Learninsta presents the core concepts of Biology with high-quality research papers and topical review articles.
Cardio Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
In 1956, James Elam and Peter Safar were the first to use mouth to mouth resuscitation. CPR is a life saving procedure that is done at the time of emergency conditions such as when a person’s breath or heart beat has stopped abruptly in case of drowning, electric shock or heart attack.
CPR includes rescue of breath, which is achieved by mouth to mouth breathing, to deliver oxygen to the victim’s lungs by external chest compressions which helps to circulate blood to the vital organs.
CPR must be performed within 4 to 6 minutes after cessation of breath to prevent brain damage or death. Along with CPR, defibrillation is also done. Defibrillation means a brief electric shock is given to the heart to recover the function of the heart.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure that combines chest compressions often with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore spontaneous blood circulation and breathing in a person who is in cardiac arrest.
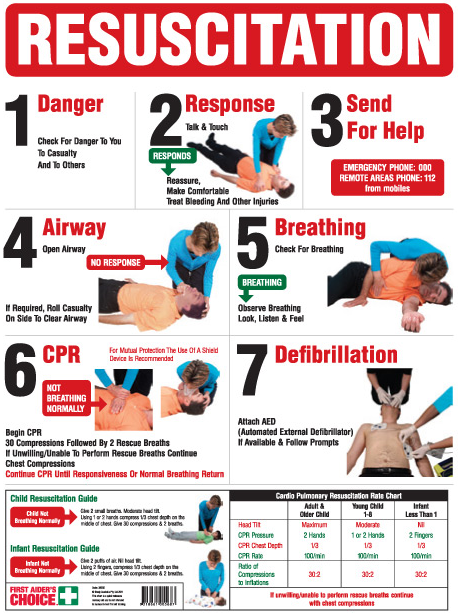
5 Steps for Performing CPR
- Check the patient’s responsiveness.
- Shake the unresponsive person by the shoulders and speak loudly to them in an attempt to rouse them.
- Check their breathing and pulse.
- Administer chest compressions.
- Recheck breathing and pulse.
After every 30 chest compressions at a rate of 100 to 120 a minute, give 2 breaths. Continue with cycles of 30 chest compressions and 2 rescue breaths until they begin to recover or emergency help arrives.
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a lifesaving technique. It aims to keep blood and oxygen flowing through the body when a person’s heart and breathing have stopped. CPR can be performed by any trained person. It involves external chest compressions and rescue breathing.
Types of CPR
High-Frequency Chest Compressions. This technique involves imitating hear beats by giving more chest compressions at intervals of time in high frequency. Open-Chest CPR. Open chest CPR is a procedure in which the heart is retrieved through thoracotomy. Interposed Abdominal Compression CPR.
How is CPR Performed? There are two commonly known versions of CPR: For healthcare providers and those trained: conventional CPR using chest compressions and mouth-to-mouth breathing at a ratio of 30:2 compressions-to-breaths.
CPR stands for cardiopulmonary resuscitation. It is an emergency life-saving procedure that is done when someone’s breathing or heartbeat has stopped.
The three basic parts of CPR are easily remembered as “CAB”: C for compressions, A for airway, and B for breathing. C is for compressions. Chest compressions can help the flow of blood to the heart, brain, and other organs.