Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Advancements In Modern Biotechnology
Modern biotechnology embraces all the genetic manipulations, protoplasmic fusion techniques and the improvements made in the old biotechnological processes. Some of the major advancements in modern biotechnology are described below.
Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering or recombinant DNA technology or gene cloning is a collective term that includes different experimental protocols resulting in the modifiation and transfer of DNA from one organism to another.
The definition for conventional recombination was already given in Unit II. Conventional recombination involves exchange or recombination of genes between homologous chromosomes during meiosis. Recombination carried out artificially using modern technology is called recombinant DNA technology (r-DNA technology). It is also known as gene manipulation technique.
This technique involves the transfer of DNA coding for a specific gene from one organism into another organism using specific agents like vectors or using instruments like electroporation, gene gun, liposome mediated, chemical mediated transfers and microinjection.
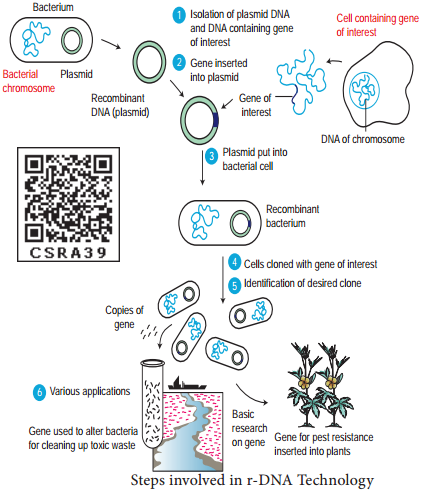
Steps involved in Recombinant DNA Technology
The steps involved in recombinant DNA technology are:
- Isolation of a DNA fragment containing a gene of interest that needs to be cloned. This is called an insert.
- Generation of recombinant DNA (rDNA) molecule by insertion of the DNA fragment into a carrier molecule called a vector that can self-replicate within the host cell.
- Selection of the transformed host cells is carrying the rDNA and allowing them to multiply thereby multiplying the rDNA molecule.
- The entire process thus generates either a large amount of rDNA or a large amount of protein expressed by the insert.
- Wherever vectors are not involved the desired gene is multiplied by PCR technique. The multiple copies are injected into the host cell protoplast or it is shot into the host cell protoplast by shot gun method.