CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Paper 7 are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Paper 7.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Paper 7
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Physics |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 7 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
- All questions are compulsory. There are 26 questions in all.
- This question paper has five sections: Section A, Section B, Section C, Section D and Section E.
- Section A contains five questions of 1 mark each. Section B contains five questions of 2 marks each. Section C contains twelve questions of 3 marks each. Section D contains one value based question of 4 marks and Section E contains three questions of 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 1 question of 2 marks, 1 question of 3 marks and all the 3 questions of 5 marks weightage. You have to attempt only 1 of the choices in such questions.
- You may use the following values of physical constants wherever necessary :
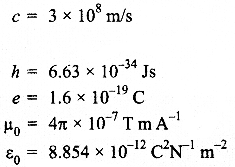

Questions
SECTION : A
Question 1.
What is the range of frequencies used in satellite communication? What is common between these waves and light waves?
Question 2.
Define capacitor reactance. Write its S.I. units.
Question 3.
A concave lens of refractive index 1.5 is immersed in a medium of refractive index 1.65. What is the nature of the lens ?
Question 4.
What is the electric flux through a cube of side 1 cm which encloses an electric dipole?
Question 5.
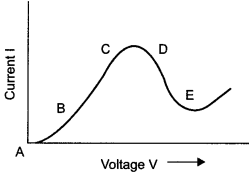
Graph showing the variation of current versus voltage for a material GaAs is shown in the figure, Identify the region of :
- negative resistance
- where Ohm’s law is obeyed.
SECTION : B
Question 6.
Name the parts of the electromagnetic spectrum which is
- suitable for radar systems used in aircraft navigation
- used to treat muscular strain
- used as a diagnostic tool in medicine
Write in brief, how these waves can be produced.
Question 7.
Distinguish between ‘intrinsic’ and ‘extrinsic’ semiconductors.
Question 8.
Show that the radius of the orbit in hydrogen atom varies as n2, where n is the principal quantum number of the atom.
Question 9.
Use the mirror equation to show that an object placed between f and 2f of a concave mirror produces a real image beyond 2 f.
OR
Find an expression for intensity of transmitted light when a Polaroid sheet is rotated between two crossed Polaroids. In which position of the Polaroid sheet will the transmitted intensity be maximum ?
Question 10.
A proton and an a-particle have the same de Broglie wavelength. Determine the ratio of
(i) their accelerating potentials
(ii) their speeds.
SECTION : C
Question 11.
State the principle of working of a galvanometer. A galvanometer of resistance G is converted into a voltmeter to measure up to V volts by connecting a resistance R1 in series with the coil. If a resistance R2 is connected in series with it, then it can measure up to V/2 volts. Find the resistance, in terms of R1 and R2, required to be connected to convert it into a voltmeter that can read up to 2 V. Also find the resistance G of the galvanometer in terms of R1 and R2.
Question 12.
Two capacitors of unknown capacitance C1 and C2 are connected first in series and then in parallel across a battery of 100 V. If the energy stored in the two combinations is 0.045 J and 0.25 J respectively, determine the value of Cj and C2. Also calculate the charge on each capacitor in parallel combination.
Question 13.
With what considerations in view, a photo diode is fabricated ? State its working with the help of a suitable diagram. Even though the current in the forward bias is known to be more than in the reverse bias, yet the photo diode works in reverse bias. What is the reason ?
Question 14.
(a) Write Einstein’s photoelectric equation and mention which important features in photoelectric effect can be explained with the help of this equation.
(b) The maximum kinetic energy of the photo electrons gets doubled when the wavelength of light incident on the surface changes from λ1 to λ2. Derive the expressions for the threshold wavelength X0 and work function for the metal surface.
Question 15.
LFse Kirchhoff’s rules to obtain conditions for the balance condition in a Wheatstone bridge.
Question 16.
In the study of Geiger-Marsdan experiment on scattering of α-particles by a thin foil of gold, draw the trajectory of α-particles in the Coulomb field of target nucleus.
Explain briefly how one gets the information on the size of the nucleus from this study. From the relation R = R0 A1/3, where R() is constant and A is the mass number of the nucleus, show that nuclear matter density is independent of A.
OR
Distinguish between nuclear fission and fusion. Show how in both these processes energy is released. Calculate the energy release in MeV in the deuterium-tritium fusion reaction :
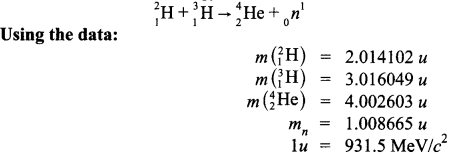
Question 17.
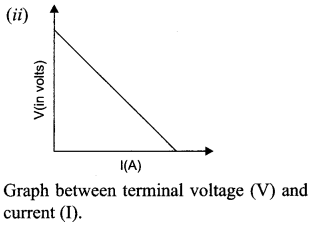
A cell of emf ‘E’ and internal resistance V is connected across a variable load resistor R. Draw the plots of the terminal voltage V versus
(i) R and
(ii) the current I. It is found that when R = 4 Ω, the current is 1A and when R is increased to 9 Ω, the current reduces to 0.5 A. Find the values of the emf E and internal resistance r.
Question 18.
An inductor L of inductance XL is connected in series with a bulb B and an ac source. How would brightness of the bulb change when
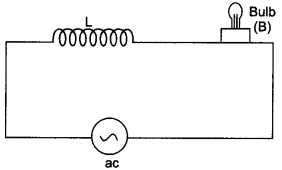
- number of turn in the inductor is reduced,
- an iron rod is inserted in the inductor and
- a capacitor of reactance Xc = XL is inserted in series in the circuit. Justify your answer in each case.
Question 19.
Draw a block diagram of a detector for AM signal and show, using necessary processes and the wave forms, how the original message signal is detected from the input AM wave.
Question 20.
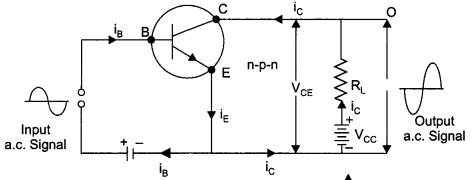
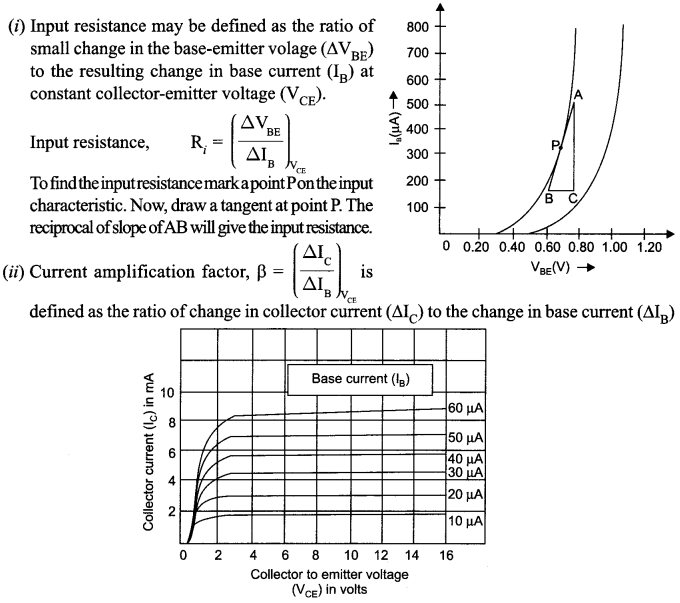
Draw a circuit diagram of a transistor amplifier in CE configuration. Define the terms :
(i) Input resistance and
(ii) Current amplification factor.
How are these determined using typical input and output characteristics ?
Question 21.
Answer the following questions :
(a) In a double slit experiment using light of wavelength 600 nm, the angular width of the fringe formed on a distant screen is 0.1°. Find the spacing between the two slits.
(b) Light of wavelength 5000 Å propagating in air gets partly reflected from the surface of water. How will the wavelengths and frequencies of the reflected and refracted light be affected?
Question 22.
(i) A giant refracting telescope has an objective lens of focal length 15 m. If an eyepiece of focal length 1.0 cm is used. What is the angular magnification of the telescope ?
(ii) If this telescope is used to view the moon. What is the diameter of the image of the moon formed by the objective lens ? The diameter of the moon is 3.48 x 108 m and the radius of lunar orbit is 3.8 x 108 cm.
SECTION : D
Question 23.
A group of students while coming from the school noticed a box marked “Danger H.T. 2200 V” at a substation in the main street. They did not understand the utility of a such a high voltage, while they argued the supply was only 220 V. They asked their teacher this question the next day. The teacher thought it to be an important question and therefore, explained to the whole class. Answer the following questions :
- What device is used to bring the high voltage down to low voltage of a.c. current and what is the principle of its working ?
- Is it possible to use this device for bringing down the high dc voltage to the low voltage? Explain.
- Write the values displayed by the students and the teacher. 4
SECTION : E
Question 24.
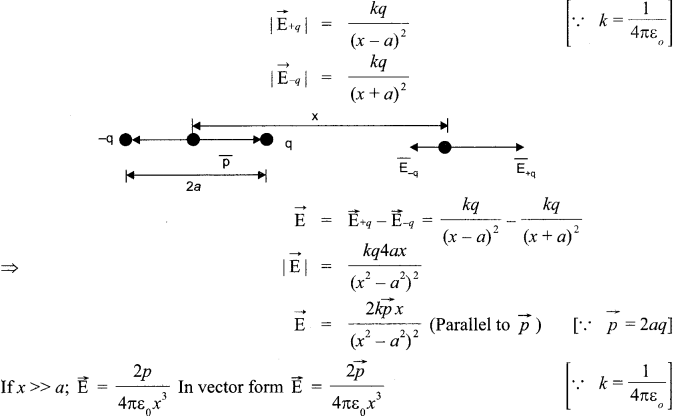
(a) An electric dipole of dipole moment P consists of point charges +q and -q separated by a distance 2a apart. Deduce the expression for the electric field E due to the dipole at a distance x from the centre of the dipole on its axial line in terms of the dipole moment P Hence show that in the limit
![]()
(b) Given the electric field in the region E = 2×1, find the net electric flux through the cube and the charge enclosed by it.
OR
(a) Explain using suitable diagrams, the difference in the behaviour of a
(i) conductor and
(ii) dielectric in the presence of external electric field. Define the terms polarization of a dielectric and write its relation with susceptibility.
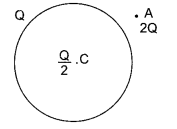
(b) A thin metallic spherical shell of radius carries a charge Q on its surface. A point charge Q/2 is placed at its centre C and another charge +2Q is placed outside the shell at a distance x from the centre as shown in the figure.
Find
(i) the force on the charge at the centre of shell and at the point A,
(ii) the electric flux through the shell.
Question 25.
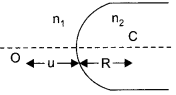
(a) A point object ‘O’ is kept in a medium of refractive index n1 in front of a convex spherical surface of radius of curvature R which separate the second medium of refractive index n2 from the first one as shown in the figure. Draw the ray diagram showing the image formation and deduce the relationship between the object distance and the image distance in terms of n1 n2 and R.
(b) When the image formed above acts as a virtual object for a concave spherical surface separating the medium n2 from n1 (n2> n1) draw this ray diagram and write the similar (similar to (a)) relation. Hence obtain the expression for the Lens Makers formula.
OR
(a) What is polarisation of light? Under what condition does a beam of light reflected by a transparent medium becomes plane polarised? Use the condition to establish a relation between the angle of incidence and the refractive index of the transparent medium.
(b) State the essential condition for Rayleigh scattering to occur.
(c) Compare the intensity of scattering of light of wavelength 400 nm and 600 nm in the earth’s atmosphere.
Question 26.
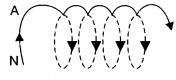
(a) State Ampere’s Circuital law. Use this law to obtain the expression for the magnetic field inside an air cored toroid of average radius, having V turns per unit length and carrying a steady current I.
(b) An observer to the left of a solenoid of N turns each of cross section area A observes that a steady current I in it flows in the clockwise direction. Depict the magnetic field lines due to the solenoid specifying its polarity and show that it acts as a bar magnet of magnetic momentum M = NIA.
OR
(a) Define mutual inductance and write its S.I. units.
(b) Derive an expression for the mutual inductance of two long co-axial solenoids of same length wound one over the other.
(c) In an experiment two coils c1, and c2 are placed close to each other. Find out the expression for the emf induced in the coil c1 due to a change in the current through the coil c2.
Answers
SECTION : A
Answer 1.
Range of frequencies used in satellite communication is
- Uplink = 5.925 – 6.425 GHz
- Downlink = 3.7 – 4.2 GHz
- Both space waves and light waves are electromagnetic.
Answer 2.
Capacitor reactance is the resistance offered by a capacitor to the flow of a.c. It is given by
![]()
Where co (Angular frequency of the source) = 2nf;
f = frequency of the source
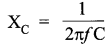
C = Capacitance of the capacitor
Answer 3.
Since μg lens < μm surroundings. It behaves like a converging lens.
Answer 4.
The electric flux through a cube of side 1 cm which encloses an electric dipole will be zero, as net charge enclosed by a cube is zero.
Answer 5.
- DE is the region of negative resistance because the slope of curve in this part is negative.
- BC is the region where Ohm’s law is obeyed because in this part, the current varies linearly with the voltage.
SECTION : B
Answer 6.
- Microwaves are suitable for radar systems that are used in aircraft navigation. These rays are produced by special vacuum tubes, namely -klystrons, magnetrons and Gunn diodes.
- Infrared waves are used to treat muscular strain. These rays are produced by hot bodies and molecules.
- X-rays are used as a diagnostic tool in medicine. These rays are produced when high energy electrons are stopped suddenly on a metal of high atomic number.
Answer 7.

Answer 8.
According to the Bohr’s theory of hydrogen atom, the angular momentum of a revolving electron is given by
![]()
Here,
m = Mass of the electron
v = Velocity of the electron
r = Radius of the orbit
h = Planck’s constant
n = Principal quantum number
If an electron of mass m and velocity v is moving in a circular orbit of radius r, then the centripetal force required is given by
![]()
Also, if the charge on the nucleus is Ze, then the force of electrostatic attraction between the nucleus and the electron will provide the necessary centripetal force.
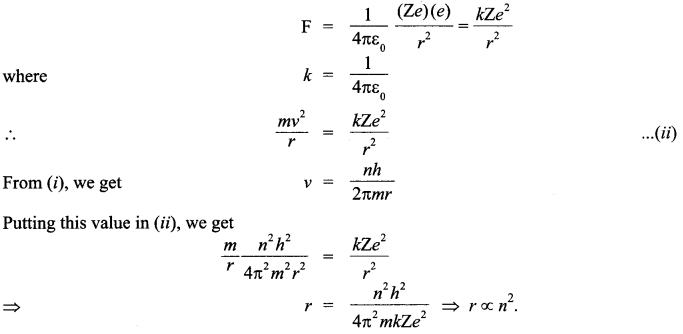
Answer 9.
Mirror equation is
![]()
Where u is distance of object from the mirror, v is the distance of image from the mirror and f is the focal length of the mirror.
For a concave mirror/is negative i.e.,f < 0,u < 0 For a real object (on the left of mirror)
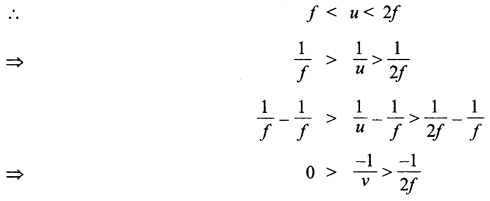
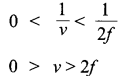
This implies that v is negative and greater than 2f This means that the image lies beyond 2f and it is real.
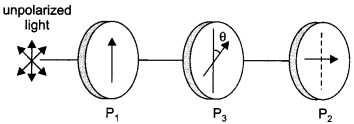
Let us consider two crossed polarisers P1 and P2 with a polaroid sheet P3 placed between them. Let IQ be the intensity of polarized light after passing through the first polarizer P1. If 0 is the angle between the axes of P1 and P2 then the intensity of the polarized light after passing through P3 will be I = I0 cos2 θ.
As P1 and P2 are crossed, the angle between the axes of P1 and P2 = 90°.
∴ Angle between the axes of P2 and P3 = (90° – θ)

Answer 10.
(i) The de Broglie wavelength of a particle is given by
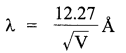
where, V is the accelerating potential of the particle
It is given that
λproton = λalpha
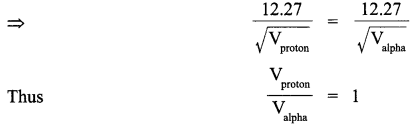
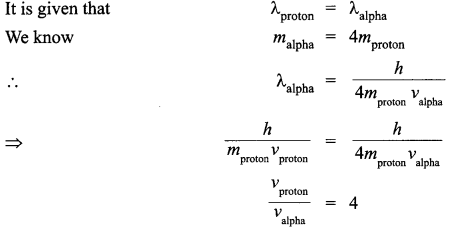
(ii) We can also write de Broglie wavelength as λ = h/mv where h is Planck’s constant, m is mass of the particle and v is speed of the particle.
SECTION : C
Answer 11.
Principle :
When a current-carrying coil is placed in a magnetic field, it experiences a torque. From the measurement of the deflection of the coil, the strength of the current can be computed. A high resistance is connected in series with the galvanometer to convert it into voltmeter. The value of the resistance is given by
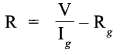
Here,
V = Potential difference across the terminals of the voltmeter
Ig = Current through the galvanometer
G = Resistance of the galvanometer
When the resistance R1, is connected in series with the galvanometer,
V = I (G + R1)
When the resistance R1 is connected in series with the galvanometer,
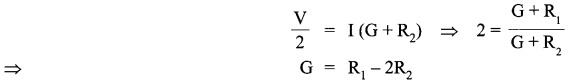
Let R3 be the resistance required for conversion into voltmeter of range 2V
∴ 2 V = Ig (G + R3)
Also
V = Ig(G + R1)
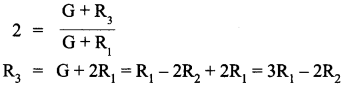
Answer 12.
When the capacitors are connected in parallel. Equivalent capacitance, Cp = C1+ C2 The energy stored in the combination of the capacitors,

When the capacitors are connected in parallel, the charge on each of them can be obtained as follows:
Q1 = C1V = 38.2 x 10-6 x loo = 38.2 x 10-4 C
Q2 = C2V= 11.8 x x 10-6 x 100= 11.8 x x 10-4 C
Answer 13.
A photo diode is used to observe the change in current with change in the light intensity under reverse bias condition. In fabrication of photo diode, material chosen should have band gap -1.5 eV or lower so that solar conversion efficiency is better. This is the reason to choose Si or GaAs material. Working: It is a p-n junction fabricated with a transparent window to allow light photons to fall on it. These photons generate electron hole pairs upon absorption. If the junction is reverse biased using an electrical circuit, these electron hole pair move in opposite directions so as to produce current in the circuit. This current is very small and is detected by the micro ammeter placed in the circuit.
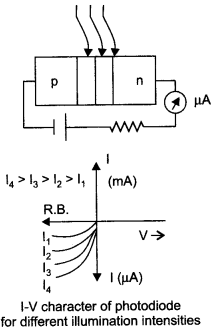
A photo diode is preferably operated in reverse bias condition. Consider an «-type semiconductor. Its majority carrier (electron) density is much larger than the minority hole density. When illuminated with light, both types of carriers increase equally in number
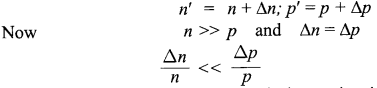
That is, the fractional increase in majority carriers is much less than the fractional increase in minority carriers. Consequently, the fractional change due to the photo-effects on the minority carriers dominated reverse bias current is more easily measurable than the fractional change in the majority carrier dominated forward bias current. Hence, photo diodes are preferably used in the reverse bias condition for measuring light intensity.
Answer 14.
(a) Einstein’s photoelectric equations is given by
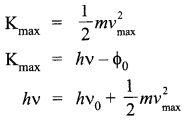
Where
Kmax = Maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron
vmax = Maximum velocity of the emitted photoelectron
m = Mass of the photoelectron
v = Frequency of the light radiation
Φ0 = Work function h = Planck’s constant
If vo is the threshold frequency, then the work function can be written as
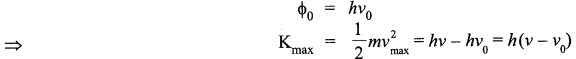
The above equations explains the following results.
- If v < vo, then the maximum kinetic energy is negative, which is impossible. Hence, photoelectric emission does not take place for the incident radiation below the threshold frequency. Thus, the photoelectric emission can take place only if
v > vo. - The maximum kinetic energy of emitted photo electrons is directly proportional to the frequency of the incident radiation. This means that maximum kinetic energy of photo electron depends only on the frequency of incident light.
(b) According to the photoelectric equation,
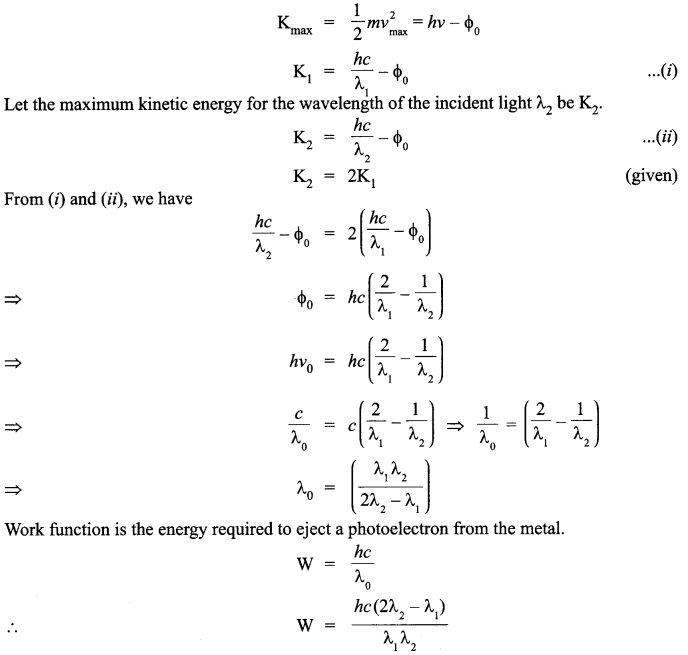
Answer 15.
Let us consider a Wheatstone bridge arrangement as shown below :
Wheatstone bridge is a special bridge type circuit which consists of four resistances, a galvanometer and a battery. It is used to determine unknown resistance. In figure four resistance P, Q, R and S are connected in the form of four arms of a quadrilateral. Let the current given by battery in the balanced position be I. This current on reaching point A is divided into two parts I1 and I2. As there is no current in galvanometer in balanced state, therefore current in resistances P and Q is I1 and in resistances R and S it is I1.
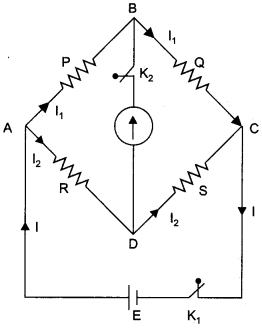

This is condition of balanced Wheatstone bridge
Answer 16.
From this experiment, the following is observed :
- Most of the alpha particles pass straight through the gold foil. It means that they do not suffer any collision with gold atoms.
- About one alpha particle in every 8000 alpha particles deflects by more than 90°. As most of the alpha particles go undeflected and only a few get deflected, this shows that most of the space in an atom is empty and at the centre of the atom, there exists a nucleus. By the number of the alpha particles deflected, the information regarding size of the nucleus can be known.
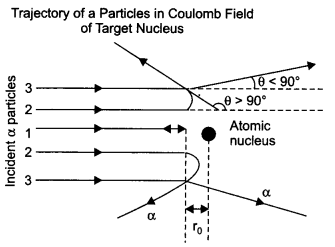
If m is the average mass of a nucleon and R is the nuclear radius, then mass of nucleus = mA, where A is the mass number of the element. This shows that the nuclear density is independent of A.
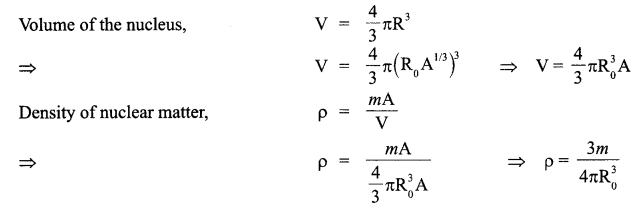
OR
Nuclear fission :
Nuclear fission is a disintegration process, in which a heavier nucleus gets split up into two lighter nuclei, with the release of a large amount of energy.

Answer 17.
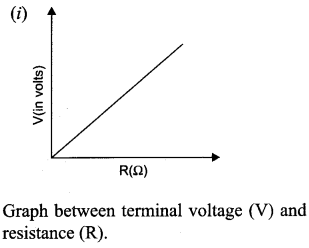

Answer 18.
- When the number of turns in the inductor is reduced, its reactance XL decreases. The current in the circuit increases and hence brightness of the bulb increases.
- When an iron rod is inserted in the inductor, the self inductance increases. Consequently, the inductive reactance XL = coL increases. This decreases the current in the circuit and the bulb glows dimmer.
- With capacitor of reactance Xc = XL, the impedance
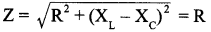
becomes minimum, the current in circuit becomes maximum. Hence the bulb glows with maximum brightness.
Answer 19.
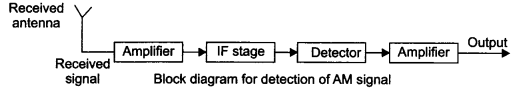
When a message is received, it gets attenuated through the channel therefore, receiving antenna is to be followed by an amplifier and a detector. The signal frequency is usually changed to a lower frequency in an Intermediate Frequency (IF) stage. The detected signal may not be strong enough to be made use of and hence is required to be amplified. In order to obtain the original message signal m(t) of angular frequency a simple method is used which is shown in the form of a block diagram.
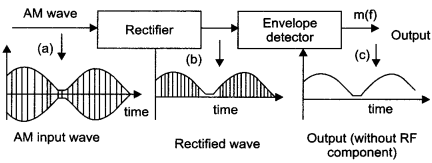
When the received modulated signal is passed through a rectifier, an envelope signal is produced. This envelope signal is the message signal. In order to retrieve the message, the signal is passed through an envelope detector.
Answer 20.
Answer 21.
(a) Angular width (0) of fringe in double-slit experiment is given by 0 = λ/d
Where, d = Spacing between the slits
Given, Wavelength of light, X = 600 nm
Angular width of fringe,
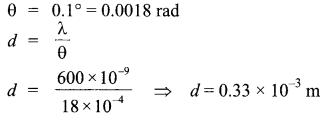
(b) The frequency and wavelength of reflected wave will not change. The refracted wave will have same frequency, only wavelength will change. The velocity of light in water is given by v = λf
where,
v = Velocity of light
f= Frequency of light
λ = Wavelength of light
As light ray is travelling from rarer (air) medium to denser medium, its speed will decrease. Hence, wavelength (λ) will also decrease.
Answer 22.
(i) Let
f0 = Focal length of the objective lens = 15 m = 1500 cm
fe = Focal length of the eye lens = 1.0 cm
Angular magnification of the giant refracting telescope is given by
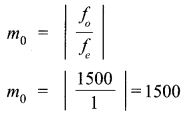
(ii) Diameter of the image of the moon formed by the objective lens, d = αfo
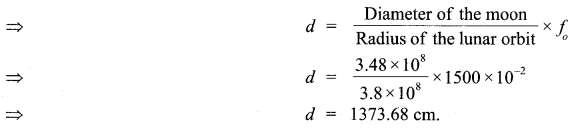
SECTION : D
Answer 23.
- The device that is used to bring high voltage down to low voltage of an a.c. current is a transformer. It works on the principle of mutual induction of two windings or circuits. When current in one circuit changes, emf is induced in the neighbouring circuit.
- The transformer cannot convert d.c. voltages because it works on the principle of mutual induction. When the current linked with the primary coil changes, the magnetic flux linked with the secondary coil also changes. This change in flux induces emf in the secondary coil. If we apply a direct current to the primary coil the current will remain constant. Thus, there is no mutual induction and hence no emf is induced.
- The value of gaining knowledge and curiosity about learning new things is being displayed by the students. The value of providing good education and undertaking the doubts of students has been displayed by the teacher.
SECTION : E
Answer 24.
(a) Electric field at a point on the axial line
(b) Since, the electric field is parallel to the faces, parallel to xy and xz planes, the electric flux through them is zero.
Electric flux through the left face
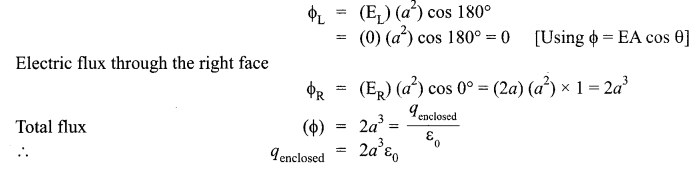
OR
(a) (i) Conductor :
E0 → external field
Em → internal field created by the redistribution of electrons inside the metal.
When a conductor like a metal is subjected to external electric field, the electrons experience a force in the opposite direction collecting on the left hand side. A positive charge is therefore induced on the right hand side. This creates an opposite electric field (Em) that balances out (E0).
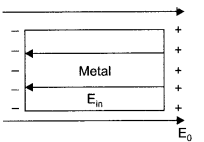
∴ The net electric field inside the conductor becomes zero.
(ii) Dielectric :
When external electric field is applied, dipoles are created (in case of non-polar dielectrics). The placement of dipoles is as shown in the given figure. An internal electric field is created which reduces the external electric field. Polarization of dielectric (P) is defined as the dipole moment per unit volume of the polarized dielectric.
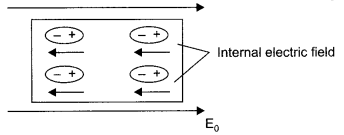
p = Xes0 E
Xe = susceptibility
E = Electric field

Answer 25.
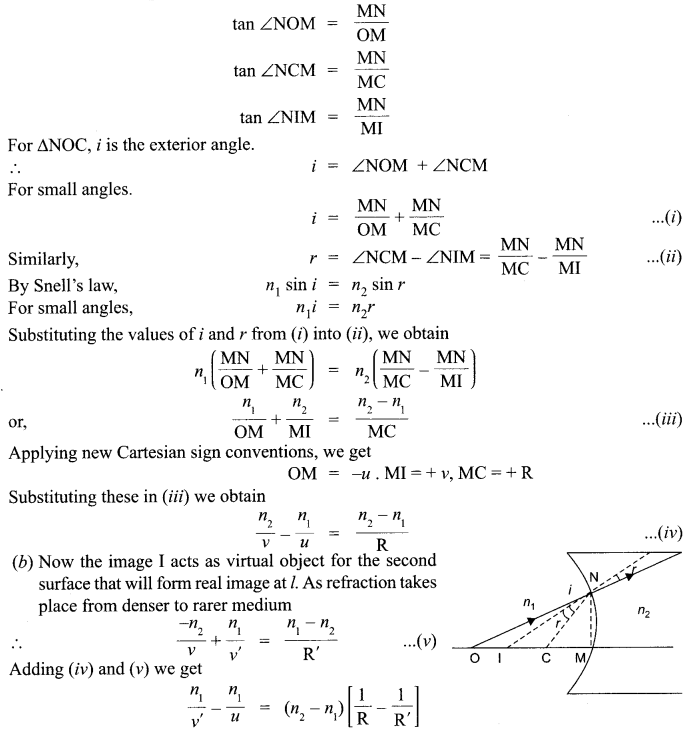
(a) Let a spherical surface separate a rarer medium of refractive index n1 from denser medium of refractive index n2. Let C be the centre of curvature and R = MC be the radius of the surface.
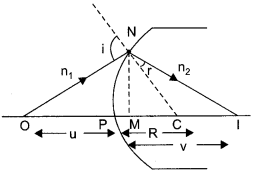
Consider a point object O lying on the principal axis of the surface. Let a ray starting from O incident normally on the surface along OM and pass straight. Let another ray of light incident on NM along ON and refract along NI. From M, draw MN perpendicular to 01.
The figure shows the geometry of formation of image I of an object O and the principal axis of a spherical surface with centre of curvature C and radius of curvature R.
Let us make the following assumptions :
- The aperture of the surface is small as compared to the other distance involved.
- NM will be taken as nearly equal to the length of the perpendicular from the point N on the principal axis.
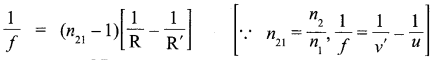
OR
(a) Restricting the vibrations of electric vector (light) in a single direction perpendicular to the direction of propagation of light is called polarisation of light. At polarising angle refracted and reflected components of light are perpendicular to each other. In fig.

Answer 26.
(a) Amperes circuital law in electro magnetism is analogous to Gauss law in electrostatics. This law states that “The line integral of resultant magnetic field along a closed plane curve is equal to p0 time the total current crossing the area bounded by the closed curve provided the electric field inside the loop remains constant. Thus ƒ B .dl = μ.0Ienc, where p0 is permeability of free space and Ienc is the net current enclosed by the loop.
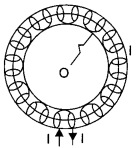
A toroid is a hollow circular ring on which a large number of turns of a wire are closely wound. Consider an air-cored toroid (as shown here) with centre O.
Given,
r = Average radius of the toroid
I = Current through the solenoid .
n = Number of turns per unit length
To determine the magnetic field inside the toroid, we consider three amperian loops (loop 1, loop 2 and loop 3) as show in the figure below.

This is the expression for magnetic field inside air-cored toroid.
(b) Given that the current flows in the clockwise direction for an observer on the left side of the solenoid. This means that left face of the solenoid acts as south pole and right face acts as north pole. Inside a bar magnet the magnetic field lines are directed from south to north. Therefore, the magnetic field lines are directed from left to right in the solenoid. Magnetic moment of single current carrying loop is given by
m = IA
where
I = Current flowing through the loop;
A = Area of the loop So, Magnetic moment of the whole solenoid is given by
M = Nm = N(IA)
OR
(a) Mutual inductance is the property of two coils by the virtue of which each opposes any change in the value of current flowing through the other by developing an induced emf. The SI unit of mutual inductance is henry and its symbol is H.
(b) Consider two long solenoids S1 and S2 of same length / such that solenoid S2 surrounds
solenoid S, completely.

We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Paper 7 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Physics Paper 7, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.