Learninsta presents the core concepts of Microbiology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Concept of Gene Microbial
The fundamental unit of information in living systems is the gene. Genome is the set of all genes and genetic signals of a cell. The information contained in genes is converted to molecules that determine the metabolism, structure and form of microorganisms.
Gene is expressed through a sequence of events. A gene can be defined biochemically as a segment of DNA (or, in a few cases, RNA) that encodes the information required to produce a functional biological product.
The final product is usually a protein. Not all genes are involved in protein synthesis; some code instead for rRNA and tRNA. The central dogma of molecular biology, comprises the three major processes (Figure 12.1). The first is replication, the copying of parental DNA to form daughter DNA molecules with identical nucleotide sequences. The information contained in the base sequence of DNA is copied into protein molecule through an RNA molecule.
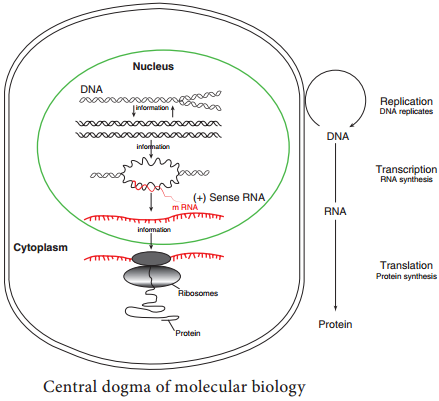
The second is transcription, production of mRNA from DNA. It is the process by which the segment corresponding to a particular gene is selected and an RNA molecule is synthesized. The third is translation, The production of an amino acid sequence from an RNA base sequence. The genetic message encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA) is translated on the ribosomes into a polypeptide with a particular sequence of amino acids. The order of amino acid in a polypeptide chain is determined by DNA base sequence.