Check the below NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 2 Theory of Consumer Behaviour with Answers Pdf free download. MCQ Questions for Class 11 Economics with Answers were prepared based on the latest exam pattern. We have provided Theory of Consumer Behaviour Class 11 Economics MCQs Questions with Answers to help students understand the concept very well.
Class 11 Economics Chapter 2 Theory of Consumer Behaviour MCQ With Answers
Economics Class 11 Chapter 2 MCQs On Theory of Consumer Behaviour
MCQ Questions For Class 11 Economics Chapter 2 Question 1.
Who gave the cardinal concept of utility?
(a) Marshall
(b) Pigou
(c) Hicks
(d) Samuelson
Answer
Answer: (a) Marshall
Theory Of Consumer Behaviour MCQ Question 2.
Consumer’s behaviour is studied in:
(a) Micro Economics
(b) Macro Economics
(c) Income Analysis
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Micro Economics
Class 11 Economics Chapter 2 MCQ Question 3.
Which of the following statement is true ?
(a) Utility means want-satisfying power
(b) Utility is a function of intensity of desire
(c) Desire of consumption gives birth to utility
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
Economics Class 11 Chapter 2 MCQ Question 4.
Which is the First Law of Gossen?
(a) Law of Demand
(b) Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
(c) Law of Equi-marginal Utility
(d) Consumer’s Surplus
Answer
Answer: (b) Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
MCQ On Theory Of Consumer Behaviour Question 5.
Which of the following is a characteristic of utility ?
(a) Utility is a psychological phenomenon
(b) Utility is subjective
(c) Utility is a relative concept
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
Question 6.
How we calculate marginal utility ?
(a) ∆TU/∆Q
(b) ∆MU/∆Q
(c) ∆Q/∆TU
(d) ∆Q/∆MU
Answer
Answer: (a) ∆TU/∆Q
Question 7.
When TU becomes maximum, MU is:
(a) Positive
(b) Negative
(c) Zero
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Zero
Question 8.
Which of the following is true ?
(a) TU increases till MU is positive
(b) TU is maximum when MU is equal to zero
(c) TU declines when MU is negative
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
Question 9.
Who basically propounded the concept of Law of Equimarginal Utility ?
(a) Marshall
(b) Gossen
(c) Ricardo
(d) J. S. Mill
Answer
Answer: (c) Ricardo
Question 10.
In difference curve is:
(a) Convex to the origin
(b) Concave to the origin
(c) Both (a) and (b) true
(d) All of these false
Answer
Answer: (a) Convex to the origin
Question 11.
The ability of satisfying human want in a goods is called its:
(a) Productivity
(b) Satisfaction
(c) Utility
(d) Profitability
Answer
Answer: (c) Utility
Question 12.
Slope of budget line or price line is:
(a) –\(\frac{P_x}{P_y}\)
(b) –\(\frac{P_y}{P_x}\)
(c) +\(\frac{P_x}{P_y}\)
(d) +\(\frac{P_y}{P_x}\)
Answer
Answer: (a) –\(\frac{P_x}{P_y}\)
Question 13.
Utility is related to:
(a) Usefulness
(b) Morality
(c) Satisfaction of human wants
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 14.
Utility can be measured by:
(a) Money
(b) Exchange of goods
(c) Weight of the good
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Money
Question 15.
Law of Equi-marginal utility is called:
(a) Law of increasing utility
(b) Law of diminishing utility
(c) Law of substitution
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Law of substitution
Question 16.
Indifference curve slopes:
(a) From right to left
(b) From left to right
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) From left to right
Question 17.
The addition of utilities obtained from all units of a goods is called :
(a) Marginal Utility
(b) Total Utility
(c) Maximum Satisfaction
(d) Additional Utility
Answer
Answer: (b) Total Utility
Question 18.
Who propounded the ordinal utility theory’ ?
(a) Marshall
(b) Pigou
(c) Hicks and Allen
(d) Ricardo
Answer
Answer: (c) Hicks and Allen
Question 19.
The propounder of law of diminishing marginal utility is:
(a) Gossen
(b) Adam smith
(c) Chapman
(d) Hicks
Answer
Answer: (a) Gossen
Question 20.
Consumer’s equilibrium takes at a point where:
(a) MU = Price
(b) MU < Price
(c) MU > Price
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) MU = Price
Question 21.
The capability of a commodity to satisfy human wants is:
(a) Consumption
(b) Utility
(c) Quality
(d) Taste
Answer
Answer: (b) Utility
Question 22.
For the maximum satisfaction of consumer:
(a) Marginal utility of a good should be equal to its price.
(b) Marginal utility of a good should be greater than its price.
(c) There is no relation between marginal utility and price.
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Marginal utility of a good should be equal to its price.
Question 23.
When marginal utility is negative, then total utility:
(a) is maximum
(b) Starts decreasing
(c) increases at decreasing rate
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Starts decreasing
Question 24.
According to the law of equi-marginal utility, the condition for consumer’s equilibrium is:
(a) \(\frac{MU_A}{P_A}\)
(b) \(\frac{MU_B}{P_B}\)
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Undefined
Answer
Answer: (c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 25.
According to Marshall, utility of a commodity:
(a) Can be measured by money
(b) Cannot be measured by money
(c) Can be measured in cardinal numbers
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
Answer: (c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 26.
Which element is essential for demand ?
(a) Desire to consume
(b) Availability of adequate resources
(c) Willingness to consume
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
Question 27.
Demand Curve generally slopes:
(a) Upward from left to right
(b) Downward from left to right
(c) Parallel to X-axis
(d) Parallel to Y-axis
Answer
Answer: (b) Downward from left to right
Question 28.
In which goods, price fall does not make any increase in demand ?
(a) Necessities Goods
(b) Comfort Goods
(c) Luxuries Goods
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Necessities Goods
Question 29.
Which of the following factor affects demand ?
(a) Price
(b) Change in income
(c) Taste of the Consumer
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
Question 30.
Goods, which can alternatively be used, are called:
(a) Complementary Goods
(b) Substitutes
(c) Comforts
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Substitutes
Question 31.
Law of Demand is a:
(a) Qualitative Statement
(b) Quantitative Statement
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Qualitative Statement
Question 32.
Which of the following is a demand function ?
(a) PX
(b) DX = PX
(c) Dx = (Px)
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (c) Dx = (Px)
Question 33.
When change in the price of goods-X affects the demand of goods-Y, this demand is called:
(a) Price Demand
(b) Income Demand
(c) Cross Demand
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
Question 34.
For normal goods, Law of Demand states the relationship between price and quantity of goods:
(a) Direct
(b) Positive
(c) Indirect
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (c) Indirect
Question 35.
Which of the following is a reason for fall in demand ?
(a) Fall in Income
(b) Fall in Number of Buyers
(c) Fall in Taste of Consumer
(d) All the above
Answer
Answer: (d) All the above
Question 36.
With rise in coffee price, the demand of tea:
(a) Rises
(b) Falls
(c) Remains stable
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Rises
Question 37.
Contraction in demand appears when:
(a) Price rises and demand falls
(b) Price rises and demand also rises
(c) Price remains stable and demand falls
(d) Price falls but demand remains stable
Answer
Answer: (a) Price rises and demand falls
Question 38.
Which is a reason of change in demand ?
(a) Change in consumer’s income
(b) Change in price of related goods
(c) Population increase
(d) All pf these
Answer
Answer: (d) All pf these
Question 39.
For a change in which of the following, there is no change in demand ?
(a) Change in price
(b) Change in income
(c) Change in taste and fashion
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (d) None of these
Question 40.
With a rise in price the demand for ‘Giffin’ goods:
(a) increases
(b) decreases
(c) remains constant
(d) becomes unstable
Answer
Answer: (a) increases
Question 41.
Hie slope of the demand Curve of a normal goods is:
(a) Negative
(b) Positive
(c) Zero
(d) Undefined
Answer
Answer: (a) Negative
Question 42.
With an increase in income consumer decreases the consumption of which goods ?
(a) Inferior goods
(b) Normal goods
(c) Giffin goods
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer
Answer: (c) Giffin goods
Question 43.
The demand curve of a good shifts from DD’ to dd
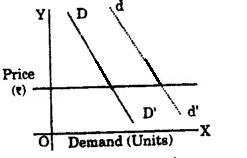
(a) fail in the price of the goods
(b) rise in the price of the goods
(c) rise in the price of substitute goods
(d) rise in the price of complementary goods
Answer
Answer: (c) rise in the price of substitute goods
Question 44.
Elasticity of demand is a:
(a) Qualitative Statement
(b) Quantitative Statement
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of the above
Answer
Answer: (b) Quantitative Statement
Question 45.
Which of the following is a formula for measuring the elasticity of demand ?

Answer
Answer: (a)
Question 46.
For Giffin goods, price elasticity of demand is :
(a) Negative
(b) Positive
(c) Zero
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Positive
Question 47.
Following figure shows:
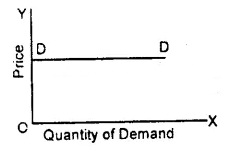
(a) High Elastic Demand
(b) Perfectly Elastic Demand
(c) Perfectly Inelastic Demand
(d) Inelastic Demand
Answer
Answer: (b) Perfectly Elastic Demand
Question 48.
Which of the following shows elasticity less than one ?
(a) Necessity Goods
(b) Comforts
(c) Luxuries
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Necessity Goods
Question 49.
With which method, elasticity of demand is measured ?
(a) Total Expenditure Method .
(b) Percentage or Proportionate Method
(c) Point Method
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
Question 50.
Elastic demand is shown by:
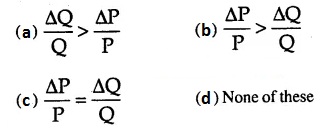
Answer
Answer: (a) \(\frac{ΔQ}{Q} > \frac{ΔP}{P}\)
Question 51.
What is the price elasticity in following example ?

(a) -2.5
(b) + 3.5
(c) + 4.0
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (a) -2.5
Question 52.
Who propounded the percentage or proportionate method of measuring elasticity of demand ?
(a) Marshall
(b) Flux
(c) Hicks
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) Flux
Question 53.
Which of the following factor affects elasticity of demand ?
(a) Nature of Goods
(b) Price Level
(c) Income Level
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (d) All of these
Question 54.
How many types elasticity of uemand has ?
(a) Three
(b) Five
(c)Six
(d) Seven
Answer
Answer: (b) Five
Question 55.
Elasticity of demand for necessities is :
(a) Zero
(b) Unlimited
(c) Greater than unity
(d) Less than unity
Answer
Answer: (a) Zero
Question 56.
Price elasticity of demand means :
(a) Change in demand due to change in price
(b) Change in demand
(c) Change in real income
(d) Change in Price
Answer
Answer: (a) Change in demand due to change in price
Question 57.
The elasticity of demand at the mid-point of a straight line demand curve:
(a) will be zero
(b) will be unity
(c) will be infinity
(d) None of these
Answer
Answer: (b) will be unity
Question 58.
If the demand for a good changes by 60% due to 40% change in price, the elasticity of demand is :
(a) 0.5
(b) -1.5
(c) 1
(d) zero
Answer
Answer: (b) -1.5
Question 59.
For luxury goods the demand is:
(a) Inelastic
(b) Elastic
(c) Highly elastic
(d) Perfectly Inelastic
Answer
Answer: (c) Highly elastic
Question 60.
Any statement about demand for a good is considered complete only when the following is/are mentioned in:
(a) Price of the good
(b) Quantity of the good
(c) Period of time
(d) All of these
Answer
Answer: (a) Price of the good
Question 61.
Consumer is in equilibrium when:
(a) MUx = PUx
(b) MUx > PUx
(c) MUx < Px
(d) MUx ÷ Px
Answer
Answer: (a) MUx = PUx
Question 62.
Marshall has given the law of Equimarginal utility related:
(a) Related to goods
(b) Related to money
(c) In relation to both
(d) None of these.
Answer
Answer: (a) Related to goods
Question 63.
How many tremendous curves can touch the budget line:
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Several
(d) Depends on the basis of indifference maps.
Answer
Answer: (a) One
Question 64.
Indifference curves were first introduced by the English economist in 1881 by:
(a) Edge worth
(b) Pareto
(c) Myers
(d) Hicks.
Answer
Answer: (a) Edge worth
Question 65.
Any statement about the demand of an object is considered complete when it is mentioned in the following:
(a) Price of good
(b) Demand of good
(c) Time period
(d) All of the above.
Answer
Answer: (d) All of the above.
Question 66.
If price of goods ‘X’ falls leading to increase in demand of goods ‘ Y’ then both the goods are:
(a) Substitute goods
(b) Complementary goods
(c) Not related
(d) Competitor.
Answer
Answer: (b) Complementary goods
Question 67.
According to total outlay method, the demand of a good is sinelastic when:
(a) Price will fall with the increase in amount spent
(b) When price of good decreases and money spent decreases
(c) Expenditure remains the same, even if price falls
(d) Expenditure decreases with the increase in price.
Answer
Answer: (b) When price of good decreases and money spent decreases
Fill in the blanks:
1. Consumer is a …………. human being.
Answer
Answer: Rational
2. If the price of substitute goods increases then the demand curve shifts to the ………….
Answer
Answer: Right
3. …………. propounded the law of Diminishing Returns.
Answer
Answer: Gossen
4. According to Marshall utility can be measured in terms of ………….
Answer
Answer: Money
5. An indifference curve gives …………. level of satisfaction to the consumers.
Answer
Answer: Equal
6. Car and Petrol are goods ………….
Answer
Answer: Substitute
7. There is …………. relation between price and demand.
Answer
Answer: inverse
State true or false:
1. Utility is an intensive assumption.
Answer
Answer: True
2. The proportion of the cost of two goods measures the slope of budget line.
Answer
Answer: True
3. Demand curve is generally negative sloped.
Answer
Answer: False
4. Budget set is a collection of all bundles that a consumer purchases from their income at market prices.
Answer
Answer: True
5. The elasticity of the demand of the object and the expenditure on the object is closely related.
Answer
Answer: True
Match the following:
| ‘A” | ‘B’ |
| 1. Inelastic | (a) Utility analysis |
| 2. Substitute goods | (b) Demand of Necessary or Essential goods |
| 3. Marshall | (c) Gossen’s second law |
| 4. Indifference curve | (d) Cross demand |
| 5. Law of equi marginal utility | (e) Does not cut each ether |
Answer
Answer:
| ‘A” | ‘B’ |
| 1. Inelastic | (b) Demand of Necessary or Essential goods |
| 2. Substitute goods | (d) Cross demand |
| 3. Marshall | (a) Utility analysis |
| 4. Indifference curve | (e) Does not cut each ether |
| 5. Law of equi marginal utility | (c) Gossen’s second law |
We hope the given NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 11 Economics Chapter 2 Theory of Consumer Behaviour with Answers Pdf free download will help you. If you have any queries regarding CBSE Class 11 Economics Theory of Consumer Behaviour MCQs Multiple Choice Questions with Answers, drop a comment below and we will get back to you soon.
Class 11 Microeconomics MCQ:
