Chapter 14 Sources of Energy Class 10 Science Important Questions with Answers PDF will help you in scoring more marks. This consists of 1 mark Questions, 3 Mark Numericals Questions, 5 Marks Numerical Questions and previous year questions from Chemical Reactions and Equations Chapter.
Sources of Energy Class 10 Important Questions and Answers Science Chapter 14
Very Short Answer Questions
Based on Non-renewable or conventional sources of energy
Question 1.
What is meant by non-renewable sources of energy ? (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
The sources of energy which have been formed in nature long ago under certain conditions of temperature and pressure. For example, fossil fuels like coal and petroleum.
More Resources
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10
- HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science
Question 2.
Name two non-renewable or conventional sources of energy.
Answer:
- Coal,
- Petroleum.
Question 3.
What is a fossil fuel ? (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
The combustible substance formed from the dead remains of the animals and plants which were buried deep under the surface of the earth over millions of years is called fossil fuel.
Question 4.
Give two examples of fossil fuels.
Answer:
Coal and petroleum.
Question 5.
How is the increase in demand for energy affecting our environment adversely ? [CBSE (Delhi) 2008]
Answer:
More use of fossil fuels for fulfilling the increasing demand for energy is polluting the air, which is a great health hazard.
Question 6.
What does “LPG” stands for ?
Answer:
LPG stands for “Liquid Petroleum Gas”.
Question 7.
Write the name of the main constituent of “LPG”.
Answer:
The main constitutent of “LPG” is butane.
Question 8.
What does “CNG stand for ?
Answer:
CNG stands for “compressed Natural Gas”.
Question 9.
Write the name of the main constituent of “CNG”.
Answer:
The main constituent of CNG is methane.
Question 10.
Name the device/technique to produce electricity by burning fossil fuels.
Answer:
Thermal power plant produces electricity by burning fossil fuels.
Question 11.
What is the disadvantage of a thermal power plant ?
Answer:
Disadvantage : The burning of coal or oil in a thermal power plant causes environmental pollution and global warming.
Question 12.
Name any two gases released on burning of fossil fuels. (CBSE 2013, 2014)
Answer:
CO2, SO2.
Question 13.
Name two gases, other than carbon-dioxide, that are given out during burning of fossil fuel and contribute towards acid rain formation. (CBSE Sample Paper)
Answer:
- Sulphur dioxide
- Nitrogen dioxide.
Based on Hydro power (hydel electicity)
Question 14.
Justify in one sentence that hydro power (hydel electricity) is a renewable source of energy.
(CBSE Sample Paper)
Answer:
Since hydro power is derived from the renewable source of energy i.e., sun, so it is also a renewable source of energy.
Question 15.
Construction of dams submerges large areas of forests, how does this contribute to the greenhouse effect ?
(CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Depletion of forests means deforestation which is responsible for green house gases such as CO2 and methane. on Biogas
Question 16.
What is bio-mass ? (CBSE 2010, 2012)
Answer:
Plants and animals waste material which can be used as fuel is called biomass.
Question 17.
How is charcoal obtained from wood ? [CBSE (All India) 2009]
Answer:
Charcoal is obtained from wood by heating the wood in the absence of air. This process is known as destructive distillation of wood.
Question 18.
Which type of micro-organisms are able to carry out the process of decomposition in a biogas plant ? (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Anaerobic micro-organisms.
Question 19.
Name the residue obtained when wood is burnt in a limited supply of air. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Charcoal.
Question 20.
What is a biogas ? [CBSE (All India) 2006 (c); CBSE (Delhi) 2009, 2010]
Answer:
Biogas is a mixture of four gases namely methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide.
Question 21.
Name the main constituent of a biogas and its approximate percentage content in it.
(CBSE 2010, 2012, 2013)
Answer:
Methane gas. 75% of total volume.
Question 22.
Name two main combustible components of biogas. (CBSE (Foreign) 2004, 2012, 2015)
Answer:
Methane gas and hydrogen gas.
Question 23.
Classify the two fuels-CNG and hydrogen as renewable and non-vcnewable. (CBSE (All India) 2008)
Answer:
CNG – Non-renewable
Hydrogen – Renewable.
Question 24.
Mention one feature of biogas that makes it an ideal fuel.
Answer:
It causes no air pollution and has no residue.
Question 25.
List two nutrients that the slurry left behind in the biogas plant contains. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
Nitrogen and phosphorus, on Wind energy
Question 26.
What is meant by renewable sources of energy ?
Answer:
The sources of energy which are continuously supplied by nature. For example, the sun, the wind.
Question 27.
Name two renewable or non-conventional sources of energy.
Answer:
- The sun,
- The wind.
Question 28.
What is the main basic cause for winds to blow ? (CBSE 2004, 2012)
Answer:
The pressure of a region where maximum sunlight falls decreases as compared to the region where minimum sunlight falls. The air moves from a region of high pressure (i.e., cold region) to the region of low pressure (i.e., hot region). This moving air is the wind.
Question 29.
What is the minimum wind velocity required to obtain useful energy with a wind mill ? (AI CBSE 2007)
Answer:
15 km/h.
Question 30.
What is a wind energy farm ? (CBSE 2010, 2013)
Answer:
The region where large number of wind mills are erected to produce electricity is called wind energy farm.
Question 31.
Name the kind of energy possessed by wind. [AI CBSE 1992 (C)]
Answer:
Kinetic energy.
Question 32.
Name a part of India where wind energy is commercially harnessed. (CBSE 2004)
Answer:
‘Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu.
Question 33.
Wind mill is used to produce electricity. Write the sequence of energy conversion in a wind mill.
Answer:
Wind energy —> Mechanical energy —> Electricity (i.e. electric energy).
Based on Solar Energy
Question 34.
Name two activities in our daily life in which solar energy is used.
Answer:
- For cooking food using solar cookers.
- For dryring clothes and food grains.
Question 35.
Name the device which directly converts solar energy into electric energy. [CBSE (Delhi) 1998, 2010, 2011]
Answer:
Solar cell.
Question 36.
What is the range of temperature attained inside a box type solar cooker when placed in the sun for two to three hours ? [CBSE (Delhi) 2001 (C)]
Answer:
From 100°C to 140°C.
Question 37.
A solar cell transforms energy of one form into another form. What are these two forms of energy ?
[CBSE (Delhi) 1995]
Or
State the energy conversion taking place in solar panels. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Solar energy(sunlight) to electrical energy.
Question 38.
State one limitation of solar energy available from solar cells. [CBSE (All India) 2007]
Answer:
These cells do not operate during night and on a cloudy day.
Question 39.
What is solar panel ? (CBSE 2010, 2011, 2012)
Answer:
A group of solar cells connected to each other in a certain pattern forms a solar panel.
Question 40.
Name chief component of solar cells. What energy conversion takes place in a solar cell ? (CBSE 2012, 2015)
Answer:
Silicon. Solar energy is converted into electric energy by a solar cell.
Based on energy from the sea or ocean
Question 41.
Name the factor which enables the ocean to act as a store house of energy. [CBSE (Delhi) 1999 (C)]
Answer:
The high value of specific heat capacity of water enables the ocean to act as a store house of heat energy.
Question 42.
What type of energy possessed by huge waves near the sea shore ? (CBSE 2010, 2015)
Answer:
Wave possesses kinetic energy.
Question 43.
What does “OTE” stand for ?
Answer:
OTE stands for “Ocean Thermal Energy.”
Question 44.
Name the device used for obtaining ocean thermal energy.
Answer:
Ocean thermal energy conversion power plant.
Question 45.
What type of energy possessed by huge waves near the sea shore ?
Answer:
Kinetic energy.
Question 46.
Write two different ways of harnessing energy from ocean.
Answer:
- Ocean waves,
- Tides,
- OTEC.
Question 47.
Name two sources of energy which are pollution free.
Answer:
The sun, wind and water.
Question 48.
Mention the minimum temperature difference required between surface water and the water at depths of upto 2km in an ocean thermal energy plant. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
20°C.
Question 49.
What are hot spots inside earth’s crust ? (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
The hot magma rises up and is collected in the crust of the earth due to some geological changes. The regions in the crust where the hot magma is collected are called hot spots inside earth’s crust, on Nuclear Energy
Question 50.
What is nuclear energy ? (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
The energy which is obtained from the conversion of nuclear mass is called nuclear energy.
Question 51.
What is a nuclear fission ?
Answer:
The process of splitting of a heavy nucleus into lighter nuclei is known as nuclear fission.
Question 52.
Which process is carried out at a higher temperature ? Nuclear fission or nuclear fusion ? (AI CBSE 1994)
Answer:
Nuclear fusion.
Question 53.
The mass number of three elements A, B and C are 2, 180 and 235- Which one of them is suitable to make a hydrogen bomb ? [AI CBSE 1995 (C)]
Answer:
Hydrogen bomb is based on nuclear fusion reaction which occurs due to the fusion of light elements. So element A is suitable to make a hydrogen bomb.
Question 54.
What is a fusion reaction ?
Answer:
The process by which two or more light nuclei fuse together (or combine) to form a heavy nucleus along with the release of energy is called fusion reaction.
Question 55.
Name the reaction responsible for large energy production in the sun. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Nuclear fusion.
Question 56.
What is green house effect ? (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
The warming of earths atmosphere due to the trapping of heat radiation i.e. infirared radiation is known as green-house effect.
Short Answer Questions ( 2 & 3 Marks)
Based on Non-renewable or conventional sources of energy
Question 1.
Mention any three qualities of an ideal source of energy. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
A good source of energy should have the following characteristics. It should
- supply enough amount of useful energy.
- be easily stored.
- be easily transported.
Question 2.
Would your choice regarding choice regarding a fuel for cooking food be different if you lived
(a) in a forest,
(b) in a remote mountain or small island,
(c) in New Delhi and
(d) five centuries ago ? If yes, name the type of fuel used in different cases.
Answer:
Yes.
(a) wood would be used for cooking food in a forest.
(b) Wind energy from a wind mill or energy of flowing water would be used for cooking food in a remote mountain or small island.
(c) LPG would be used for cooking food in New Delhi.
(d) Wood and cakes of cow dung were used for cooking food five centuries ago.
Question 3.
Why are fossil fuels known as a non-renewable sources of energy ?
Or
State the reason for calling fossil fuels as non-renewable source of energy. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Fossil fuels like coal, petroleum and natural gases take millions of years for their forma-don. If these fuels are exhausted today, then they will not be formed very soon. Hence, they are known as non-renewable sources of energy.
Question 4.
Why are many thermal power plants set up near coal or oil fields ? (CBSE 2011, 2013, 2015)
Answer:
In a thermal power plants, fuel like coal or oil is used in large quantity to produce electricity. These plants are usually set up near coal or oil fields so that the fuel is easily available and the problem of air pollution while transporting the fuel may be minimised.
Question 5.
What steps can be taken to minimize environmental pollution caused by the burning of fossil fuels ?
(CBSE 2010)
Answer:
We can minimize environmental pollution caused by the burning of fossil fuel by
- growing more and more trees,
- Using smokeless chulahs and
- smokeless chimneys in thermal power plants.
Question 6.
What are fossil fuels ? “Burning of fossil fuels leads to acid rain”, fustify this statement. (CBSE 2011)
Answer:
For fossil fuels: The combustible substance formed from the dead remains of the animals and plants which were buried deep under the surface of the earth over millions of years is called fossil fuel.
Gases produced due to the burning of fossil fuels react with water vapours in air to produce acids like carbonic acid, sulphuric acid and nitric acid. These acids come down to earth with rain known as acid rain.
Question 7.
List three energy sources that are considered to be inexhaustible. State three reasons in support your answer.
(CBSE 2012)
Answer:
- Coal,
- Petroleum
- Natural gas.
These are inexhaustible energy’ source because
- their deposit under earth is limited,
- their continuous use will ultimate consume them and
- they are formed in very long period of time.
Question 8.
Explain how burning of fossil fuels cause acid rain. (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
Gases produced due to burning of fossil fuels give rise to acids after reacting with water vapours in air. For example.
CO2+ Water ———> Carbonic acid
SO2 + Water ——–> Sulphuric acid
NO2+ Water ———> Nitric acid
These acids come down to the earth with rain. The rain containing these acids is called acid rain.
Question 9.
List two steps of energy transformation that take place in a thermal power plant. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
Chemical energy of fossil fuie is converted into heat energy. This heat energy is converted into mechanical energy which is then converted into electrical energy.
Based on Hydropower (hydel electricity)
Question 10.
Write any four advantages of hydroelectric power. [CBSE (Delhi) 2006]
Or
List two advantages of producing hydroelectricity. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Advantages of Hydroelectric Power
- Hydroelectric power is pollution free.
- Fiydroelectric power- is dependable source of energy.
- Lot of water is available in rivers, so the hydroelectric power is available free of cost. Money is spent only to construct dams and power stations.
Question 11.
What is the importance of hydropower plants in India ? Describe how electric energy is generated in such plants. [CBSE (Delhi) 2008, 2012, 2013]
Answer:
In India, hydropower plants fulfills l/4th or 25% demand for the total energy requirement.
Hydro Power or Hydro Electric Power Plant:
Flowing water is the major source of energy. The electricity produced by the flowing water is known as hydro-electric power. A plant used to produce hydro-electric power is known as hydro-electric power plant (For the generation of electric energy in hydropower plant).
Question 12.
Write the problems faced in construction of big dams. (CBSE 2010, 2011, 2012)
Answer:
- A large area of fertile land is submerged in water at the site of the dam.
- A large number of people residing near the site of dam are dislocated. Hence, lot of problems are to be faced in rehabilitating this population.
- A large number of plants and wild life in the area of the dam is submerged in water.
Question 13.
Write any three disadvantages associated with hydro power plant. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
Disadvantages of Hydroelectric Power :
- Hydroelectric power is generated only near the rivers having water throughout the year. This electric power has to be carried to the substations for distribution to the houses and factories situated far off from the sites of hydro electric power stations. This is done through the transmission wires, so lot of money is to be spent on this process.
- A large area of fertile land is submerged at the site of the dam constructed for tapping energy from the flowing water.
- A large number of people residing near the site of a dam are dislocated. So, a lot of problems are to be faced in rehabilitating this population. That is why, there is a lot of opposition by the people around the site of dam for the construction of dam.
- A large number of plants and wild life in the area of the dam are submerged in water. So, a large variety of flora (plants) and fauna (animals) is destroyed.
- Hydroelectric dams cannot be constructed everywhere. They are constructed mostly in hilly areas.
Question 14.
What are the advantages of constructing dams over rivers. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
Dams are helpful to :
- control floods over rivers.
- generate hydro electricity.
- irrigate agriculture land.
- develop water sports for recreation
- develop fishing zones.
Based on Renewable sources of energy
(Improvements in the technology for using conventional sources of energy)
Question 15.
List reasons why we need to look for alternate sources of energy. (CBSE 2011, 2012, 2013)
Or
Why is there a need to harness non-conventional sources of energy ? Give two main reasons. (CBSE Sample paper 2017-18)
Answer:
- To fulfill the requirement of increasing demand of energy.
- To ease out the pressure on the conventional sources of energy.
- To reduce the pollution caused by the use of conventional sources of energy.
Question 16.
“Why is there a need to harness non-conventional sources of energy ?”
Answer:
- Non-conventional sources of energy are pollution free, whereas fossil fuels cause lot of pollution.
- Non-conventional sources of energy are in exhanstitle, whereas fossil fuels are limited.
- Our demand of energy is increasing day by day.
Question 17.
- Name four gases commonly present in biogas.
Or
List four gases generated in a biogas plant. (CBSE 2011) - List two advantages of using biogas over fossil fuels. [CBSE (All India) 2006]
Answer:
- Methane, CO2, hydrogen, Hydrogen
- Biogas is used for cooking food and heating water. It is a good source of energy because
- biogas does not produce smoke during burning and hence there in no air pollution.
- it is a cheaper source of energy.
Question 18.
Give advantages of a biogas as fuel. (CBSE 2010)
Or
Why is biogas considered an ideal fuel for domestic use ? [CBSE (Delhi) 2009, 2012]
Answer:
Biogas is considered as an ideal fuel for domestic use because
- it causes no air pollution and
- it is cheaper source of energy.
Question 19.
What is biogas ? How can biogas be obtained ? Why is the use of biogas obtained from cow-dung advised in preference to burning of cow-dung cakes ? [CBSE(All India) 2006(c), 2015]
Or
Why is biogas a better fuel than animal dung cakes ? [CBSE(All India) 2005, 2013]
Answer:
Biogas is a mixture of four gases namely methane, carbon dioxide, hydrogen and hydrogen sulphide.
Biogas is obtained from anaerobic decomposition of cow dung and plants and animal wastes in a biogas plants. This is because, biogas does not produce smoke during burning and hence there is no air pollution. On the other hand, burning of animal dung cakes causes air pollution. Moreover, biogas gives more heat energy than the burning of animal dung cakes.
Question 20.
What is geothermal energy ? What are its advantages ? [CBSE (Delhi) 2007]
Answer:
The heat energy stored in the hot spots of the earth’s crust is called geo-thermal energy.
For advantages:
- Geo-thermal energy can be converted continuously into electricity for 24 hours in a day throughout the year.
- Geo-thermal energy causes no pollution, so it is environment friendly.
- The cost of converting geo-thermal energy into electricity is very less.
Question 21.
Justify the statement, “Hydrogen is a cleaner and better fuel than CNG”. [CBSE (All India) 2008, 2012]
Answer:
- Hydrogen on buring produces more heat energy than producted by the burning of CNG.
- Burning of hydrogen produces water vapours and burning of CNG produces CO2. So, burning of hydrogen causes less air pollution than the burning of CNG.
Hence, hydrogen is a cleaner and better fuel than CNG.
Question 22.
Write two advantages of classifying energy sources as renewable and non-renewable. [CBSE (Delhi) 2008]
Answer:
Advantages of classifying Sources of Energy:
- It helps us to decide which of the non-renewable sources of energy (like coal, petroleum, natural gas and fissionable materials) need to be conserved for future generations.
- It also helps the scientists to accelerate the pace of developing new technologies and devices suitable for harnessing energy from the renewable or non-conventional sources of energy.
Question 23.
(a) Distinguish between renewable and non-renewable sources of energy with one example for each. [CBSE 2010, 2011, 2014]
(b) Choose the renewable sources of energy from the following list : coal, biogas, sun, natural gas. [CBSE (Delhi) 2008]
Answer:
(a) Renewable Sources of Energy
The sources of energy which are inexhaustible (i.e. which can never be finished) and are being continuously supplied by nature are known as renewable sources of energy. These sources of energy are also known as non-conventional sources of energy.
For example :
- Wind
- Hydro Power
- The sun
- Ocean Tidals Energy
- Interior of the Earth
- Biogas
- Plants, vegetable waste etc.
Non-Renewable Sources of Energy
The sources of energy which are exhaustible (i.e. which can be finished) and have been formed in nature long ago are known as non-renewable sources of energy. These sources of energy are also known as conventional sources of energy.
For example :
- Coal
- Petroleum
- Natural Gas
- Fissionable materials like Uranium.
Non-renewable sources of energy like coal, petroleum and natural gas have a huge deposit under the earth. However, the continuous extraction of these sources for the purpose of usable energy is a matter of concern and worry because ultimately the deposit of these sources will be completely finished. It may be noted that the formation of fossil fuel take very long period. Therefore, we should use these fuels judiciously so that their deposit may last long for future.
On the other hand, renewable sources of energy will last forever. For example, it is estimated that the sun would continue to shine for another 5 billion years. Therefore, the sun as the source of energy will be available for a very long period of time. Similarly, bio-mass as the source of energy will be available for a longer period of time if we grow more and more plants periodically {i.e. at regular intervals of time). The wind energy will be at our disposal as long as the sun exists. Geo-thermal energy is another source which will be available forever.
(b) Biogas and the sun are renewable sources of energy.
Question 24.
Why is the use of wood as a fuel not advised although forests can be replenished ? [CBSE (All India) 2006]
Or
The use of dry wood as domestic fuel is not considered as good. State two reasons for it.
[CBSE(Delhi) 2004 (S), 2010]
Answer:
This is because
- Deforestation (i.e., cutting of trees in large number) causes many problems like floods, erosion of fertile land and environmental imbalance.
- Replenishment of forests takes long time and as such wood cannot be available to supply continuous energy.
Question 25.
Charcoal is a better fuel than wood. Explain why ? (CBSE 2010)
Or
Why is charcoal considered a better fuel than wood. [CBSE (All India) 2009, 2015]
Answer:
It is because
- charcoal burns easily as compared to wood,
- charcoal does not produce smoke on burning and hence it causes no air pollution and
- the amount of heat produced by the burning charcoal is much more than the heat produced by the burning wood.
Question 26.
How does biogas plant help to reduce the problem of pollution ? (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
- Biogas obtained from biogas plant does not produce smoke during burning and hence there is no air pollution.
- Biogas plant operates with the materials like cow dung and waste of plants. These materials lying in open can cause air and water pollution.
Question 27.
Suggest two materials that can be used to produce bio-gas. Mention two tises of bio-gas and two advantages of bio-gas plant. (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
- Animal wastes like cow-dung
- Fruits and vegetable wastes.
Uses : Bio-gas is used to cook food and heat water.
Advantages :
- It causes no pollution.
- The slurry in bio-gas plant is used as manure by the farmers.
Question 28.
Biogas is considered to be a boon to the farmers. Give reasons. (CBSE 2010)
Or
List any three reasons due to which bio-gas is considered to be an excellent fuel. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
- Bio-gas is pollution free.
- It is cheap as raw material {i.e., cow dung and waste of plants and vegetables) to produce biogas is available free of cost to the farmers.
- The remains or used slurry in a bio-gas plant is used as manure by the farmers in the fields to get good yields of crops.
Question 29.
Name an efficient fuel obtained from cow dung and other animal and plant wastes. Also mention its main constituent. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Biogas. Methane and hydrogen gases.
Based on wind energy
Question 30.
Mention any two uses of wind energy. [CBSE (Delhi) 1997 (C), 2012]
Answer:
Wind energy is used to
- operate water pumps to draw underground water,
- produce electricity.
Question 31..
What are the limitations in obtaining energy from wind ? (NCERT Questions Bank, 2012)
Answer:
- We cannot depend upon wind energy as it is available only when air is in motion. The appliances or machines operating with wind energy stop working as soon as wind stops. The minimum speed of wind to operate generator to produce electricity is about 15 km/h. As soon as the speed of the wind becomes less than 15 km/h, the generator stops working.
- There are certain regions where wind is not available, so the use of wind energy is limited to certain places where wind is in plenty and blows most of the time.
- Wind energy is not sufficient to operate very heavy machines.
- Wind energy cannot be used to operate all types of machines.
- Wind mills are usually broken during storms and hence lot of money is spent for the maintenance of a wind energy form.
Question 32.
Give
- two limitations and
- two advantages of wind energy. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
Limitations:
- Wind energy is not sufficient to operate very heavy machines.
- Wind energy cannot be used to operate all types of machines.
Advantages:
- Wind energy produces no smoke and no harmful gases. So this form of energy is pollution free or environment-friendly.
- Wind energy is free of cost and hence devices operated by wind energy are economical.
- This source of energy is a renewable source of energy and is available for all times to come under favourable conditions.
Question 33.
State in brief the process of harnessing kinetic energy of the wind to do work. Mention any four limitations of harnessing wind energy on a large scale.
Answer:
Electricity is produced when an armature of a generator rotates between two poles (North and South poles) of a strong magnet. When wind falls on the wheel of a windmill, it rotates. The axle of the armature is connected to the shaft of the wind mill. So the armature of the generator rotates between two poles of a magnet along with the rotation of the wheel of the wind mill (Figure 6).
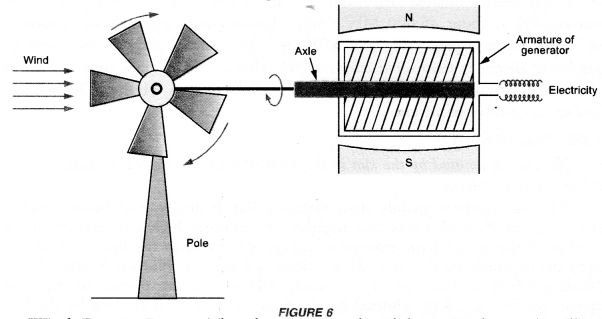
Thus, electric current is produced. This is how, the kinetic energy of the wind is converted into electrical energy.
- We cannot depend upon wind energy as it is available only when air is in motion. The appliances or machines operating with wind energy stop working as soon as wind stops. The minimum speed of wind to operate generator to produce electricity is about 15 km/h. As soon as the speed of the wind becomes less than 15 km/h, the generator stops working.
- There are certain regions where wind is not available, so the use of wind energy is limited to certain places where wind is in plenty and blows most of the time.
- Wind energy is not sufficient to operate very heavy machines.
- Wind energy cannot be used to operate all types of machines.
- Wind mills are usually broken during storms and hence lot of money is spent for the maintenance of a wind energy form.
Question 34.
How has the traditional use of wind and water energy been modified for our convenience 1 (CBSE 2010)
Answer:
Traditional use of wind energy was to sail boats and grinding grains. The wind energy is now used to produce electricity using wind mills.
Similarly, water energy is utilised to produce electricity on a large scale at hydroelectric power plant.
Based on solar energy
Question 35.
(a) Name the device used to convert
- Solar energy into heat and
- Solar energy into electricity.
(b) Explain the working of a wind will. [CBSE (All India) 2006 (C)]
Answer:
(a)
- Solar cooker
- Solar cell.
(b) When wind blows with a minimum speed of 15 km/h, the kinetic energy of the wind is used to rotate the blades of wind mill. The rotational energy of the blades is used to rotate the armature of the generator to produce electricity.
Question 36.
On what principle does a solar water heater operate ? (CBSE 2004)
Answer:
A black surface absorbs more heat from the sunlight. This absorbed heat is used to heat the water in a solar water heater.
Question 37.
List any four areas where solar cells are being used as a source of energy. [CBSE (All India) 2008, 2012]
Or
Mention three advantages of a solar cell. (NCERT Question Bank, CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Advantages of Solar Cells:
- They directly convert solar energy into electrical energy.
- They are environment-friendly i.e. they do not cause pollution.
- They are used to operate radio sets in remote areas.
Question 38.
(a) What is the role of a plane mirror and a glass sheet in a solar cooker 1 (NCERT Question Bank)
(b) Why is energy of water flowing in a river considered to be an indirect form of solar energy ?
(c) Why is nuclear fusion reaction considered better. [CBSE (Delhi) 2007]
Answer:
(a) Plane mirror reflects solar light to fall on the glass sheet of the solar cooker. Plane glass plate does not
allow the infrared or heat radiation entered in the box to go out side the box. Thus, the box becomes hot. The phenomenon is known as green house effect.
(b) Solar energy evaporates water in rivers, lakes and oceans. These water vapours are converted into clouds (K.E. + P.E.). The clouds give rise to rain and hence water flows in rivers. Thus, energy of flowing water in the form of kinetic energy is the indirect form of solar energy.
(c) Nuclear fusion reaction gives rise to energy which is pollution-free.
Question 39.
Out of two solar cookers, one was covered by a plane glass slab and the other was left open. Which of the two
solar cookers will be more efficient and why ? (CBSE Sample Paper, CBSE 2010, Term I)
Or
You are given two solar cookers, one with a glass cover and other with top open. Which one is more efficient ? Give reason for your answer. (CBSE 2011)
Or
Why should solar cookers are to be coverted with glass plate ? (CBSE 2010, 2012)
Or
State one use of glass cover in box type solar cookers. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
A solar cooker covered by a plane glass slab will be more efficient.
This is because glass slab does not allow the heat radiation to escape from the solar cooker and hence the temperature of the solar cooker covered with glass slab increases more than the temperature of the solar cooker which is left open.
Question 40.
- Why are solar heating devices painted black ?
- Name two such devices and state two limitations of these. (CBSE 2012, 2013, 2015)
Answer:
- It is because black surfaces are good absorber of heat.
- Solar cooker and solar furnace.
They cannot be used
- during night and on cloudy days
- to cook food quickly.
Question 41.
A student constructed a box type solar cooker and covered it with a glass plate. Write the purpose served by glass plate in the cooker. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Glass plate covering solar cooker prevents heat radiations to escape the solar cooker. In other words, glass plate traps the heat radiation inside the cooker.
Based on energy from the sea or ocean
Question 42.
Name three forms in which energy from ocean is made available for use. What are OTEC power plants ?
How do they operate ? (CBSE (Delhi) 2005, 2015)
Answer:
- Tidal energy,
- Ocean waves energy
- Ocean thermal energy.
OTEC power plants are Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion Plants. For the operation of OTEC,
The heat energy due to the temperature difference between the different layers of water in the ocean is known as ocean thermal energy (OTE). The temperature of water at the surface of the ocean is much more than the temperature of water deep into the ocean. Due to this temperature difference, heat energy can be drawn from the sea or ocean water. This heat energy is used to produce electricity.
Question 43.
The water in deeper sections of ocean is much colder than that at the surface. Discuss how this difference in temperature be exploited to obtain energy.
Answer:
The warm surface water of ocean is used to boil liquid like ammonia or chlorofluoro carbon in OTEC power plant. The vapours of this liquid at high pressure rotates the turbine of a generator to produce electricity. The dead steam is again converted into liquid by the cold water pumped up from the deep ocean. This process is repreated continuously to convert ocean thermal energy into electrical energy.
Question 44.
Explain the principle and process of converting ocean thermal energy into electricity. (CBSE 2014, 2015)
Answer:
A device used to obtain ocean thermal energy is known as Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) power plant (figure 12).
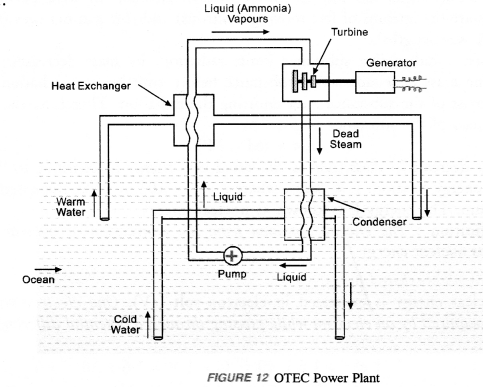
For operating OTEC power plant, temperature difference of 20°C or more between the surface water of ocean and water deep into the ocean is required. The warm surface water of ocean is used to boil liquid like ammonia or chlorofluo’ro carbon (CFC). The vapours of this liquid at high pressure are used to rotate the turbine of the generator to produce electricity. The unused vapours (known as dead steam) are again converted into liquid by the cold water pumped up from the deep ocean. This process is repeated time and again to convert ocean thermal energy into electric energy (i.eelectricity). The main advantage of OTEC power plant is that it can be operated for 24 hours in a day throughout the year.
Question 45.
Are geothermal energy and nuclear energy different from bio-mass energy, wind energy and ocean thermal energy ? If yes, Why ?
Answer:
Geothermal energy and nuclear energy are different from the bio-mass energy, wind energy and ocean thermal energy. This is because, bio-mass energy, wind energy and ocean thermal energy are derived from a single source of energy, that is the sun. On the other hand, geothermal and nuclear energies are not derived from the sun. Based on Nuclear energy
Question 46.
What is nuclear energy ? Give two advantages and two hazards of nuclear energy. (CBSE 2012)
Answer:
Advantages :
- A small quantity of nuclear fuel gives a large amount of energy.
- Nuclear fuel is inserted once in a nuclear power plant to get continuous energy over a long period of time.
Hazards : Nuclear radiation causes :
- diseases like cancer and leukemia.
- genetic disorder in a human body.
Question 47.
State three limitations of harnessing nuclear energy. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
Disadvantages of Nuclear Fission Energy over the Fossil Fuel Energy
- Nuclear fission causes more serious pollution problem than the burning of fossil fuel. The radiation emitted during nuclear fission are very harmful. They cause dangerous diseases like cancer, leukemia and sterility.
- The biggest problem of using nuclear fission energy is the safe disposal of nuclear waste. Nuclear waste continues to emit harmful nuclear radiation. No method has been evolved for the complete elimination of the nuclear waste. But no such problem is faced in the disposal of the fossil fuel waste. For example, burning of coal give rise to ash which can be thrown in the fields. That is why, it is advised not to use nuclear fission for the production of energy on very large scale.
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
Question 1.
Describe the construction of a box type solar cooker or show it with the help of a diagram. How is the rise in temperature obtained in this set up ? Mention two advantages and two limitations of solar cookers.
[CBSE (Delhi) 2004 (S), 2012]
Answer:
Solar Cooker (Box Type)
Construction:
It consists of a wooden box (rectangular in shape) in which a metallic box painted black is fitted. The space between wooden box and metallic box is filled with an insulating material like thermocol. The insulating material minimizes the heat lose by conduction and radiation.
The metallic box is covered by a thick glass sheet. A plane mirror reflector is used to reflect the sun rays and attached to the box (Figure 7).
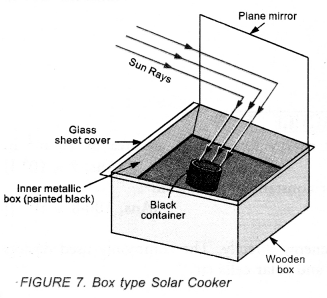
The un-cooked food placed in the black container is put inside the box.
Working:
The plane mirror reflector is adjusted in such a way that maximum sun light falls on it. The light reflected by the plane mirror falls on the thick glass sheet cover.
The heat radiation (i.e. infra-red rays coming from the sun have short wavelength and high energy) pass through the glass sheet and are absorbed by the black container or any other object placed in the box and black surface of the box. The heat radiation entered in the box are not able to come out of the box through the glass sheet. Thus, the heat radiation are trapped in the box and the inner part of the box becomes hot. The effect is known as green house effect. (For the detail of green house effect, Refer Additional Topic at the end of this chapter). The temperature inside the box increases from 100° C to 140° C. Thus, the food in the container is cooked.
Advantages of Box type Solar cooker
- Economical : The cost of cooking food in the solar cooker is very small as money is only spent to purchase the solar cooker.
- Pollution : No pollution is caused as there is no burning of fuel.
Disadvantages of Solar cooker
- Food cannot be cooked at night.
- Food cannot be cooked on a cloudy day.
- Food cannot be cooked quickly as solar cooker takes 4 to 5 hours to cook it.
Question 2.
What are
(i) Solar concentrators and
(ii) Solar cell panels ? How are they improvement on simple devices ? Why is it that solar panels are costly ? [CBSE (Foreign) 2004)]
Answer:
(i) Solar concentrators:
Solar concentrators are the devices used to concentrate the solar energy over a small area. When a parallel beam of sunlight falls on a polished concave surface (like concave mirror), then the beam of sunlight concentrates at the focus (F) of the concave surface after reflection (Figure 8).
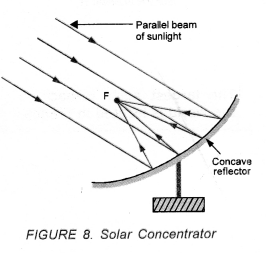
As a result of this concentrated beam of sunlight, the temperature at point F increases considerably. If we place a piece of paper at F, then it begins to burn after some time. A concave spherical surface which concentrates the beam of sunlight at a point is called solar concentrator.
(ii) Solar cell panels:
A group of solar cells connected to each other in a certain pattern forms a solar panel (Figure 10).
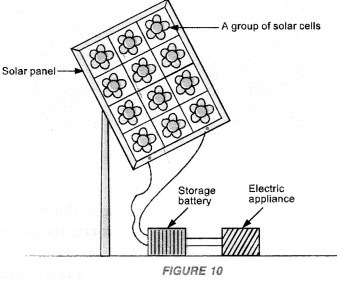
A solar panel converts sunlight into electrical energy. The efficiency of solar panel is very large as compared to the efficiency of a solar cell.
During day time, sunlight falling on the solar panel is converted into electrical energy which is stored in a battery connected to it. As soon as sunlight stops falling on it (during night and cloudy day), the battery begins to supply electric current to the appliances like electric bulbs and electric tubes connected to it.
Solar panels have limited uses. They can not be used to meet our domestic needs of electricity.
This is because of the following reasons :
- The solar cells used in a solar panel are made of pure silicon. The production of pure silicon is very costly’ affair. These solar cells in a solar panel are joined to each other with a best conductor silver to reduce the resistance of the solar panel to get maximum electricity.
But silver metal is also costly. Thus, we find that the cost of fabricating a solar panel is very high. - The storage battery connected to a solar panel can supply direct current (D.C.). So only those electric appliances can operate with the solar panel which require direct current. However, the electric appliances which require alternating current (A.C.) cannot be operated with the solar panel.
- Solar panel can supply the electricity continuously only if the sun shines during day time.
Question 3.
Name any three forms of energy of the oceans which can be converted into usable energy forms. Describe how it is done in each case. What is the likelihood of their use on a large scale ? [CBSE (Foreign) 2004)]
Answer:
The energy from sea or ocean water is available in the following forms :
- Energy of sea waves
- Tidal energy
- Ocean thermal energy
Energy of sea waves:
High winds blow across the sea. These winds produce high waves on the surface of water in the sea or ocean. Thus, the water in the sea moves as water waves’. The kinetic energy of this moving water rotates the turbine of a generator. Hence, electricity is produced.
Limitation of Energy of Sea waves: Energy of sea waves can be used only if strong winds blow all the times across the sea and there are high water waves in the sea. However, as soon as strong winds stop to blow, the electric generator stops producing electricity. Hence, we cannot depend much on the energy of sea waves.

Tidal energy:
The alternate rise and fall of water of the ocean twice in nearly 24 hours is known as tide. The tides are caused due to the gravitational force of attraction exerted by the moon and to some extent by the sun on the water of the ocean. At the time of new and full moon, when the sun and the moon are in a straight line, tides are very high. When the sun and the moon are at right angle from the earth, tides are low. The kinetic energy of water waves during tides is used to produce electricity.
Tidal power plants are constructed near narrow Bays (Figure 11).
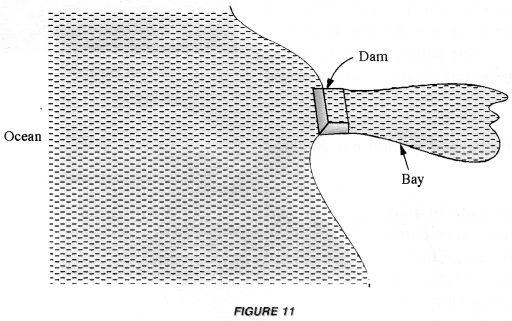
During tides, the gates of the dam are opened. The rising water is allowed to fall on the turbine of the generator which produces electricity.
Thus, kinetic energy of the water is converted into electrical energy. During low tides, gates of the dam are closed and hence the water level behind the dam rises. 1 his raised water has potential energy. Again the gates are opened and the water is allowed to fall back into the bay. This falling water is used to rotate the turbine of the generator. Hence the electricity is produced continuously.
Ocean thermal energy:
A device used to obtain ocean thermal energy is known as Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion (OTEC) power plant (figure 12).
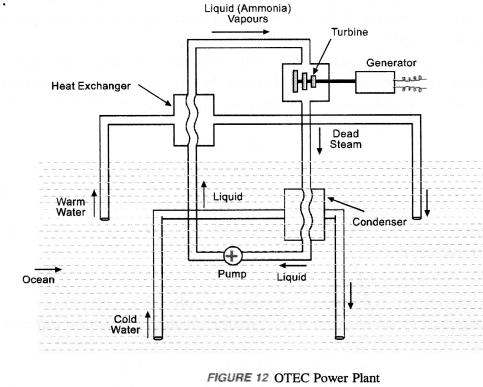
For operating OTEC power plant, temperature difference of 20°C or more between the surface water of ocean and water deep into the ocean is required. The warm surface water of ocean is used to boil liquid like ammonia or chlorofluo’ro carbon (CFC). The vapours of this liquid at high pressure are used to rotate the turbine of the generator to produce electricity. The unused vapours (known as dead steam) are again converted into liquid by the cold water pumped up from the deep ocean. This process is repeated time and again to convert ocean thermal energy into electric energy (i.eelectricity). The main advantage of OTEC power plant is that it can be operated for 24 hours in a day throughout the year.
Question 4.
Name the major components of biogas. What are its combustible components. Draw a simple labelled diagram of a fixed dome type biogas plant. What is the use of the residual slurry and why ?
[CBSE (Delhi) 2004)]
Answer:
Question 5.
How can solar energy be harnessed ? Mention any two limitations in using ? Solar energy. How are these limitations overcome ? (NCERT Question Bank)
Answer:
The energy emitted by the sun in the form of heat and light (i.e. radiation) is known as solar energy.
The Sun contains mainly light elements like hydrogen and helium. When the nuclei of these elements fuse together at extremely high temperature in the interior of the Sun, a large amount of energy’ is radiated in the form of heat and light continuously by the Sun. This process is known as Nuclear fusion.
All the planets of the solar system receive the energy emitted by the Sun. The energy is emitted by the Sun in the form of radiation. These radiations are visible rays, infra-red rays (i.e., heat radiation), ultraviolet rays, gamma rays, X-ray and radio waves. It may be noted that only some fraction of the total energy emitted by the Sun reach the surface of the earth.
Measurements have shown that the outer edge of the earth’s atmosphere receives solar energy equal to 1.4 kilojoule per second per square metre (1.4 kj/s m2). This amount is known as Solar constant.
Traditional Uses of Solar Energy : It is used
- for cooking food using solar cookers.
- for heating water using solar water heaters.
- for producing steam by heating water to produce electricity.
- by green plants to make their food.
- to produce electricity using solar cells.
- to melt metals using solar furnaces.
- for drying clothes and food grains.
Question 6.
Name the process used to harness nuclear energy. Explain it.
Or
Which is the process used to harness nuclear energy these days. Explain it briefly.
(NCERT Question Bank)
Answer:
Definition : The energy obtained from the conversion of nuclear mass is known as nuclear energy.
Units of Nuclear Energy:
Nuclear energy is expressed in electron-volt (eV). One electron-volt is the energy acquired by an electron while passing through a potential difference of one volt.
1 eV = 1.6 x 1(T-19 C x 1 V = 1.6 x 10-19 CV or
1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19 J (∴ 1 CV = 1J)
Bigger unit of nuclear energy is mega electron-volt (MeV).
1 MeV = 106 eV = 106 x 1.6 x 10-19 J = 1.6 x 10-13 J
Nuclear energy is obtained by the splitting of a heavy nucleus into light nuclei and by combining light nuclei to form a large nucleus. The process of splitting of a heavy nucleus into light nuclei is known as nuclear fission. The process of combining light nuclei to form a large nucleus is known as nuclear fusion.
Hazards of using nuclear energy:
The nuclear radiation can change or damage the structure of cells in the human body.
- They cause diseases like cancer, leukemia and blindness.
- They cause genetic disorder in a human body.
- They cause sterility in young generation.
Question 7.
Draw a labelled schematic diagram of a biogas plant. What use is made 6f the slurry left behind in biogas plant. (CBSE 2009)
Or
Explain the principle and working of a biogas plant using a labelled diagram. (CBSE 2010, 2013)
Answer:
The arrangement of producing biogas from animals dung, human excreta, industrial and domestic wastes is known as biogas plant.
Fixed-dome type biogas plant:
Construction: Fixed—dome type biogas plant in shown in figure 3.
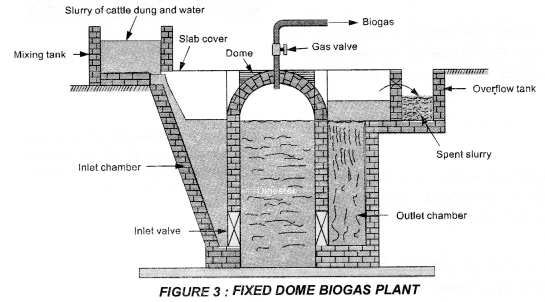
It consists of a well like underground tank made of bricks and cement. This tank is called digester and has inlet and outlet valves. The roof of the tank is dome shaped. A gas outlet pipe at the top of the dome is fitted. The dome of the digester acts as a storage tank of biogas. There is a mixing tank made above the ground level which is connected to the inlet value of the digester through a slopping inlet chamber below the ground level. On the other side of the digester, a rectangular tank called outlet chamber is constructed with bricks and cement. This outlet chamber is connected to the overflow tank which collects the used slurry.
Working: Animals-dung is mixed with water to make slurry in the mixing tank. This slurry enters the digester through the inlet chamber. The digester is filled partially with slurry so that enough space is left above it in the dome for the collection of biogas. The slurry in the digester is left for about two months for fermentation. Anaerobic micro organisms are responsible for this action. As a result of fermentation, biogas is formed which is collected in the dome. When sufficient amount of biogas is collected in the dome, it exerts a large pressure on the slurry and forced it to go into the overflow tank through the outlet chamber. The biogas is taken out from the dome through a pipe and used for cooking food or heating water whenever required.
Once the biogas plant starts functioning, more and more slurry may be fed into the digester to get the continuous supply of biogas. The used slurry collected in the overflow tank is rich in nitrogen and phosphorus which are essential for the growth of crops and plants. Hence this used slurry can be used as manure.
Question 8.
Sun is the ultimate source of energy. Explain.
Or
Energy from various sources is considered to have been desired from the sun. Do you agree ? Justify your answer. (NCERT Question Bank)
Answer:
- Renewable sources of energy or inexhaustible sources of energy.
- Non-renewable sources of energy or exhaustible sources of energy.
1. Renewable Sources of Energy
The sources of energy which are inexhaustible (i.e. which can never be finished) and are being continuously supplied by nature are known as renewable sources of energy. These sources of energy are also known as non-conventional sources of energy.
For example :
- Wind
- Hydro Power
- The sun
- Ocean Tidals Energy
- Interior of the Earth
- Biogas
- Plants, vegetable waste etc.
2. Non-Renewable Sources of Energy
The sources of energy which are exhaustible (i.e. which can be finished) and have been formed in nature long ago are known as non-renewable sources of energy. These sources of energy are also known as conventional sources of energy.
For example :
- Coal
- Petroleum
- Natural Gas
- Fissionable materials like Uranium.
Non-renewable sources of energy like coal, petroleum and natural gas have a huge deposit under the earth. However, the continuous extraction of these sources for the purpose of usable energy is a matter of concern and worry because ultimately the deposit of these sources will be completely finished. It may be noted that the formation of fossil fuel take very long period. Therefore, we should use these fuels judiciously so that their deposit may last long for future.
On the other hand, renewable sources of energy will last forever. For example, it is estimated that the sun would continue to shine for another 5 billion years. Therefore, the sun as the source of energy will be available for a very long period of time. Similarly, bio-mass as the source of energy will be available for a longer period of time if we grow more and more plants periodically {i.e. at regular intervals of time). The wind energy will be at our disposal as long as the sun exists. Geo-thermal energy is another source which will be available forever.
Hope given Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 14 Sources of Energy are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.