Here we are providing Class 12 Chemistry Important Extra Questions and Answers Chapter 13 Amines. Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions are the best resource for students which helps in Class 12 board exams.
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 13 Important Extra Questions Amines
Amines Important Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1.
Arrange the following in decreasing order of solubility in water:
(CH3)3N, (CH3)2H, CH3NH2 (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
CH3NH2 > (CH3)2NH > (CH3)3N
Question 2.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their solubility in water:
C6H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH, C2H5NH2 (CBSE Delhi 2011, CBSE 2013)
Answer:
C6H5NH2 < (C2H5)2NH < C2H5NH2
Question 3.
Write the structure of n-methylhexanamine. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
CH3 – NH – CH2CH3
Question 4.
Write the structure of 2-amino toluene. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
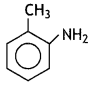
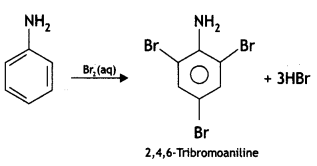
Question 5.
Write the IUPAC name of the given compound: (CBSE Delhi 2016)
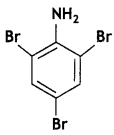
Answer:
2, 4, 6-Tribromoaniline
Question 6.
Arrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength in an aqueous solution:
CH3NH2, (CH3)3N, (CH3)2NH (CBSE Delhi 2013)
Answer:
(CH3)3N < CH3NH2 < (CH3)2NH
Question 7.
Write the IUPAC name of the compound (CBSE Delhi 2014)
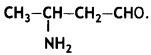
Answer:
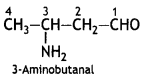
Question 8.
Arrange the following in increasing order of base strength in the gas phase:
(C2H5)3N, C2H5NH2, (C2H5)2NH (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
(C2H5)3N > (C2H5)2NH > C2H5NH2
Question 9.
Arrange the following in increasing order of boiling points:
(CH3)3N, C2H5OH, C2H5NH2 (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
(CH3)3N < C2H5NH2 < C2H5OH
Question 10.
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their pKb values.
C6H5NH2, C2H5NH2, C6H5NHCH3 (CBSE AI 2018)
Answer:
C2H5NH2 < C6H5NHCH3 < C6H5NH2
Question 11.
Write IUPAC name of the following compound:
CH3NHCH(CH3)2 (CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
N-Methylpropan-2-amine
Question 12.
Write IUPAC name of the following compound: (CH3CH2)2NCH3 (CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
N-Ethyl-N-methylhexanamine
Question 13.
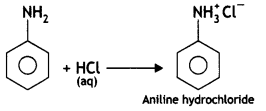
Give a chemical test to distinguish between ethylamine and aniline. (CBSE AI 2011)
Answer:
Aniline gives azo dye test while ethylamine does not give azo dye test.
Question 14.
Arrange the following in increasing order of their basic strength:
C6H5NH2, C6H5N(CH3)2, (C6H5)2NH, and CH3NH2 (CBSE AI 2011)
Answer:
(C6H5)2 NH < C6H5NH2 < C6H5N (CH3)2 < CH3NH2
Question 15.
Write the IUPAC name of the compound: (CBSE AI 2016)
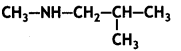
Answer:
N-Methyl-2-methyl propanamine
Amines Important Extra Questions Short Answer Type
Question 1.
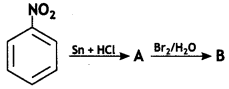
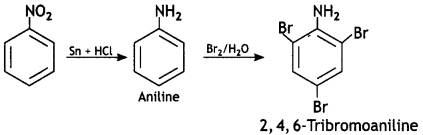
Give the structures of A, B, and C in the following reactions: (CBSE Delhi 2013)
![]()
Answer:
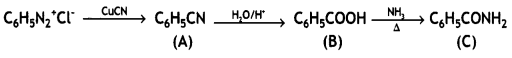
![]()
Answer:
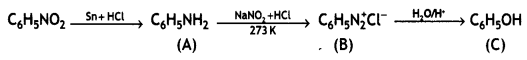
Question 2.
Complete the following reaction equations:
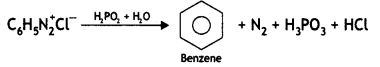
(i) C6H5N2CI + H3PO2 + H20 →
Answer:
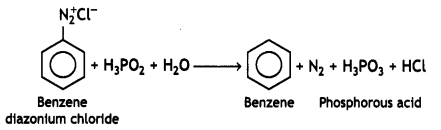
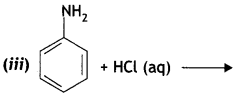
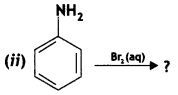
(ii) C6H5NH2 + Br2(oq) → (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
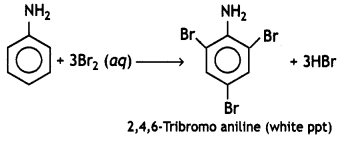
Question 3.
Give the structures of products A, B, and C in the following reactions: (CBSE Delhi 2013)
![]()
Answer:
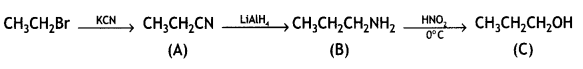
![]()
Answer:
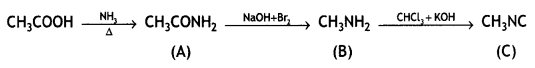
Question 4.
Write the structures of A, B, and C in the following reactions: (CBSE 2016)
![]()
Answer:
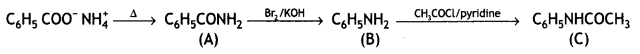
![]()
Answer:
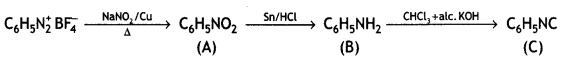
Question 5.
Write the structures of A, B, and C In the following: (CBSE Delhi 2016)
![]()
Answer:
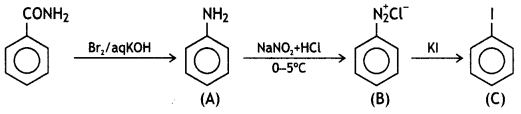
![]()
Answer:
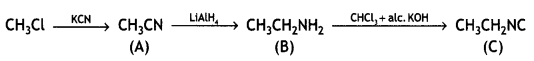
Question 6.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between ethylamine and aniline. (CBSE AI 2011)
Answer:
These can be distinguished by the azo dye test. Dissolve the compound in a cone. HCl and add an ice-cold solution of HNO2 (NaNO2 + dil. HCl) and then treat it with an alkaline solution of 2-naphthol. The appearance of brilliant orange or red dye indicates aniline.
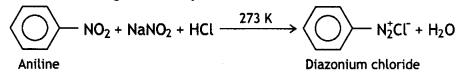
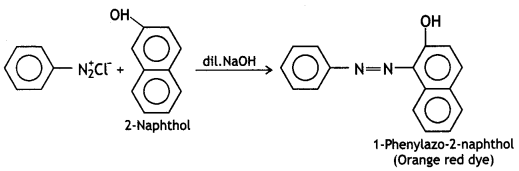
Ethylamine does not form a dye. It will give brisk effervescence due to the evolution of N2 but the solution remains clear.
Question 7.
How will you distinguish between the following? Give one chemical test:
(i) Aniline and benzylamine
Answer:
These can be distinguished by the azo dye test. Aniline reacts with HNO2 (NaNO2 + dil. HCl) at 273-278K to form stable benzene diazonium chloride which on treatment with an alkaline solution of 2-naphthol gives an orange dye (as given above).
Benzylamine does not give azo dye tests.
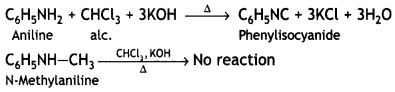
(ii) Aniline and N-methylaniline. (CBSE AI 2010)
Answer:
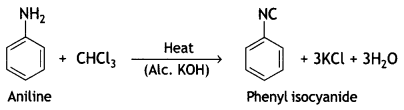
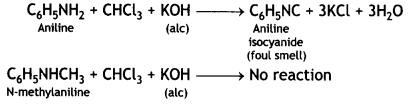
These can be distinguished by carbylamine test. Aniline being primary amines gives carbylamine test, i.e. when heated with an alcoholic solution of KOH and CHCl3, it gives the foul smell of phenyl isocyanide.
Question 8.
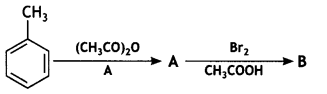
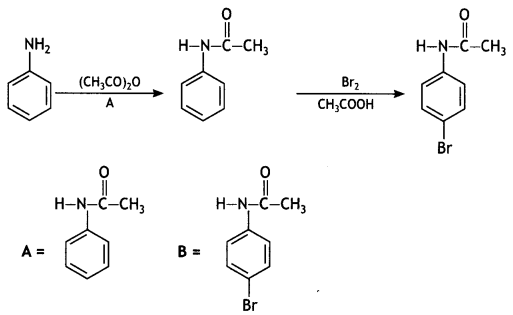
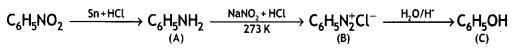
An aromatic compound ‘A’ on treatment with aqueous ammonia and heating forms compound ‘B’ which on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound ‘C’ of molecular formula C6H7N. Write the structures and IUPAC names of compounds A, B, and C. (CBSE Sample Paper 2011)
Answer:
(i) Since the compound C of molecular formula C6H7N is formed from B on treatment with Br2 and KOH (Hoffmann bromamide reaction), therefore, the compound ‘B’ must be an amide and ‘C’ must be an amine. The only aromatic amine having molecular formula C6H7N is C6H5NH2 (aniline).
(ii) Since ‘C’ is aniline, the amide from which it is formed must be benzamide (C6H5CONH2).
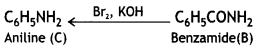
Thus, B is benzamide.
(iii) Since B is formed from A with aqueous ammonia and heating, therefore, compound ‘A’ must be benzoic acid.
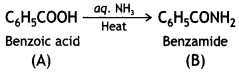
Thus, A = C6H5COOH, B = C6H5CONH2, C = C6H5NH2.
Question 9.
Account for the following:
(a) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is not preferred for preparing aromatic primary amines.
Answer:
Gabriel phthalimide synthesis is not preferred for preparing aryl amines because aryl halides do not undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction with phthalimide.
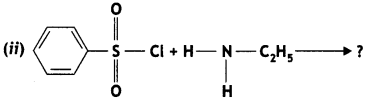
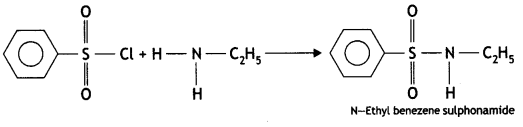
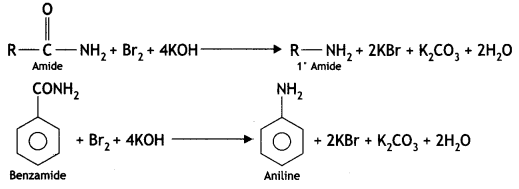
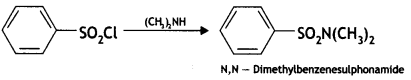
(b) On reaction with benzene sulphonyl chloride, primary amine yields product soluble in alkali whereas secondary amine yields product insoluble in alkali. (CBSE Al 2019)
Answer:
Answer:
The sulphonamide formed by the reaction of secondary amine and benzene sulphonyl chloride does not contain any hydrogen atom attached to the N atom, so it is not acidic.
Therefore, it is insoluble in alkali.
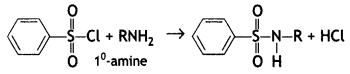
Due to the presence of ‘H’ on nitrogen, it is soluble in alkali.
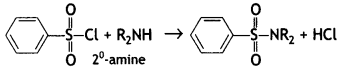
Since there is no ‘H’ on nitrogen, it is insoluble in alkali.
Amines Important Extra Questions Long Answer Type
Question 1.
Write equations of the following reactions:
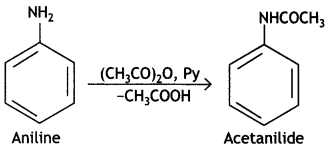
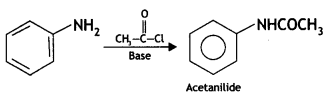
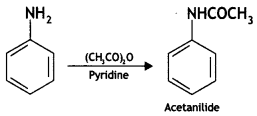
(i) Acetylation of Aniline
Answer:
Acetylation of Aniline:
(ii) Coupling reaction
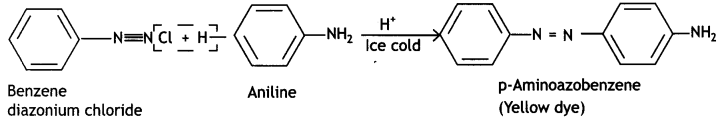
Answer:
Coupling reaction:
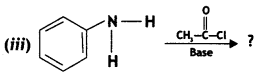
(iii) Carbylamine reaction (CBSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
Carbylamine reaction:
![]()
Question 2.
An aromatic compound ‘A’ on heating with Br2 and KOH forms a compound ‘B’ of molecular formula C6H7N which on reacting with CHCl3 and alcoholic KOH produces a foul-smelling compound ‘C’.
Write the structures and IUPAC names of compounds A, B, and C. ((SSE Delhi 2019)
Answer:
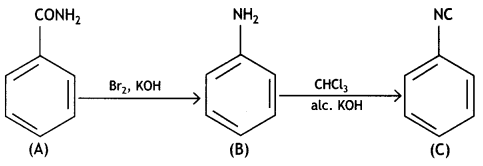
A: C6 H5CONH2: Benzamide B: C6H5NH2: Benzenamine C: C6H5NC: Phenyt isocyanide
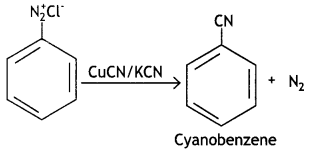
Question 3.
Write the structures of main products when benzene diazonium chloride reacts with the following reagents: (CBSE Delhi 2019)
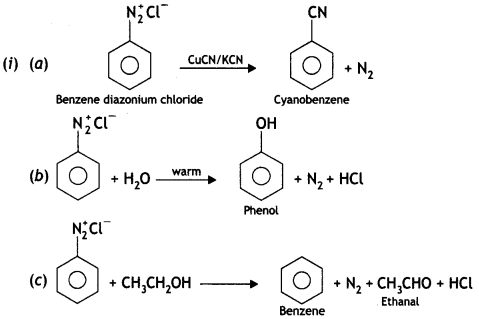
(i) CuCN
Answer:
(ii) CH3CH2OH
Answer:
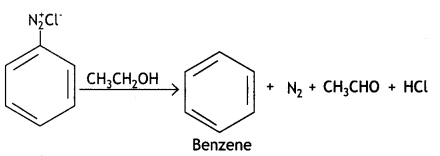
(iii) Kl
Answer:
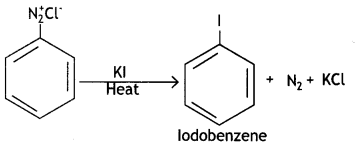
Question 4.
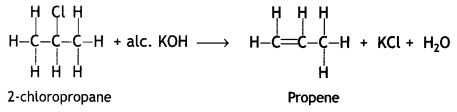
(a) Write the product formed when
(i) 2-chioropropane is treated with aic. KOH.
Answer:
(ii) Aniline reacts with conc. H2SO4 at 453 – 473 K.
Answer:
Sulphonation: Sulphonation of aniline is carried out by heating aniline with sulphuric acid. The product formed is anilinium hydrogen sulfate which on heating gives sulphanilic acid.
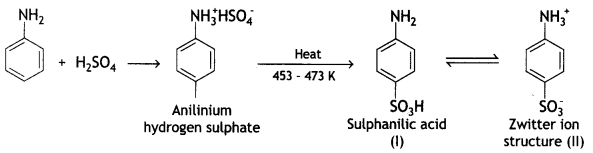
The sulphanilic acid exists as a dipolar ion (structure II) which has acidic and basic groups in the same molecule. Such ions are called Zwitter ions or inner salts.
(b) When aniline is heated with CHCl3 and aic. KOH, a foul-smelling compound is formed. What is this compound? (CBSE 2019C)
Answer:
Pheriyt isocyanide is formed.
Question 5.
(a) Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’ In the following reaction:
Answer:
(b) Why does aniline not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction? (CBSE 2019C)
Answer:
Aniline being a Lewis base reacts with Lewis acid such as AlCl3 to form a salt.
![]()
As a result, N of aniline acquires +ve charge and hence it acts as a strong deactivating group for electrophilic substitution reaction. Hence aniline does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
Question 6.
Complete the following reactions: (CBSE 2013)
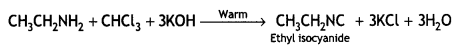
(i) CH3CH2NH2 + CHCl3 + ale. KOH →
Answer:

(ii) C6H5N2+Cl– →
Answer:
Answer:
Question 7.
Write the main products of the following reactions: (CBSE 2013, CBSE AI 2013)
![]()
Answer:
Answer:
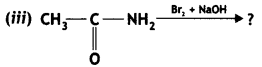
Answer:
Question 8.
Write the main products of the following reactions: (CBSE 2013)
![]()
Answer:
![]()
Answer:
Answer:
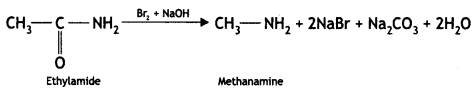
Question 9.
Account for the following:
(i) Primary amines (R-NH2) have a higher boiling point than tertiary amines (R3N).
(ii) Aniline does not undergo Friedel — Crafts reaction.
(iii) (CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N in an aqueous solution.
OR
Give the structures of A, B, and C in the following reactions: (CBSE 2014)
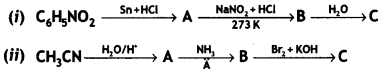
Answer:
(i) Primary amines (RNH2) have two hydrogen atoms on the N atom and therefore, form intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
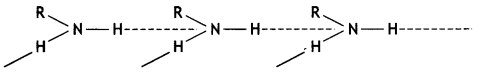
Tertiary amines (R3N) do not have hydrogen atoms on the N atom and therefore, these do not form hydrogen bonds. As a result of hydrogen bonding in primary amines, they have higher boiling points than tertiary amines of comparable molecular mass. For example, b.p. of n-butylamine is 351 K while that of tert-butylamine is 319 K.
(ii) Aniline being a Lewis base reacts with Lewis acid such as AlCl3 to form a salt.
![]()
As a result, N of aniline acquires +ve charge and hence it acts as a strong deactivating group for electrophilic substitution reactions. Hence aniline does not undergo Friedel Crafts reaction.
(iii) Due to the presence of lone pair of electrons on the N atom, amines are basic in nature. The methyl group is the electron releasing group (+I inductive effect) and therefore, it increases the electron density on the N atom, and therefore, basic character increases, so that (CH3)3N should be more basic than (CH3)2NH. But tertiary ammonium ion formed from tertiary amines is less hydrated than secondary ammonium ion formed from secondary amine. Therefore, (CH3)3N has less tendency to form ammonium ion, and consequently, it is less basic than (CH3)2NH. Thus, (CH3)2NH is more basic than (CH3)3N due to the combined effect of inductive effect and hydration effect.
OR
Question 10.
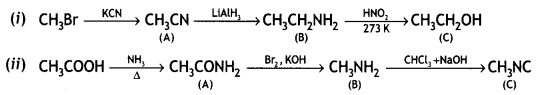
Give the structures of A, B, and C in the following reactions:
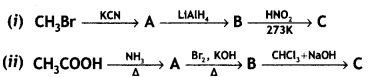
OR
How will you convert the following:
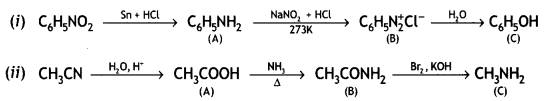
(i) Nitrobenzene into aniline
(ii) Ethanoic acid into methanamine
(iii) Aniline into N-phenylethylamine
(Write the chemical equations involved.) (CBSE Delhi 2014)
Answer:
OR
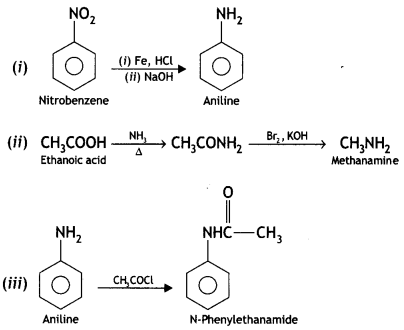
Question 11.
Write chemical equations for the following conversions:
(i) Nitrobenzene to benzoic acid.
Answer:
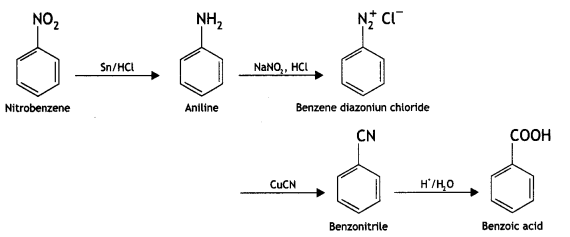
(ii) Benzyl chloride to 2-phenytethanamine.
Answer:
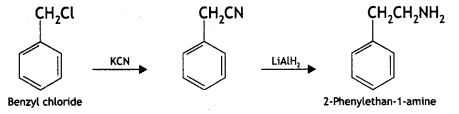
(iii) Aniline to benzyl alcohol. (CBSE Delhi 2012)
Answer:
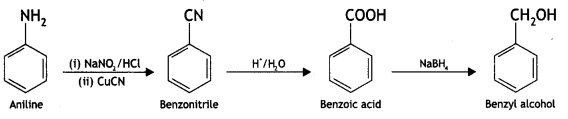
Question 12.
(a) Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’ in the following reaction:
Answer:
(b) Why is ethylamine soluble in water whereas aniline is not?
Answer:
Ethylamine dissolves in water due to intermolecular hydrogen bonding as shown below:
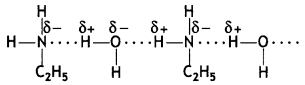
However, because of the large hydrophobic part (i.e. hydrocarbon part) of aniline, the extent of hydrogen bonding is less and therefore, aniline is insoluble in water.
Question 13.
(a) Identify X and Y in the following:
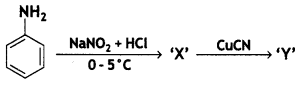
Answer:
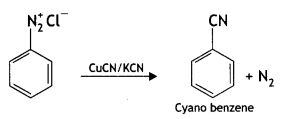
X =
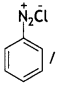 benzene diazonium ch(orlde,
benzene diazonium ch(orlde,
Y =
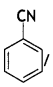 Cyanobenzene
Cyanobenzene
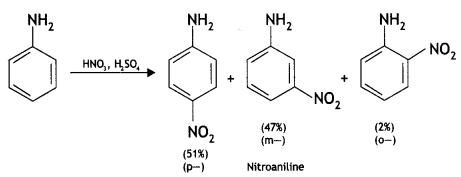
(b) Amino group is o, p-directing for aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions. Why does aniline on nitration give m-nitroaniline? (CBSE 2019C)
Answer:
Under strongly acidic conditions of nitration, most of the aniline is converted into anilinium ion having an NH3+ group. This group is an m-directing group, therefore, m-nitro aniline is also obtained along with o- and p-products.
Question 14.
Give the structures of A, B, and C in the following reactions: (CBSE Delhi 2013)
![]()
Answer:
![]()
![]()
Answer:
Question 15.
Do as directed:
(i) Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their basic strength in an aqueous solution:
CH3NH3, (CH3)3N, (CH3)2NH.
Answer:
(CH3)3N < CH3NH2 < (CH3)2 NH
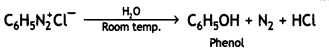
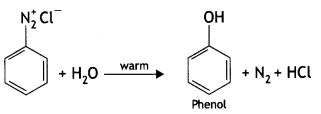
(ii) Identify ‘A’ and ‘B’:
![]()
Answer:
A: C6H5N2+ Cl- B: C6H5OH
(iii) Write the equation of carbylamine reaction. (CBSE 2018C)
Answer:
![]()
Question 16.
(i) Illustrate the following reactions giving a suitable example in each case:
(a) Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction
(b) Diazotisation
(c) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
(ii) Distinguish between the following pairs of compounds:
(a) Aniline and N-methylaniline
(b) (CH3)2NH and (CH3)3N
OR
(i) Write the structures of main products when benzene diazonium chloride (C6H5N2+Cl–) reacts with the following reagents:
(a) CuCN/KCN
(b) H20
(c) CH3CH2OH
(ii) Arrange the following:
(a) C2H5NH2, C2H5OH, (CH3)3N – in the increasing order of their boiling point.
(b) Aniline, p-nitroaniline, p-methyl aniline – in the increasing order of their basic strength. (CBSE Delhi 2015)
Answer:
(i) (a) Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction: Primary amines can be prepared from amides by treatment with Br2 and KOH solution. The amine formed contains one carbon atom less than the parent amide.
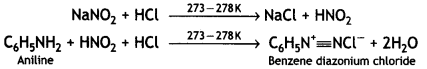
(b) Diazotisation: The reaction of aniline or other aromatic amines, with nitrous acid at 0-5 °C to form diazonium salts is called diazotization. Nitrous acid needed for this reaction is prepared in situ by the action of dil. HCl on NaNO2.
(c) Gabriel’s phthalimide synthesis. This method is used for preparing only primary amines. In this method, phthalimide is treated with alcoholic KOH to give potassium phthalimide, which is treated with an alkyl halide or benzyl halide to form N-alkyl or aryl phthalimide. The hydrolysis of N-alkyl phthalimide with 20% HCl under pressure or refluxing with NaOH gives primary amine.
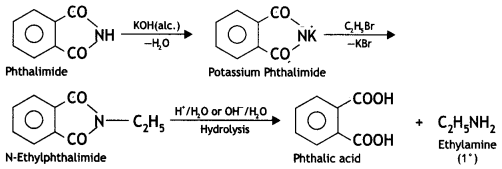
Phthalic acid can again be converted into phthalimide and is used again and again. This method is very useful because it gives pure amines. Aryl halides cannot be converted to arylamines by Gabriel synthesis because they do not undergo nucleophilic substitution with potassium phthalimide.
(ii) (a) Add an alcoholic solution of KOH and CHCl3 to the compounds. Aniline gives the foul smell of isocyanide whereas N-methyl aniline does not give a foul smell.
(b) When treated with Hinsberg’s reagent (benzene sulphonyl chloride, C6H5SO2CI), dimethylamine, (CH3)2NH gives precipitate which is insoluble in aqueous KOH.
![]()
(CH3)3N does not react with Hinsberg’s reagent.
Or
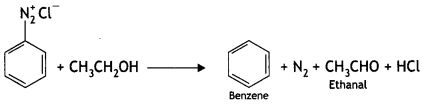
(ii) (a) (CH3)2 N < C2H5NH2 < C2H5OH
(b) p-nitroaniline < aniline < p-methylaniline
Question 17.
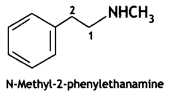
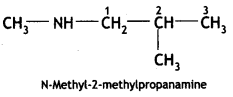
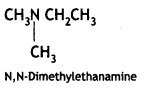
Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds:
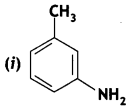
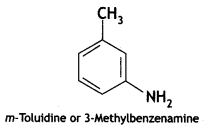
Answer:
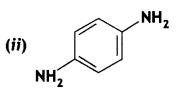
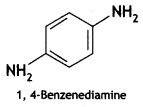
Answer:
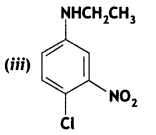
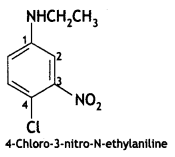
Answer:
Answer:
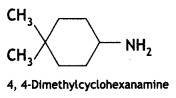
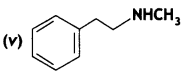
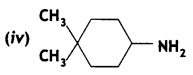
Answer:
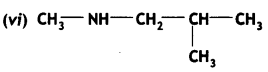
Answer:
![]()
(CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
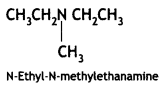
![]()
(CBSE Delhi 2017)
Answer:
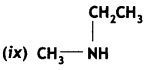
Answer:
![]()
Question 18.
Complete the following reactions:
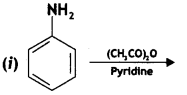
Answer:
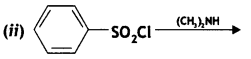
Answer:
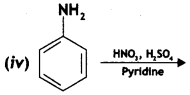
![]()
Answer:

Answer:
![]()
Answer:

Question 19.
Write the main products when benzene diazonium chloride (C6H5N2+Cl–) reacts with the following:
(i) CuCN/KCN
Answer:
(ii) H20
Answer:
(iii) CH3CH2OH (CBSE AI 2015, 2018)
Answer:
(iv) Copper powder/HCI
Answer:
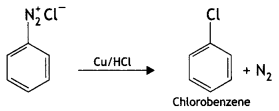
Question 20.
Complete the following chemical equations:
![]()
(CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
![]()
![]()
(CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
![]()
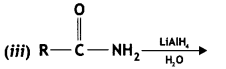
(CBSE Delhi 2011)
Answer:
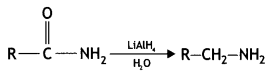
![]()
(CBSE AI 2013)
Answer:
![]()
(CBSE AI 2013)
Answer:
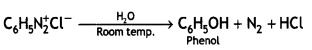
![]()
(CBSE AI 2013)
Answer:
Answer:
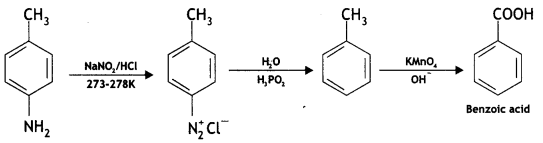
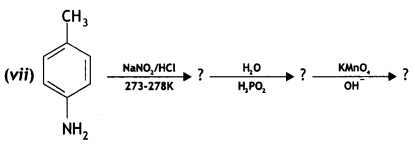
Question 21.
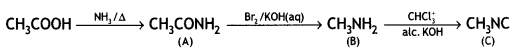
Give the structures of A, B, and C In the following reactions:
![]()
(CBSE AI 2017)
Answer:
![]()
(CBSE AI 2017)
Answer:
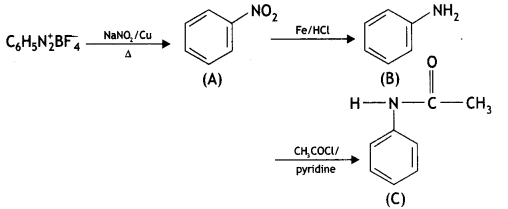
![]()
(CBSE Delhi 2016)
Answer:
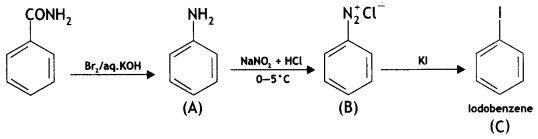
![]()
(CBSE Delhi 2016)
Answer:
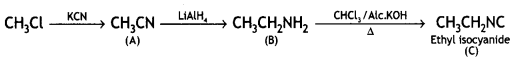
![]()
(CBSE AI 2016)
Answer:
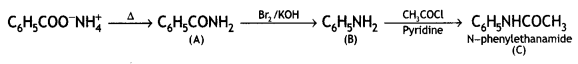
![]()
(CBSE AI 2016)
Answer:
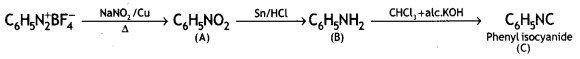
![]()
Answer:
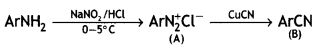
Question 22.
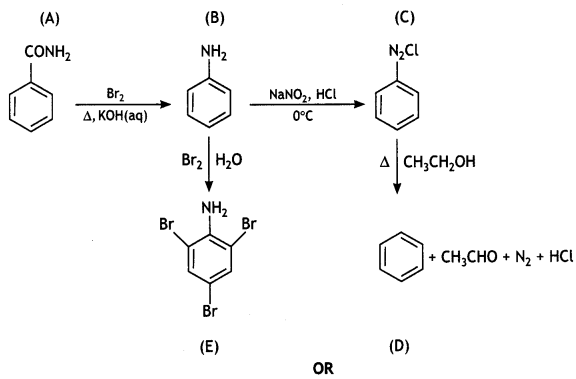
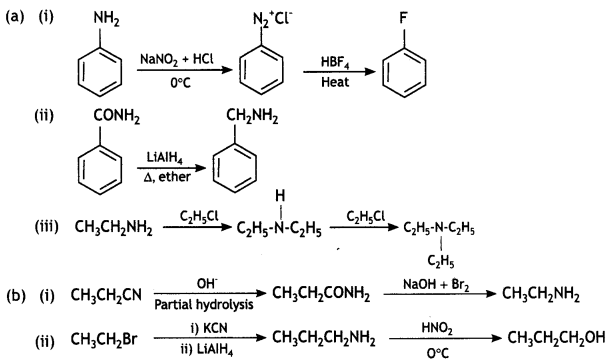
An organic compound A’ with molecular formula C7H7NO reacts with Br2/aq KOH to give compound B’, which upon reaction with NaNO2 and HCI at OC gives C’. Compound C’ on heating with CH3CH2OH gives a hydrocarbon D’. Compound B’ on further reaction with Br2 water gives a white precipitate of compound E’. Identify the compounds A, B, C, D, and E; also justify your answer by giving relevant chemical equations. (CBSE Sample Paper 2019)
OR
(a) How will you convert:
(i) Aniline into Fluorobenzene?
(ii) Benzamide into Benzylamine?
(iii) Ethanamine into N, N-Diethylethanamine?
(b) Write the structures of A and B in the following:
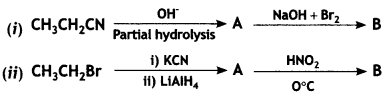
Answer: