Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
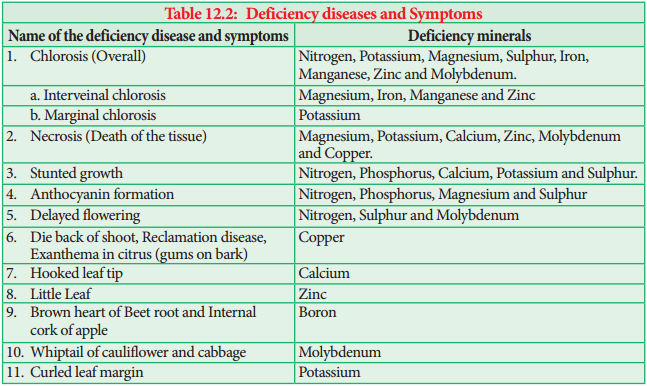
Deficiency Diseases and Symptoms
The following table (Table 12.2) gives you an idea about Minerals and their Deficiency symptoms:
Signs and symptoms of vitamin deficiency anemia include:
- Fatigue
- Shortness of Breath
- Dizziness
- Pale or yellowish Skin
- Irregular Heartbeats
- Weight Loss
- Numbness or tingling in your hands and feet
- Muscle Weakness
7 Nutrient Deficiencies:
That Are Incredibly Common
- Iron deficiency. Iron is an essential mineral
- Iodine Deficiency
- Vitamin D Deficiency
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Calcium Deficiency
- Vitamin A Deficiency
- Magnesium Deficiency
Any currently treated or untreated nutrient deficiency or disease. These include, but are not limited to, Protein Energy Malnutrition, Scurvy, Rickets, Beriberi, Hypocalcemia, Osteomalacia, Vitamin K Deficiency, Pellagra, Xerophthalmia, and Iron Deficiency.
Nutritional Deficiencies can lead to conditions such as anemia, scurvy, rickets.
- Calcium
- Magnesium
- Omega-3 fatty acid
- Folate
- Potassium
- Vitamin A
- Vitamin E
- Copper
Copper deficiency is more common among people with untreated celiac disease than the general population. Stopping behaviors that contribute to the deficiency, such as unhealthy eating, smoking, and heavy alcohol use, can help prevent vitamin deficiency anemia. Eating a healthy diet can lower your risk of developing the condition. Some people take a daily vitamin supplement to help prevent the condition.
These deficiencies can result in many disorders including anemia and goitre. Examples of mineral deficiency include, zinc deficiency, iron deficiency, and magnesium deficiency.
A deficiency disease can be defined as a disease which is caused by the lack of essential nutrients or dietary elements such as vitamins and minerals in the human body. Deficiency disease examples: Vitamin B1 deficiency causes beriberi, lack of iron in the body can lead to anaemia.
There are four main types of disease: infectious diseases, deficiency diseases, hereditary diseases (including both genetic diseases and non-genetic hereditary diseases), and physiological diseases. Diseases can also be classified in other ways, such as communicable versus non-communicable diseases.
Vitamin and nutrition blood tests can detect gluten, mineral, iron, calcium and other deficiencies, telling you which vitamins you lack and which you are getting enough of through natural sources.
What are the causes of zinc deficiency? A poor diet can cause zinc deficiency. So it is more common in malnourished children and adults and in people who are unable to eat a normal diet due to circumstances or illness. Lots of zinc intake is from meat and seafood, so vegetarians may be more prone to deficiency.
There is a very simple and efficient test for zinc deficiency. For an adult, mix fifty mg of zinc sulphate in a half a glass of water. If it tastes sweet, pleasant or like water, then your body needs it. If it has a strong metallic or unpleasant taste, you are not zinc deficient.
Vitamin E deficiency may cause impaired reflexes and coordination, difficulty walking, and weak muscles. Premature infants with the deficiency may develop a serious form of anemia. The diagnosis is based on symptoms and results of a physical examination. Taking vitamin E supplements corrects the deficiency.