ML Aggarwal Class 7 Solutions Chapter 14 Symmetry Objective Type Questions for ICSE Understanding Mathematics acts as the best resource during your learning and helps you score well in your exams.
ML Aggarwal Class 7 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 14 Symmetry Objective Type Questions
Mental Maths
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) The hands of a clock rotate only in ………. direction.
(ii) While opening the cap of a bottle, the direction of rotation is ……….
(iii) The number of lines of symmetry of an isosceles right-angled triangle is …………
(iv) A figure has ……….. symmetry if it is its own image under a reflection.
(v) The centre of rotation of an equilateral triangle is the point of intersection of its ………..
(vi) The centre of rotation of a rhombus is the point ……….
(vii) A regular polygon of n-sides has ……….. the number of lines of symmetry.
(viii) The angle of rotational symmetry in an equilateral triangle is ……….
(ix) The angle of rotational symmetry in a regular pentagon is ……..
(x) If after a rotation of 45° about a fixed point the figure looks exactly the same, then the order of rotational symmetry is ……….
Solution:

Question 2.
State whether the following statements are true (T) or false (F):
(i) The letter A has line symmetry but no rotational symmetry.
(ii) A rhombus is also a parallelogram and hence it does not have line symmetry.
(iii) A parallelogram has two lines of symmetry.
(iv) The order of rotational symmetry of a rhombus is four.
(v) A circle has exactly four lines of symmetry.
(vi) In a regular pentagon, the perpendicular bisector of the sides are the only lines of symmetry.
(vii) In a regular hexagon, the perpendicular bisector of the sides are the only lines of symmetry.
(viii) In a rectangle, the angle of rotational symmetry is 90°.
(ix) A semicircle has rotational symmetry of order 2.
(x) An isosceles triangle has neither a line symmetry nor a rotational symmetry.
(xi) If a figure possesses a rotational symmetry, then it must look exactly the same atleast once up to a rotation of 180°.
(xii) The angle of rotation of a figure is obtained by dividing 360° by the order of rotational symmetry.
(xiii) A regular triangle has 3 lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry of order 3.
(xiv) A regular pentagon has 5 lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry of order 5.
Solution:


Multiple Choice Questions
Choose the correct answer from the given four options (3 to 14):
Question 3.
A quadrilateral having four lines of symmetry is a
(a) parallelogram
(b) rectangle
(c) rhombus
(d) square
Solution:
![]()
Question 4.
The letter Z has
(a) one horizontal line of symmetry
(b) one vertical line of symmetry
(c) two lines of symmetry
(d) no line of symmetry
Solution:
![]()
Question 5.
A figure that does not have any rotational symmetry is
(a) circle
(b) parallelogram
(c) kite
(d) regular pentagon
Solution:
![]()
Question 6.
The number of lines of symmetry in the given figure is
(a) 1
(b) 3
(c) 6
(d) infinitely many

Solution:
![]()
Question 7.
Rotating a figure by 60° anticlockwise is equivalent to a clockwise rotation of
(a) 60°
(b) 120°
(c) 240°
(d) 300°
Solution:
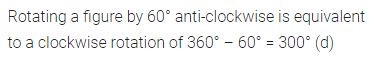
Question 8.
A figure having 1 line of symmetry and whose order of rotational symmetry is also 1 is
(a) rhombus
(b) parallelogram
(c) kite
(d) scalene triangle
Solution:

Question 9.
The order of rotational symmetry of a line segment is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Solution:
![]()
Question 10.
The order of the rotational symmetry in the given figure is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 4
(d) infinitely many
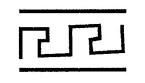
Solution:
![]()
Question 11.
A possible angle of rotation of a figure having rotational symmetry of order greater than 1 is
(a) 36°
(b) 144°
(c) 150°
(d) 360°
Solution:

Question 12.
The figure which does not have both reflection and rotational symmetry is
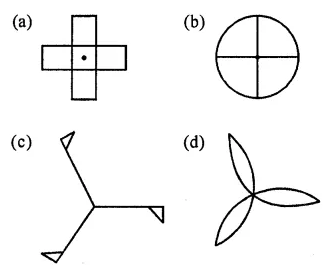
Solution:

Question 13.
In the word ’MATHS’ which of the following pairs of letters have rotational symmetry?
(a) M and T
(b) A and S
(c) T and S
(d) H and S
Solution:

Question 14.
The letter which has both reflection and rotational symmetry is
(a) H
(b) M
(c) S
(d) Y
Solution:
