NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 3 How the State Government Works are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 3 How the State Government Works.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 7 |
| Subject | Social Science Civics |
| Chapter | Chapter 3 |
| Chapter Name | How the State Government Works |
| Number of Questions Solved | 20 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 3 How the State Government Works
NCERT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
Question 1.
Use the terms ‘constituency’ and ‘represent’ to explain who an MLA is and how is the person elected?
Answer.
- The entire state is divided into constituencies equal to the number of seats in the State Legislature Assembly.
- The voters of each constituency cast their votes in favour of the candidates of their choice.
- The candidate who secures the highest number of votes gets elected as an MLA and represents the constituency in the legislative r assembly of the State.
Question 2.
How did some MLAs become Ministers? Explain.
Answer.
- The Party which obtains more than 50 percent of total seats in an Assembly is termed as the ruling party.
- The ruling party members {MLAs) choose their leader.
- The leader is the leader of the ruling party.
- The Governor appoints and gives an oath to the leader as Chief Minister.
- The Chief Minister forms the cabinet by nominating ministers from among the ruling party MLAs or from outside, from among the party members.
- He sends the names of the ministers to the Governor who appoints them as ministers.
- The Governor then gives an oath to these ministers.
Question 3.
Why should decisions are taken by the Chief Minister and other ministers be debated in the Legislative Assembly?
Answer.
- In a democracy, all Government decisions must be approved by the people.
- The people cannot do this directly, so their representatives in the Legislative Assembly approve or disapprove the decisions taken by the Chief Minister and other ministers after taking part in a debate on the issues.
Question 4.
What was the problem in Patalpuram? What discussion/action was taken by the following? Fill in the table.

Answer.
The problem in Patalpuram was that diarrhea had broken out in the city. The discussion/decision taken by the following:
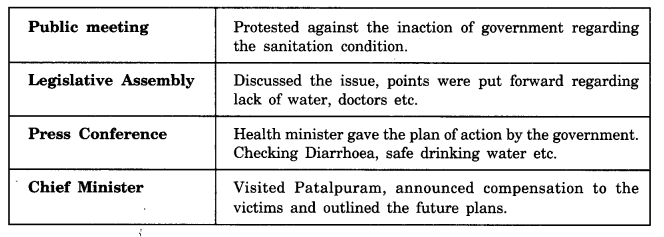
Question 5.
What is the difference between the work that MLAs do in the Assembly and the work done by government departments?
Answer.
Difference between the work that MLAs do in the Assembly and the work done by the government departments:
- MLAs raise the issues in the Assembly and want a solution to the problems facing the masses. They also make decisions.
- Government departments implement the decisions taken by the Assembly.
INTEXT QUESTIONS
Question 1.
What is happening in Patalpuram? (NCERT Page 31)
Answer.
People are facing acute water shortages. Due to unclean water diarrhea has spread. Children are the worst affected.
Question 2.
Why is this problem serious? (NCERT Page 31)
Answer.
This problem is serious as numerous people are dying daily due to diarrhea.
Question 3.
What action do you think can be taken in the above situation and who do you think should take this action? Discuss. (NCERT Page 31)
Answer.
Health services should be improved immediately. The Health Department should provide mobile health services to the people at once. Proper sanitation drive can be carried out. Clean drinking water should be made available.
Question 4.
Discuss the following terms with your teacher—
The public meeting, States in India, constituency, majority, the ruling party, and opposition. (NCERT Page 32)
Answer.
- Public meeting: Meeting of the general public/people about current problems.
- Constituency: Area represented by MLA or MP.
- Majority: Representatives having more than 50% of members (MLAs or MPs).
- Ruling Party: Party or parties which rule the state or the country (with more than 50%) of the total strength of the house.
- Opposition: Parties with less than 50% majority.
Question 5.
Can you explain the following terms— a majority, the ruling party, opposition with reference to your state? (NCERT Page 32)
Answer.
- State: Delhi
- Majority: Aam Aadmi Party (AAP) has a majority in the Delhi Assembly with 67 MLAs out of a total of 70 MLAs.
- Ruling Party: AAP.
- Opposition: Bharatiya Janata Party, Indian National Congress, B.S.P., Janata Dal (S), and some independent MLAs.
Note: Students are requested to find out answers to/about questions for their own state.
Question 6.
Construct a table, similar to the one given for Himachal Pradesh, for your state. (NCERT Page 33)
Answer.
Do this exercise yourself.
Hints: Delhi: Total Assembly seats: 70.
Political Party Number of MLAs
Aam Aadmi Party 67
Indian National Congress 00
Bharatiya Janata Party 03
Bahujan Samaj Party 00
NCP 00
Others 00
Question 7.
At times, the ruling party may not be a single party but a group of parties working together. This is called a coalition. Discuss with your teacher. (NCERT Page 33)
Answer.
- When no party gets a clear majority, few parties come together and elect their leader.
- They go to the Governor and inform him about the leader. The Governor appoints him as C.M.
- The Governor gives the leader and his council of ministers an oath of secrecy and allegiance to the constitution.
- The coalition parties prepare a common minimum programme (CMP) and work to implement the programme during the tenure of the coalition.
Question 8.
What were the main arguments put forward by different MLAs who thought that the government was not taking the situation in a serious manner? (NCERT Page 36)
Answer.
Main Issues
- Spread of an epidemic.
- Shortage of drinking water.
- Bad/Poor condition of hospitals.
- The dearth of doctors.
Question 9.
If you were the health minister, how would you respond to the above discussion? (NCERT Page 36)
Answer.
I would have started the mobile health care vans with the necessary equipment and doctors immediately.
Question 10.
Do you think the above debate would have been useful in some ways? How? Discuss. (NCERT Page 36)
Answer.
Yes, because it has brought the issues to the fore and is solved in minimum time.
Question 11.
In the working of the government, explain the difference between being an MLA and an MLA who is also a minister. (NCERT Page 36)
Answer.
- An MLA highlights the burning issues and can suggest some solutions.
- Minister takes the decision and implements it.
Question 12.
Write two measures that the government undertook for controlling diarrhea. (NCERT Page 37)
Answer.
- Removal of garbage.
- Arrangement’ of drinking water through tanker trucks.
Question 13.
What is the purpose of a press conference? How does the press conference help you get information on what the government is doing? (NCERT Page 37)
Answer.
- To highlight the steps taken by the government.
- The press conference is broadcast or telecast.
- It is also printed in newspapers for the common people.
Question 14.
| Name of department | Examples of their work |
| School Education | |
| Public Works Department | |
| Agriculture |
Find out with the help of your teacher, the work done by the government departments mentioned above, and fill in the table. (NCERT Page 39)
Answer.

Question 15.
Do a similar wallpaper project about any issue connected with the working of your State Government like an education programme, any law and order issue, midday meal scheme, etc. (NCERT Page 40)
Answer.
Hints:
- Students can take photographs of the distribution of mid-day meals in their own school for six days of a week.
- Then, they should arrange them in order.
- Now they put them on a chart paper in a sequence.
- Write their observations days and put them on another chart paper.
- Lastly, they paste them on the wall of their classroom.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 3 How the State Government Works helps you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Social Science Civics Chapter 3 How the State Government Works, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.