NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resource and Development
These Solutions are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resource and Development.
TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
Question 1.
(a) What type of resource is iron ore?
(b) Which is a replenishable type of resource?
(c) State one cause of land degradation in Punjab.
(d) In which state is terrace cultivation practised?
(e) Mention one state where black soil is found.
Answer:
(a) Non-renewable.
(b) Tidal energy.
(c) Intensive cultivation.
(d) Uttarakhand.
(e) Gujarat.
Question 2.
Answer the following questions in about 30 words :
- Name three states having black soil and the crop which is mainly grown in it.
- What type of soil is found in the river deltas of the eastern coast? Give three main features of this type of soil.
- What steps can be taken to control soil erosion in the hilly areas?
- What are the biotic and abiotic resources? Give some examples.
Answer:
(1) The states of Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh have black soil. The crop which is mainly grown in this soil is cotton. This soil is also called ‘Regur’ or black cotton soil.
(2) The river deltas of the eastern coast have alluvial soil.
Alluvial soil consists of various proportions of sand, silt, and clay.
The main features of alluvial soil are:
- These soils are very fertile and so ideal for cultivation.
- They contain adequate quantities of potash, phosphoric acid and lime good for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, and other crops.
- In drier areas, these soils are more alkaline.
(3) In hilly areas, soil erosion can be controlled by contour ploughing which is ploughing along contour-lines, using terrace farming techniques, and using strips of grasses to check soil erosion by wind and water.
(4) Biotic Resources: The resources which are obtained from the biosphere and have life are called Biotic Resources. Examples of biotic resources are animals, plants, human beings, fish, livestock, etc.
Abiotic Resources: The resources which are composed of non-living things are called Abiotic Resources.
Examples of abiotic resources are water, minerals, metals, wind, solar energy, etc.
Question 3(1).
Answer the following questions in about 120 words :
(1) Explain land use pattern in India and why has the land under forest not increased much since
1960-61.
Answer:
(1) The land use for different purposes in the year 1960-61 and 2002-03 is as given B below:
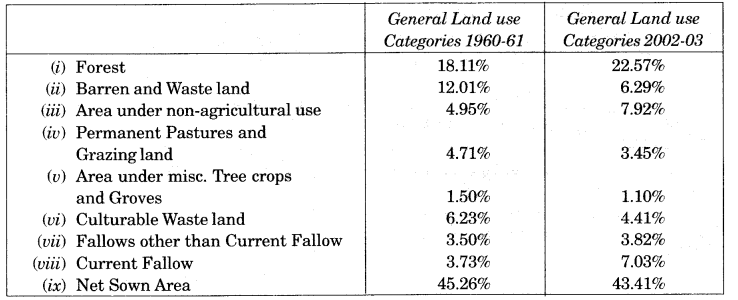
(2) On the basis of the above chart and other facts available, the main features of the land use pattern in India are as mentioned below :
- The total geographical area of India is 3.28 million sq. km.
- Land use data, however, is available only for 93 percent of the total area because the land use reporting for most of the north-east states except Assam has not been done fully. Moreover, some areas of Jammu and Kashmir occupied by Pakistan and China have also not been surveyed.
(3) The land under permanent pasture has decreased.
(4) The pattern of the net sown area varies greatly from one state to another. It is over 80 per tent of the total area in Punjab and Haryana and less than 10 percent in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur, and Andaman Nicobar Islands.
(5) The land under forest has changed a little from 18.11% in 1960-61 to 22.57% in 2002-03. It is still far lower than the desired 33 percent of the geographical area as it was outlined in the National Forest Policy (1952). Land under forest has not increased due to various factors, namely, agricultural expansion, large-scale development projects or river valley projects, grazing and fuel collection.
(6) A part of the land is termed as wasteland and land put to other non-agricultural uses.
Question 3(2).
How has technical and economic development led to more consumption of resources?
Answer:
Technical and economic development has led to more consumption of resources due to reasons as mentioned below :
- Higher level of technological development needs more and more resources for production activities.
- As Gandhiji said the exploitative nature of modem technology is the root cause of resource depletion at the global level.
- It was primarily the higher level of technological development of the colonising countries that helped them to exploit resources of other regions and establish their supremacy over the colonies. Thus resources can contribute to development only when they are accompanied by appropriate technological development and institutional changes. India has experienced all this in different phases of colonisation.
Thus, it is true that technical and economic development leads to more consumption of resources. Water resources are being exploited to expand the irrigated areas and dry season agriculture. As the result as in the case of Punjab and Haryana, the water level has gone down creating problems for the farmers.
Question 4.
Imagine if oil supplies get exhausted, how will this affect our lifestyle?
Answer:
- If oil supplies get exhausted, the world would come to a halt. People would end up living wherever they were. There will be no more planes, operating boats and trains.
- Pricing for any transportation would be out of reach but for the richest for a limited period.
- We would be limited to existing supplies of coal, natural gas, etc.
- A lot of jobs would be lost because many factories, restaurants, etc. would be shut down.
- Many would leave cities to live in rural areas.
- Cities would become ghost towns. There may be killed in order to control the necessary things needed for survival in the world. We would not only lose our lifestyle but lose contact with the whole world. However, as scientists are doing research to find out alternative sources of energy, it is hoped that they would be successful in their efforts. They may be able to use solar or wind energy in place of petroleum products and in that case, if the oil supplies get exhausted, it would not make any difference in our lives. Perhaps, life would become better in the future.
Question 5.
Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.

- Natural endowments in the form of land, water, vegetation and minerals.
- A type of non-renewable resource.
- Soil with high water retaining capacity.
- Intensively leached soils of the monsoon climate.
- Plantation of trees on a large scare to check soil erosion.
- The Great Plains of India are made up of these soils.
Answer:
- Resource
- Minerals
- Laterite
- Black
- Afforestation
- Alluvial.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resource and Development help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Social Science Geography Chapter 1 Resource and Development, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.