
On this page, you will find Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 9 Pdf free download. CBSE NCERT Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals will seemingly help them to revise the important concepts in less time.
CBSE Class 8 Science Notes Chapter 9 Reproduction in Animals
Reproduction in Animals Class 8 Notes Understanding the Lesson
1. Reproduction is the process of continuation of similar kinds of individuals, generation after generation. In this process, all living beings produce their young ones for continuity of life on the planet earth.
2. There are two modes by which animals reproduce. These are:
- Sexual reproduction and
- Asexual reproduction.
3. Reproduction resulting from the fusion of male and female gametes is called sexual reproduction; e.g., frog, fish, cow, human beings, etc., reproduce by sexual reproduction.
4. Reproduction in which young ones are formed from the cells of a single parent and are identical copies of their parents is called asexual reproduction. This type of reproduction is seen in Amoeba, yeast, worms, etc.
5. There are different reproductive organs in male and female. The main reproductive organs in males are testes, sperm ducts, urethra and penis , whereas those in females are ovaries, oviducts, uterus and vagina
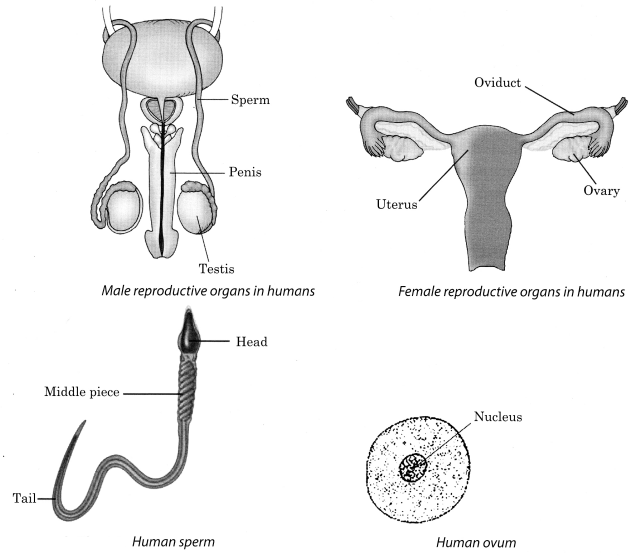
6. In male, the testes produce the male gametes called sperms , whereas in female, the ovary produces female gametes called ova (eggs)
In human beings, a single matured egg is released into the oviduct by one of the ovaries every month.
7. Uterus is the part where development of the baby takes place.
8. When sperms come in contact with an egg, one of them may fuse with the egg. Such fusion of egg and the sperm is called fertilisation
9. The nuclei of the sperm and the egg fuse to form a single nucleus forming a fertilised egg called zygote
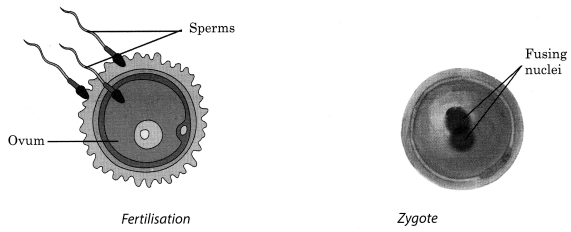
10. Fertilisation which takes place inside the female body is called internal fertilisation and that in which the fusion of a male and a female gametes takes place outside the female body is called external fertilisation. Internal fertilisation occurs in many animals including humans, cows, dogs and hens whereas external fertilisation is very common in aquatic animals like fish, frogs, starfish, etc.
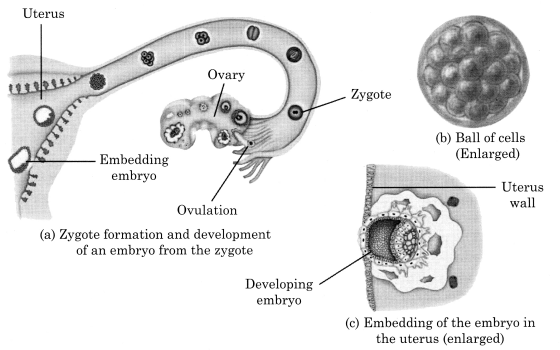
11. The zygote formed after fertilisation begins to develop into an embryo . The zygote divides repeatedly to give rise to a ball of cells which then begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs of the body termed as embryo.
12. The embryo gets embedded in the wall of the uterus for further development.
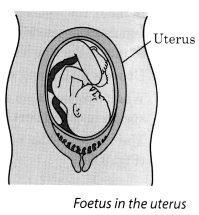
13. The stage of the embryo in which all the body parts can be identified is called a foetus. When the development of the foetus is complete, the mother gives birth to the baby.
14. The animals which give birth to their young ones are called viviparous animals and those which lay eggs to reproduce are called oviparous animals.
15. The immature free-living form of most invertebrates (animals lacking a backbone) and amphibians and fish which at hatching from the egg is fundamentally unlike its parent and must metamorphose is called larva.
16. The transformation of the larva into an adult through drastic changes is called metamorphosis.
17. In Hydra, new individuals develop from buds. This method of asexual reproduction is called budding.
18. Amoeba reproduces by dividing itself into two. This type of asexual reproduction is called binary fission.
Class 8 Science Chapter 9 Notes Important Terms
Asexual reproduction: The mode of reproduction in which a single organism is able to produce one or more of its kind by itself is known as asexual reproduction; e.g., Amoeba, yeast, Hydra, etc., undergo asexual reproduction.
Binary fission: The type of reproduction in which an animal reproduces by dividing into two individuals is called binary fission; e.g., Amoeba reproduces by dividing itself into two.
Budding: This kind of reproduction is seen in Hydra and yeast. It is the process of reproduction in which new individuals develop as outgrowths from a single parent. The outgrowths developed on parent body is called buds and the process of reproduction is known as budding.
Embryo: When cells produced by the division of the zygote begin to form groups that develop into different tissues and organs of the body is called embryo.
External fertilisation: The fusion of male and female gametes takes place outside the female body. This is called external fertilisation. Most of the aquatic animals undergo this type of fertilisation.
Fertilisation: The process of union of male gametes or sperms and female gametes or ova (egg) is called fertilisation.
Foetus: The stage of the development of embryo in which the development and emergence of the various body parts like the hands, the feet and eyes, etc., can be identified is called the foetus.
Internal fertilisation: The fusion of male and female gametes or fertilisation that takes place inside the female body is called internal fertilisation. All insects, birds and mammals including human beings undergo this type of fertilisation.
Metamorphosis: A biological process in which larva drastically changes into an adult in an invertebrate or amphibian during their life cycle is known as metamorphosis.
Ova or Eggs: Female gametes produced by ovary in female are called ova or eggs.
Oviparous animals: The animals which lay eggs and hatch them to produce their young ones are called oviparous animals; e.g., frog, butterflies, hen, crow, etc.
Reproduction: The process of producing the offspring of one’s own kind for continuity of life in the earth is known as reproduction.
Sexual reproduction: The type of reproduction which involves fusion of male and female gametes is called sexual reproduction.
Sperms: Sperms are the male gametes produced by the testes in male.
Viviparous animals: The animals which give birth to their young ones are called viviparous animals; e.g., cow, buffalo, cat, dog, human beings, etc.
Zygote: The nucleus of the sperms and the egg fuse to form a single nucleus during the process of fertilisation. The fertilised egg is called zygote.