Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
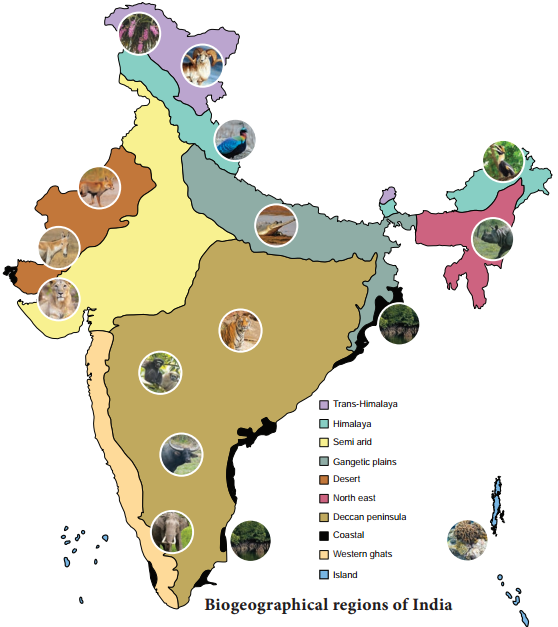
Biogeographical Regions of India
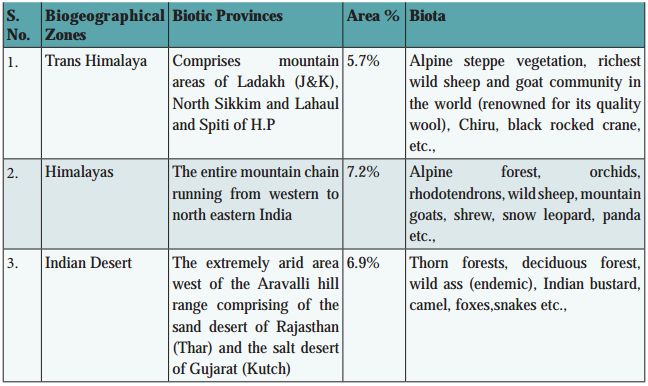
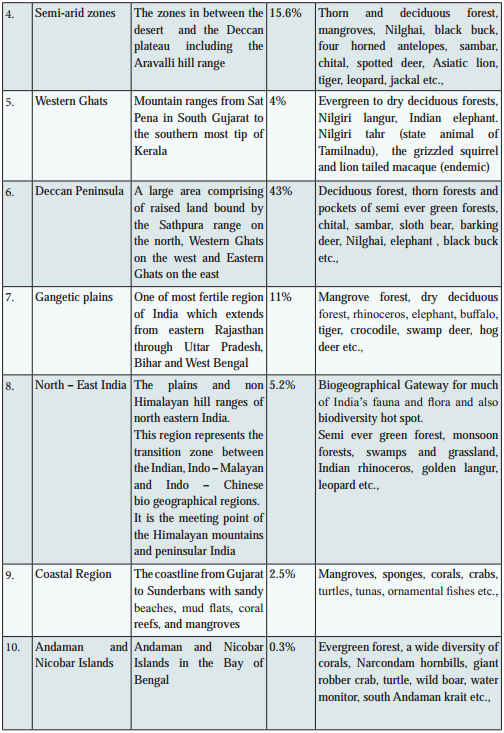
As per the international ‘biome’ type of classification based upon climate, fauna and flora and the soil conditions, India can be divided into ten different biogeographic zones, (Fig. 11.3 and table 11.1) namely:
Biogeographic classification of India is the division of India according to biogeographic characteristics. Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species (biology), organisms, and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. There are ten biogeographic zones in India.
Biogeographic regions are geographical areas that are defined based on the species found in them, which provides invaluable information to ecologists and natural resources managers for understanding large scale processes that affect species and ecosystems.
India is known for its rich heritage of biological diversity, having already documented more than 91,000 species of animals and 45,500 species of plants in its 10 biogeographical regions. Almost 6,500 native plants are still widely used in indigenous health care systems.
The country’s diverse physical features and climatic conditions have resulted in a variety of ecosystems such as forests, wetlands, grasslands, desert, coastal and marine ecosystems which harbour and sustain high biodiversity and contribute to human well-being.
India is one of the eight Vavilov’s centers of origin of cultivated plants in the world and has twenty distinct agro-ecosystems, characterized by variations in edaphic, climatic and geographic features, and consequently a diverse cropping pattern.