Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 2 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Term 2 Set 2 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- This Question paper is divided into five sections-Section A, B, C, D and E.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A: Question no. 1 to 5 are very short answer type questions of 2 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 40 words.
- Section-B: Question no. 6 to 8 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
- Section-C: Question no. 9 and 10 are long answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
- Section-D: Question no. 11 and 12 are Case Based questions.
- Section-E: Question no. 13 is map based, carrying 3 marks with two parts, 13.1 from History (1 mark) and 13.2 from Geography (2 marks).
- There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in a few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
- In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever necessary.
SECTION-A [2 × 5 = 10]
(Very Short Answer Type Questions)
Question 1.
The Quit India movement was the final nail in the coffin of the British government. Support this statement by giving one reason. (2)
Answer:
The Quit India movement was aimed at the immediate overthrow of British administration and transfer of powers of administration to Indians.
Caution:
Each movement had different objectives and hence should be remembered clearly. For example, the Civil disobedience movement only asked for more autonomy and self-governing institutions while the Quit India movement asked for complete withdrawal of the British from the country
Question 2.
Define a tidal port. Also give an example of one. (2)
Answer:
Tidal ports are those ports in which the level of water within the port varies with the change in the level of water in the oceans. For example, Kandla port.
Related Theory:
Tidal ports also refer to the place where energy is derived from the waves of the ocean. Tidal energy is the energy driven out of the waves of the oceans which arise and fall during the tides, caused due to various reasons.
Question 3.
How does information and communication technology boost foreign trade? (2)
Answer:
Telecommunication facilities are used to contact one another around the world, to access information instantly, and to communicate from remote areas. These facilities help boost foreign trade.
Related Theory:
Telecommunications facilities include mails, telephonic communications with mobiles and fax etc help the sellers and buyers contact each other and access information about one another.
![]()
Question 4.
Read the given data and answer the following questions.
The Indian Railway Network runs on multiple gauge operations extending over 68,442 km.
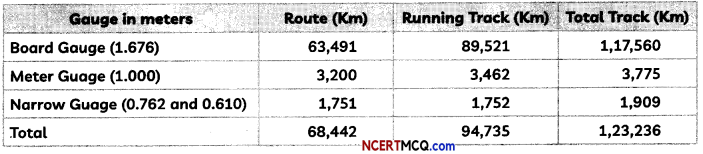
(A) Define the term gauge? (1)
Answer:
The gauge of a railway track is the distance between two running rails.
(B) What is the criterion of classifyingrailway tracks into Broad Gauge and Narrow Gauge? (1)
Answer:
They are classified based on distances between two rails or the width between the two rails.
Related Theory:
Broad Gauge is also called wide gauge.
Question 5.
The Left front is an alliance. What does an alliance mean? (2)
Answer:
Multi-parties join hands for the purpose of contesting elections and winning power and are called an alliance or a front. For example, Left front.
Related Theory
Coalition of multiple parties form alliances and fronts. Two more examples are the National Democratic Alliance and United Progressive Alliance. Both of these alliances are functional in contemporary politics.
SECTION – B [3 × 3 = 9]
(Short Answer Type Questions)
Question 6.
The understanding of plantation workers of Assam of the concept of Swaraj was different and descriptive of their situations. Support the statement.
OR
The Jallianwala Bagh incident was a result of the rising nationalist sentiments among Indians. Mention some circumstances which expressed these emotions. (3)
Answer:
Their understanding can be underlined in the following points:
- The plantation workers of Swaraj were extremely exploited by their employers.
- They were not allowed to leave the plantations and were made to work in miserable conditions.
- They understood Swaraj as the right to move freely in and out of the plantations and thus defied the authorities and left for their homes as a sign of protest.
OR
The circumstances that led to the Jallianwala Bagh incident are as follows:
- The hartals, strikes and rallies launched by Gandhi after the Rowlatt Act were met with brutal resistance.
- Alarmed by popular upsurge, the British decided to clamp down on the nationalist leaders.
- General Dyer took command of Punjab and imposed martial law censoring national movements and repressing these sentiments.
Thereafter, he openly fired on the public to spread fear among them.
Question 7.
The use of money spans a very large part of our everyday life. Do you agree? Elaborate upon your stand. (3)
Answer:
Money definitely plays a central role in our daily life. It fulfills the following functions:
- It is used as a medium of exchange to carry out transactions, whether immediate or deferred.
- Money buys us every commodity of necessity including food, clothing, shelter and water etc.
- Money provides us with social security. It is needed to procure services like transport, education, healthcare, entertainment, recreation, and so on.
Related Theory:
- In an economy where money is in use, by providing the crucial intermediate step, money eliminates the need for double coincidence of wants.
- Payment can also be made through cheques. For that, the payer who has an account with the bank, makes out a cheque for a specific amount.
![]()
Question 8.
Opposition parties mobilise opposition against the government. Validate the given statement. (3)
Answer:
Opposition parties are those political parties which are unable to achieve the required majority in the elections.
These political parties play the role of opposition in legislative institutions and fulfill the following functions:
- They question the relevance and appropriateness of government’s schemes and steps.
- They educate the people politically and help people mobilise demands in front of the government for better rules and regulations.
- They present alternative solutions and draft regulations through their manifestos and public appearances to mould public opinion.
SECTION – C [2 × 5 = 10]
(Long Answer Type Questions)
Question 9.
Expectations from democracy also function as the criterion for judging any democratic country. What Is the meaning of the given statement?
OR
Discuss the timeUne of the Awadh Rebellion. Highlight the issues raised by the peasants in that revolt. (5)
Answer:
- Expectations from democracy keep on increasing every minute, even more so when democracy begins to fulfill their existing expectations. This works in the favour of democracy.
- People come up with more expectations when asked about how good a democracy functions.
- The very fact that they come up with more expectations and complaints demonstrates how actively a democracy has succeeded in educating the people about political processes, their rights and expectations.
- Hence, the fact that people are complaining is itself a testimony to the success of democracy.
- This shows that people have developed awareness and the ability to expect and to look critically at power holders and the high and the mighty which is the very purpose of democracy.
OR
In Awadh, peasants led by Baba Ramchandra, revolted against the talukdars and landlords who demanded from peasants exorbitantly high rents and a variety of other cesses.
- Peasants had to work at landlords’ farms without any payment.
- As tenants, they had no security of tenure. They could acquire no right over the leased land.
- The peasant movement demanded reduction of revenue, abolition of begar, and social boycott of oppressive landlords.
- Jawaharlal Nehru and Baba Ram Chandra together toured around Awadh, collecting grievances and trying to integrate this movement of rebellion with the Non-Cooperation struggle.
- The movement took a violent turn and there were several attacks on talukdars, grain hoards were looted and taken over.
Question 10.
The key to the decision of the factory Location is the Least cost. What does the given statement mean?
OR
Banks are willing to Lend to the poor women when organised in SHGs, even though they have no collateral as such. Validate the statement. (5)
Answer:
The given statement means that an ideal factory location is basically chosen after considering multiple factors but the most functional factor is the least cost.
- Any location is an ideal factory location if it facilitates the minimal cost of production.
- The cost of production which includes multiple costs including that of raw materials, rent of the place, wages of the labour involved, cost of transportation to the market should be the least for it to be called an ideal factory location.
- An Ideal factory location should be close to an abundant source of raw materials to reduce the transportation costs to a minimum.
- It should be well connected to a market to reduce the marketing and promotion costs.
OR
Banks are willing to lend to the poor women when organised in SHGs, even though they have no collateral as such. This can be asserted as follows:
- SHG are formed of 15-20 people as members usually belonging to one neighborhood.
- SHGs encourage regular saving habits. The members of an SHG meet and save regularly and thus a habit of regularity and compliance is inculcated.
- Members borrow small amounts of money at less rates of interest. In return, no collateral is demanded to encourage economic habits and spending among these people.
- Small loans are given to members of SHGs by the banks without any collateral because members are responsible to return the borrowed amount by themselves.
- It reduces their dependence on informal sources of credit. It saves them from debt traps and brings them into formal economy.
SECTION -D [4 × 2 = 8]
(Case Based Questions)
Question 11.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
Ford Motors is one of the world’s largest automobile manufacturers with production spread over 26 countries of the world. Ford Motors came to India in 1995 and spent Rs. 1700 crore to set up a large plant near Chennai.
This was done in collaboration with Mahindra and Mahindra, a major Indian manufacturer of jeeps and trucks.
By the year 2017, Ford Motors was selling 88,000 cars in the Indian markets, while another 1,81,000 cars were exported from India to South Africa, Mexico, Brazil and the United States of America. The company wants to develop Ford India as a component supplying base for its other plants across the globe.
(A) Why does Ford Motors want to develop Ford India as a component supplying base for its other plants across the globe? (1)
Answer:
Ford Motors wants to develop Ford India as a component supplying base for its other plants across the globe because raw material is easily available here. This makes India a prospective producer and supplier of components required to make the motors.
(B) Using the given case as an example, explain how Globalisation has helped the producer company. (2)
Answer:
It is only because of globalisation that Ford Motors was able to establish a unit in Ford India. Globalisation has helped to reduce the trade barriers imposed by countries. It has helped companies come closer and exchange information, technology and share markets.
Explanation:
Globalisation has helped Ford Motors establish a unit in India and earn better profits by reducing the cost of production. Here in the given case, the unit in India will help Ford Motors reduce their cost of production because raw materials are easily available.
Caution:
Including examples along with theory in the answer will always get the students more marks. The key to answering questions is to look for keywords like elucidate, validate, justify.
(C) If other native companies request the government to raise tariff against Ford’s products, what would the measure be called? (1)
Answer:
Raising any tariff will lead to closing of the economy. Hence the measure would be known as raising the trade barriers.
![]()
Question 12.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follow:
In order to strengthen the flow of information from the grassroot to the higher level, the government has made special provision to extend the twenty-four hours STD facility to every village in the country. There is a uniform rate of STD facilities all over India. It has been made possible by integrating the development in space technology with communication technology.
Mass communication provides entertainment and creates awareness among people about various national programmes and policies. It includes radio, television, newspapers, magazines, books and films. All India Radio (Akashwani) broadcasts a variety of programmes in national, regional and local languages for various categories of people, spread over different parts of the country. The national television channel of India, is one of the largest terrestrial networks in the world.
It broadcasts a variety of programmes from entertainment, educational to sports, etc. for people of different age groups.
(A) What is the full form of STD? (1)
Answer:
Subscriber Trunk Dialing is the full form of STD.
(B) How do telecom networks help in connecting Indians with one another? (1)
Answer:
Telecom networks in India help Indians connect to each other all the time through telephone lines. They are connected even during the times of calamities, pandemics and outbreaks of diseases. This helps in sending medical help to these regions as well.
Related Theory:
Telecom sector also strengthens the flow of information from the grassroot to the higher level and for that the government has made special provision to extend the twenty-four hours STD facility to every village in the country.
(C) How has it been made possible to have uniform STD networks all round the country? (2)
Answer:
This has been made possible by launching artificial satellites which revolve around the earth. By integrating the development in space technology with communication technology, uniform STD prices and lines has been made possible.
SECTION – E [1 × 3 = 3]
(Map Skill Based Questions)
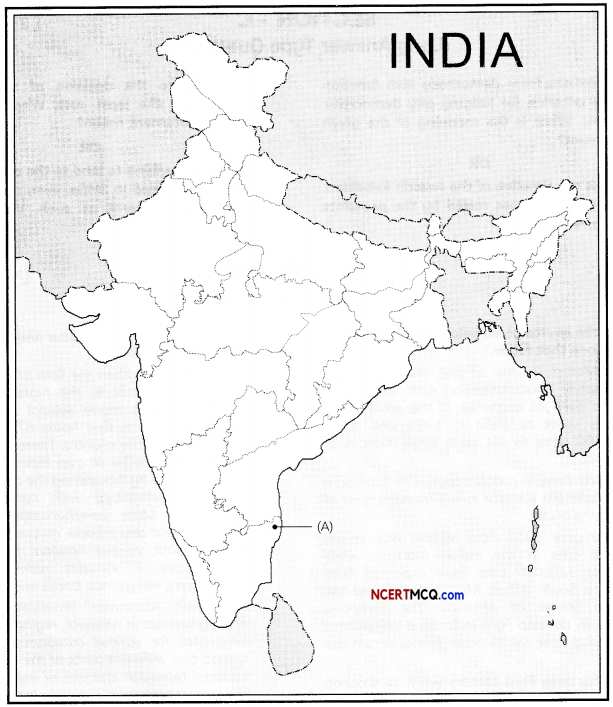
Question 13.
(A) On the given outline Political Map of India, identify the place marked as A with the help of following information and write its correct name on the line marked near it.
(a) Identify the place where the session of Indian National Congress was held in 1927. (1)
(B) On the same given map of India, locate the following:
(a) Vijayanagar Iron and Steel Plant
OR
Noida Software Technology Park (1)
(b) Chhatrapati Shivaji Airport (1)
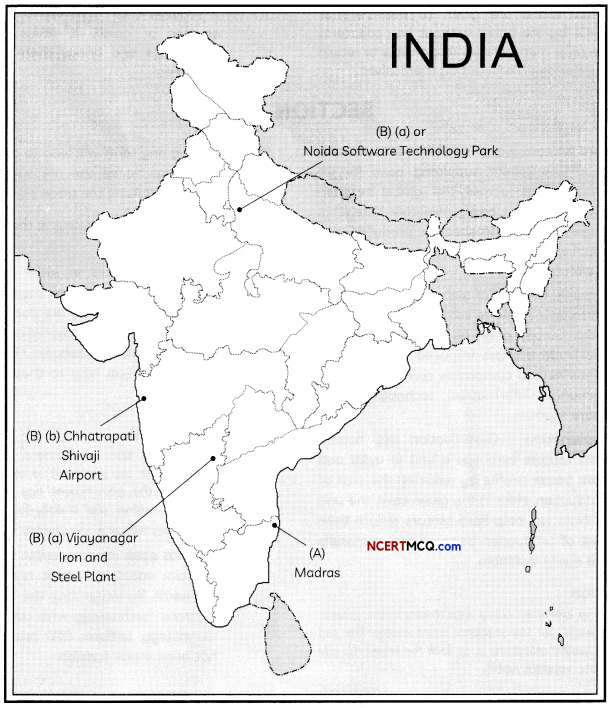
Answer:
(A) Madras
(B) (a) Vijayanagar Iron and Steel Plant
OR
Noida Sofware Technology Park
(b) Chhatrapati Shivaji Airport