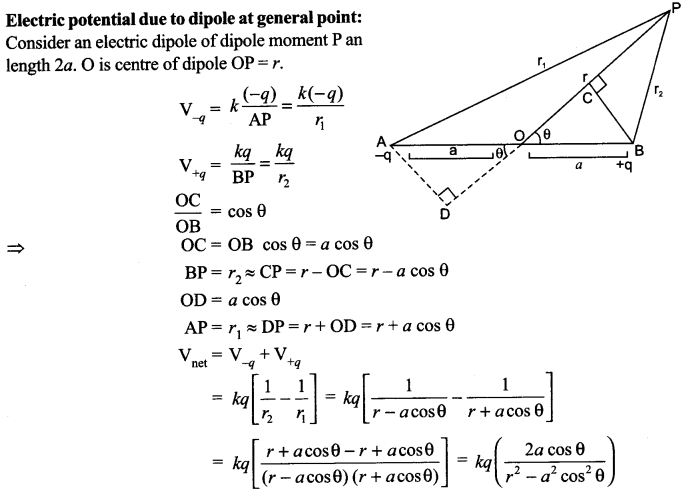
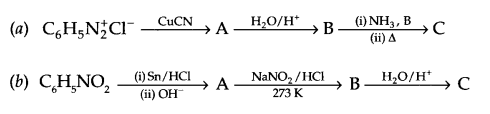
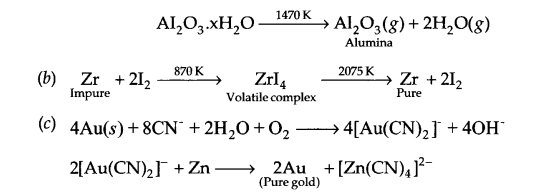
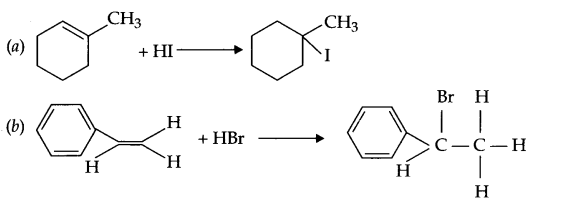
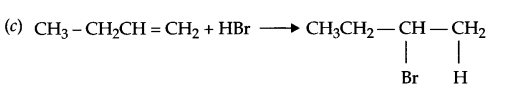
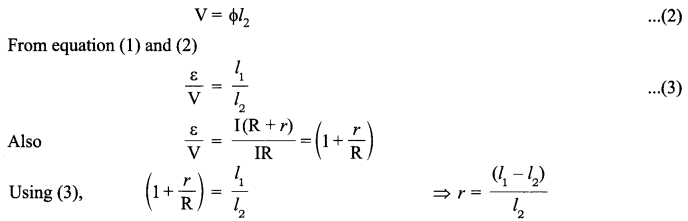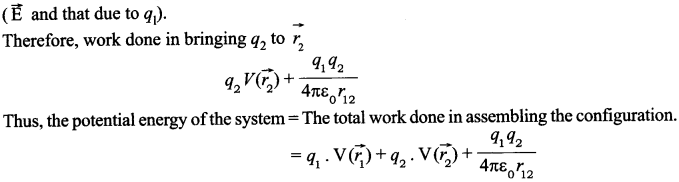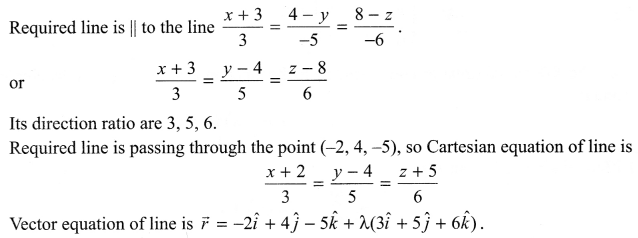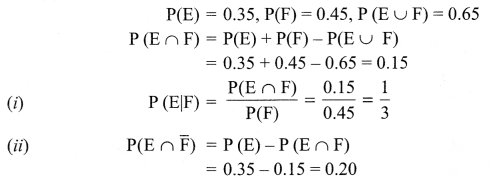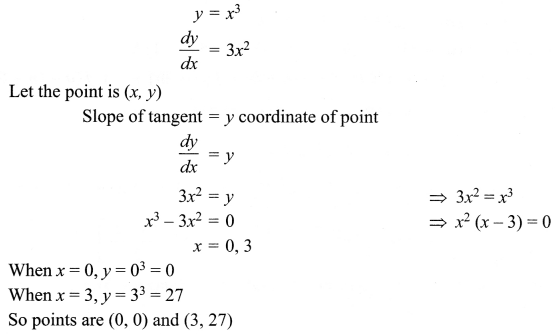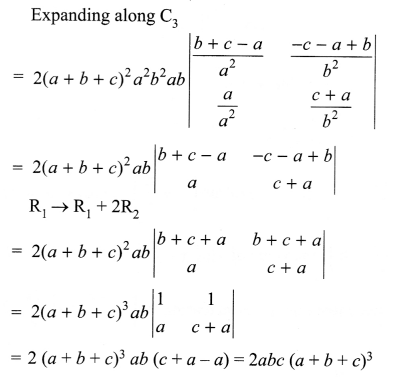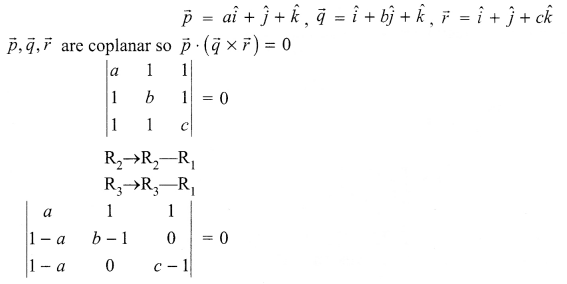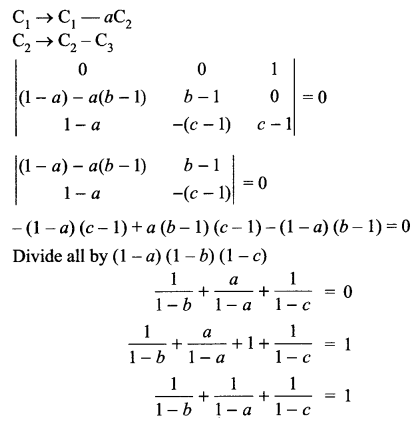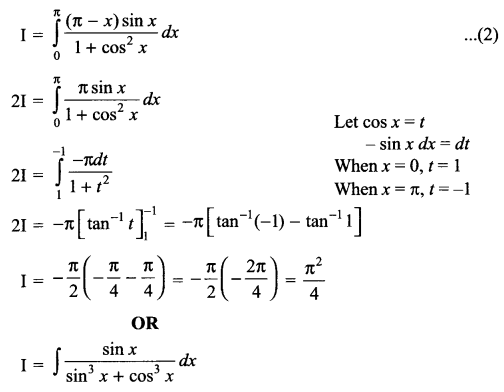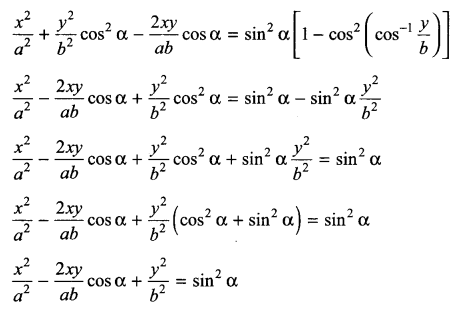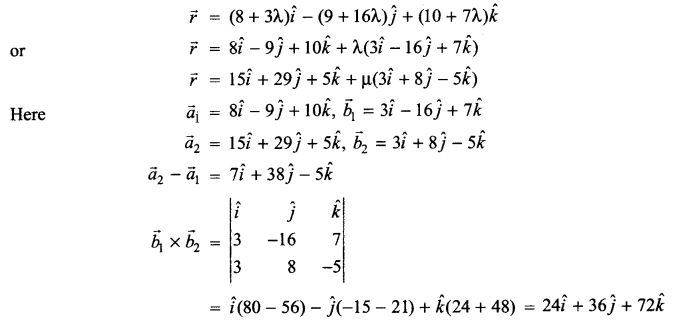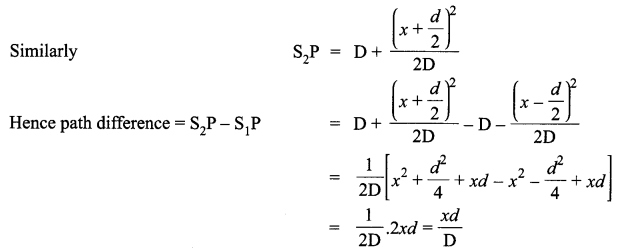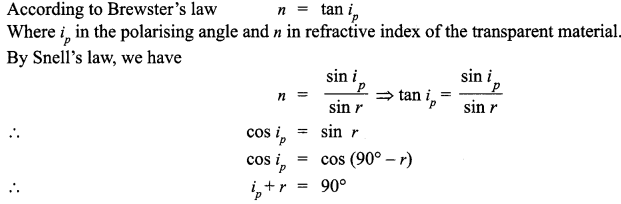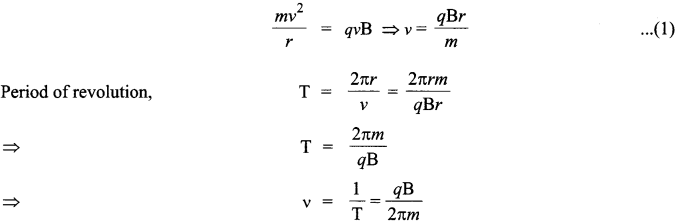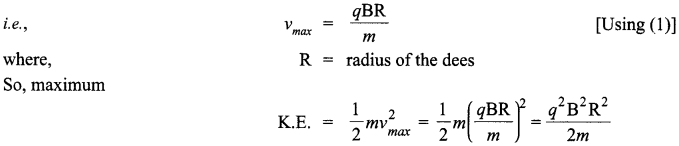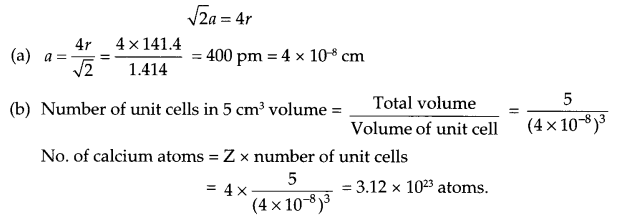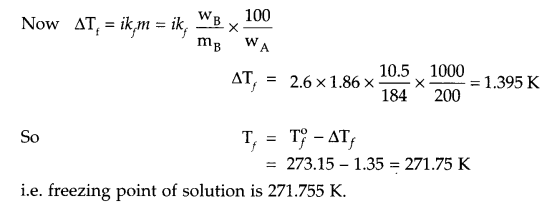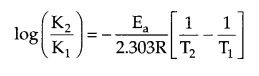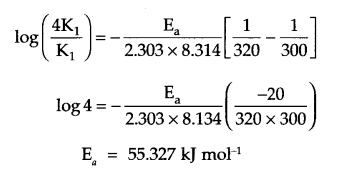These Sample papers are part of CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology. Here we have given CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 5.
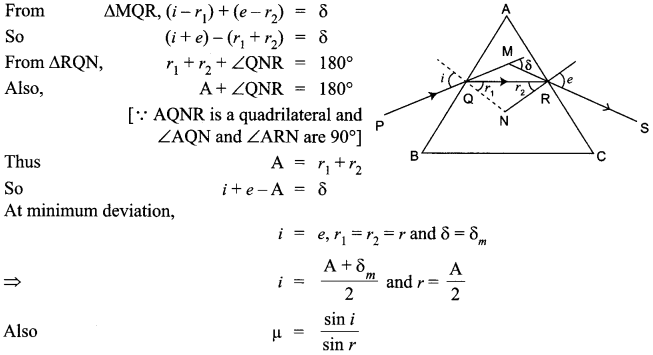
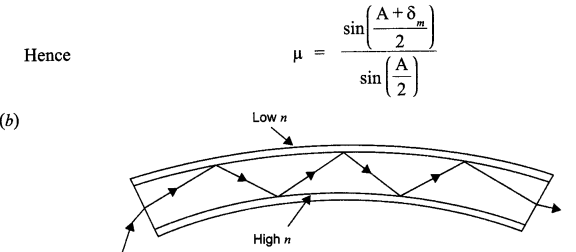
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 5
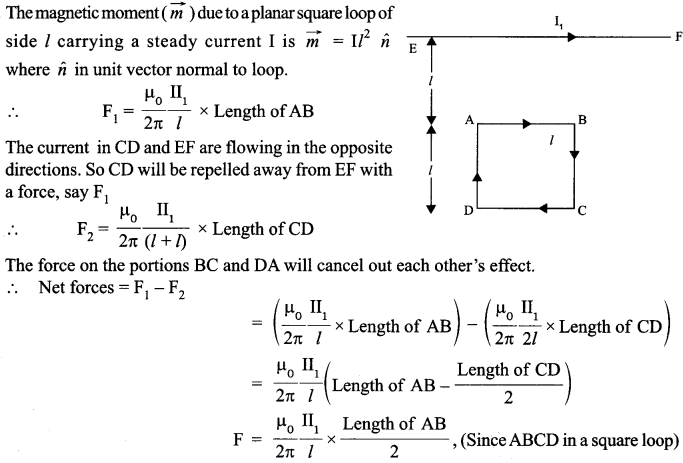
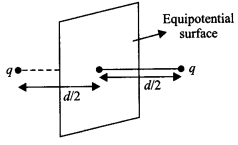
| Board | CBSE |
| Class | XII |
| Subject | Biology |
| Sample Paper Set | Paper 5 |
| Category | CBSE Sample Papers |
Students who are going to appear for CBSE Class 12 Examinations are advised to practice the CBSE sample papers given here which is designed as per the latest Syllabus and marking scheme as prescribed by the CBSE is given here. Paper 5 of Solved CBSE Sample Paper for Class 12 Biology is given below with free PDF download solutions.
Time Allowed: 3 hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
- There are total 26 questions and five sections in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
- Section A contains question number 1 to 5, Very Short Answer Type Questions of one mark each.
- Section B contains question number 6 to 10, Short Answer Type Questions of two marks each.
- Section C contains question number 11 to 22, Short Answer Type Questions of three marks each.
- Section D contains question number 23, Value Based Question of four mark.
- Section E contains question number 24 to 26, Long Answer Type Questions of five marks each.
- There is no overall choice in the question paper, however, an internal choice is provided in one question of two marks, one question of three marks and all three questions of five marks. An examiner is to attempt any one of the question out of the two given in the question paper with the same question number.
- No. of printed pages are three.
SECTION-A
Question 1.
What is the number of chromosome in human zygote?
Question 2.
What is totipotency?
Question 3.
What are palindromic sequences?
Question 4.
What is Allen’s rule?
Question 5.
How do you define NPP?
SECTION-B
Question 6.
Write the transcription product sequence for
(a) 5 ‘ATGCACTGATCCAA 3’
(b) 3 ‘ GTACGTACGTAC 5’
Question 7.
Complete the table:
| Cross | Ratio |
| Monohybrid | ………. |
| ………. | 1:2:1 |
Question 8.
What are the types of acquired immunity?
Question 9.
Which microbe converts milk to curd?
Question 10.
Give some examples of diseases and their insect vector.
OR
What are the different methods of breeding?
SECTION-C
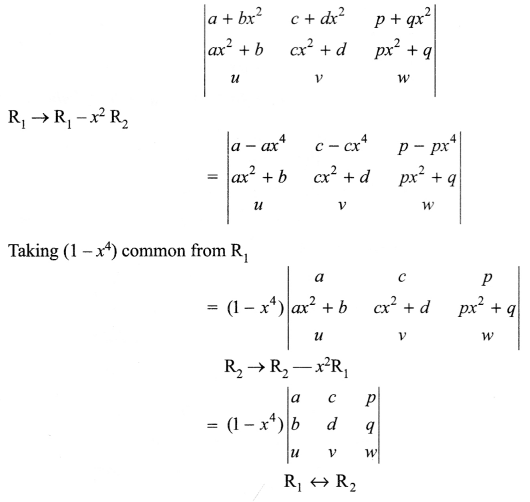
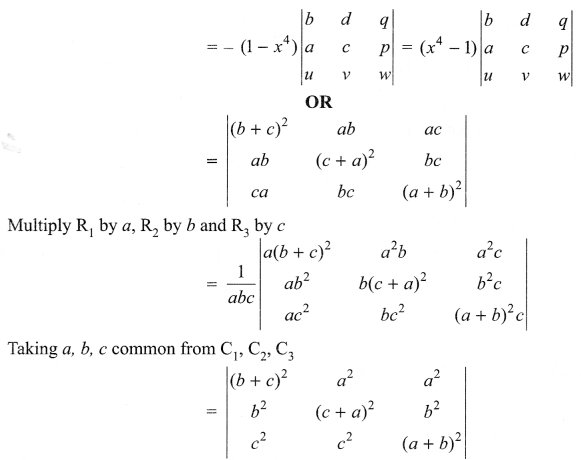
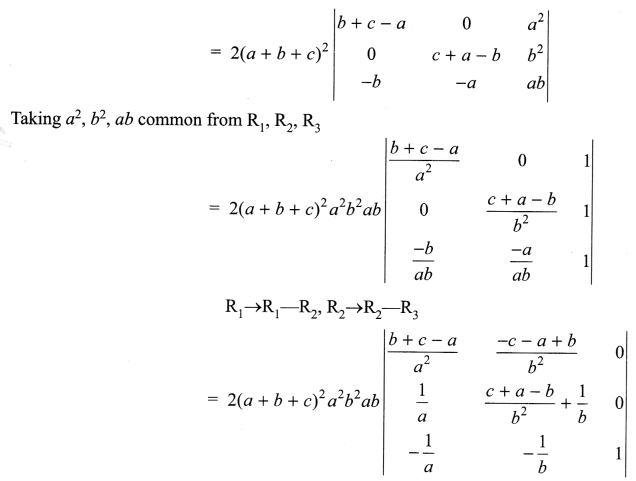
Question 11.
List the salient features of DNA double helix model.
Question 12.
What is the fate of the product of fertilization in humans?
Question 13.
How was the genetic code elucidated?
Question 14.
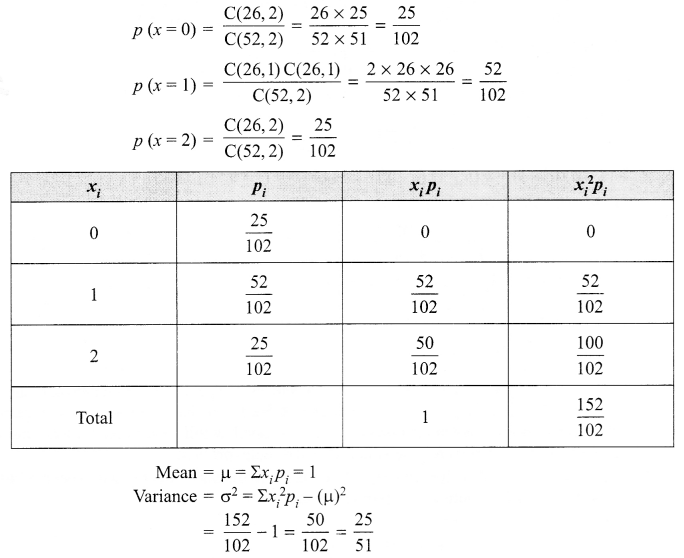
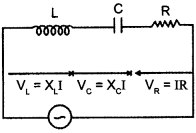
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1.Explain this equation.
Question 15.
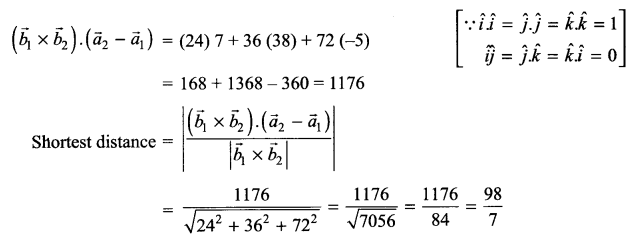
What are the different levels at which gene regulation can be achieved?
Question 16.
What are the primary lymphoid organs?
Question 17.
Explain gene therapy with an example?
Question 18.
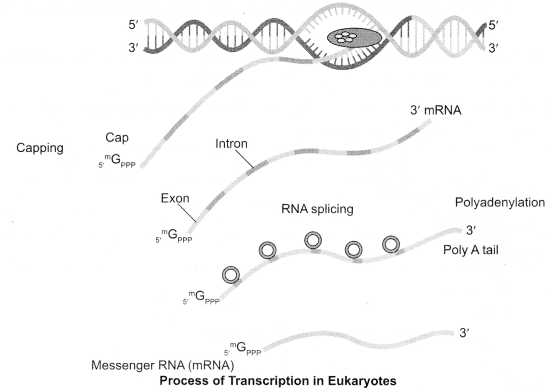
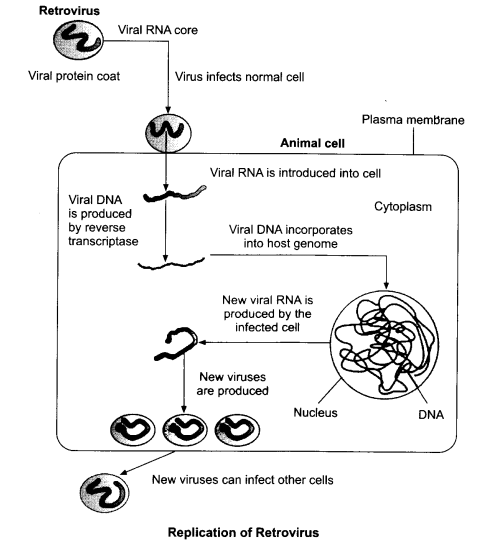
Diagrammatically represent the replication of retrovirus.
Question 19.
How have cry proteins been utilized?
OR
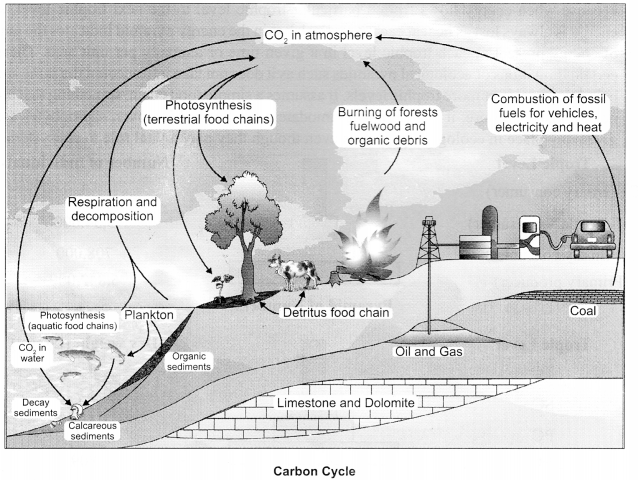
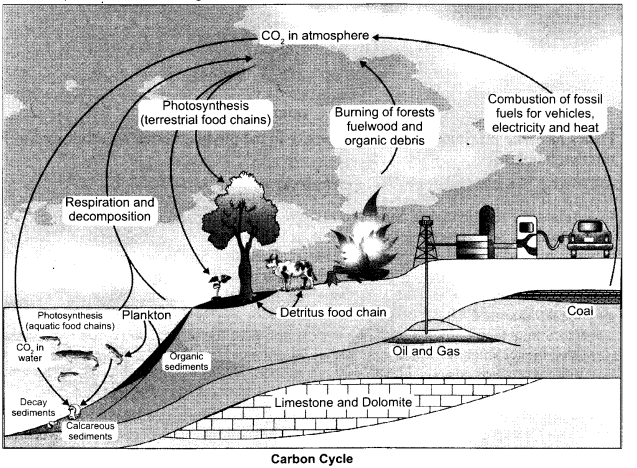
Explain carbon cycle with diagram.
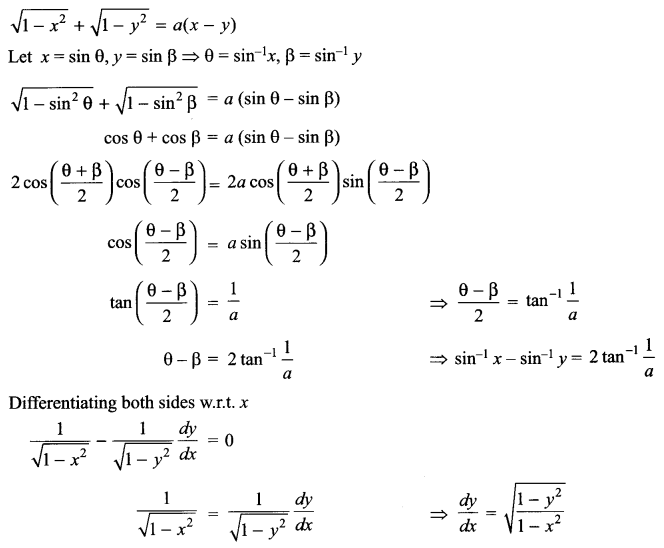
Question 20.
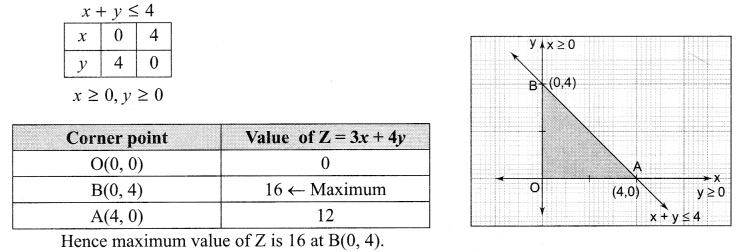
Explain two reasons for loss of biodiversity.
Question 21.
Give some adaptations of desert plants to survive the heat.
Question 22.
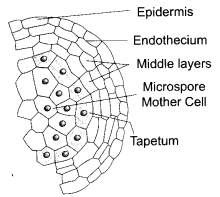
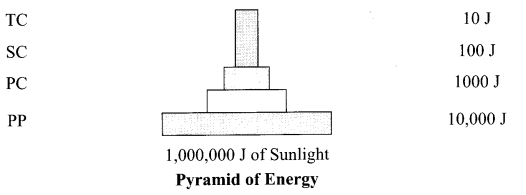
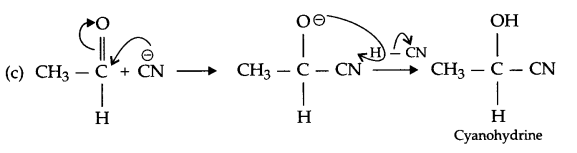
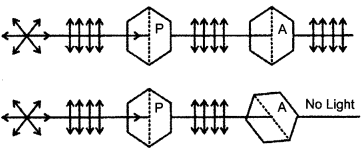
What does the picture represent?
SECTION-D
Question 23.
In art class the teacher asked Sunita to mix green and red paint and report on the combined colour formed. Sunita could not find red colour in her box and was scolded by the teacher who found it lying right in front. Suddenly Vijay realized that Sunita was not able to identify red colour and reported the matter to the teacher who was of the opinion that she lacked colour concept. After school was over, Vijay reported this matter to Sunita’s parents. (a) What values did Vijay possess?
(b) Did Sunita lack knowledge of colours? If not, give the biological reason for the same.
(c) Give the technical term for this type of inheritance. Explain with a typical example
SECTION-E
Question 24.
Explain with diagram the experiment that proved that DNA is a genetic material.
OR
Explain pollination by wind and water.
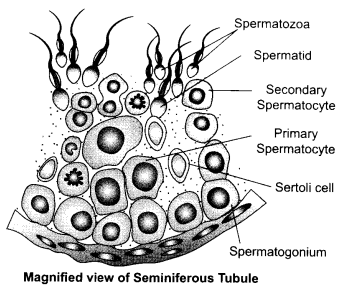
Question 25.
Give the journey of sperm formation with diagram. What are the hormones involved?
OR
Explain the technique of fingerprinting with diagram.
Question 26.
What is parasitism? What are the types?
OR
What are ecosystem services?
Answers
SECTION-A
Answer 1.
46
Answer 2.
Capacity of generating a whole plant from cell/explant is called totipotency.
Answer 3.
The palindrome in DNA is a sequence of base pairs on the two strands that reads the same when orientation of reading is kept same
Answer 4.
Mammals from colder climates generally have shorter ears and limbs to minimise heat loss. This is known as Allen’s rule.
Answer 5.
NPP stands for Net Primary Productivity. It is the available biomass for the consumption by heterotrophs (herbivores and decomposers) NPP = GPP – R. Where ‘GPP’ is Gross Primary Productivity, ‘R’ is Respiration losses.
SECTION-B
Answer 6.
(a) 3 ‘TACGTGACTAGGTT 5’ ‘
(b) 5 ‘AUGCACUGAUCCAA 3 ’
Answer 7.
| Cross | Ratio |
| Monohybrid | 3:1 |
| Incomplete dominance | 1:2:1 |
Answer 8.
1. Antibody mediated immunity or humoral immune response by the production of antibodies against antigens.
2. Cell mediated immunity initiated by T lymphocytes.
Answer 9.
Micro-organisms such as Lactobacillus and others commonly called lactic acid bacteria (LAB) grow in milk and convert it to curd. During growth, the LAB produce acids that coagulate and partially digest the milk proteins. A small amount of curd added to the fresh milk as inoculum or starter contain millions of LAB, which at suitable temperatures multiply, thus converting milk to curd.
Answer 10.
(1) Malaria – female Anopheles mosquito
(2) Dengue or Chikungunya – Aedes mosquito.
OR
Different methods of breeding are:
(a) Inbreeding;
(b) Out breeding;
(c) Out crossing;
(d) Cross breeding; and
(e) Interspecific hybridisation
SECTION-C
Answer 11.
The salient features of the Double-helix structure of DNA are as follows:
- It is made of two polynucleotide chains, where the backbone is constituted by sugar phosphate, and the bases project inside.
- The two chains have anti-parallel polarity. It means, if one chain has the polarity 5’→3′, the other has
3′ → 5′. - The base in two strands are paired through hydrogen bond (H-bonds) forming base pairs (bp). Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with Thymine from opposite strand and vice-versa. Similarly, Guanine is bonded with Cytosine with three H-bonds. As a result, always a purine comes opposite to a pyrimidine. This generates approximately uniform between the two strands of the helix.
- The plane of one base pair stacks over the other in double helix. This, in addition to H-bonds, confersstability of the helical structure.
Answer 12.
The product of fertilization is the zygote. The mitotic division starts as the zygote moves through the isthmus of the oviduct called cleavage towards the uterus and forms 2,4,8,16 daughter cells called blastomeres. The embryo with 8 to 16 blastomeres is called a morula. The morula continues to divide and transforms into blastocyst as it moves further into the uterus. The blastomeres in the blastocyst are arranged into an outer layer called trophoblast and an inner group of cells attached to trophoblast called the inner cell mass. The trophoblast layer then gets attached to the endometrium and the inner cell mass gets differentiated as the embryo. After attachment the uterine cells divide rapidly and cover the blastocyst. As a result, the blastocyst becomes embedded in the endometrium of the uterus. This is called implantation and it leads to pregnancy.
Answer 13.
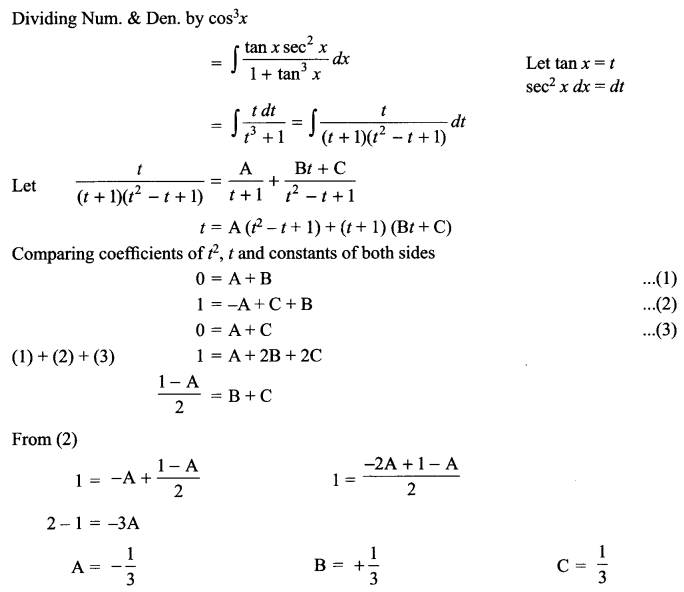
Har Govind Khorana, Marshall Nirenberg and Severo Ochoa elucidated the genetic code. Genetic Code directs the sequence of amino acids during protein synthesis of proteins. The chemical method was developed by Har Gobind Khorana to synthesise RNA molecules with defined combinations of bases (homopolymers and copolymers). Marshall Nirenberg’s cell-free system for protein synthesis finally helped the code to be deciphered. Further, Severo Ochoa enzyme (polynucleotide phosphoryalse) was also helpful in polymerizing RNA with defined sequences in a template independent manner (enzymatic synthesis of RNA). This finally gave rise to the checker-board, for genetic code. The salient features of genetic code are as follows:
(a) The codon is triplet 43 = 64. (61 codons code for amino and 3 codons do not code for any amino acids, hence they function as stop codons.)
(b) One codon codes for only one amino acid, hence, it is unambiguous and specific.
(c) Some amino acids are coded by more than one codon, hence the code is degenerate.
(d) The codon is read in mRNA in a contiguous fashion. There are no punctuations.
(e) The code is nearly universal: for example, from bacteria to human UUU would code for Phenylalanine (phe).
(f) AUG has dual functions. It codes for Methionine (met), and it also as initiator codon
Answer 14.
p2 + 2pq + q2 = 1, equation represents the gene frequency of a given population as stated by Hardy-Weinberg law. It states that the frequencies of allele in a given population are stable and constant.
Where p2 = frequency of homozygous dominant alleles (AA).
q2 = frequency of homozygous recessive alleles (aa).
2pq = frequency of heterozygous alleles (Aa).
This is also referred to as genetic equilibrium and is a binomial expansion of (p + q)2.
Answer 15.
Gene regulation could be exerted at
- Transcriptional level (formation of primary transcript).
- Processing level (regulation of splicing).
- Transport of mRNA from nucleus to the cytoplasm.
- Translational Level.
Answer 16.
The primary lymphoid organs are bone marrow and thymus where immature lymphocytes differentiate into antigen-sensitive lymphocytes. Both provide micro-environments for the development and maturation of T-lymphocytes.The bone marrow is the main lymphoid organ where all blood cells including lymphocytes are produced.
The thymus is a lobed organ located near the heart and beneath the breastbone. The thymus is quite large at the time of birth but keeps reducing in size with age and by the time puberty is attained, it reduces to a very small size.
Answer 17.
Gene therapy is a collection of methods that allows correction of a gene defect that has been diagnosed in child/embryo. Here, genes are inserted into a person’s cells and tissues to treat a disease. Correction of a genetic defect involves delivery of a normal gene into the individual or embryo to take over the function of and compensate for the non-functional gene.
The first clinical gene therapy was given to a 4-year-old girl with adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency. This disorder is caused due to the deletion of the gene for adenosine deaminase. In some children, ADA deficiency can be cured by bone marrow transplantation; in others it can be treated by enzyme replacement therapy, in which functional ADA is given to the patient by injection. Both of these approaches are not completely curative.
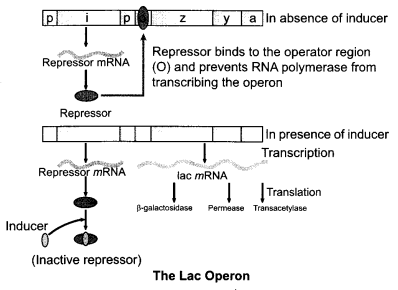
Answer 18.
Answer 19.
The Bt toxin is coded by a gene named cry protein. The proteins encoded by the genes crylAc and crylAb control the cotton bollworms that of crylAb control com borer. B. thuringiensis forms protein crystals during a particular phase of their growth. These crystals contain a toxic insecticidal protein. The Bt toxin protein exist as inactive protoxin but once an insect ingest 1 the inactive toxin, it is converted into an active form of toxin due to the alkaline pH of the gut which solubilise the crystals. The activated toxin binds to the surface of midgut epithelial cells and create pores that cause cell swelling and lysis and eventually cause death of the insect.
OR
Carbon cycling occurs through atmosphere, ocean and through living and dead organisms. A considerable amount of carbon returns to the atmosphere as CO2 through respiratory activities of the producers and consumers. Decomposers also contribute substantially to CO2 pool by their processing of waste materials and dead organic matter of land oceans. Some amount of the fixed carbon is lost to sediments and removed from circulation. Burning of wood, forest fire and combustion of organic matter, fossil fuel, volcanic activity are additional sources for releasing CO2 in the atmosphere.
Answer 20.
Two reasons for the loss of biodiversity are:
1. Habital Loss and Fragmentation: The degradation of many habitats by pollution also threatens the survival of many species. When large habitats are broken up into small fragments due to various human activities, mammals and birds requiring large territories and certain animals with migratory habits are badly affected, leading to population declines.
2. Co-extinctions: When a species becomes extinct, the plant and animal species associated with it in an obligatory way also become extinct. When a host fish species becomes extinct, its unique assemblage of parasites also meets the same fate. Another example is the case of a coevolved plant-pollinator mutualism where Extinction of one invariably leads to the extinction of the other.
Answer 21.
Some adaptive features that the desert plants have are:
- Thick cuticle on their leaf surfaces.
- Their stomata arranged in deep pits to minimize water loss through transpiration.
- Special photosynthetic pathway (CAM) enables their stomata to remain closed during day time.
- Some plants like opuntia, have no leaves-they are reduced to spines-and the photosynthetic function is taken over by the flattened stems
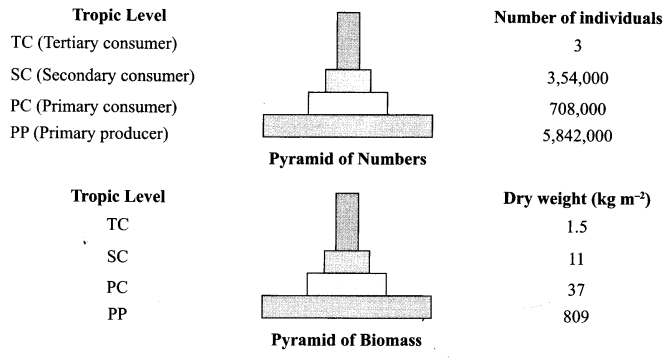
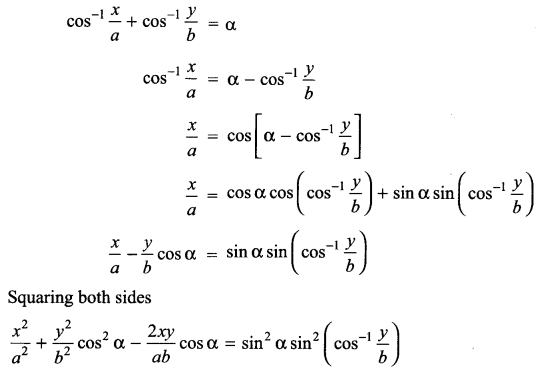
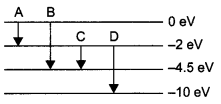
Answer 22.
The following picture represents the global biodiversity
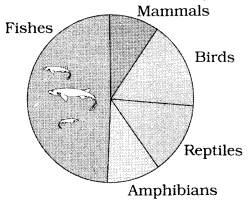
Fishes have the maximum global biodiversity in the phylum vertebrates followed by birds, reptiles, amphibians and mammals.
SECTION-D
Answer 23.
(a) Vijay was alert, curious, clever and a responsible child.
(b) According to the teacher, Sunita lacks the concept of colours. When she could not identify red colour, it proved to be a case of colour blindness. It is a sex linked inherited disorder.
(c) This is a human disease which causes the loss of ability to differentiate between red and green colour. The gene for this red-green colour blindness is present on X chromosome. Colour blindness is recessive to normal vision. If a colour blind man (XcY) marries a girl with normal vision (XX), the daughters would have normal vision but would be a carrier, while sons would also be normal. If the carrier girl (heterozygous for colour blindness, XcX) now marries a colour blind XcY the off spring would show 50% females and 50% males. Of the females, 50% would be the carrier for colour blindness and the rest 50% would be colour blind. Of the males, 50% would have normal vision and the 50% would be colour blind.
SECTION-E
Answer 24.
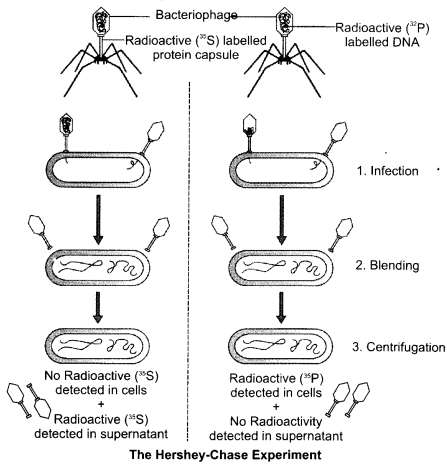
Hershey and Chase grew some viruses on a medium that contained radioactive phosphorus and some others on medium that contained radioactive sulfur. Viruses grown in the presence of radioactive phosphorus contained radioactive DNA but not radioactive protein because DNA contains phosphorus but not protein. Similarly, viruses grown on radioactive sulfur contained radioactive protein but not radioactive DNA because DNA does not contain sulfur. Radioactive phages were allowed to attach to E. coli bacteria. Then, as the infection proceeded, the viral coats were removed from the bacteria by agitating them in a blender. The virus particles were separated from the bacteria by spinning them in a centrifuge. Bacteria which were infected with viruses that had radioactive DNA were radioactive, indicating that DNA was the material that passed from the virus to the bacteria. Bacteria that were infected with viruses that had radioactive proteins were not radioactive. This indicates that proteins did not enter the bacteria from the viruses. DNA is therefore the genetic material that is passed from virus to bacteria.
Pollination By Wind:
(a) Wind pollination requires that the pollen grains are light and non-sticky so that they can be transported in wind currents.
(b) Possess well-exposed stamens so that the pollens are easily dispersed into wind currents.
(c) Ltirgc and feathery stigma to easily trap air-bome pollen grains.
(d) Have a single ovule in each ovary and numerous flowers packed into an inflorescence.
(e) Quite common in grasses.
Pollination By Water:
(a) Water pollination is quite rare in flowering plants and is limited to mostly monocotyledons.
(b) Water is a regular mode of transport for the male gametes among the lower plant groups such as algae, bryophytes and pteridophytes.
(c) Some examples of water pollinated plants are Vallisneria and Hydrilla which grow in fresh water and several marine sea-grasses such as Zostera.
(d) In Vallisneria, the female flower reach the surface of water by the long stalk and the male flowers or pollen grains are released on the surface of water. They are carried passively by water currents some of them eventually reach the female flowers and the stigma.
(e) In sea grasses, female flowers remain submerged in water and the pollen grains are released inside the water.
(f) Pollen grains in many such species are long, ribbon like and they are carried passively inside the water; some of them reach the stigma and achieve pollination. In most of the water- pollinated species, pollen grains are protected from wetting by a mucilaginous covering.
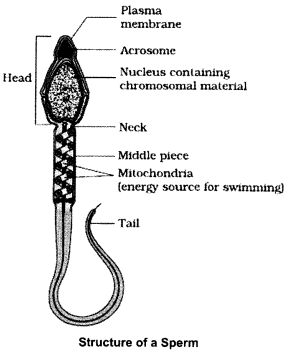
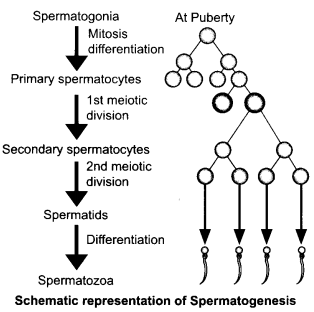
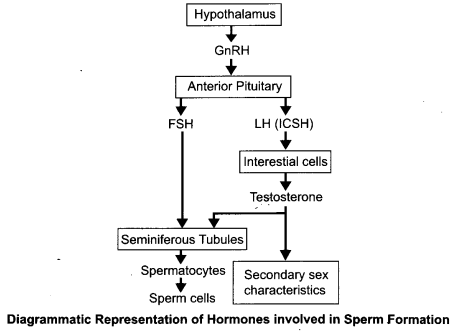
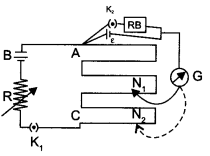
Answer 25.
In testis, the immature male germ cells (spermatogonia) produce sperms by spermatogenesis that begins at puberty. The spermatogonia (sing, spermatogonium) present on the inside wall of seminiferous tubules multiply by mitotic division and increase in numbers. Each spermatogonium is diploid and contains 46 chromosomes. Some of the spermatogonia called primary spermatocytes periodically undergo meiosis. A primary spermatocyte completes the first meiotic division (reduction division) leading to formation of two equal, haploid cells called secondary spermatocytes, which have only 23 chromosomes each. The secondary spermatocytes undergo the second meiotic division to produce four equal, haploid spermatids. The spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperms) by the process called spermiogenesis. After spermiogenesis, sperm heads become embedded in Sertoli cells, and are finally released from the seminiferous tubules by the process called sperimation.
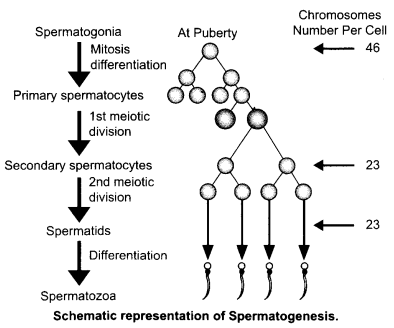
The hormones involved are:
- GnRH – Gonadotropin Releasing Hormone
- LH – Luteinising Hormone
- FSH – Follicle Stimulating Hormone.
OR
DNA fingerprinting involves identifying differences in some specific regions in DNA sequence called as repetitive DNA, because in these sequences, a small stretch of DNA is repeated many times.
• These repetitive DNA are separated from bulk genomic DNA as different peaks during density gradient centrifugation.
- The bulk DNA forms a major peak and the other small peaks are reffered to as satellite DNA.
- Depending on base composition (A : T rich or G:C rich), length of segment, and number of repetitive units, the satellite DNA is classified into many categories, such as micro- satellities, mini-satellites etc.
- These sequences normally do not code for any proteins, but they form a large portion of human genome.
- These sequence show high degree of polymorphism and form the basis of DNA fingerprinting.
The technique of DNA fingerprinting involves the following steps:
- Isolation of DNA, i.e., extraction from the nuclei of the different possible cells.
- The DNA molecules are digested with the help of enzyme restriction endonuclease (called chemical knife) that cuts them into fragments. The fragments of DNA also contains the VNTRs.
- The fragments are separated according to the size by the gel electrophoresis.
- Multiplication of fragments of a particular size having VNTRs through PCR technique.
Here they are treated with alkaline chemicals to split them into single stranded DNAs. - Blotting/transferring of separated fragments of a single stranded DNA to a nylon membrane.
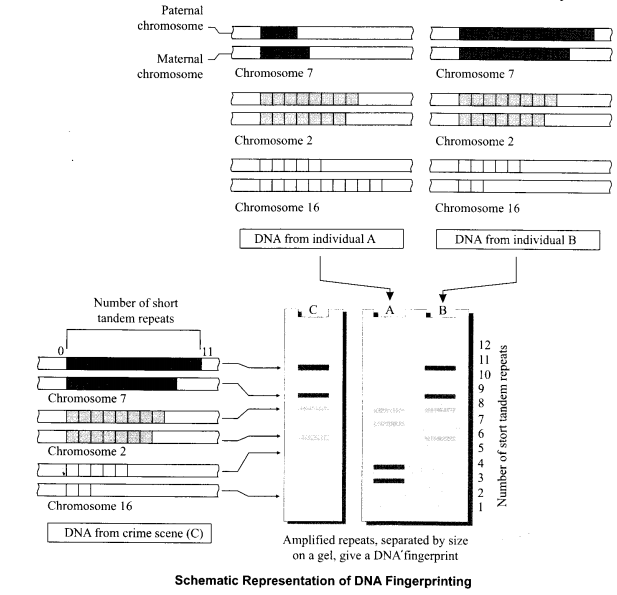
- Radioactive DNA probes having repeated base sequences complementary to possible VNTRs are poured over the nylon membrane. Some of them will bind to the single stranded VNTRs. Hybridisation of DNA with probes is called Southern Blotting. The nylon membrane is washed to remove extra probes.
- Autoradiography: An X-ray film is exposed to the nylon membrane to mark the place where the radioactive DNA probes have bound to the DNA fragments. These places are marked as dark bands when X-ray film is developed.
- The dark bands so formed on X-ray film represent the DNA fingerprints (= DNA profiles).
Answer 26.
Parasitism is an interspecies relationship in which one organism gets benefitted and the other is harmed. Parasites evolve special adaptations such as the loss of unnecessary sense organs, presence of adhesive organs or suckers to cling on to the host, loss of digestive system and high reproductive capacity. The life cycles of parasistes are often complex, involving one or two intermediate hosts or vectors to facilitate parasitisation of its primary host. The human liver fluke (a trematode parasite) depends on two intermediate hosts (a snail and a fish) to complete its life cycle. The malarial parasite needs a vector (mosquito) to spread to other hosts.
There are three types of parasitism:
(1) Ecoparasitsm: Parasites feeding on the external surface of the host organism. For example the lice on humans and ticks on dogs, marine fish are infested with ectoparasitic copepods and, cuscuta found growing on hedge plants, to derive its nutrition from the host plant which it parasitizes.
(2) Endoparasitism: Parasites living inside the host body at different sites, /.<?., liver, kidney, lungs, red blood cells etc. The life cycles of endoparasites are more complex because of their extreme specialisation. Their morphological and anatomical features are greatly simplified while emphasising their reproductive potential.
(3) Brood parasitism: Parasitisism in which birds lays its eggs in the nest of its host and lets the host incubate them. The eggs of the parasitic bird have evolved to resemble the host’s egg in size and colour to reduce the chances of the host bird detecting the foreign eggs and ejecting them from the nest.
OR
The benefits that people obtain from ecosystems are termed as ecosystem services. The four categories of ecosystem services are supporting, provisioning, regulating and cultural. These services forms a base for a wide range of economic, environmental and aesthetic goods and services. Out of the total cost of various ecosystem services, the soil formation accounts for about 50 percent, and contributions of other services like recreation and nutrient cycling, are less than 10 per cent each. The cost of climate regulation and habitat for wildlife are about 6 per cent each. Examples of such services are as follows:
(a) Healthy Forest ecosystems.
(b) Purify air and water.
(c) Mitigate droughts and floods.
(d) Cycle nutrients.
(e) Generate fertile soils.
(f) Provide wildlife habitat.
(g) Maintain biodiversity.
(h) Pollinate crops.
(i) Provide storage site for carbon.
We hope the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 5 help you. If you have any query regarding CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Paper 5, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.