In Online Education Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 Science Important Questions and Answers PDF will help you in scoring more marks. This consists of 1 mark Questions, 3 Mark Numericals Questions, 5 Marks Numerical Questions and previous year questions from Chemical Reactions and Equations Chapter.
Online Education Carbon and its Compounds Class 10 Important Questions and Answers Science Chapter 4
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the essential constituents of all organic compounds ?
Answer:
Carbon and hydrogen are the essential constituents of all organic compounds. However, carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) is an exception.
More Resources
- Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science
- NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 10 Science
- Value Based Questions in Science for Class 10
- HOTS Questions for Class 10 Science
Question 2.
What is the valency of carbon in its compounds ?
Answer:
Carbon is tetravalent in its compounds.
Question 3.
Why are organic compounds present in such a large number ?
Answer:
This is due to the self linking property of carbon known as catenation.
Question 4.
Which is common in all the members of a family ?
Answer:
They have the common functional group.
Question 5.
A family of organic compounds has the functional group ‘al’. What is its name ?
Answer:
The family is of aldehydes also called alkanals.
Question 6.
Out of ketonic and aldehydic groups, which is the terminal functional group ?
Answer:
Aldehydic group

Question 7.
Why is candle flame generally yellow ?
Answer:
Candle flame is generally yellow due to the presence of unburnt carbon particles. When light falls on these particles, they scatter yellow colour. This shows that the combustion of hydrocarbons present in wax or candle is not complete.
Question 8.
The formula of a hydrocarbon is CnH2n. Name the family to which it belongs and also predict its nature.
Answer:
The hydrocarbon belongs to alkene family. It is unsaturated in nature.
Question 9.
An unknown compound has the smell of vinegar. Identify it.
Answer:
The compound is ethanoic acid also called acetic acid.
Question 10.
What do we get when ethanoic acid reacts with ethanol in the presence of concentrated sulphuric acid ?
Answer:
Ethyl ethanoate (CH3COOC2H5) is formed by esterification reaction. It has fruity smell.
Question 11.
Name the second member of alkyne family. Give its structure.
Answer:
The second member of alkyne family is propyne. Its structural formula is H3C—C = CH.
Question 12.
Vapours of a hydrocarbon were passed through bromine dissolved in carbon tetrachloride. The yellow colour of bromine got discharged ? Predict the nature of the hydrocarbon.
Answer:
The hydrocarbon is unsaturated. It is either an alkene or alkyne.
Question 13.
Give a test to identify the presence of ethanoic acid.
Answer:
Dip a strip of blue litmus paper in the solution of ethanoic acid. Its colour will change to red.
Question 14.
Out of butter and ground nut oil, which is unsaturated in nature ?
Answer:
Ground nut oil is unsaturated in nature.
Question 15.
What is the role of soap in cleansing of clothes ?
Answer:
Soap helps in forming a stable emulsion between oil drops carrying dirt particles and water. The emulsion is also known as micelle.
Question 16.
Which organic compound is added to make ethanol unfit for drinking purposes ? What is the name of the mixture formed ?
Answer:
Methanol which is highly poisonous is added in small amount to ethanol in order to make it unfit for drinking purposes. The mixture is called methylated spirit or denatured alcohol.
Question 17.
Can you check hard water by using a detergent ?
Answer:
No, it is not possible because detergents give lather with both soft and hard waters.
Question 18.
When do you get yellow soot in the burner flame ?
Answer:
Yellow soot is obtained when the holes of the burner are not clean. The combustion is incomplete. The yellow – soot or yellow flame is because of unburnt carbon particles.
Question 19.
Write IUPAC and common names of CH3COCH3, C2H5COOH.
Answer:
CH3COCH3 : Propanone, Acetone
C2H5COOH : Propanoic acid, Propionic acid.
Question 20.
Which of the following belong to the same homologous series ?
C3H8, C4H8, C4H6, C3H6.
Answer:
C3H6 and C4H8 belong to the same homologous series which is alkenes with general formula CnH2n.
Question 21.
Which has a triple bond; C2H2, C3H4 and ?
Answer:
C3H4 has triple bond with the formula CH3C ≡ CH
Question 22.
The molecular formula of butane is C4H10. What is the formula of butene ?
Answer:
The formula of butene is C4H8.
Question 23.
A compound with molecular forumla C2H6O is used as a fuel. Identify the compound.
Answer:
The compound is ethanol with formula C2H5OH.
Question 24.
What is common in the structures of the compounds methonal and ethanol ?
Answer:
They have the same functional group (—OH) known as alcoholic group.
Question 25.
Which functional groups are present in the family of
(i) alcohols
(ii) aldehydes
(iii) carboxylic acids ?
Answer:
(i) —OH
(ii) —CHO
(iii) —COOH.
Question 26.
Identify from the following the hydrocarbons that undergo addition reactions :
C3H4, C2H6, CH4, C2H4. Justify your answer
Answer:
The hydrocarbons are C2H4 (ethene) with formula CnH2n and C3H4 (propyne) with formula CnH2n-2 both are unsaturated.
Question 27.
Which element exhibits the property of catenation to maximum and why ? (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
The element is carbon. This is because of very small size of carbon atom (77 pm) and high strength of C—C bond (355 kj mol-1).
Question 28.
Select the saturated hydrocarbons from the following
C3H6; C5H10; C4H10; C6H14; C2H4 (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
The compounds C4H10 (butane) and C6H14 (hexane) are saturated hydrocarbons. They correspond to the molecular formula CnH2n+2.
Question 29.
Write the molecular formula of the first two members of the homologous series having functional group >C=0. (CBSE 2017)
Answer:
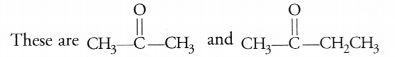
Question 30.
Name the functional group present in the compound CH3CH2CH2COOH.
Answer:
The functional group (—COOH) is known as carboxyl group.
Short Answer Questions
Question 31.
Write the structures of
(i) Ethanoic acid
(ii) Butanone
(iii) Hexanal
(iv) But-2-ene.
Answer:
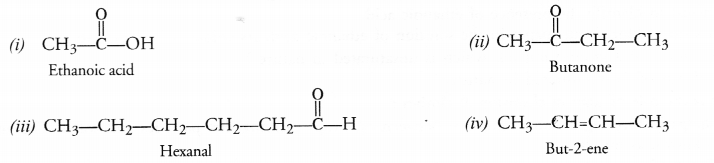
Question 32.
How will you name the following compounds ?
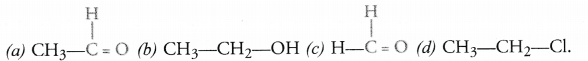
Answer:
(a) Ethanal
(b) Ethanol
(c) Methanal
(d) Chloroethane.
Question 33.
Identify the name of the functional groups in the following compounds.
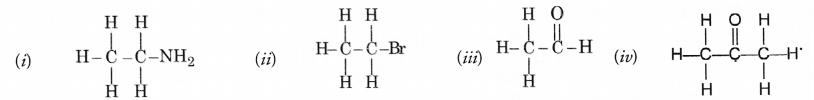
Answer:
(i) —NH2 (amino) (ii) —Br (bromo)
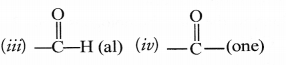
Question 34.
Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds.
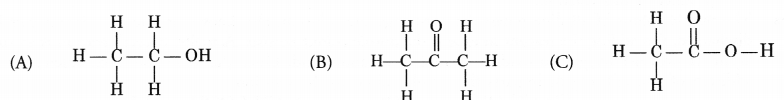
Answer:
(A) Ethanol
(B) Propanone
(C) Ethanoic acid.
Question 35.
Give the electron dot structure and structural formula of first member of alkene and alkyne families.
Answer:
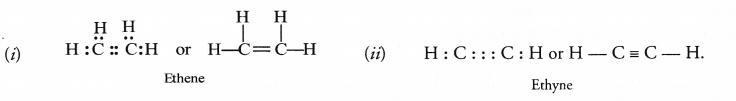
Question 36.
Draw the structural formulae of the possible isomers for the compound with molecular formula C3H6O ?
(CBSE Sample Paper 2017)
Answer:
The given organic compounds represents two structural isomers which are actually functional isomers in nature.
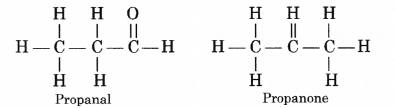
Question 37.
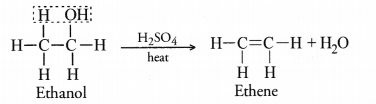
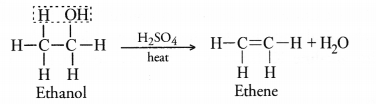
How will you convert ethene into ethanol ? Give the chemical reaction involved.
Answer:
Ethene is converted into ethanol by passing its vapours through water in the presence of sulphuric acid. This reaction is called hydration of ethene.
![]()
Question 38.
What is an homologous series ? Which two of the following organic compounds belong to the same homologous series ?
C2H6, C2H6O, C2H6O2,
Answer:
Homologous series represent different families of organic compounds into which these are divided. Two characteristics of homologous series are listed.
The compounds CH4O and C2H6O belong to the same homologous series known as alkanols.
Question 39.
State two characteristic features of carbon which when put together give rise to a large number of carbon compounds.
Answer:
- The size of carbon atom is very small (Atomic radius = 77 pm)
- The strength C—C bond is quite high (355 kj mol-1)
Therefore, any number of carbon atoms can be linked by covalent bonds, f his self linking property is called catenation.
Question 40.
Why is petrol regarded as a better fuel than kerosene ?
Answer:
In petrol, the combustion of hydrocarbons present is complete and they burn with blue flame. However, in kerosene, the combustion is not complete. It burns with smoky flame accompanied by the release of unburnt carbon atoms. Therefore, petrol is regarded as a better fuel than kerosene.
Question 41.
The molecular formula C3H6O can represent an aldehyde as well as ketone. Write their structures and name them. How are they related to each other ?
Answer:
The aldehyde and ketone with formula C3H6O are propanal and propanone. Having the same molecular formula, these are isomers. As the functional groups are different, these are regarded as functional isomers.
For example,

Question 42.
(i) Take about 3mL, of ethanol in a test tube and warm it gently in a water bath.
(ii) Add a 5% solution of alkaline potassium permanganate drop by drop to the solution.
(iii) What happens to the colour of KMnO4 added initially and then in excess ? Give reason. Name the product of this reaction.
Answer:
The purple colour of alkaline potassium permanganate solution, also known as Baeyer’s reagent gets initially discharged. On adding the reagent in excess, the purple colour persists. Actually, Baeyer’s reagent is an oxidising agent. It provides oxygen to oxidise ethanol to ethanoic acid. Once the oxidation is complete, the further addition of Baeyer’s reagent imparts the purple colour to the solution.

Question 43.
Give the names of the following :
(i) An aldelyde derived from methane
(ii) Ketone derived from butane
(iii) The compound obtained by the oxidation of ethanol with chromic anhydride.
Answer:
(i) Methanal (HCHO)
(ii) Butanone (CH3COCH2CH3)
(iii) Ethanal (CH3CHO)
Question 44.
Write chemical equations for the reactions of ethanoic acid with :
(i) sodium
(ii) sodium carbonate
(iii) ethanol in the presence for cone. H2SO4
Answer:
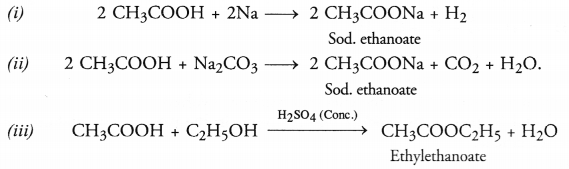
Question 45.
A compound ‘X’ has the molecular formula C3H6O with structural formula CH3CH2CHO. Give its IUPAC name. Can another compound have the same molecular formula ? Give the structure and IUPAC name of that compound also ?
Answer:
The IUPAC name of X is : Propanal. Another compound Y can also have the same molecular formula but different structural formula. It is propanone.

The compounds X and Y are related to each other as functional isomers.
Question 46.
An organic compound ‘X’ has the molecular formula C2H4O2. It has a pleasent smell. It does not turn blue litmus red; nor does it give any effervescence with sodium hydrogen carbonate solution. Predict the com pound. Give its structural formula as well as IUPAC name.
Answer:
Two different structural formulae are possible for the compound ‘X’ with molecular formula C2H4O2. These are known as functional isomers and may be written as :

Structure I is that of a carboxylic acid, ethanoic acid. Since the compound ‘X’ does not turn blue litmus red and also does not give effervescence with NaHCO3 solution, it cannot be an acid.
As the compound has a pleasent smell, it seems to be an ester with structure II. Please note that the esters have pleasant smell. The IUPAC name of the compound is methylmethanoate.
Question 47.
Acetic acid was added to a solid ‘X’ kept in a test tube. A colourless and odourless gas was evolved. The gas turned lime water milky when passed through it. Predict the nature of the solid.
Answer:
Since the gas was colourless as well as odourless and turned lime water milky, it is carbon dioxide gas. The solid ‘X’ which has liberated the gas on reacting with acetic acid is either a metal carbonate (e.g. Na2CO3) or some hydrogen carbonate of metal (e.g. NaHCO3)
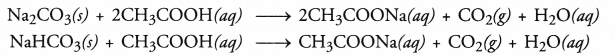
Question 48.
An organic compound A’ is a constituent of antifreeze and has the molecular formula C2H6O. Upon reaction with alkaline KMnO4, the compound A’ is oxidised to another compound ‘B’ with formula C2H6O2. Identify the compounds A and ‘B’. Write the chemical equation for the reaction which leads to the formation of ‘B’.
Answer:
The compound A is ethanol and with alkaline KMnO4 it is oxidised to ethanoic acid ‘B’. The chemical equation for the reaction is :
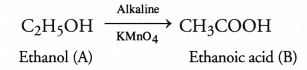
Question 49.
Name the functional groups present in the following compounds :
(i) CH3—CH2—CH2—OH
(ii) CH3—CH2—CH2—COOH
(iii) CH3—CH2—CHO
(iv) CH3—CO—CH2—CH3
Answer:
(i) —OH (ol)
(ii) —COOH (oic acid)
(iii) —CHO (al)
(iv) —CO— (one)
Question 50.
(a) Draw the structure of the following compounds :
(i) Ethanoic acid
(ii) Butanone.
(b) Why is conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid considered an oxidation reaction ?
Answer:
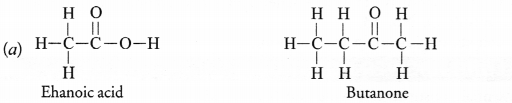
(b) When ethanol (C2H5OH) changes with ehanoic acid (CH3COOH)
- There is a decrease in the number of hydrogen atoms by two.
- There is an increase in the number of oxygen atoms by one.
Therefore, the conversion represents an oxidation reaction.
Question 51.
(a) What are esters ? How are they formed ?
(b) Write two uses of esters ? (CBSE 2017)
Answer:
(a) Esters are the group of organic compounds which contain the function group (—COOR) called ester group. The value of R may change as —CH3, —C2H5, —C3H7, etc. A few examples of esters are

Esters are formed as a result of chemical reaction called esterification.
(b) Uses of esters
- Esters have pleasent smell. These are used as flavouring agents and also in perfumes.
- Esters of glycerol known as triglycerides, are used in the manufacture of soaps.This reaction is called saponification reaction.
Question 52.
Write the names and moleculer formula of two organic compounds having functional group suffixed as ‘-oic acid’.
With the help of a balanced equations, explain what happens when any of them reacts with sodium hydroxide.
Answer:
The organic compounds with functional group-oic acid are known as carboxylic acids or alkanoic acids. These are represented by general formula RCOOH (Where R may be H atom or alkyl group). For example,
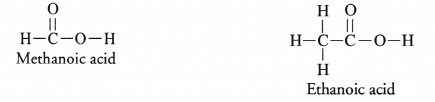
On reacting a carboxylic acid with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), corresponding sodium salt and water are formed. The reaction is known as neutralisation.
![]()
Question 53.
Write the name and molecular formula of an organic compound having its name suffixed with of and having two carbon atoms in the molecule. With the help of a balanced chemical equation indicate what happens when it is heated with excess of cone. H2SO4. (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
The compound is ethanol and its molecular formula is C2H5OH. Upon heating with excess of cone. H2SO4, it loses a molecule of H2O and forms ethene. The reaction is known as dehydration reaction.
Question 54.
Explain with the help of chemical equations, the following properties of carbon.
(i) Combustion
(ii) Oxidation.
Answer:
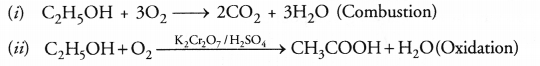
Question 55.
A neutral organic compound A of molecular formula C2H6O on heating with excess of cone. H2SO4 gives compound B of molecular formula C2H4. Compound B on reduction gives compound C of molecular formula C2H6.
(a) Name A, B and C.
(b) Write chemical equation for the conversion of A to B.
(c) What is the role of cone. H2SO4 in the above equation.
Answer:
(a) The compounds A, B and C are ethanol (C3H6O), ethene(C2H4) and ethane(C2H6) respectively.
(b) For the chemical equation,
(c) Cone. H2SO4 is used as a dehydrating agent in the reaction.
Long Answer Questions
Question 56.
An organic compound ‘A’ is an essential constituent of wine and beer. Oxidation of ‘A’ yields an organic acid ‘B’ which is present in vinegar. Name the compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ and write their strucutral formulae. What happens when ‘A’ and ‘B’ react in the presence of an acid catalyst ? Write the chemical equation for the reaction.
(CBSE All India 2010)
Answer:
The available information suggests that the compound ‘A’ is ethanol and the compound ‘B’ formed by the oxidation of ‘A’ is ethanoic acid. Their structural formulae are :

When ‘A’ and ‘B’ react in the presence of an acid like cone. H2SO4, the compound is ethyl ethanoate (ester) with a pleasant smell.
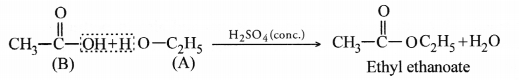
Question 57.
Give a chemical test to distinguish between :
(i) Ethane and ethene
(ii) Ethanol and ethanoic acid
(iii) Soaps and detergents.
Answer:
(i) Ethene decolorises the yellow colour of bromine water while ethane does not.
(ii) Ethanoic acid gives a brisk effervescence with sodium hydrogen carbonate while ethanol does not.
(iii) Soaps form curdy white precipitate or scum with hard water while detergents do not form any precipitate.
Question 58.
(a) What are homologous series of compounds ? List any two characteristics of homologous series.
(b) What would be observed by adding a 5% solution of alkaline potassium permanganate drop by drop to warm ethanol taken in a test tube ? (c) Write the name of the compound formed during the chemical reaction. How would you distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid on the basis of a chemical property.
Answer:
(a) Homologous series represent different families of organic compounds into which these are divided. Two characteristics of homologous series are listed.
- All the members in a particular homologous series of family have the same characteristic functional group. For example, in organic acids, the functional group is carboxyl group (—COOH).
- Any two consecutive members in a particular family have the same common difference of CH2 in their molecular formulae. For example, the first three members of the family of alkanes are : CH4 (methane), C2H6 (ethane) and propane (C3H8).
(b) On adding a 5% solution of alkaline potassium permanganate to ethanol, it will be oxidised to ethanoic acid.
The pink colour of the solution will get discharged upon warming.
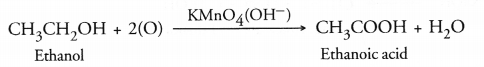
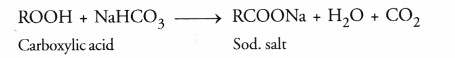
(c) A carboxylic acid gives a brisk effervescence when an aqueous solution of sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO3) is added to it. This is due to the evolution of CO2 gas. However, alcohol will not give any reaction.
Question 59.
(a) How are carboxylic acids different from mineral acids from ionisation point of view ?
(b) Describe an activity to show how ethanoic acid reacts with sodium carbonate. Name the gas evolved. How can it be tested ?
(c) State the principle on which the cleansing action of soap is based.
Answer:
(a) Carboxylic acids (organic acids) are less ionised in solution as compared to mineral acids (HCl, HNO3, H2SO4 etc.) Due to this reason, these are weaker acids than the mineral acids.
(b) Take a small volume of ethanoic acid in a tube. Add a few drops of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3) solution prepared in water to the tube. A colourless gas with brisk effervescence will evolve. When the gas is passed through lime water, it will become milky.
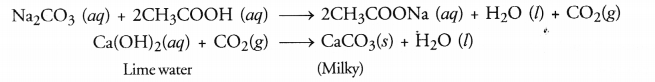
(c) The cleansing action of soap is based on its tendency to act as a bridge between water and oil drops containing dirt particles. As a result, oil and water get mixed. They form a stable emulsion also called micelle. This helps in removing oil drops containing dirt particles from clothes. The clothes become clean.
Question 60.
(a) Distinguish between esterification and saponification reactions of organic compounds.
(b) With the help of a labelled diagram, describe an activity to show the formation of an ester.
Answer:
(a) In the esterification reaction an acid reacts with alcohol in the presence of cone. H2SO4 to form an ester with a pleasant or fruity smell. For example,
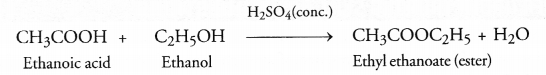
Saponification is quite different from esterification because in this case an ester reacts with an alkali (NaOH or KOH) to form salt of acid and alcohol. For example,

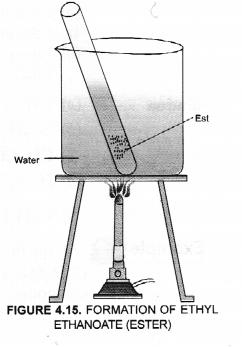
(b) For the activity,
Esters can be easily formed in the laboratory also. Take equal volumes of ethyl alcohol and glacial acetic acid (say 2 mL) alongwith a few drops of concentrated sulphuric acid in a test tube. In the mean time, warm water in a beaker as shown in the figure. Keep the test tube in warm water for some time. You will experience a pleasant smell. This shows that ethyl acetate (ester) has been formed in the reaction.
Esters as pointed, are pleasant smelling compounds. These are therefore, commonly used as flavouring agents and also in perfumes. When an ester is reacted with water in the presence of a dilute acid like dilute HCl, acid and alcohol are formed as the product. The reaction is called ester hydrolysis.
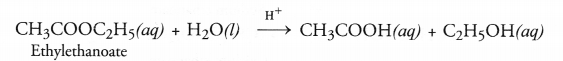
Ester hydrolysis is the reverse of esterification reaction.
When an ester is reacted with an aqueous solution of base like NaOH or KOH, the product is an alcohol and salt of the acid. For example,
The reaction is known as saponification reaction because it is the basis for the formation of soap.
Question 61.
An ester has the molecular formula C4H8O2. Write its structural formula. What happens when this ester is heated in the presence of sodium hydroxide solution ? Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction and name the products. What is a saponification reaction ?
Answer:
For the molecular formula C4H8O2, two isomeric esters are possible which differ in structural formulae.
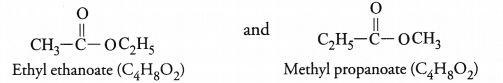
Both will react with sodium hydroxide upon heating to form the sodium salt of the acid and alcohol.
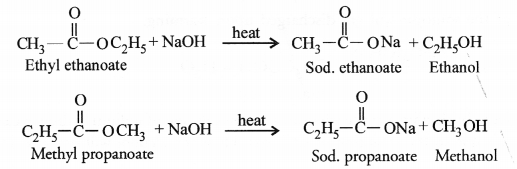
Both the reactions are the examples of saponification reactions. In these, an ester reacts with an alkali upon heating to form corresponding salt and alcohol.
Question 62.
Two carbon compounds ‘A’ and ‘B’ have the molecular formula C3H8 and C3H6 respectively. Which one of the two is most likely to show addition reactions ? Justify your answer. Explain with the help of a chemical equation, how an addition reaction is useful in vegetable ghee industry.
Answer:
The compound ‘A’ with formula C3H8(propane) is a saturated hydrocarbon and corresponds to general formula CnH2n+2. The compound ‘B’ with formula C3H6 (propene) is an unsaturated hydrocarbon and corresponds to general formula CnH2n. It has a double bond (C=C) and is therefore, unsaturated.
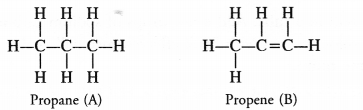
The compound ‘B’ will take part in the addition reactions. As a result, double bond will change to single bond. For example,
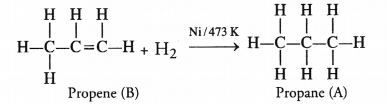
The addition reaction is quite useful in the hydrogenation of oils i.e., to convert edible oils like ground nut oil and cotton seed oil which are unsaturated in nature into solid fats which are of saturated nature.
Hope given Previous Year Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds helpful to you. If you have any doubts, please comment below. We try to provide online math tutoring for you.