Find free online Chemistry Topics covering a broad range of concepts from research institutes around the world.
Biomolecules of Lipids:
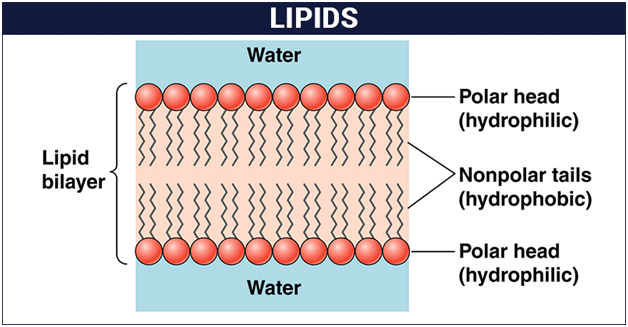
Lipids are organic molecules that are soluble in organic solvents such as chloroform and methanol and insoluble in water. The word lipid is derived from the Greek work ‘lipos’ meaning fat. They are the principal components of cell membranes. In addition, they also act as energy source for living systems. Fat provide 2-3 fold higher energy compared to carbohydrates/proteins.
Classification of Lipids:
Based on their structures lipids can be classified as simple lipids, compound lipids and derived lipids. Simple lipids can be further classified into fats, which are esters of long chain fatty acids with glycerol (triglycerides) and waxes which are the esters of fatty acids with long chain monohydric alcohols (Bees wax).
Compound lipids are the esters of simple fatty acid with glycerol which contain additional groups. Based on the groups attached, they are further classified into phospholipids, glycolipids and lipoproteins. Phospholipids contain a phospho-ester linkage while the glycolipids contain a sugar molecule attached. The lipoproteins are complexes of lipid with proteins.
Biological Importance of Lipids
- Lipids are the integral component of cell membrane. They are necessary of structural integrity of the cell.
- The main function of triglycerides in animals is as an energy reserve. They yield more energy than carbohydrates and proteins.
- They act as protective coating in aquatic organisms.
- Lipids of connective tissue give protection to internal organs.
- Lipids help in the absorption and transport of fat soluble vitamins.
- They are essential for activation of enzymes such as lipases.
- Lipids act as emulsifier in fat metabolism.
They include fats, waxes, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes and function as energy-storage molecules and chemical messengers. Together with proteins and carbohydrates, lipids are one of the principal structural components of living cells.
Biological substances that are insoluble in water are classified as lipids. This characteristic physical property of lipids makes them very different from other biomolecules like carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids. Some lipids are used to store energy.
The four main groups of lipids include:
- Fatty acids (saturated and unsaturated)
- Glycerides (glycerol-containing lipids)
- Nonglyceride lipids (sphingolipids, steroids, waxes)
- Complex lipids (lipoproteins, glycolipids)
Carbohydrates, nucleic acids, and proteins are often found as long polymers in nature. Lipids are not usually polymers and are smaller than the other three, so they are not considered macromolecules by some sources 1, 2 start superscript, 1, comma, 2, end superscript.
Fats and Oils. A fat molecule consists of two main components-glycerol and fatty acids. Glycerol is an organic compound (alcohol) with three carbons, five hydrogens, and three hydroxyl (OH) groups.
A lipid is any of various organic compounds that are insoluble in water. They include fats, waxes, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes and function as energy-storage molecules and chemical messengers.