Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Apomixis Definition and its Types
Reproduction involving fertilization in flowering plants is called amphimixis and wherever reproduction does not involve union of male and female gametes is called apomixis.
The term Apomixis was introduced by Winkler in the year 1908. It is defied as the substitution of the usual sexual system (Amphimixis) by a form of reproduction which does not involve meiosis and syngamy. Maheswari (1950) classifid Apomixis into two types – Recurrent and Non recurrent
Recurrent apomixis:
It includes vegetative reproduction and agamospermy.
Non recurrent apomixis:
Haploid embryo sac developed aftr meiosis, develops into a embryo without fertilization. The outline classifiation of Recurrent apomixis is given below.
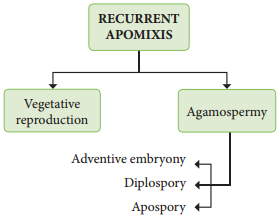
Vegetative reproduction:
Plants propagate by any part other than seeds
Bulbils – Fritillaria imperialis; Bulbs – Allium; Runner – Mentha arvensis; Sucker Chrysanthemum
Agamospermy:
It refers to processes by which Embryos are formed by eliminating meiosis and syngamy.
Adventive embryony:
An Embryo arises directly from the diploid sporophytic cells either from nucellus or integument. It is also called sporophytic budding because gametophytic phase is completely absent. Adventive embryos are found in Citrus and Mangifera.
Diplospory (Generative apospory):
A diploid embryo sac is formed from megaspore mother cell without a regular meiotic division Examples. Eupatorium and Aerva.
Apospory:
Megaspore mother cell (MMC) undergoes the normal meiosis and four megaspores formed gradually disappear. A nucellar cell becomes activated and develops into a diploid embryo sac. This type of apospory is also called somatic apospory. Examples Hieracium and Parthenium.