Learninsta presents the core concepts of Microbiology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Food Borne Disease
Food borne disease has been defined by the world health organization (WHO) as a disease of an infectious or toxic nature caused by or thought to be caused by the consumption of food or water.
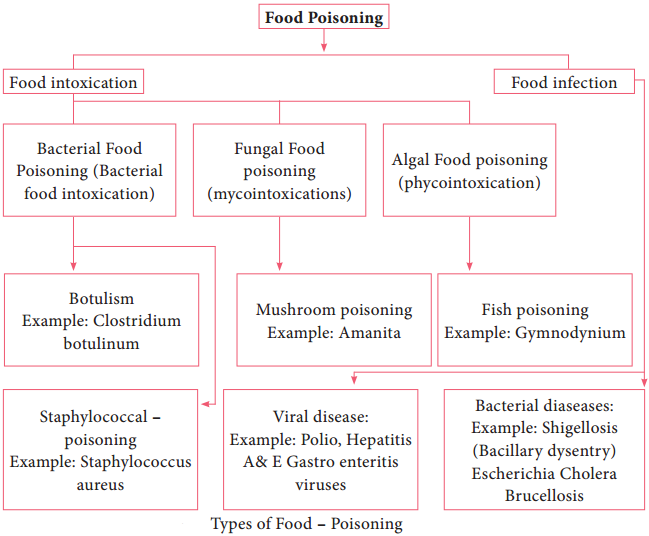
The term “food poisoning” as applied to diseases caused by microorganisms is used very loosely to include both illness caused by the ingestion of toxins elaborated by the organisms and those resulting from infection of the host through the intestinal tract. A further classification of food borne disease is shown in flowchart 5.1.
All these food – borne diseases are associated with poor hygienic practices.
Whether by water or food transmission, the fecal – oral route is maintained, with the food providing the vital link between hosts. Fomites, such as sink faucets, drinking cups, and cutting boards, also play a role in the maintenance of fecal – oral route of contamination.
There are two primary types of food related diseases: food – borne infections and food intoxications or food poisoning.
Food Borne Infection
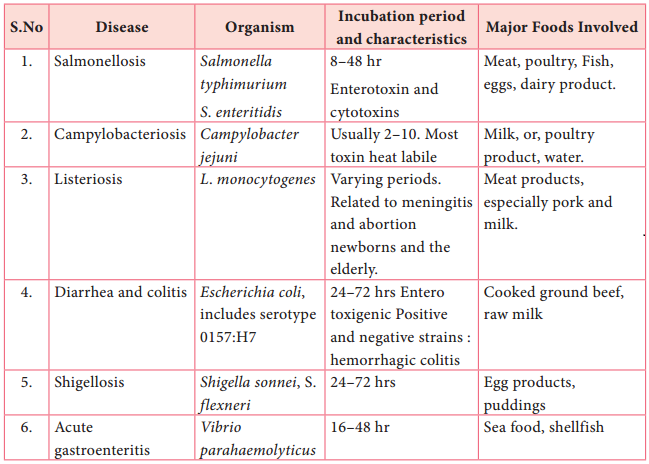
Food borne infection involves the ingestion of the pathogen followed by growth in the host, including tissue invasion and/or the release of toxins. The major diseases of this type are summarized in table (5.1).
Major Food – Borne Infectious Diseases
Food Poisoning
Food borne intoxication (or) food poisonings is caused by ingesting food containing toxins formed by bacteria which resulted from the bacterial growth in the food item. Food poisoning refers to the toxicity introduced into food by microorganisms and their products.
Microbial growth in food products also can results in food intoxication.
Intoxication produces symptoms shortly after the food is consumed because growth of the disease – causing microorganism is not required. Toxins produced in the food can be associated with microbial cells or can be released from the cells.
Food poisoning is caused by various factors as follows.
- Microorganism of plant food products.
- Microorganism of Animal food products.
- Microorganism of processed food.
- Standard chemicals added to the food.
- Excess use of preservatives in food.
- Presence of higher population of Microorganism in food.
- Toxin produced by various types of Microorganism.