Here we are providing Class 12 Chemistry Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 9 Coordination Compounds. Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions are the best resource for students which helps in Class 12 board exams.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Important Extra Questions Coordination Compounds
Coordination Compounds Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Give an example of linkage isomerism. (CBSE Delhi 2010)
Answer:
[Co (NH3)5 (N02)] Cl2 and [Co (NH3)5 (ONO)]Cl2
Question 2.
Give an example of coordination isomerism. (CBSE Delhi 2010)
Answer:
[CO(NH3)6] [Cr(CN)6] and [Cr(NH3)6] [Co (CN)6]
Question 3.
Which of the following is more stable complex and why? (CBSE Delhi and Al 2014)
[CO(NH3)6]3+ and [Co(en)3]3+
Answer:
[Co(en)3]3+ because bidentate ligand (ethylenediamine) forms chelate which is more stable.
Question 4.
A coordination compound with molecular formula CrCl3.4H20 precipitates one mole of AgCl with AgN03 solution. Its molar conductivity is found to be equivalent to two ions. What is the structural formula and name of the compound? (CBSE Sample Paper 2017-18)
Answer:
[CrCl2(H20)4]Cl: Tetraaquadichloridochrom ium(III) chloride.
Question 5.
What is coordination isomerism? Give one example. (CBSE Delhi 2010)
Answer:
Coordination isomerism arises when both the cation and anion are complexes and the ligands are exchanged. For example, [CO(NH3)6] [Cr(CN)6] and [Cr(NH3)6] [Co(CN)6]
Question 6.
Write IUPAC name of the complex [Co(en)2(H20)(CN)]2+
OR
Using IUPAC norms, write the formula of Ammonium tetrafluoride cobaltates (II). (CBSE AI 2019)
Answer:
Aquacyanidobis (ethane-1,2-diamine) cobalt (III) ion
OR
(NH4)2[Co F4]
Question 7.
Write the IUPAC name of the complex K3[Cr(C204)3].
OR
Using IUPAC norms write the formula of Hexaamminecobalt(III) sulphate. (CBSE AI 2019)
Answer:
Potassium trioxalatochromate(III)
OR
[Co(NH3)6]2 (S04)3
Question 8.
Write IUPAC name of the complex [Co(en)2CI2]
OR
Using IUPAC norms, write the formula of Sodium tetrachloridonickelate(II). (CBSE AI 2019)
Answer:
Dichloridobis (ethylenediamine) cobalt(III) ion.
OR
Na2[NlCl4]
Question 9.
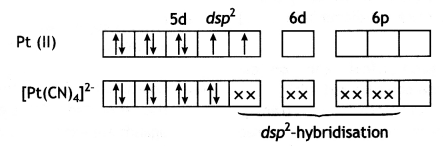
Predict the number of unpaired electrons in the square planar [Pt(CN)4]2- ion. (CBSE 2019C)
Or
Amongst [Fe(C204)3]3- and [Fe(NH3)6]3+ which is more stable and why?
Answer:
The Pt (II) ion has 5d8 electronic configuration. For square planar geometry, dsp2 hybridisation is involved. For this, one empty d-orbital is needed for hybridisation. Therefore, the pairing of electrons takes place in the remaining d-orbitals. Hence, there are no unpaired electrons in [Pt(CN)4]2- ion and it is diamagnetic.
OR
[Fe(C204)3]3- is more stable because it is a chelate. C2042- is a didentate ligand.
When a didentate or a polydentate ligand uses its two or more donor atoms to bind to the same central metal atom or ion forming a ring structure it is called chelation.
The resulting complex has a ring structure and the ligand coordinating through two or more donor groups is called a chelating ligand. Some common examples of chelating ligands are carbonate ion, oxalate ion (ox2-), ethylenediamine (en), ortho-phenanthroline (ph) and ethylenediaminetetraacetate ion (EDTA).
Chelate ligands form more stable complexes than similar ordinary complexes in which the ligand acts as monodentate. This is called a chelate effect.
Coordination Compounds Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
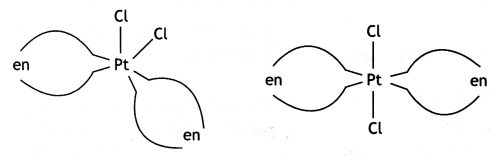
Write IUPAC name of the complex [Pt(en)2Cl2]. Draw structures of geometrical isomers for this complex.
OR
Using IUPAC norms write the formulae for the following:
(i) Hexaamminecobalt(III) sulphate
(ii) Potassium trioxalatochromate(III) (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Dichlorido bis(ethane-1,2-diamine) platinum (II)
Geometrical isomers.
OR
(i) [CO(NH3)6]2(S04)3
(ii) K3[Cr(ox)]3
Question 2.
Out of [COF6]3- and [Co(en)3]3+, which one complex is
(i) paramagnetic
Answer:
[CoF6]3- is paramagnetic due to the presence of 4 unpaired electrons.
(ii) more stable
Answer:
[Co(en)3]3+ is more stable because of chelation.
(iii) inner orbital complex and
Answer:
[Co(en)3]3+ forms inner orbital complex involving d2sp3 hybridisation.
(iv) high spin complex (Atomic no. of Co = 27) (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
[COF6]3- forms a high spin complex (sp3d2 hybridisation).
Question 3.
(i) Write down the IUPAC name of the following complex: (CBSE Delhi 2015)
[Cr(NH3)2Cl2 (en)]Cl
(en = ethylenediamine)
Answer:
Diamminedichlorido(ethane-1,2,- diamine)chromium(III) chloride
(ii) Write the formula for the following complex:
Pentaamminenitrito-O-cobalt (III).
Answer:
[Co(NH3)5 (ONO)]2+
Question 4.
(i) Write down the IUPAC name of the following complex [Co(NH3)5(N02)] (N03)2
Answer:
Pentaamminenitrito-N-cobalt(III) nitrate
(ii) Write the formula for the following complex: Potassium tetracyanonickelate (II) (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
K2[Ni(CN)4]
Question 5.
When a coordination compound CrCl3.6H20 is mixed with AgN03, 2 moles of AgCI are precipitated per mole of the compound. Write (CBSE Delhi 2016)
(i) Structural formula of the complex.
Answer:
For one mole of the compound, two moles of AgCI are precipitated with AgN03, which indicates two ionisable chloride ions in the complex. Hence structural formula is [CrCl(H20)5]Cl2. H20
(ii) IUPAC name of the complex.
Answer:
Pentaaquachloridochromium (III) chloride hydrate
Question 6.
(i) For the complex [Fe(CN)6]3-, write the hybridisation type, magnetic character and spin nature of the complex. (At. number: Fe = 26).
Answer:
[Fe(CN)6]3-:
The oxidation state of Fe = +3
Fe(III)
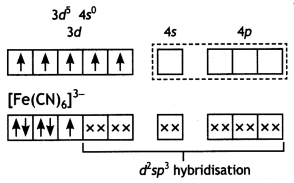
Hybridisation: d2sp3
Magnetic character: Paramagnetic
Spin type: Low spin complex
(ii) Draw one of the geometrical isomers of the complex [Pt(en)2Cl2]2+ which is optically active. (CBSE Delhi 2016)
Answer:
cis- form is optically active
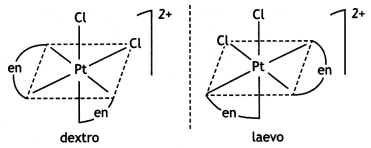
Question 7.
When a coordination compound NiCl2.6H20 is mixed with AgNO3, 2 moles of AgCI are precipitated per mole of the compound. Write (CBSE 2016)
(i) Structural formula of the complex
(ii) IUPAC name of the complex
Answer:
For one mole of the compound, 2 moles of AgCI are precipitated with AgNO3, which indicates 2 ionisable Cl” ions in the complex.
- Structural formula: [Ni (H20)6]Cl2
- IUPAC name: Hexaaquanickel (II) chloride
Question 8.
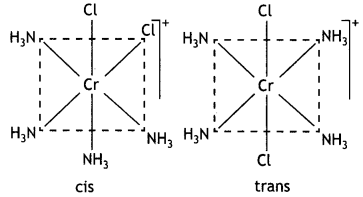
Write IUPAC name of the complex [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]+. Draw structures of geometrical isomers for this complex.
OR
Using IUPAC norms write the formulae for the following:
(i) Pentaamminenitrito-O-cobalt(III) chloride
(ii) Potassium tetracyanidonickelate(II) (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
IUPAC name: Tetramminedichloridochromi um(III) ion.
Geometrical isomers:
OR
(i) [CO(NH3)5(ONO)]Cl2
(ii) K2[Ni(CN)4]
Question 9.
Write the hybridisation and magnetic character of the following complexes:
(i) [Fe(H2O)6]2+
(ii) [Fe(CO)5] (Atomic no. of Fe = 26) (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
[Fe(H20)6]2+
Hybridisation: sp3d2
Magnetic character: Paramagnetic due to 4 unpaired electrons.
Fe(C0)5
Hybridisation: dsp3
Magnetic character: It is diamagnetic.
Question 10.
Draw one of the geometrical isomers of the complex [Pt(en)2Cl2]2+ which is optically inactive. Also, write the name of this entity according to the IUPAC nomenclature.
Or
Discuss the bonding in the coordination entity [Co(NH3)6 ]3+ on the basis of valence bond theory. Also, comment on the geometry and spin of the given entity. (Atomic no. of Co= 27) (CBSE Sample Paper 2019)
Answer:
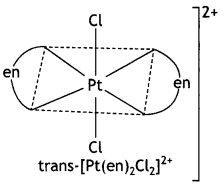
IUPAC Name of the entity:
Dichloridobis(ethane – 1,2-diamine) platinum(IV) ion
Or
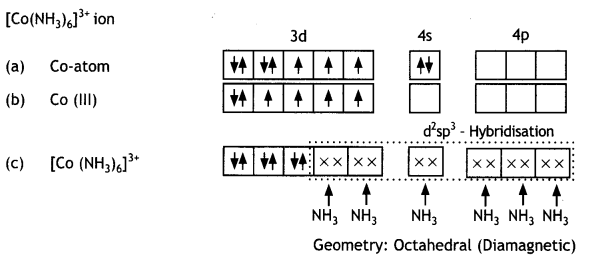
Coordination Compounds Important Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
(a) Draw the structures of geometrical isomers of [Fe(NH3)2 (CN)4]–
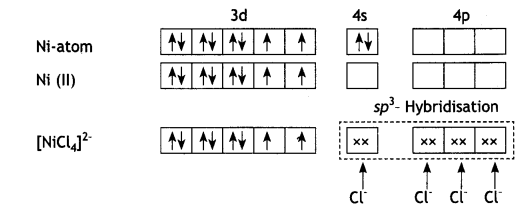
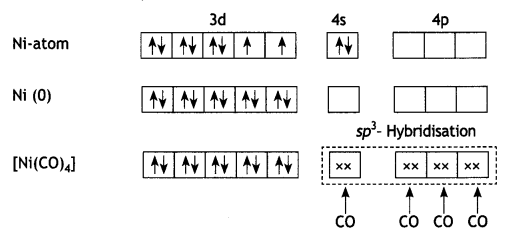
(b) [NiCl4]2- is paramagnetic while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic though both are tetrahedral. Why? [Atomic number of Ni = 28]
OR
Define the following:
(a) Ambidentate ligands
(b) Spectra chemical series
(C) Heteroleptic complexes
Answer:
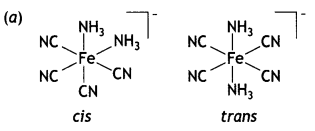
(b) In the presence of strong field ligand CO, the unpaired d-electrons of Ni pair up so [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic but Cl– being a weak ligand is unable to pair up the unpaired electrons, so [Ni(Cl4)]2- is paramagnetic.
and
OR
Answer:
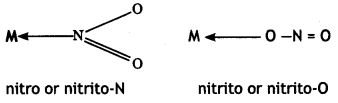
(a) Ambidentate ligands: The monodentate ligands which can coordinate with the central atom through more than one site are called ambidentate ligands.
These ligands contain more than one coordinating atoms in their molecules.
For example, NO2 can coordinate to the metal atom through N or 0 as
Similarly, CN– can coordinate through C or N as
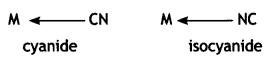
Thiocyanato (SCN) can coordinate through S or N
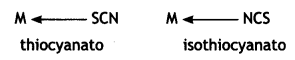
(b) The arrangement of ligands in the increasing order of crystal field splitting is called spectrochemical series. This is shown below:
I– < Br– < SCN– < Cl– < F– < OH– < Ox2- < O2- < H20 < NCS– < py = NH3 <en <NO2– < CN– < CO.
Weak field ligands are those which cause less crystal field splitting. These form high spin complexes. For example, Cl–, F–, etc.
Strong field ligands are those which cause greater crystal field splitting. These form low spin complexes. For example, CN–, NO2–, CO.
(c) The complexes in which the metal is bound to more than one kind of donor groups (ligands) are called heteroleptic complexes. Some common examples of heteroleptic complexes are [NiCl2(H2O)4], [CoCl2(NH3)4]+, etc.
Question 2.
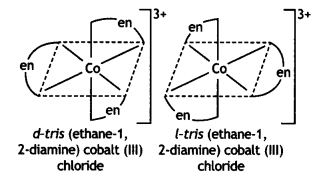
Write the structures and names of all the stereoisomers of the following compounds:
(i) [Co(en)3]Cl3
Answer:
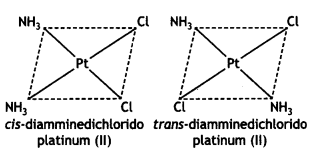
(ii) [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]
Answer:
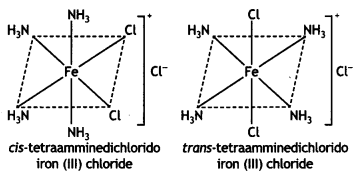
(iii) [Fe(NH3)4Cl2]Cl (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Question 3.
Write the name, stereochemistry and magnetic behaviour of the following:
(i) K4[Mn(CN)6]
(ii) [Co(NH3)2 C1]Cl2
(iii) K2[Ni(CN)4] (CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
| Complex | Name | Stereochemistry | Magnetic behaviour |
| (i) K4[Mn(CN)6] | Potassium hexacyanomanganate (I) | Octahedral | Paramagnetic |
| (ii) [Co(NH3)5Cl]Cl2 | Pentaamminechtorido cobalt (III) chloride | Octahedral | Diamagnetic |
| (iii) K2[Ni(CN)4) | Potassium tetracyanonicketate (II) | Square planar | Diamagnetic |
Question 4.
For the complex [Fe(en)2Cl2]Cl identify the following:
(i) Oxidation number of iron
Answer:
III.
(ii) Hybrid orbitals and shape of the complex
Answer:
d2sp3 hybridisation, octahedral
(iii) Magnetic behaviour of the complex
Answer:
Paramagnetic due to one unpaired electron
(iv) Number of its geometric isomers
Answer:
Two
(v) Whether there may be optical isomer also
Answer:
One optical, an isomer of cls-geometrical isomer.
(vi) Name the complex. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Dichloridobis(ethylenediamine) iron (III) chloride.
Question 5.
Give the formula of each of the following coordination entities:
(i) CO3+ ion is bound to one Cl–, one NH3 molecule and two bidentate ethylene diamine (en) molecules.
(ii) Ni2+ ¡on is bound to two water molecules and two oxalate ions. Write the name and magnetic behaviour of each of the above coordination entitles. (At. nos. CO = 27, Ni = 28) (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
(i) [Co(NH3) (Cl) (en)2]2+ Amminechtoriðo bls-(ethane -1, 2-diamine) cobalt (III) ion Co(27):
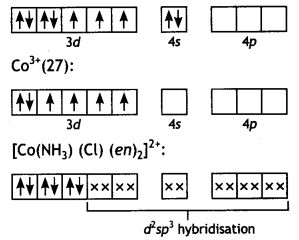
Since there are no unpaired electrons,
complex is diamagnetic.
(ii) [Ni(H2O)2 (C2O4)2]2- Diaquadioxatatonickelate (II) ion Ni(28):
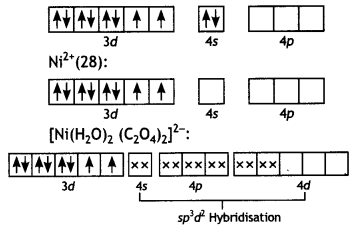
The complex has two unpaired electrons, therefore, it will be paramagnetic.
Question 6.
State a reason for each of the following situations:
(i) CO2+ is easily oxidised to CO3+ in presence of a strong ligand.
Answer:
The configuration of CO2+ is t2g6 eg1 and for CO3+, it is t2g6. The crystal field stabilisation energy is more than compensated for the third ionisation enthalpy. Therefore, CO2+ is easily oxidised to CO3+ in the presence of a strong ligand.
(ii) CO is a stronger complexing reagent than NH3.
Answer:
CO is a stronger complexing ligand than NH3 because it contains both σ and π character and can form a back bond (M → CO) also. Therefore, CO forms a stronger bond with the metal. It is also called a strong field ligand.
(iii) The molecular shape of Ni(CO)4 is not the same as that of [Ni(CN)4]2-. (CBSE Delhi 2012)
Answer:
The molecular shape of [Ni(C0)4] is tetrahedral because this complex nickel involves sp3 hybridisation. In [Ni(CN)4]2-, nickel involves dsp2 and its shape is square planer.
Question 7.
Name the following coordination entities and draw the structures of their stereoisomers:
(i) [Co(en)2Cl2]+(en = ethane-1, 2-diamine)
Answer:
(Co(en)2Cl2]+
Name: Dichloridobis (ethane-1, 2-diamine) cobalt(III) ion. It shows two geometrical isomers cis- and trAnswer:c/s-shows optical isomerism.
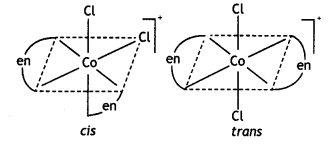
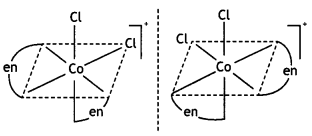
c/s-[Co(en)2Cl2]+ is optically active.
(ii) [Cr(C204)3]3-
Answer:
[Cr(C204)3]3-
Name: trioxalatochromate(III) ion. This complexion shows optical isomerism and their dextro and laevo forms are shown below:
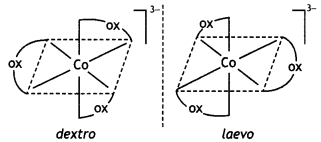
(iii) [CO(NH3)3Cl3]
(Atomic numbers Cr = 24, CO = 27) (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
[Co(NH3)3Cl3]
Name Triamminetrichloridocobalt (III) It shows two geometrical isomers known as facial (fac) and meridional or merisomer as shown below:
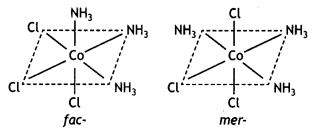
Question 8.
Name the following coordination entities and describe their structures:
(i) [Fe(CN)6]4-
(ii) [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]+
(iii) [Ni(CN)4]2-
(Atomic numbers Fe = 26, Cr = 24, Ni = 28) (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
(i) [Fe(CN)6]4-: Hexacyanoferrate (II) ion.
Structure. In this case, iron is in a +2 oxidation state having the outer electronic configuration 3d6. To account for the diamagnetic character, all the electrons get paired leaving two vacant orbitals.
The hybridisation scheme and bonding are as shown below:
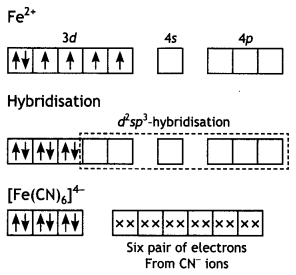
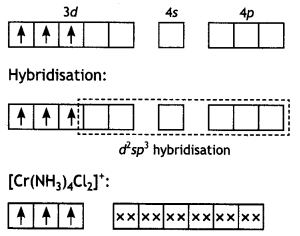
(ii) [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]+: Tetraamminedichlorido chromium (III) ion.
The chromium (Z = 24) has the electronic configuration 3d5 4s1. The chromium in this complex is in + 3 oxidation state and the ion is formed by the loss of one 4s and two of the 3d-electrons as shown in Fig. The inner d-orbitals are already vacant and two vacant 3d, one 4s and three 4p-orbitals are hybridised to form six d2sp3-hybrid orbitals. Six pairs of electrons one from each NH3 molecule and Cl- ions (shown by xx) occupy the six vacant hybrid orbitals. The molecule has octahedral geometry.
Since the complex contains three unpaired electrons, it is paramagnetic.
Cr (III):
(iii) [Ni(CN)4]2-: Tetracyanonickelate (II) ion.

Question 9.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
(i) [Cr(NH3)3Cl3]
Answer:
Triamminetrichloridochromium (III)
(ii) K3[Fe(CN)6]
Answer:
Potassium hexacyanoferrate (III)
(iii) [CoBr2(en)2]+, (en = ethylenediamine) (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
Dibromidobis(ethylenediamine) cobalt (III) ion
Question 10.
Write the types of isomerism exhibited by the following complexes:
(i) [Co(NH3)5Cl]S04
Answer:
ionisation isomerism
(ii) [Co(en)3]3+
Answer:
optical isomerism
(iii) [Co(NH3)6] [Cr(CN)6] (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
coordination isomerism
Question 11.
For the complex [NiCl4]2-, write
(i) the IUPAC name.
(ii) the hybridisation type.
(iii) the shape of the complex (Atomic no. of Ni = 28)
Or
What is meant by crystal field splitting energy? On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration of d4 in terms to f2g and eg in an octahedral field when
(i) Δo > P
(ii) Δo < P (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
(i) Tetrachloridonickelate(II)ion
(ii) sp3 hybridisation
(iii) tetrahedral
OR
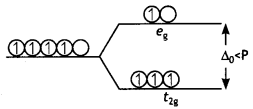
The difference between two sets of energy levels when the five degenerate d-orbitals splits in the presence of the electrical field of Ligands is called crystal field splitting energy. In the octahedral field, it is represented as Δo.
Electronic configurations of d4
- When Δo >P;t2g4
- When Δo < P; t2g3 eg1
Question 12.
Write the IUPAC name of the complex [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]. What type of Isomerism does it exhibit? (CBSE Delhi 2014)
Answer:
Tetraammlnedlchloridochromium( III) ion. It shows cis and trans isomerism and cis form shows optical isomerism.
Question 13.
(i) Write the IUPAC name of the complex [Cr(NH3)4 Cl2] Cl.
(ii) What type of Isomerism is exhibited by the complex [Co(en)3]3+?
(en = ethane-1, 2-diamine)
(iii) Why Is [NIC(412 paramagnetic but [Ni(CO)4] Is diamagnetic?
(At. nos.: Cr = 24, Co = 27, Ni = 28) (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
(i) TetraamminedichLorìdochromium (III) chloride.
(ii) Optical isomerism
(iii) In [NICl4]2- complexion, nickel is in +2 oxidation state and the configuration is 3d8. Since the molecule is tetrahedral, it involves sp3 hybridisation as shown below:
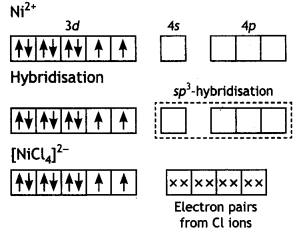
The molecule is paramagnetic because it contains two unpaired electrons. In [Ni(CO)4], nickel is in O oxidation state and has the configuration 4s2 3d8 or 3d10. The molecule is tetrahedral and involves sp3-hybridisation as given below:
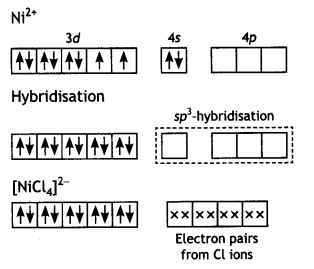
Each CO donates a pair of electrons forming four Ni—CO bond. The compound is diamagnetic since it contains no unpaired electron.
Question 14.
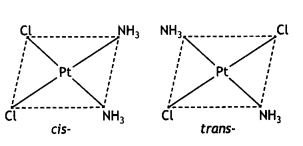
(i) Draw the geometrical isomers of the complex [Pt(NH3)2Cl2].
Answer:
(ii) On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if Δ0 < P.
Answer:
t2g3 eg1
(iii) Write the hybridization and magnetic behaviour of the complex [Ni(CO)4]. (At.no. of Ni = 28) (CBSE Delhi 2015)
Answer:
[Ni(CO)4] involves sp3 hybridization of nickel and the complex is tetrahedral. Magnetic behaviour: Diamagnetic

Question 15.
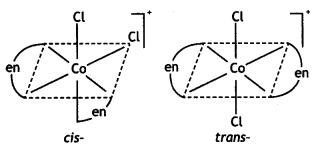
(i) Draw the geometrical isomers of complex [Co(en)2Cl2]+.
Answer:
Geometrical isomers of complex [Co(en)2Cl2]+:
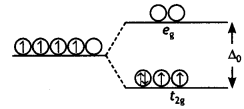
(ii) On the basis of crystal field theory, write the electronic configuration for d4 ion if Δ0 > P.
Answer:
t2g4
(iii) [NiCl4]2- is paramagnetic while [Ni(CO)4] is diamagnetic, though both are tetrahedral. Why? (Atomic number of Ni = 28) (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
In [NiCl4]2- complexion, nickel is in +2 oxidation state and the configuration is 3d8. Since the molecule is tetrahedral, it involves sp3 hybridisation as shown below:
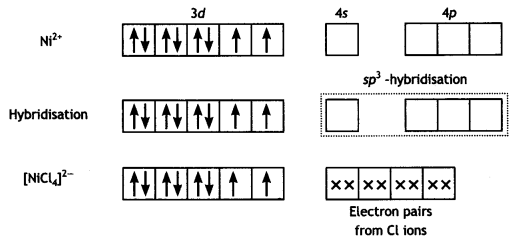
The molecule is paramagnetic because it contains two unpaired electrons.
In [Ni(CO)4], nickel is in 0 oxidation state and has the configuration 4s2 3d4 or 3d10. The molecule is tetrahedral and involves sp3-hybridisation as given below :
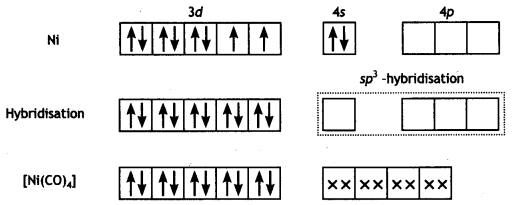
Each CO donates a pair of electrons forming four Ni-CO bonds. The compound is diamagnetic since it contains no unpaired electron.
Question 16.
What type of isomerism is shown by the complex
(i) [Co (NH3)5 (SCN)]2+ (CBSE AI 2017)
Answer:
Linkage isomerism
(ii) [Co (NH3)6] [Cr (CN)6] (CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
Coordination isomerism
(iii) [Co (en)3] Cl3 (CBSE AI 2014)
Answer:
Optical isomerism
Question 17.
A metal ion Mn+ having d4 valence electronic configuration combines with three bidentate ligands to form a complex compound. Assuming Δo > P:
(i) Write the electronic configuration of the d4 ion.
Answer:
t2g4 eg0
(ii) What type of hybridisation will Mn+ ion have?
Answer:
d2sp3
(iii) Name the type of isomerism exhibited by this complex. (CBSE Sample Paper 2017 – 18)
Answer:
Optical isomerism
Question 18.
Write the state of hybridisation, the shape and the magnetic behaviour of the following complex entities :
(a) [Cr(NH3)4Cl2] Cl
(b) [Co(en)3]Cl3
(c) K3[Ni(CN)4] (CBSE AI 2011)
Answer:
| Complex | Hybridisation | Shape | Magnetic behaviour |
| (a) [Cr(NH3)4Cl2]Cl | d2sp3 | Octahedral | Paramagnetic |
| (b) [Co(en)3]Cl3 | d2sp3 | Octahedral | Diamagnetic |
| (c) K2[Ni(CN)4] | dsp2 | Square planar | Diamagnetic |
Question 19.
(a) Give one chemical test as evidence to show that [Co(NH3)5Cl] S04 and [Co(NH3)55(S04)]Cl are ionisation isomers.
Answer:
When [Co(NH3)5(S04)]Cl is treated with silver nitrate solution, a white precipitate of AgCl is formed. But [Co(NH3)5Cl]S04 does not give white ppt with AgN03 solution.
[Co(NH3)5S03 ]Cl+AgN03 (Ag) → AgCl White ppt
[Co(NH3)5 Cl]S04 + AgN03 (Ag) → No white ppt
(b) [NiCl4]2- is paramagnetic while [Ni(C0)4] is diamagnetic though both are tetrahedral. Why? (Atomic no. of Ni = 28)
Answer:
In [NiCl4]2-, the oxidation state of nickel is +2 and it has the electronic configuration: 3d8
![]()
Cl– ion is a weak field ligand and it causes the pairing of electrons. Since it has two unpaired electrons, it is paramagnetic. It undergoes sp3 hybridisation forming a tetrahedral structure.
In Ni (CO)4, the oxidation state of nickel is 0 and it has the electronic configuration: 3d8 4s2. CO is a strong field ligand and therefore, it causes the pairing of electrons as
![]()
Since it has no unpaired electron, it is diamagnetic. It also undergoes sp3 hybridisation resulting in tetrahedral geometry of the complex,
(c) Write the electronic configuration of Fe(III) on the basis of crystal field theory when it forms an octahedral complex in the presence of (i) strong field ligand, and (ii) weak field ligand. (Atomic no. of Fe = 26) (CBSEAI2019)
Answer:
Fe (III): 3d5
(i) Strong field ligand: t2g5 eg0
(ii) Weak field ligand: t2g3 eg2
Question 20.
A metal complex having the composition Cr (NH3)4Cl2Br has been isolated in two forms A and B. Form A reacts with AgN03 to give a white precipitate readily soluble in dilute aqueous ammonia whereas B gives a pale yellow precipitate soluble in concentrated ammonia.
(i) Write the formulae of isomers A and B.
Answer:
Isomer A: [Cr(NH3)4 BrCl]Cl
Isomer B: [Cr (NH3)4 Cl2]Br
(ii) State the hybridisation of chromium in each of them.
Answer:
The hybridisation of Cr in isomer A and B is d2sp3.
(iii) Calculate the magnetic moment (spin only value) of the isomer A. (CBSE Sample Paper 2018)
Answer:
The number of unpaired electrons in Cr3+(3d3) is 3.
Magnetic moment = \(\sqrt{n(n+2)}\)
= \(\sqrt3(3 + 2)\) = 3.87 BM
Question 21.
(a) Write the formula of the following coordination compound: Iron(III) hexacyanoferrate(II)
Answer:
Fe4[Fe (CN)6]3
(b) What type of isomerism is exhibited by the complex [Co(NH3)5Cl]S04?
Answer:
Ionisation isomerism
(c) Write the hybridisation and number of unpaired electrons in the complex [COF6]3-. (Atomic No. of Co = 27) (CBSE 2018)
Answer:
sp3d2, 4
Question 22.
Write the IUPAC names of the following :
(a) [Ag(NH3)2][Ag(CN)2]
Answer:
diamminesilver(I)
dicyanidoargentate(I)
(b) K3[Fe(C204)3]
Answer:
potassium trioxalatoferrate(III)
(c) [CoCl2(en)2]Cl
Answer:
dichloridobis (ethane-1, 2-diamine) cobalt (III) chloride
(d) K3[Cr(C204)3]
Answer:
potassium trioxalatochromate(III)
(e) K4[Ni(CN)4]
Answer:
potassium tetracyanidonickelate (0)
(f) [Pt(NH3)2Cl(N02)]
Answer:
diamminechloridonitrito-N-platinum(II)
(g) [CoBr2(en)2]+ (CBSE Delhi 2012)
Answer:
dibromidobis (ethylenediamine) cobalt(III) ion
(h) [Co(NH3)5ONO]Cl2
Answer:
pentaamminenitrito-O-cobalt(III) chloride
(i) [Co(NH3)5(N02)](N03)2 (CBSE Al 2015)
Answer:
pentaamminenitrito-N-cobalt(III) nitrate
(j) [Cr(NH3)2Cl2 (en)]Cl (CBSE Delhi 2015)
Answer:
diamminedichlorido(ethane-1, 2-diamine)chromium (III) chloride
Question 23.
Write the formulae of the following coordination compounds:
(a) hexaamminecobalt(III) sulphate
Answer:
[CO(NH3)6]2(S04)3
(b) potassium tetrachloridopalladate(II)
Answer:
K2[PdCl4]
(c) diamminechloridonitrito -N- platinum(II)
Answer:
[Pt(NH3)2Cl(N02)]
(d) pentaamminenitrito -N- cobalt(III)
Answer:
[CO(N02)(NH3)5]2+
(e) pentaamminenitrito – 0- cobalt(III) (CBSE Delhi 2015)
Answer:
[CO(ONO)(NH3)5]2+
(f) sodium dicyanidoaurate(I) (CBSE AI 2017)
Answer:
Na [Au (CN)2]
(g) tetraamminechloridonitrito-N- platinum(IV) sulphate (CBSE AI 2017)
Answer:
[Pt(NH3)4Cl (N02)] S04
(h) potassium tetracyanidonickelate(II) (CBSE AI 2015)
Answer:
K2[Ni(CN)4]
(i) potassium trioxatatachromate(III)
Answer:
K3[Cr(ox)3]
(j) tetracarbonylnickel(O)
Answer:
[Ni(C0)4]
Question 24.
Write IUPAC names of the following :
(i) K3[AI(C204)3]
Answer:
Potassium trioxalatoaluminate (III)
(ii) [Ni(CO)4]
Answer:
tetracarbonylnickel(O)
(iii) Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3
Answer:
iron hexacyanidoferrate(III)
(iv) [CoCI(NH3)5]Cl2
Answer:
pentaamminechloridocobalt (III) chloride
(v) [PtCl2(C5H5N)(NH3)]
Answer:
amminedichlorido (pyridine) platinum(II)
(W) Na[PtBrCI(N02)(NH3)]
Answer:
sodium amminebromidochloridonitri- to-N-platinate(II)
(v/i) [Cr(NH3)3Cl3] (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
triamminetrichloridochromium (III)
(viii) K3[Fe(CN)6] (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
potassium hexacyanoferrate (III)
(ix) Na3[AlF6]
Answer:
sodium hexafluoridoaluminate (III).
(x) [Co(en)3]2(S04)3 (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
tris(ethylenediamine)cobalt(III) sulphate
Question 25.
For the complex [Fe(en)2Cl2]Cl, identify the following:
(i) Oxidation number of iron.
Answer:
III.
(ii) Hybrid orbitals and shape of the complex.
Answer:
d2sp2 hybridisation, octahedral.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour of the complex.
Answer:
Paramagnetic due to one unpaired electron.
(iv) Number of its geometrical isomers.
Answer:
Two.
(v) Whether there may be optical isomer also?
Answer:
An optical isomer of cis-geometrical isomer.
(vi) Name of the complex. (CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
Dichloridobis (ethane-1, 2-diamine) iron (III) chloride.