NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare
These Solutions are part of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology. Here we have given NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology chapter 7 Evolution
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The vitamin whose content increases following the conversion of milk into curd by lactic acid bacteria is
(a) vitamin C
(b) vitamin D
(c) vitamin B12
(d) vitamin E.
Answer:
(c) : Curd is more nutritious than milk as it contains a number of organic acids and vitamins including B12 .
Question 2.
Wastewater treatment generates a large quantity of sludge, which can be treated by
(a) anaerobic digesters
(b) floe
(c) chemicals
(d) oxidation pond.
Answer:
(a) : The sediment of settling tank is r called activated sludge. A part of it is used as inoculum in aeration tanks. The remaining is passed into a large tank called anaerobic sludge digesters.
Question 3.
Methanogenic bacteria are not found in
(a) rumen of cattle
(b) gobar gas plant
(c) bottom of water-logged paddy fields
(d) activated sludge.
Answer:
(d) : Methanogens are strict anaerobes. Nutritionally they are “autotrophs” which obtain both energy and carbon from decomposition products. They occur in marshy areas where they convert formic acid and carbon dioxide into methane with the help of hydrogen. This capability is commercially exploited in the production of methane and fuel gas inside gobar gas plants c.g., Methanobacterium, Methanococcus. Some of the methanogen archaebacteria live as symbionts (e.g., Methanobacterium) inside rumen or first chamber in the stomach of herbivorous animals that chew their cud (ruminants, e.g., cow, buffalo).
These archaebacteria are helpful to the ruminants in fermentation of cellulose. The warm, water logged soil of paddy fields provide ideal condition for methanogenesis and though some of the methane produced is usually oxidised by methanotrophs in the shallow overlying area, vast majority is released into atmosphere. Methanogenic bacteria are not found in activated sludge instead activated sludge contains aerobic microorganisms.
Question 4.
Match the following list of bacteria and their commercially important products.
Bacterium Product

Choose the correct match.
(a) i-(B), ii-(C), iii-(D), iv-(A)
(b) f-(B), ii-(D), iii-(C), iv-(A)
(c) i-(D), ii-(C), iii-(B), iv-(A)
(d) i-(D), ii-(A), iii-(C), iv-(B)
Answer:
(c)
Question 5.
Match the following list of bioactive substances and their roles. Role
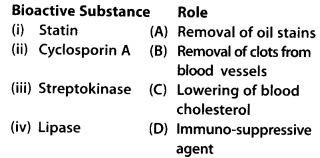
Choose the correct match
(a) i-(B), ii-(C), iii-(A), iv-(D)
(b) i-(D), ii-(B), iii-(A), iv-(C)
(c) i-(D), ii-(A), iii-(B), iv-(C)
(d) i-(C), ii-(D), iii-(B), iv-(A)
Answer:
(d)
Question 6.
The primary treatment of waste water involves the removal of
(a) dissolved impurities
(b) stable particles
(c) toxic substances
(d) harmful bacteria.
Answer:
(b) : Primary or physical treatment is the process of removal of small and large, floating and suspended solids from sewage through two processes of filtration and sedimentation. First floating and suspended matter is removed through sequential filtration with progressively smaller pore filters. The filtrate is then kept in large open settling tanks where grit (sand, silt, small pebbles) settles down. Aluminium or iron sulphate is added in certain places for flocculation and settling down of solids. The sediment is called primary sludge, while the supernatant v is called effluent.
Question 7.
BOD of waste water is estimated by measuring the amount of
(a) total organic matter
(b) biodegradable organic matter
(c) oxygen evolution
(d) oxygen consumption.
Answer:
(d) : Degree of impurity of water due to organic matter is measured in terms of BOD. It is the oxygen in milligrams required for five days in one liter of water at 20°C for the microorganisms to metabolise organic waste.
Question 8.
Which one of the following alcoholic drinks is produced without distillation?
(a) Wine
(b) Whisky
(c) Rum
(d) Brandy
Answer:
(a) : Wine and beer are produced without distillation whereas whisky, brandy and rum are produced by distillation of the fermented broth.
Question 9.
The technology of bio gas production from cow dung was developed in India largely due to the efforts of
(a) Gas Authority of India
(b) Oil and Natural Gas Commission
(c) Indian Agricultural Research Institute and Khadi & Village Industries Commission
(d) Indian Oil Corporation.
Answer:
(c)
Question 10.
The free-living fungus Trichoderma can be used for
(a) killing insects
(b) biological control of plant diseases
(c) controlling butterfly caterpillars
(d) producing antibiotics.
Answer:
(b) : Abiological control being developed for use in the treatment of plant disease is the fungus Trichoderma. Trichoderma species are free-living fungi that are very common in the root ecosystems. They are effective biocontrol agents of several plant pathogens.
Question 11.
What would happen if oxygen availability to activated sludge floes is reduced?
(a) It will slow down the rate of degradation of organic matter.
(b) The center of floes will become anoxic, which would cause death of bacteria and eventually breakage of floes.
(c) Floes would increase in size as anaerobic bacteria would grow around floes.
(d) Protozoa would grow in large numbers.
Answer:
(a,b) : Floes are masses of bacteria associated with fungal filaments to form mesh like structures. If oxygen availability to activated sludge floes is reduced, their rate of decomposition of organic matter will decrease. And as the center of floes will become anoxic, the bacterial cells will die, thus causing breakage of floes.
Question 12.
Mycorrhiza does not help the host plant in
(a) enhancing its phosphorus uptake capacity
(b) increasing its tolerance to drought
(c) enhancing its resistance to root pathogens
(d) increasing its resistance to insects.
Answer:
(d) : Fungi are also known to form symbiotic associations with plants (mycorrhiza). Many members of the genus Glomus form mycorrhiza. The fungal symbionts in these associations absorb phosphorus from soil and passes it to the plant. Plants having such associations show other benefits also, such as resistance to root- 1 borne pathogens, tolerance to salinity and drought, and an overall increase in plant growth and development.
Question 13.
Which one of the following is not a nitrogen fixing organism?
(a) Anabaena
(b) Nostoc
(c) Azotobacter
(d) Pseudomonas
Answer:
(d) : Pseudomonas is not a nitrogen fixing bacteria. Pseudomonas are used in antibiotic formation and biodegradation of organic pollutant like petroleum spillage. Azotobacter is a free living nitrogen fixing bacteria. Anabaena and Nostoc are free living nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria.
Question 14.
Big holes in Swiss cheese are made by a
(a) a machine
(b) a bacterium that produces methane gas
(c) a bacterium producing a large amount of carbon dioxide
(d)a fungus that releases a lot of gases during its metabolic activities.
Answer:
(c) : Ripened cheese is prepared from unripened cheese by first dipping in brine, wiping and then maturation with different strain of bacteria and fungi. It takes 1-16 months for ripening. Large holed Swiss cheese is ripened with the help of CO2 producing (causing holes) bacterium called Propionibacterium sharmanii.
Question 15.
The residue left after methane production from cattle dung is
(a) burnt
(b) burried in landfills
(c) Used as manure
(d) used in civil construction.
Answer:
(c) : Biogas is a methane rich fuel gas produced by anaerobic breakdown or digestion of biomass with the help of methanogenic bacteria. Biogas is made up of methane (50-70%), carbon dioxide (30-40%) with traces of nitrogen, hydrogen sulphide and hydrogen. The effluent and residue left after the fermentative generation of biogas is rich in minerals, lignin and a part of cellulose. It is an ideal manure.
Question 16.
Methanogens do not produce
(a) oxygen
(b) methane
(c) hydrogen sulphide
(d) carbon dioxide.
Answer:
(a) : Refer answer 15.
Question 17.
Activated sludge should have the ability to settle quickly so that it can
(a) be rapidly pumped back from sedimentation tank to aeration tank
(b) absorb pathogenic bacteria present in waste water while sinking to the bottom of the settling tank
(c) be discarded and anaerobically digested
(d) absorb colloidal organic matter.
Answer:
(a) : Bacterial floes are allowed to sediment into the settling tank, this sediment is called activated sludge. A small part of activated sludge is pumped back into aeration tank to serve as inoculum. So, it must have ability to settle quickly.
Question 18.
Match the items in Column ‘A’ and Column ‘B’ and choose correct answer.

The correct answer is
(a) (i)-Q, (ii)-S, (iii)-R, (iv)-P
(b) (i)-p, (ii)-S, (iii)-Q, (iv)-P
(c) (i)-S, (ii)-P, (iii)-Q, (iv)-R
(d) (i)-R, (ii)-Q, (iii)-P, (iv)-S
Answer:
(b)
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why does ‘Swiss cheese’ have big holes?
Answer:
cheese is prepared by bacteria Propionibncterium shanmnii. It produces large quantity of CO, which causes large holes in cheese.
Question 2.
What are fermentors?
Answer:
Fermentors are the containers where fermentation is carried out, also known as bioreactors.
Question 3.
Name a microbe used for statin production. How do statins lower blood cholesterol level?
Answer:
Statin is produced by yeast Monascus purpureus. It is used as blood cholesterol lowering agent by acting as a competitive inhibitor of enzyme for cholesterol synthesis.
Question 4.
Why do we prefer to call secondary waste water treatment as biological treatment?
Answer:
Secondary waste water treatment is also called biological treatment because in this step microbes digest organic matter and convert it into microbial biomass and release minerals.
Question 5.
What for nucleo poly hedroviruses are being used now a days?
Answer:
Nucleo poly hedroviruses are baculo- virus. These are biological control agents that attack insects and other arthropods. TheY are species-specific, narrow spectrum insecticides and do not harm plants, mammals, birds and fish.
Question 6.
How has the discovery of antibiotics helped mankind in the field of medicine?
Answer:
Antibiotics are the chemical substances produced by microorganisms which are used for treatment of pathogenic or infectious diseases. Antibiotics have greatly improved our capacity to treat deadly diseases such as plague, whooping cough (kali khansi), diphtheria (gal ghotu).
Question 7.
Why is distillation required for producing certain alcoholic drinks?
Answer:
Production of hard liquors require distillation of fermented broth to increase the alcoholic content. Beer and wine are formed without distillation and have 3-6% alcoholic content while rum, brandy and gin are formed by distillation and have 40% alcohol content.
Question 8.
Write the most important characteristic that Aspergillus niger, Clostridium butylicum, and Lactobacillus share.
Answer:
the three microbes, Aspergillus niger, Clostridium butylicum and Lactobacillus are used for commercial and industrial production of organic acids through fermentation. Organic acids produced are citric acid, butyric acid and lactic acid respectively.
Question 9.
What would happen if our intestine harbours microbial flora exactly similar to that found in the rumen of cattle?
Answer:
If humans also had microbes in their intestine like ruminants, then they would also have been capable of digesting cellulose presentin food itemsbecause microbes present in the rumen of cattle, called methanogens are capable of digesting cellulose as they have cellulase enzyme.
Question 10.
Give any two microbes that are useful in biotechnology.
Answer:
Two microbes that are used in bio-technology are:-
- Escherichia coil
- Bacillus thuringiensis
Question 11.
What is the source organism for EcoRI, restriction endonuclease?
Answer:
Bacterium Escherichia coil of strain RY13.
Question 12.
Name any genetically modified crop.
Answer:
cotton is a genetically modified crop that has been modified to resist attack by insect pests.
Question 13.
Why are blue-green algae not popular as biofertilisers?
Answer:
Blue -green algae add organic matter to the soil and increase its fertility but still these are not popular as biofertilisers. This is due to several constraints that limit the application or implementation of the biofertiliser technology. The constraints may be environmental, technological, infrastructural, financial, unawareness, quality, marketing etc.
Question 14.
Which species of Penicillium produces Roquefort cheese?
Answer:
Penicillium roqueforti
Question 15.
Name the states involved in Ganga action plan.
Answer:
Uttaranchal, Uttar Pradesh, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Bihar etc.
Question 16.
Name any two industrially important enzymes.
Answer:
- Lipase – lipid dissolving enzymes, added in detergents for removing oil stains from laundry.
- Pectinase – used along with protease in clearing fruit juices.
Question 17.
Name an immune immunosuppressive agent.
Answer:
Cyclosporin-A is used as immuno-suppressive agent in organ transplantation.
Question 18.
Give an example of a rod shaped virus.
Answer:
Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV).
Question 19.
What is the group of bacteria found in both the rumen of cattle and sludge of sewage treatment?
Answer:
Methanogens or Methanobacterium are found in the rumen of cattle and anaerobic sludge of sewage treatment.
Question 20.
Name a microbe used for the production of Swiss cheese.
Answer:
Propionibacterium sharmanii
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why are floes important in biological treatment of waste water?
Answer:
Floes are masses of bacteria held together by fungal filament in mesh like structure in aeration tank for secondary sewage treatment. They digest organic matter and convert it into microbial biomass.
Question 2.
How has the bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis helped us in controlling caterpillars of insect pests?
Answer:
Bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis is used to control butterfly caterpillars. These are available in sachets as dried spores which are mixed with water and sprayed onto vulnerable plants such as brassicas and fruit trees, where they are eaten by the insect larvae. In the gut of larvae, the toxin is released and the larvae get killed.
Question 3.
How. do mycorrhizal fungi help the plants harbouring them?
Answer:
Mycorrhiza is a mutually beneficial or symbiotic association of a fungus with the roots of a higher plant. Mycorrhizal roots show a sparse or dense wooly growth of fungal hyphae on their surface.
Mycorrhiza perform several functions for the plant:
- Absorption of water.
- Solubilisation of organic matter of the soil humus, release of inorganic nutrients, absorption and their transfer to root.
- Direct absorption of minerals (e.g., phosphorus) from the soil over a large area and bending over the same to the root. Plants having mycorrhizal associations show resistance to root-borne pathogens, tolerance to salinity and drought, and overall increase in plant growth and development.
Question 4.
Why are cyanobacteria considered useful in paddy fields?
Answer:
Cyanobacteria are used as biofertilisers. They fix atmospheric nitrogen in specialised cells called heterocysts. These organism form symbiotic association with plant, add organic matter and extra nitrogen to the soil and do not interfere with plant growth, e.g., Azolla- Anabaena association is of great importance to paddy fields. Anabaena azollae resides in the leaf cavities of the fern. It fixes nitrogen. A part of the fixed nitrogen is excreted in the cavities and becomes available to the fern. The decaying fern plants release the same for the utilisation of rice plants.
Question 5.
How was penicillin discovered?
Answer:
Discovery of an antibiotic penicillin was serendipitous. It was discovered by Alexander Fleming, he found that petri dish containing culture of Staphylococcus got contaminated by mould. Mould inhibited the bacterial growth. Fleming isolated the mould and proved that filtrate of broth culture Penicillium notatum has antibacterial properties and discovered penicillin.
Question 6.
Name the scientists who were credited for showing the role of penicillin as an antibiotic.
Answer:
Penicillin was discovered by Alexander Fleming, while working on staphylococci bacteria. However its full potential as an effective antibiotic were established much later by Ernest Chain and Howard Florey and used it for treating wounded soldiers in World War II. Fleming, Chain and Florey were awarded the Noble prize, in 1945 for this discovery.
Question 7.
How do bioactive molecules of fungal origin help in restoring good health of humans?
Answer:
Bioactive molecules of fungal origin which help in restoring good health are :
- Cyclosporin A is obtained from fungus Trichotderma pohjsporum. It has anti-fungal, anti-inflammatory and immunosuppres¬sive properties. It inhibits activation of T-cells and prevent graft rejection during organ transplantation.
- Statin is produced from yeast Monascus purpureas, which helps in lowering blood cholesterol by inhibiting the enzyme responsible for cholesterol synthesis.
Question 8.
What roles do enzymes play in detergents that we use for washing clothes? Are these enzymes produced from some unique microorganisms?
Answer:
ipases are lipid dissolving enzymes that are added in detergents for removing oily stains from laundry. They are obtained from Candida lipoh/tica and Gcotrichum candiduiu.
Question 9.
What is the chemical nature of biogas? Name an organism which is involved in biogas production.
Answer:
Biogas is a methane rich fuel gas produced by anaerobic breakdown or digestion of biomass with the help of methanogenic bacteria. Biogas is made up of methane (50-70%), carbon dioxide (30-40%) with traces of nitrogen, hydrogen sulphide and hydrogen. Mcthanobactcrium is a common methanogenic bacteria involved in biogas production.
Question 10.
How do microbes reduce the environmental degradation caused by chemicals?
Answer:
Chemicals from fertilisers and pesticides are highly toxic to human beings and animals alike, and have been polluting our environment. To reduce the environmental degradation caused by chemicals, microbes can be used both as fertilisers and pesticides and are called biofertiliser and biopesticides, respectively. E.g., Rhizobium acts asbiofertiliser, as it can fix atmospheric nitrogen and Bacillus thuringiensis acts as biopesticide to control growth of insect pest.
Question 11.
What is a broad spectrum antibiotic? Name one such antibiotic.
Answer:
Broad spectrum antibiotic is an antibiotic which can kill or destroy a number of pathogens that belong to different groups with different structure and wall composition. e.g., Streptomycin.
Question 12.
What are viruses parasitising bacteria called? Draw a well labelled diagram of the same.
Answer:
Viruses parasitising bacteria are called bacteriophages. These viruses do not eat bacteria, but they infect and replicate within the bacteria.
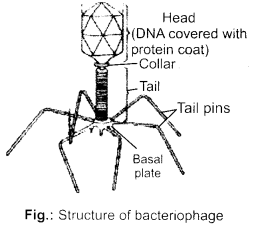
Question 13.
Which bacterium has been used as clot buster? What is its mode of action?
Answer:
BacteriumBacterium Streptococcus has been modified genetically to function as clot buster. It produces enzvme streptokinase and has fibrinolytic effect. It helps in clearing blood dots inside blood vessels through dissolution of intravascular fibrin.
Question 14.
What are biofertilisers? Give two examples.
Answer:
Biofertilisers are microorganisms which bring about nutrient enrichment of the soil by enhancing the availability7 of nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus to the crops. e.g.,
- Nostoc, a free-living nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria,
- Rhizobium, a symbiotic nitrogen-fixing bacteria which form nodules on roots of leguminous plants. They develop the ability to fix nitrogen only, when the) are present inside the root nodules, so in this way give fixed nitrogen to the plant.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why is aerobic degradation more important than anaerobic degradation for the treatment of large volumes of waste waters rich in organic matter. Discuss.
Answer:
During aerobic conditions bacteria gets associated with fungal hyphae and form floes,
They multiply very, rapidly and decompose large amount of organic waste matter present in waste water in the presence of oxygen. But in absence of oxygen i.e. anaerobic conditions, some toxic gases are also produced which kill many bacteria and fungi. That is why aerobic degradation of waste water treatment is more important than anaerobic degradation.
Question 2.
(a) Discuss about the major programs that
the Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India, has initiated for saving major Indian rivers from pollution.
(b) Ganga has recently been declared the National river. Discuss the implication with respect to pollution of this river.
Answer:
(a) Before 1985, very few cities and towns had sewage treatment plants. The municipal wastewater was discharged directly into rivers resulting in their pollution and high incidence of water borne diseases. The Ministry of Environment and Forests has initiated Yamuna Action Plan and Ganga Action Plan, to save these major rivers of our country from pollution. Under these plans it is proposed to build large number of sewage treatment plants so that only treated sewage is discharged into the rivers.
(b) Ganga Action Plan – Ganga, along with its tributaries, is the largest and very important I river of the country. It has been a symbol of purity, but today it is highly polluted with solid, biological and chemical pollutants. Major causes of pollution in Ganga are:
- Urban liquid and solid wastes
- Dead bodies of animals and humans
- Wallowing of cattle Ganga action plan was started in 1986 by Late Sh. Rajiv Gandhi, the Prime Minister of India. by interception, diversion and treatment of domestic sewage and industrial wastes. Under the Ganga Action Plan JI programme, which started in 1993, the Pollution Control Research Institute (PCRI) of Bharat Heavy Electricals Ltd. at Haridwar has been conducting monthly studies to analyse the quality of Ganga river water. It is still under implementation.
Question 3.
Draw a diagrammatic sketch of biogas plant, and label its various components given below: Gas holder. Sludge chamber, Digester, Dung + Water chamber.
Answer:
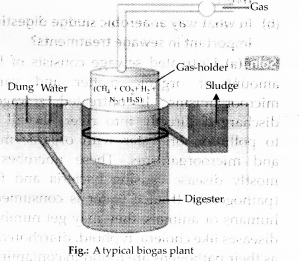
Question 4.
Describe the main ideas behind the biological control of pests and diseases.
Answer:
The natural method of pest and pathogen control involving the use of viruses, bacteria and other insects is called biocontrol or biological control. Main ideas behind biological control of pests and diseases were to replace or supplement the use of chemical pesticides in order to reduce their ill effects. The bio-control agents are non-toxic, non persistent and biodegradable.
A few examples are as follows:
- Lady bird beetles – Natural predator of aphids
- Dragonflies – Control mosquitoes
- Baculoviruses – Species specific, narrow spectrum insecticidal applications. They dre virus based bioinsecticides.
- Bt cotton – Bacillus thuringiensis, a bacterium produces protein toxin which when ingested by larvae of insects, kills them.Main aim of the plan was pollution abatement to improve the water quality.
These spores are available in sachet. They are dissolved in water and sprayed on vulnerable plants to kill insect larvae. - Trichoderma species are effective biocontrol agents of several plant pathogens.
This is how biocontrol agents have decreased the use of chemical insecticides and controlled diseases biologically and have played very important role in regulating environmental pollution and eco-degradation.
Question 5.
(a) What would happen if a large volume of untreated sewage is discharged into a river?
(b) In what way anaerobic sludge digestion is important in sewage treatments?
Answer:
(a) Untreated sewage consists of large amount of organic matter and various microorganisms. If untreated sewage is discharged directly into river, it will lead to pollution of water with organic matter and microorganisms. These microbes are mostly disease causing bacteria and fungi (pathogenic). If such water is consumed by humans or animals, they may get number of diseases like cholera, typhoid, diarrhorea, etc. as their pathogens are found in contaminated water. At the same time high amount of organic waste increases biological oxygen demand and decrease the amount of dissolved oxygen in water which become toxic for animals and plants living in water and causes death of aquatic organisms like fish etc.
(b) In anaerobic sludge digestion, major part of activated sludge is pumped into anaerobic sludge digester. These anaerobic bacteria digest the bacteria and fungi and produce a mixture of gases like methane, carbon dioxide and H2S, which are used as biogas. It also produces manure at same time.
Question 6.
Which type of food would have lactic acid bacteria? Discuss their useful application.
Answer:
Dairy products such as curd, butter milk, cheese etc. have lactic acid bacteria (LAB).
- Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) like Lactobacillus are added to milk. It converts lactose sugar of milk into lactic acid. Lactic acid causes coagulation and partial digestion of milk protein casein. Milk is changed into curd, yoghurt and cheese.
- Indian curd is prepared by inoculating skimmed and cream milk with Lactobacillus acidophilus at a temperature about 40°C or less. Curd is more nutritious than milk as it contains a number of organic acids and vitamins including B12. LAB present in curd also checks growth of disease causing microbes in stomach and other parts of digestive tract.
- Yoghurt is produced by curdling milk with the help of Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus.
- Cottage cheese is prepared by single step fermentation which involves inoculation of skimmed milk with cheese culture (e.g., Lactobacillus and addition
We hope the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare help you. If you have any query regarding . NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 12 Biology chapter 10 Microbes in Human Welfare, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.