
The protein catabolism involves two reactions namely,
- Deamination and
- Transamination
Deamination is the removal of the amino group from an amino acid. Transamination is the transferring of amino group from an amino acid to an amino acid acceptor.
The organic acid resulting from deamination can be converted to pyruvate, acetyl CoA or TCA cycle intermediates to release energy. Excess nitrogen from deamination may be excreted as ammonium ion.