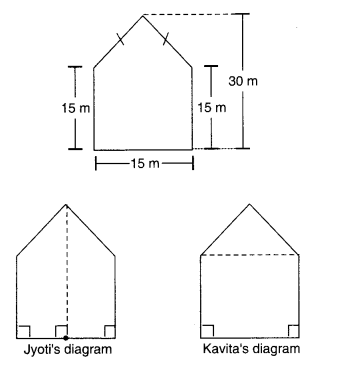
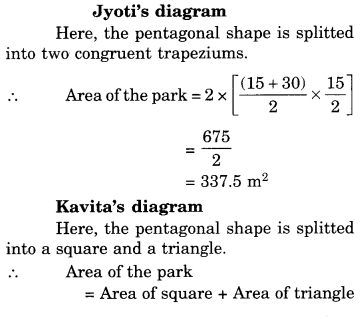
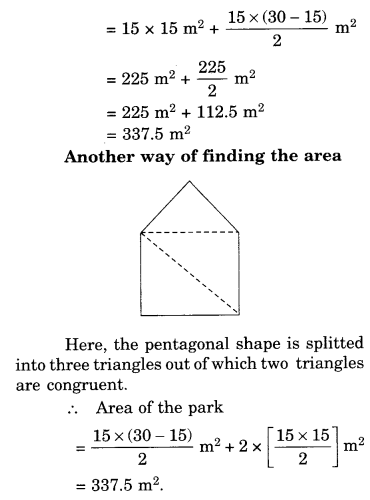
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current are part of NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science. Here we have given NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current.
| Board | CBSE |
| Textbook | NCERT |
| Class | Class 8 |
| Subject | Science |
| Chapter | Chapter 14 |
| Chapter Name | Chemical Effects of Electric Current |
| Number of Questions Solved | 12 |
| Category | NCERT Solutions |
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current
NCERT TEXTBOOK EXERCISES
Question 1.
Fill in the blanks:
- Most liquids that conduct electricity are solutions of……..,……………and …………..
- The passage of an electric current through a solution causes…………..effects.
- If you pass current through copper sulphate solution, copper gets deposited on the plate connected to the………..terminal of the battery.
- The process of depositing a layer of any desired metal on another material by means of electricity is called.………
Answer.
- acids, bases, salts
- chemical
- negative
- electroplating.
Question 2.
When the free ends of a tester are dipped into a solution, the magnetic needle shows deflection. Can you explain the reason?
Answer.
Yes, it is because the solution conducts electricity.
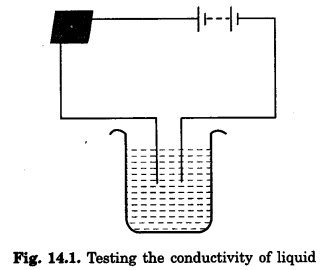
Question 3.
Name three liquids, which when tested in the manner shown in Fig. 14.1, may cause the magnetic needle to deflect.
Answer.
Tap water/sodium chloride solution, hydrochloric acid.
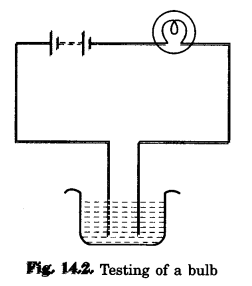
Question 4.
The bulb does not glow in the setup shown in Fig. 14.2. List the possible reasons. Explain your answer.
Answer.
List of possible reasons:
- The liquid solution might be conducting electricity, but the current produced is too small so that the filament of the bulb does not get heated and the bulb does not glow.
- Or, it is possible that the connections are loose.
- Or, the bulb is fused.
- Or, the cells are used up.
Question 5.
A tester is used to check the conduction of electricity through two liquids, labelled A and B. It is found that the bulb of the tester glows brightly for liquid A while it glows very dimly for liquid B. You would conclude that
(i) liquid A is a better conductor than liquid B.
(ii) liquid B is a better conductor than liquid A.
(iii) both liquids are equally conducting.
(iv) conducting properties of liquid cannot be compared in this manner.
Answer.
If the bulb glows brightly with liquid A, it means that liquid A is a better conductor of electricity than B. So the answer will be (i).
Question 6.
Does pure water conduct electricity? If not, what can we do to make it conducting?
Answer.
Pure water does not conduct electricity. It can be made conducting if acid, base, or salt is dissolved in it.
Question 7.
In case of a fire, before the firemen use the water hoses, they shut off the main electrical supply of the area. Explain why they do this.
Answer.
The water used in water hoses is not pure water and it conducts electricity. Firemen shut off the main electrical supply of the area because if the supply of electricity continues there may be a high risk of electrocution in the whole area due to water.
Question 8.
A child staying in a coastal region test the drinking water and also the seawater with his tester. He finds that the compass needle deflects more in the case of seawater. Can you explain the reason?
Answer.
The impure water is the conductor of electricity. Seawater contains more impurity (salt) than drinking water. Therefore, seawater conducts more electricity than drinking water. That is why the compass needle deflects more in the case of seawater.
Question 9.
Is it safe for the electrician to carry out electrical repairs outdoors during heavy downpours? Explain.
Answer.
It is not safe for the wireman to carry out electrical repairs outside during heavy downpours. Because during heavy downpour there is a high risk of electrocution.
Question 10.
Paheli had heard that rainwater is as good as distilled water. So she collected some rainwater in a clean glass tumbler and tested it using a tester. To her surprise, she found that the compass needle showed deflection. What could be the reasons?
Answer.
Rainwater is, of course, as good as distilled water but, when it passes through the atmosphere, it dissolves a lot of dust, dirt, and impurities and becomes conductive. So, when Paheli used a tester, its compass showed deflection.
Question 11.
Prepare a list of objects around you that are electroplated.
Answer.
Ornaments, wheel rims of vehicles, the handlebar of cycle and motorcycle, pots of one metal coated with other, bath taps, kitchen gas burner, the bottom of cooking utensils, handles of doors, tin cans, etc.
Question 12.
The process that you saw in Activity 14.7 (NCERT) is used for the purification of copper. A thin plate of pure copper and a thick rod of impure copper are used as electrodes. Copper from impure rod is sought to be transferred to the thin copper plate. Which electrode should be attached to the positive terminal of the battery and why?
Answer.
To perform such activity we have to arrange copper sulphate crystals and two copper plates each having a size around 10 cm long and 4 cm wide. Now take 250 mL distilled water in a clean and dry beaker. Dissolve two teaspoonfuls of copper sulphate crystals in it to obtain copper sulphate solution. (You may add few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to copper sulphate solution to make it more conducting). Clean each copper plate with sandpaper. Now rinse it with water. With the help of wires, connect one copper plate to each terminal of two cell batteries (Take care that the two plates do not touch each other).
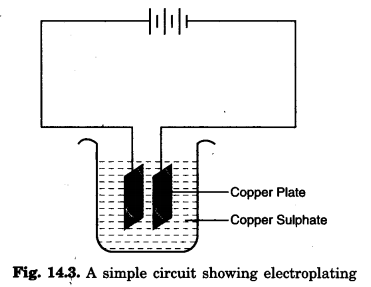
Immerse two plates in copper sulphate solution as shown in Fig. 14.3. Allow the current to pass through for 5 to 7 minutes.
When an electric current is passed through the copper sulphate solution, copper sulphate dissociates into copper and sulphate. The free copper gets drawn to the plate connected to the negative terminal of the battery and thus gets deposited on that plate. Gradually, a layer of copper builds upon the plate.
We hope the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current help you. If you have any query regarding NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects of Electric Current, drop a comment below and we will get back to you at the earliest.