Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Tissue Level of Organisation – Animal Tissues
Animal tissues are classified according to the size, shape and function of the cells. There are four primary (basic) tissue types that interweave to form the ‘fabric’ of the body. They are, the epithelial tissue (covering), the connective tissue (support), the muscle tissue (movement) and the nervous tissue (control) (Figure 3.1).
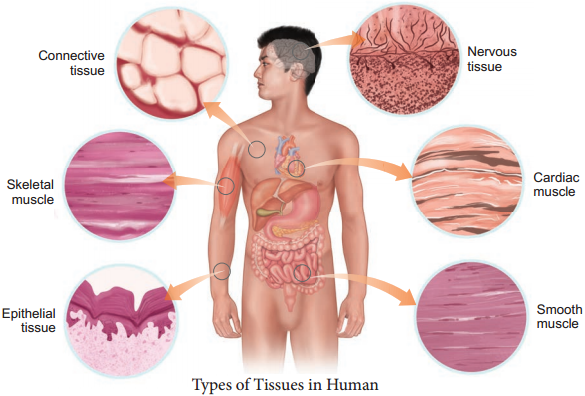
There are four types of animal tissues: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Key Outcomes: Understand the differentiation of animal tissues and the relationship between structure and function of the various tissues. Know the location of the various tissues within the animal body.
Epithelial Tissue:
They cover the body, organs, blood vessels and all body cavities.
Muscular Tissue:
Smooth, Skeletal, and Cardiac Muscles.
Connective Tissue:
Connective tissues are made up of fibrous cells.
Nervous Tissue:
Neuron Structure.
Organs are composed of tissues, which are in turn composed of cells. Plants have three tissue types: ground, dermal, and vascular. Animals have four: epithelial, connective, muscle, and bone.
Supports an animal’s body – Connective tissue(supportive) Binds different tissues together – Fibrous connective tissue.
Connective tissue assists in support and protection of organs and limbs and depending on the location in the body it may join or separate organs or parts of the body. Muscle tissue enables various forms of movement, both voluntary and involuntary.
What are Parenchyma tissues? Parenchyma is a type of simple permanent tissue that makes a major part of ground tissues in plants, where other tissues like vascular tissues are embedded. They are non-vascular and composed of simple, living and undifferentiated cells, which are modified to perform various functions.
The nervous tissue is composed of two cell types: neurons and glia. The main function of nervous tissue is the processing of information coming from the external and internal environments, and then triggers a response.
Animal tissues are grouped into four basic types: connective, muscle, nervous, and epithelial. Collections of tissues joined in units to serve a common function compose organs.
Types of Tissues
- Simple squamous
- Simple cuboidal
- Cardiac muscle
- Skeletal muscle
- Bone
- Dense fibrous tissue
- Nerve
- Cartilage