Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 MCQ With Answers
Chemistry Class 11 Chapter 7 MCQs On Equilibrium
MCQ On Equilibrium Class 11 Question 1.
The solubility of Ca3(PO4)2 in water is y mol/L. Its solubility product is:
(a) 6y²
(b) 36 y4
(c) 64 y5
(d) 108 y5
Answer
Answer: (d) 108 y5
Explanation:
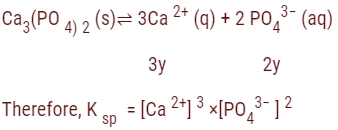
= (3y)³ × (2y)²
= 27 y³ × 4y²
= 108 y5
Buffer pH Calculator makes it easy for you to determine the theoretical yield value of the chemical reaction in fraction of seconds with steps.
Equilibrium Class 11 MCQ Question 2.
A physician wishes to prepare a buffer solution at pH = 3.85 that efficiently resists changes in pH yet contains only small concentration of the buffering agents. Which of the following weak acids together with its sodium salt would be best to use?
(a) 2, 5-Dihydroxy benzoic acid (pKa = 2.97)
(b) Acetoacetic acid (pKa = 3.58)
(c) m-Chlorobenzoic acid (pKa = 3.98)
(d) p-Chlorocinnamic acid (pKa = 4.41)
Answer
Answer: (b) Acetoacetic acid (pKa = 3.58)
Explanation:
For small concentration of buffering agent and for maximum buffer capacity
[Salt]/ [Acid] ≈ 1
i.e., pH = pKa
MCQ On Chemical Equilibrium Class 11 Question 3.
Which of the following aqueous solutions will have highest pH?
(a) NaCl
(b) CH3COONa
(c) Na2CO3
(d) NH4Cl
Answer
Answer: (c) Na2CO3
Explanation:
NaCl is salt of strong acid and strong base so it has pH of about 7.
NH4Cl is salt of strong acid and weak base so it has pH is much less than 7.
CH3COONH4 is salt of weak acid and weak base so it has pH of about 7.
Na2CO3 is salt of weak acid and strong base so it has pH is much greater than 7.
Equilibrium MCQ Class 11 Question 4.
What is the pH of a 0.10 M solution of barium hydroxide, Ba (OH)2?
(a) 11.31
(b) 11.7
(c) 13.30
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) 13.30
Explanation:
pH = 13.30
Barium hydroxide is a strong base for both stages of dissociation:
Ba (OH)2(s) → Ba2+ + 2OH–
So the solution will have 0.20 M hydroxide ions. Now use the auto dissociation product for water:
[H+][OH–] = 1.0 × 10-14M
[OH–] = 2.0 × 10-1M
[H+] = 5.0 × 10-14M
And then pH = −log10 ([H+] = 5.0 × 10-14)
= 13.30.
MCQ Of Equilibrium Class 11 Question 5.
Which of the following oxides is not expected to react with sodium hydroxide?
(a) CaO
(b) SiO2
(c) BeO
(d) B2O3
Answer
Answer: (a) CaO
Explanation:
CaO being a basic oxide does not react with NaOH, however SiO2 (acidic oxide), BeO (amphoteric oxide) and Br2O3 (acidic oxide) react with NaOH.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 MCQ Question 6.
The pH of a 10-10 M NaOH solution is nearest to
(a) 10
(b) 7
(c) 4
(d) -10
Answer
Answer: (c) 4
Explanation:
pOH= −log [OH–]
= −log 10-10
= 10 log 10
= 10pH + pOH
= 14pH
= 14−pOH
= 14−10
= 4
Chemical Equilibrium MCQs Class 11 Question 7.
A weak acid HX has the dissociation constant 1 × 10-5 M. It forms a salt NaX on reaction with alkali. The degree of hydrolysis of 0.1 M solution of NaX is
(a) 0.0001%
(b) 0.01%
(c) 0.1%
(d) 0.15%
Answer
Answer: (b) 0.01%
Explanation:
NaX: Salt of weak acid, strong base.
⇒ α = (√Kh/c)
= √ (Kw)/ (KaC)
= (10-14)/(10-5×0.1)
= 10-4
⇒ % hydrolysis = 0.01%
MCQ On Chemical Equilibrium With Answers Question 8.
When equal volumes of 0.1 M NaOH and 0.01 M HCl are mixed, the hydroxide ion concentration is
(a) 7.0
(b) 1.04
(c) 12.65
(d) 2.0
Answer
Answer: (c) 12.65
Explanation:
When equal volumes of 0.1 M NaOH and 0.01 M HCl are mixed, the hydroxide ion concentration is
(0.1 – 0.01)/(2)
= 0.045 M
The pOH of the solution is pOH = −log [OH–]
= −log 0.045
= 1.35
The pH of the solution is pH = 14 − pOH
= 14 − 1.35
= 12.65
MCQ Questions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Question 9.
Concentration of the Ag+ ions in a saturated solution of Ag2C2O4 is 2.2 x 10-4 mol L-1. Solubility product of Ag2C2O42 is
(a) 2.66 × 10-12
(b) 4.5 × 10-11
(c) 5.3 × 10-12
(d) 2.42 × 10-8
Answer
Answer: (c) 5.3 × 10-12
Explanation:
[Ag+] = 2.2 × 10-4 mol L-1
[C2O42-] = 0.5[Ag+] = 0.5 × 2.2 × 10-4 mol L-1 = 1.1 × 10-4 mol L-1
Ksp =[Ag+]² [C2O42-]Ksp
= (2.2 × 10-4 mol L-1)² × 1.1 × 10-4 mol L-1
Ksp = 5.3 × 10-12
Chemical Equilibrium Class 11 MCQ Question 10.
In a reversible chemical reaction at equilibrium, if the concentration of any one of the reactants is doubled, then the equilibrium constant will
(a) Also be Doubled
(b) Be Halved
(c) Remain the Same
(d) Become One-Fourth
Answer
Answer: (c) Remain the Same
Explanation:
Equilibrium constants are not changed if you change the concentrations of things present in the equilibrium. The only thing that changes an equilibrium constant is a change of temperature.
The position of equilibrium is changed if you change the concentration of something present in the mixture. According to Le Chateliers Principle, the position of equilibrium moves in such a way as to tend to undo the change that you have made.
According to Le Chateliers Principle, if you increase the concentration of Reactant, for example, the position of equilibrium will move to the right to decrease the concentration of reactant again.
Chapter 7 Chemistry Class 11 MCQs Question 11.
When a neutral atom undergoes oxidation, the atoms oxidation state
(a) Decreases as it gains electrons
(b) Decreases as it loses electrons
(c) Increases as it gains electrons
(d) Increases as it loses electrons
Answer
Answer: (d) Increases as it loses electrons
Explanation:
The acronym “OILRIG” can be used to remember this: Oxidation is Losing electrons, Reduction is Gaining electrons. Therefore, when an atom undergoes oxidation, it loses electrons. This makes its net charge more positive, so its oxidation state increases.
Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 MCQ With Answers Question 12.
Concentration of the Ag-4 ions in a saturated solution of Ag2C2O4 is 2.2 × (a) 10-4 mol L-1. Solubility product of Ag2C2O4 is
(b) 2.66 × 10-12
(c) 4.5 × 10-11
(d) 5.3 × 10-12
2.42 × 10-8
Answer
Answer: (c) 4.5 × 10-11
Explanation:
[Ag+] = 2.2 × 10-4 mol L-1
[C2O42-] = 0.5[Ag+] = 0.5 × 2.2 × 10-4 mol L-1 =1.1×10-4 mol L-1
Ksp = [Ag+]² [C2O42-] Ksp
= (2.2 × 10-4 mol L-1)² × 1.1 × 10-4 mol L-1
Ksp = 5.3 × 10-12
Class 11 Chemistry Equilibrium MCQ Question 13.
Among the following the weakest Bronsted base is
(a) F–
(b) Cl–
(c) Br–
(d) I–
Answer
Answer: (d) I–
Explanation:
According to this theory, an acid is a proton donor and a base is a proton acceptor. Every strong Bronsted acid has a weak conjugate base and every strong base has a weak conjugate acid. The acidity increases in halogen group atoms,
HF < HCl < HBr < HI.
So, HI is highly acidic and their conjugate bases decrease in order F– > Cl– > Br– > I–.
Chemical Equilibrium Class 11 MCQ Questions Question 14.
A certain buffer solution contains equal concentration of X– and HX. The ka for HX is 10-8. The pH of the buffer is
(a) 3
(b) 8
(c) 11
(d) 14
Answer
Answer: (b) 8
Explanation:
ka kb = kw
kb = 10-8
ka × 10-8 = 10-14
ka = 10-6 = [H+]
pH = −log [H+]
pH = −log 10-6
= 6pH + pOH
= 14 pOH
= 14−6
= 8
Class 11 Equilibrium MCQ Question 15.
What is the pH of a 0.10 M solution of barium hydroxide, Ba (OH)2?
(a) 11.31
(b) 11.7
(c) 13.30
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) 13.30
Explanation:
pH =13.30
Barium hydroxide is a strong base for both stages of dissociation:
Ba (OH)2(s) → Ba2+ + 2OH–
So the solution will have 0.20 M hydroxide ions. Now use the auto dissociation product for water:
[H+][OH–] = 1.0×10-14M
[OH–] = 2.0 × 10-1M
[H+] = 5.0 × 10-14M
And then pH = −log10 ([H+] = 5.0 × 10-14)
= 13.30.
Chemical Equilibrium MCQs Question 16.
Solubility of M2S salt is 3.5 × 10-6 then find out solubility product.
(a) 1.7 × 10-6
(b) 1.7 × 10-16
(c) 1.7 × 10-18
(d) 1.7 × 10-12
Answer
Answer: (b) 1.7 × 10-16
Explanation:
Let ”s“ be the solubility of salt M2S which undergoes dissociation as follows :-
M2S ⇌ 2M+ +S-2
Initial concentration 1 0 0
Concentration at equilibrium 1-s 2s s
Hence, the solubility product (Ksp) = (s) × (2s)²
Therefore, Ksp = 4 × s³
Or Ksp = 4× (3.5×10-6)³
⇒ Ksp
= 1.7 × 10-16
Ch 7 Chemistry Class 11 MCQ Question 17.
Among the following hydroxides, the one which has the lowest value of Ksp at ordinary temperature (about 25°C ) is
(a) Mg (OH)2
(b) Ca(OH)2
(c) Ba(OH)2
(d) Be(OH)2
Answer
Answer: (d) Be(OH)2
Explanation:
Be(OH)2 has the lowest value of Ksp at ordinary temperature because Be2+ ion is smaller than the other metal ions in the group, which results in a tighter bond with the 0H– ions, thus much lower solubility.
The solubility of a hydroxide of group 2 elements increases down the group because as you go down the group size of metal increases thereby increasing the bond length and decreasing bond energy.
Chemical Equilibrium MCQ Class 11 Question 18.
Which of the following mixtures in aqueous solution of equimolar concentration acts as a buffer solution?
(a) HNO3 and NaOH
(b) H2SO4 and KOH
(c) NH4OH(excess) + HCl
(d) CH3COOH and NaOH(excess)
Answer
Answer: (c) NH4OH(excess) + HCl
Explanation:
A mixture of ammonium hydroxide and HCl react to form ammonium chloride. This also contains unreacted ammonium hydroxide.
NH4 OH + HCl → NH4Cl + H2O
Thus, the resulting mixture of (NH4OH+NH4Cl) is a basic buffer solution. It contains a mixture of weak base ammonium hydroxide and its salt (ammonium chloride) with strong acid (HCl).
It is used in a qualitative analysis of group III radicals.
A mixture of HNO3 and NaOH is a mixture of strong acid and strong base similarly a mixture of
H2SO4 and KOH is also a mixture of strong acid and strong base, thus they do not form buffer solution.
Similarly, in option 4 mixture will form a strong base and salt of strong base weak acid hence it will not form a buffer solution.
Chemical Equilibrium MCQ With Answers Question 19.
Which of the following aqueous solutions will have highest pH?
(a) NaCl
(b) CH3COONa
(c) Na2CO3
(d) NH4Cl
Answer
Answer: (c) Na2CO3
Explanation:
NaCl is salt of strong acid and strong base so it has pH of about 7.
NH4Cl is salt of strong acid and weak base so it has pH is much less than 7.
CH3COONH4 is salt of weak acid and weak base so it has pH of about 7.
Na2CO3 is salt of weak acid and strong base so it has pH is much greater than 7.
Question 20.
Amines behave as
(a) Lewis Acids
(b) Lewis Base
(c) Aprotic Acid
(d) Neutral Compound
Answer
Answer: (b) Lewis Base
Explanation:
R−NH2 (Amines) behaves as a Lewis base because it is capable of donating a lone pair of electron.
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Equilibrium with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding CBSE Class 11 Chemistry Equilibrium MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 11 Chemistry MCQ:
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Class 11 MCQ
- Structure of Atom Class 11 MCQ
- Classification of Elements and Periodicity in Properties Class 11 MCQ
- Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Class 11 MCQ
- States of Matter Class 11 MCQ
- Thermodynamics Class 11 MCQ
- Equilibrium Class 11 MCQ
- Redox Reactions Class 11 MCQ
- Hydrogen Class 11 MCQ
- The s-Block Elements Class 11 MCQ
- The p-Block Elements Class 11 MCQ
- Organic Chemistry: Some Basic Principles and Techniques Class 11 MCQ
- Hydrocarbons Class 11 MCQ
- Environmental Chemistry Class 11 MCQ
