Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science Important Questions and Answers PDF will help you in scoring more marks. This consists of 1 mark Questions, 3 Mark Numericals Questions, 5 Marks Numerical Questions and previous year questions from Chemical Reactions and Equations Chapter.
Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Important Questions and Answers Science Chapter 1
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
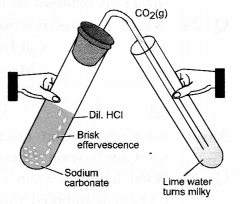
Why does not a wall immediately acquire a white colour when a coating of slaked lime is applied on it ?
Answer:
Slaked lime as such is not very white. When applied on the wall, CO2 gas present in air reacts with calcium hydroxide to form calcium carbonate. It is quite white and therefore, imparts white look to the wall.
Ca(OH)2 + CO2(g) ———> CaCO3(s) + H2O(l).
More Resources
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10
- HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science
Question 2.
What is rust ?
Answer:
It is a brown mass known as hydrated ferric oxide. Its formula is Fe2O3.xH2O.
Question 3.
Identify the most reactive and least reactive metal : Al, K, Ca, Au.
Answer:
Most reactive metal : K (potassium) ; Least reactive metal : Au (gold).
Question 4.
Which of the following is a combination reaction and which is a displacement reaction ?
(a) Cl2 + 2KI ——–> 2KCl + I2
(b) 2K + Cl2 ——–> 2KCl.
Answer:
(a) It is a displacement reaction,
(b) It is a combination reaction.
Question 5.
What is the difference between the following two reactions ?
(a) Mg + 2HCl ——–> MgCl2 + H2
(b) NaOH + HCl ——–> NaCl + H2O.
Answer:
(a) It is a single displacement reaction,
(b) It is a double displacement reaction also called neutralisation reaction.
Question 6.
Identify the compound which is oxidised in the following reaction
H2S + Br2 ———–> 2HBr + S.
Answer:
H2S is oxidised to S because H2S has lost hydrogen.
Question 7.
Suggest two ways to check the rancidity of food articles.
Answer:
(a) Keep the articles in airtight containers,
(b) Keep the articles in refrigerator.
Question 8.
Name two metals which donot get corroded.
Answer:
Gold (Au) and platinum (Pt) do not get corroded.
Question 9.
Identify the substance oxidised and reduced in the reaction :
CuO(s) + Zn(s) ———-> ZnO(s) + Cu(s).
Answer:
Zinc is oxidised to zinc oxide and copper oxide is reduced to copper.
Question 10.
How will you know whether a sample of cheese has become rancid or not ?
Answer:
If the cheese starts giving foul smell, it means that it has become rancid.
Question 11.
Why are eatables preferably packed in aluminium foils ?
Answer:
Aluminium foils donot corrode in atmosphere even if kept for a long time. Actually, a protective coating of aluminium oxide (Al2O3) is formed on the surface of the metal. It stops any further reaction of the metal with air (oxygen) and water. The eatables do not get spoiled.
Question 12.
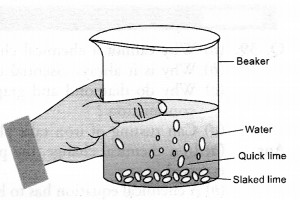
What happens chemically when quick lime is added to water ?
Answer:
Calcium hydroxide (or slaked lime) is formed accompanied by a hissing sound. So much heat is evolved during the reaction that the reaction mixture starts boiling. The chemical equation for the reaction is :
![]()
Question 13.
Give an example of exothermic reaction.
Answer:
CH4(g) + 2CO2(g) ———-> CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) + heat, (evolved)
Question 14.
Give an example of endothermic reaction.
Answer:
N2(g) + O2(g) ———> 2NO(g) – heat, (absorbed).
Question 15.
Name the gas that can be used for the storage of fresh sample of chips for a long time.
Answer:
The gas is nitrogen (N2). It checks rancidity of food articles.
Question 16.
Name the type of reaction
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ———-> 2NH3(g)
Answer:
It is an example of combination reaction.
Question 17.
Give an example of a double displacement reaction (only reaction with complete balanced equation).
Answer:
HCl(aq) + NaOH(g) ——–> NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Question 18.
Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions ? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
A decomposition reaction may be defined as the reaction in which a single substance decomposes or splits into two or more substances under suitable conditions.
For example,
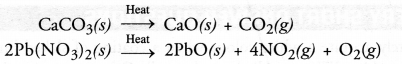
It may be concluded that a certain substance is formed or synthesised in combination reaction and it breaks or splits in decomposition reaction. Therefore, the two reactions oppose each other.
Question 19.
In the reaction MnO2 + 4HCl —————> MnCl2 + 2H2O + Cl2; identify which one is reduced and which one is oxidized ?
Answer:
In this reaction HCl is oxidised to Cl2 and MnO2 is reduced to MnCl2.
Question 20.
Take a small amount of calcium oxide or quick lime in a beaker and slowly add water to this. Is there any change in temperature ?
Answer:
Yes, the temperature increases since the process of dissolution of calcium oxide (CaO) in water is highly exothermic in nature.
Question 21.
Name two salts that are used in black and white photography.
Answer:
Both silver chloride and silver bromide are used in black and white photography.
Question 22.
State the chemical change that takes place when lime stone is heated
Answer:
Calcium carbonate decomposes on heating to give calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.
CaCO3(s) heat , CaO(s) + CO2(g)
Short Answer Questions
Question 23.
Identify the substance oxidised and substance reduced in the following reactions
(i) ZnO(s) + C(s) ———> Zn(s) + CO(g)
(ii) 2Na(s) + O2(g) ———> 2Na2O(s)
(iii) CuO(s) + H 2(g) ———> Cu(s) + H2O(l).
Answer:
(i) C is oxidised to CO and ZnO is reduced to Zn.
(ii) Na is oxidised to Na2O and O2 is reduced.
(iii) H2 is oxidised to H2O and CuO is reduced to Cu.
Question 24.
Which types of reactions are represented by the following equations ?
(a) CaO + CO2 ——-> CaCO3
(b) Mg + CuSO4 ——–> MgSO4 + Cu
(c) CH4 + 2O2 ———–> CO2 + 2H2O
(d) NH4NO2 ———-> N2 + 2H2O.
Answer:
(a) Combination reaction
(b) Displacement reaction
(c) Combustion reaction
(d) Decomposition reaction
Question 25.
What happens when :
CO2(g) is bubbled through lime water (i) in small amount (ii) in excess
Answer:
(i) Solution becomes milky due to the formation of calcium carbonate
![]()
(ii) Milkiness disappears because calcium carbonate changes to calcium hydrogen carbonate which is colourless in nature.
![]()
Question 26.
Aluminium is a reactive metal but is still used for packing food articles. Why ?
Answer:
From the position of the aluminium (Al) metal in the activity series, it seems to be quite reactive. However, it is not so reactive. Actually, when the metal is kept in air or oxygen for sometime, it is converted into its oxide called aluminum oxide (Al2O3). This gets deposited as the surface of the metal as a thin coating. It is rather passive which means that it is not reactive. Therefore, the metal is used for packing food articles which do not get spoiled under the foil.
Question 27.
Give one example each of :
(i) Thermal decomposition reaction
(ii) Electrolytic decomposition reaction
(iii) Photo decomposition reaction. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
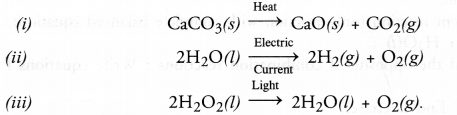
Question 28.
What are neutralisation reactions ? Why are they so named ? Give one example.
Answer:
A neutralisation reaction is a chemical reaction between an acid and base dissolved in water. For example,
KOH(aq) + HNO3(aq) ———-> KNO3(aq) + H2O (aq)
It is called neutralisation as both KN03 (salt) and H20 that are formed as the products, are of neutral nature.
Question 29.
(a) Why is combustion reaction an oxidation reaction ?
(b) How will you test whether the gas evolved in a reaction is hydrogen ?
(c) Why does not silver evolve hydrogen on reacting with dillute sulphuric acid ?
Answer:
(a) Combustion reaction is an oxidation reaction because it is always carried in the presence of air or oxygen. For example,
CH4(s) + 2O2(g) ——–> CO2(g) + 2H2O (l)
(b) Bring a burning match stick close to the mouth of the tube from which hydrogen gas escapes. The gas will immediately catch fire and this will be accompanied by pop sound.
(c) Silver is a less reactive metal in the sense that it occupies a place below hydrogen in the reactivity series. Therefore it does not evolve hydrogen gas on reacting with either dilute sulphuric acid or dilute hydrochloric acid.
Question 30.
What is an oxidation reaction ? Identify in the following reactions :
(i) the substance oxidised
(ii) the substance reduced.
Answer:
ZnO + C ———> Zn + CO
Oxidation involves the addition of oxygen or the removal of hydrogen in a chemical reaction. In the given reaction, carbon is oxidised to carbon monoxide while zinc oxide is reduced to zinc.
Question 31.
Identify the type of reaction in the following examples :
(i) Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) ———-> BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
(ii) Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) ———-> FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
(iii) 2H2(g) + O2(g) ———> 2H2O(l)
Answer:
(i) It is an example of double displacement reaction.
(ii) It is an example of displacement reaction.
(iii) It is an example of combination reaction.
Question 32.
Solid calcium oxide was taken in a container and water was added slowly to
(i) State two observations made in the experiment.
(ii) Write the name of the chemical formula of the product.
Answer:
(i) Water will start boiling and hissing noise will be produced.
(ii) Calcium hydroxide (slaked lime) will be formed.
![]()
Question 33.
A house wife wanted her house to be white washed. She bought 10 kg of quick lime from the market and dissolved in 30 litres of water.
Answer:
She noticed that water started boiling even when it was not being heated. Give reason for her observation. Write the corresponding equation and name the product formed.
A suspension of slaked lime also called calcium hydroxide is formed when water is added to quick lime.
![]()
Since the reaction is highly exothermic, the solution started boiling although it was not being heated. The suspension of slaked lime is allowed to cool for sometime, preferably overnight. It is then decanted and the liquid obtained is used for white washing.
Question 34.
(i) What is observed when a solution of potassium iodide is added to a solution of lead nitrate taken in a test tube ?
(ii) What type of reaction is this ?
(iii)Write a balanced equation to represent the above reaction.
Answer:
(i) A yellow precipitate of lead iodide appears at the bottom of the test tube.
(ii) It is an example of double displacement reaction.
(iii) The balanced equation for the reaction is :
![]()
Question 35.
What change in colour is observed when white silver chloride is left exposed to sun light ? State the type of chemical reaction in this change.
Answer:
White colour of silver chloride changes to grey due to formation of metallic silver. The reaction is known as photochemical reaction. It is also a decomposition reaction.
![]()
Question 36.
What happens when an aqueous solution of sodium sulphate reacts with an aqueous solution of barium chloride ? State the physical conditions of reactants in which the reaction between them will not take place. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction and name the type of reaction. (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
A white precipitate of barium sulphate is immediately formed when the two aqueous solutions are mixed in a test tube. No reaction will be possible if the two reactants are in the solid state. The balanced chemical equation for the double displacement reaction is :
![]()
Question 37.
What is a redox reaction ? When a magnesium ribon burns in air with a dazzling flame and forms a white ash; is magnesium oxidised or reduced ? Why ?
Answer:
A redox reaction is a chemical reaction in which one of the reactants gets oxidised while the other is reduced simultaneously. In the reaction under study, magnesium is oxidised to magnesium oxide since the metal has gained oxygen.
Question 38.
(a) What happens chemically when quick lime is added to water ? (CBSE 2012)
(b) Write the chemical equation in balanced form.
MnO2 + HCl ———-> MnCl2 + Cl2 + H2O
(c) What is decomposition reaction ? Explain it with suitable example.
Answer:
(a) When quick lime (CaO) is added to water, slaked lime Ca(OH)2 is formed. The reaction is highly exothermic in nature.
(b) The balanced chemical equation is :
MnO2 + 4HCl ———-> MnCl2 + 2H2O + 2Cl2.
(c) Decomposition reaction is a chemical reaction in which a single substance splits or breaks into two or more substances under suitable conditions. For example,
![]()
Long Answer Questions
Question 39.
(a) Why cannot a chemical change be normally reversed ?
(b) Why is it always essential to balance a chemical equation ?
(c) Why do diamond and graphite, the two allotropie forms of carbon evolve different amounts of heats on combustion ?
(d) Can rusting of iron take place in distilled water ?
Answer:
(a) In a chemical change, the products are quite different from the reactants. Therefore, it cannot be normally reversed.
(b) A chemical equation has to be balanced to meet the requirement of the law of conservation of mass. According to the law, the total mass of the reacting species taking part in the reaction is the same as that of the products formed. Since there is a direct relationship between the mass of the different species and their number, it is always essential to balance a chemical equation.
(c) Because they differ in the arrangement of carbon atoms present and have different shapes. The attractive forces among the atoms in the two cases are not same. That is why they evolve different amount of heat.
C(diamond) + O2(g) ———–> CO2(g) + 393.5 kj
C(graphite) + O2(g) ———–> CO2(g) + 395.4 kj
Please note that diamond and graphite are the two allotropie forms of carbon.
(d) No, rusting of iron cannot take place in distilled water because it neither contains dissolved oxygen nor carbon dioxide. Both are essential for the rusting of iron.
Question 40.
You are given the following materials :
(i) Iron nails
(ii) Copper sulphate solution
(iii) Barium chloride solution
(iv) Copper powder
(v) Ferrous sulphate crystals
(vi) Quick lime.
Identify the type of chemical reaction taking place when :
(a) Barium chloride solution is mixed with copper sulphate solution and a white precipitate is observed.
(b) On heating, copper powder in air in a china dish, the surface of copper powder becomes black.
(c) On heating green ferrous sulphate crystals, reddish brown solid is left and a gas having smell of burning sulphur is noticed.
(d) Iron nails when left dipped in blue copper sulphate solution become brownish in colour and blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades away.
(e) Quick lime reacts vigorously with water releasing a large amount of heat.
Answer:
(a) The reaction is double displacement in nature. ‘
![]()
(b) It is an example of combination reaction.
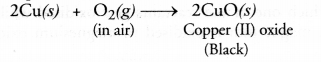
(c) The green crystals of ferrous sulphate have the chemical formula FeS04.7H20. Upon heating, they lose molecules of water of crystallisation.
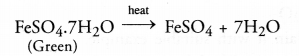
Upon further heating, ferrous sulphate undergoes decomposition reaction as follows :
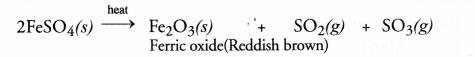
Both the gases evolved have the smell of burning sulphur.
(d) This happens because of displacement reaction. Iron displaces copper form copper sulphate solution. Brownish coating of copper gets deposited on the iron nails. As the concentration of copper sulphate in the solution decreases, the blue colour of the solution slowly fades.
![]()
(e) Calcium hydroxide is formed as a result of combination reaction. It is highly exothermic. A large amount of heat is evolved accompanied by hissing sound.
![]()
Question 41.
A silvery white metal X is in the form of ribbons. Upon ignition, it burns with a dazzling white flame to form white powder Y. When water is added to the powder Y, it partially dissolves to form a substance Z which is used as an antacid.
(a) What is metal X ?
(b) Name the white powder Y.
(c) What is the substance Z ?
(d) Write the chemical reactions that are taking place.
Answer:
(a) The metal is X is Mg.
(b) The white powder Y is MgO.
(c) White powder Y dissolves partially in water to form substance Z. It is Mg(OH), and is used as an antacid.
(d) The chemical reactions that are taking place are :
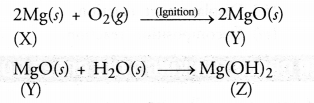
Question 42.
(i) Account for the following :
(a) White silver chloride turns grey in sunlight.
(b) Brown coloured copper powder on heating in air turns into black coloured substance.
(ii) What do you mean by
(a) Displacement reaction
(b) Reduction reaction
(c) Combination reaction ? Write balanced chemical equation.
Answer:
(i) (a) White coloured silver chloride undergoes decomposition in the presence of sunlight and forms silver (grey in colour) and chlorine.
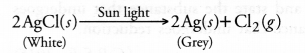
(b) Brown coloured copper powder on heating in air gets oxidised to copper oxide which is black in colour.
![]()
(ii) For the different types of reactions,
(a) In a displacement reaction, one element takes the place of another in a compound dissolved in a solution. For example,
Fe(s) + CuSO4 (aq) ———> FeSO4 (aq) + Cu(s)
(b) Combination reaction may be defined as the reaction in which two or more substances combine under suitable conditions to form a new substance. For example,

(c) A decomposition reaction may be defined as the reaction in which a single substance decomposes or splits into two or more substances under suitable conditions.
For example,
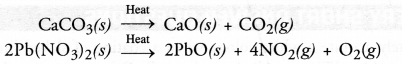
It may be concluded that a certain substance is formed or synthesised in combination reaction and it breaks or splits in decomposition reaction. Therefore, the two reactions oppose each other.
Question 43.
(a) Write the chemical equation in the balanced form.
Fe(s) + H2O(g) ———–> Fe3O4(s) + H2(g)
(b) Identify the type of reaction from the equation given below :
Na2SO4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) ———–> BaSO4(s) + NaCl(aq)
(c) You could have noted that when copper powder is heated in a china dish, the surface of copper powder gets coated with black coloured substance.
(i) Why is this black coloured substance formed ?
(ii) What is this black substance ?
(iii) Write the chemical equation of the reaction taking place.
Answer:
(a) 3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) ————> Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
(b) It is a double displacement reaction also called precipitation reaction. A white precipitate of BaSO4 is formed in the reaction.
(c)
(i) The black substance is formed due to the oxidation of copper.
(ii) The black substance is cupric oxide or copper (II) oxide with formula CuO.
![]()
Question 44.
Observe the given figure and answer the following questions.
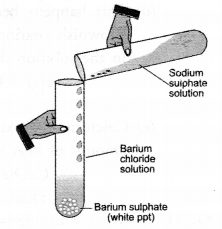
(a) Write the complete balanced reaction for the reaction that takes place.
(b) Type of reaction involved.
(c) Is there any precipitate formed.
(d) If any precipitate formed, write the colour of the precipitate.
Answer:
![]()
(b) It is a double displacement reaction
(c) Yes, a precipitate of barium sulphate is formed.
(d) The precipitate is white in colour.
Question 45.
Select (i) combination reactions (ii) decomposition reactions and displacement reactions from the following
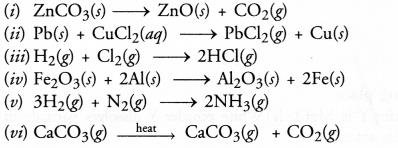
Answer:
(i) Decomposition reaction
(ii) Displacement reaction
(iii) Combination reaction
(iv) Displacement reaction
(v) Combination reaction
(vi) Decomposition reaction.
Hope given Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations are helpful to complete your science homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online science tutoring for you.