Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 7 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Term 2 Set 7 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 35
Roll No. ___________
General Instructions:
- Question paper is divided into 5 sections A, B, C, D & E
- In section A, question number 1 to 3 are Very Short Answer type questions. Attempt any 3 questions.
- In section B, question number 4 is Source based question.
- In section C, question number 5 & 6 are Short Answer type questions.
- In section D, question number 7 to 9 are Long Answer type questions.
- In section E, question number 10 is a Map based question.
Section – A
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
How does consumer cooperatives, departmental stores contribute to trade and commerce in a region? (2)
Or
Explain the different factors that affect transport.
Answer:
Consumer cooperatives and departmental stores contribute to trade and commerce in a region in following ways
- Consumer cooperatives were the first of the large-scale innovations in retailing.
- Departmental stores delegate the responsibility and authority to departmental heads for purchasing of commodities and for overseeing the sale in different sections of the stores.
Or
There are two important factors that affect transport
- Demand for Transport It is influenced by the size of population. The larger the population size, the greater is the demand for transport
- Routes It depends on location of cities, towns, villages, industrial centres and raw materials, pattern of trade between them, nature of the landscape between them, type of climate, and funds available for overcoming obstacles along the length of the route.
![]()
Question 2.
Briefly describe the steps taken by the Indian railways to revolutionise rail transport (2)
Answer:
A few steps taken by Indian railways to revolutionise rail transport are
- Indian Railways has launched extensive programme to convert the metre and narrow gauges to broad gauge.
- Moreover, steam engines have been replaced by diesel and electric engines. This step has increased the speed, as well as, the haulage capacity.
Question 3.
Define air pollution and its sources. (2)
Answer:
Air pollution is the addition of contaminants, like dust, fumes, gas, fog, odour, smoke or vapour to the air in substantial proportion and duration that may be harmful to flora and fauna and to property. Combustion of fossil fuels, mining and industries are the main sources of air pollution These processes release oxides of sulphur and nitrogen, hydrocarbons, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, lead and asbestos.
Section – B
Source Based Question
Question 4.
Read the source given below and answer the following questions by choosing the correct option.
Bio-energy refers to energy derived from biological products which includes agricultural residues, municipal, industrial and other wastes. Bioenergy is a potential source of energy conversion. It can be converted into electrical energy, heat energy or gas for cooking.
It will also process the waste and garbage and produce energy. This will improve economic life of rural areas in developing countries, reduce mental pollution, enhance self-reliance and reduce pressure on fuel wood. One such project converting municipal waste into energy is Okhla in Delhi.
The challenge of sustainable development requires integration of quest for economic development with environmental concerns. Traditional methods of resource use result into generating enormous quantity of waste as well as create other environmental problems. Hence, for sustainable development calls for the protection of resources for the future generations.
There is an urgent need to conserve the resources. The alternative energy sources like solar power, wind, wave, geothermal energy are inexhaustible resource. These should be developed to replace the exhaustible resources. In case of metallic minerals, use of scrap metals will enable recycling of metals. Use of scrap is specially significant in metals like copper, lead and zinc in which India’s reserves are meagre. Use of substitutes for scarce metals may also reduce their consumption. Export of strategic and scarce minerals must be reduced, so that the existing reserve may be used for a longer period.
i. What are the economic implications of bio-energy for rural community? (1)
Answer:
Economic implications of bio energy for rural community are reducing reliance on fuel wood, increasing availability of non-wood energy and reducing environmental damage and associated cost.
ii. Why do we need alternatives to conventional fuel resources such as fossil fuels? (1)
Answer:
We need alternatives to conventional fuel resources such as fossils fuels because conventional fuel resources led to pollution.
iii. Why should export of rare and scarce minerals be reduced? (1)
Answer:
Export of rare and scare minerals should be reduced for extended use of existing reserves in a region.
![]()
Section – C
Short Answer Questions
Question 5.
Explain agro based industries and agri-business. (3)
Or
What do you mean by large integrated industry and mini-steel mills. Outline the distribution of iron and steel industry in Asia.
Answer:
Agro-based Industries involves the processing of raw materials from the field and the farm into finished products for rural and urban markets. Major agro-processing industries are food processing, sugar, pickles, fruits juices, beverages (tea, coffee and cocoa), spices and oils fats and textiles (cotton, jute, silk), rubber, etc.
Agro processing includes carning producing cream, fruit processing and confectionery, While some preserving techniques, such as drying, fermenting and pickling, have been known since ancient times, these had limited applications to cater to the pre-Industrial Revolution demands.
Agri-business is commercial farming on an industrial scale often financed by business whose main interests lie outside agriculture, for example, large corporations in tea plantation business. Agri-business farms are mechanised, large in size, highly structured, reliant on chemicals, and may be described as ‘agro-factories’.
Or
The large integrated steel industry is traditionally located close to the sources of raw materials which are iron ore, coal, manganese and limestone or at places where these could be easily brought, e.g. near ports. On the other hand in mini steel mills, access to markets is more important than inputs. These are less expensive to build and operate and can be located near markets because of the abundance of scrap metal, which is the main input.
Traditionally, most of the steel was produced at large integrated plants, but mini mills are limited to just one-step process steel making, and are gaining ground. In Asia, the important centres of iron and steel industry include Nagasaki and Tokyo-Yokohama in Japan; Shanghai, Tienstin and Wuhan in China; and Jamshedpur, Kulti-Burpur, Durgapur, Rourkela, Bhilai, Bokaro, Salem, Visakhapatnam and Bhadravati in India.
![]()
Question 6.
Write a detailed note on Geothermal energy. (3)
Answer:
Geothermal energy is the head energy within the earth. When the magma from the interior of earth, comes out on the surface, tremendous heat is released. This heat energy can successfully be tapped and converted to electrical energy. Apart from this, the hot water that gushes out through the geyser wells is also used in the generation of thermal energy.
This energy is now considered to be one of the key energy sources which can be developed as an alternate source. The hot springs and geysers are being used since medieval period. In India, a geothermal energy plant has been commissioned at Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh.
Section – D
Long Answer Questions
Question 7.
A basic industry is responsible for providing raw material to other industries. They are important for a nation’s economy. Discuss the role of iron and steel industry as a basic industry and location of steel industries. Also explain about production of iron. (5)
Or
Elucidate the structure and distribution of cotton textile industries in the world.
Answer:
The iron and steel industry forms the base of all other industries and, therefore, it is called a basic industry. It is basic because it provides raw material for other industries such as machine tools used for further production and for building infrastructure in industries, transportation and residential settlements. It may also be called a heavy industry because it uses large quantities of bulky raw materials and its products are also heavy.
The large integrated steel industry is traditionally located close to the sources of raw materials i.e. iron ore, coal, manganese and limestone or at places where these could be easily brought, e.g. near ports. But in mini steel mills access to markets is more important than inputs. These are less expensive to build and operate and can be located near markets because of the abundance of scrap metal, which is the main input.
Traditionally, most of the steel was produced at large integrated plants, but mini mills are limited to just one-step process i.e. steel making Iron is extracted from iron ore by smelting in a blast furnace with carbon (coke) and limestone. The mineral ores commonly used for iron production are hematite and magnetite. Naturally, iron ores are found in Banded Iron Formations (BIFs) which are sedimentary rocks of Precambrian.
The molten iron is cooled and moulded to form pig iron which is used for converting into steel by adding strengthening materials like manganese. Cotton is the world’s most important fibre which is used for production of several products including textiles. Cotton textile industry has three sub-sectors i.e. handloom, powerloom and mill sectors
- Handloom sector is labour-intensive and provides employment to semi-skilled workers. It requires small capital investment. This sector involves spinning, weaving and finishing of the fabrics.
- The powerloom sector introduces machines and becomes less labour intensive and the volume of production increases.
- Cotton textile mill sector is highly capital intensive and produces fine clothes in bulk.
Cotton textile manufacturing requires good quality cotton as raw material. Cotton textile industries produces two types of products, i.e. cotton yarn and cotton cloth. These industries are spread globally in over 90+ countries, however India, China, USA, Pakistan, Uzbekistan and Egypt produce more than half of the world’s raw cotton China and India also lead the global production of cotton yarn and cloths. The UK, NW European countries and Japan also produce cotton textile made from imported yarn. Europe alone accounts for nearly half of the world’s cotton imports.
![]()
Question 8.
State the global distribution of railways in the continents of the world. (5)
Answer:
The global distribution of railways in the world is
Europe has one of the most dense rail networks in the world. There are about 4,40,000 km of railways, most of which is double or multiple-tracked. The important rail heads are London, Paris, Brussels, Milan, Berlin and Warsaw. Passenger transport is more important than freight in many of these countries.
In Russia, railways account for about 90 percent of the country’s total transport with a very dense network west of the Urals. Moscow is the most important rail head with major lines radiating to different parts of the country’s vast geographical area.
North America has one of the most extensive rail networks accounting for nearly 40 per cent of the world’s total. The railways are used more for long-distance bulky freight like ores, grains, timber and machinery than for passengers. The most dense rail network is found in the highly industrialised and urbanised region of East Central U.S.A. and adjoining Canada.
Australia has about 40,000 km of railways, of which 25 per cent are found in New South Wales alone. The west-east Australian National Railway line runs across the country from Perth to Sydney. New Zealand’s railways are mainly in the North Island to serve the farming areas.
In South America, the rail network is the most dense in two regions, namely, the Pampas of Argentina and the coffee growing region of Brazil which together account for 40 per cent of South America’s total route length. Only Chile, among the remaining countries has a considerable route length linking coastal centres with the mining sites in the interior.
![]()
Question 9.
Highlight the importance of roads in land transport. (5)
Answer:
The importance of roads in land transport is
- Roads in land transport are the most economical for short distances compared to railways.
- Freight transport by road is important because it offers door-to-door service.
- Roads play a vital role in a nation’s trade and commerce and for promoting tourism.
- The quality of the roads varies greatly between developed and developing countries because road construction and maintenance require heavy expenditure.
- In developed countries good quality roads are universal and provide long-distance links in the form of motorways, autobahns (Germany), and inter-state highways for speedy movement.
- Lorries, of increasing size and power to carry heavy loads are common.
- Road transport is most flexible and adaptable with an outreach into the most remote areas that are inaccessible by rail, air or water.
Section – E
Map Based Question
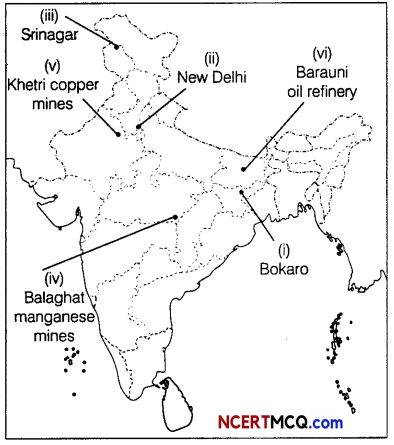
Question 10.
On a political map of India locate and label the following features (Attempt any 5). (1 × 5 = 5)
(i) Bokaro coal mines
(ii) Important town of Golden Quadrilateral in the North
(iii) Northernmost node in the North-South Corridor
(iv) Balaghat manganese mines
(v) Khetri copper mines
(vi) Barauni oil refinery
Answer: