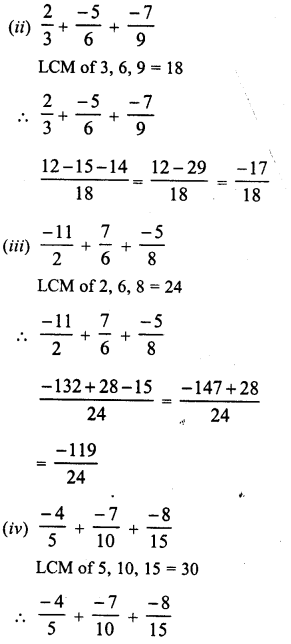
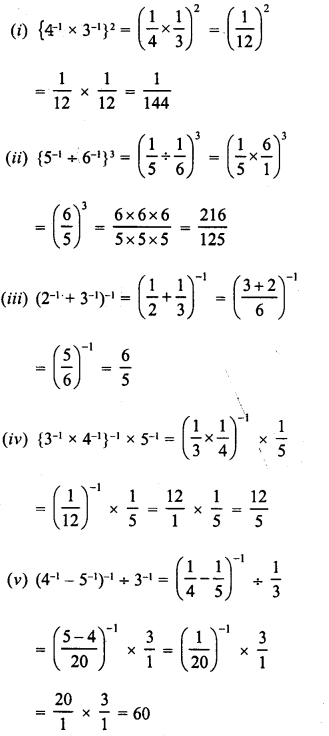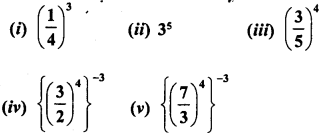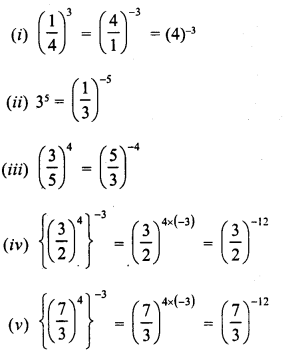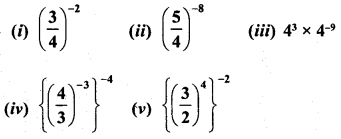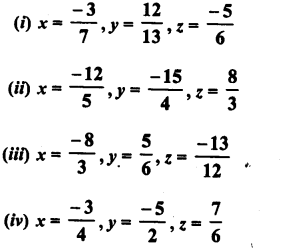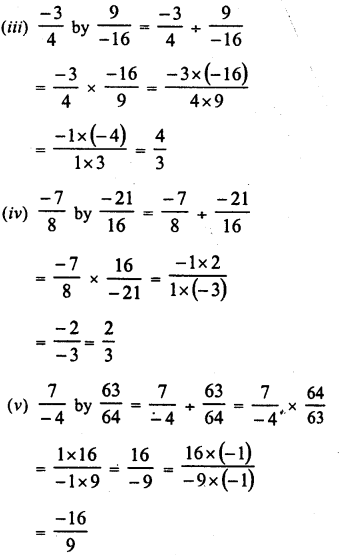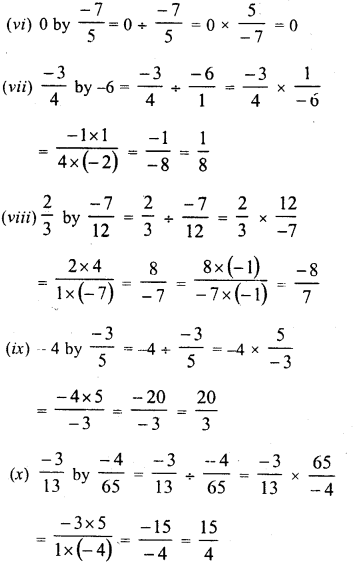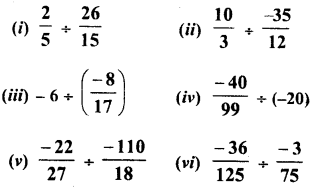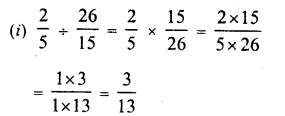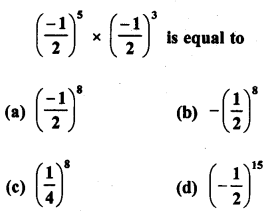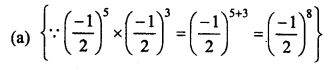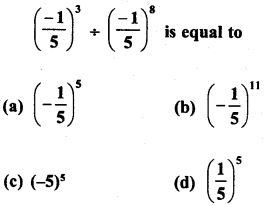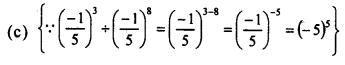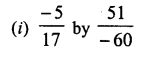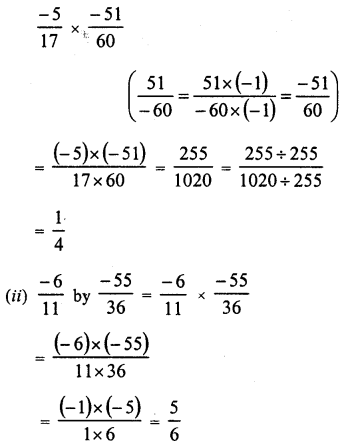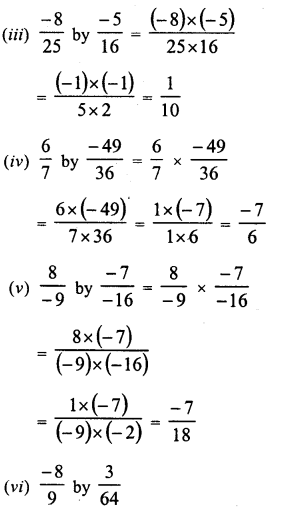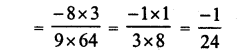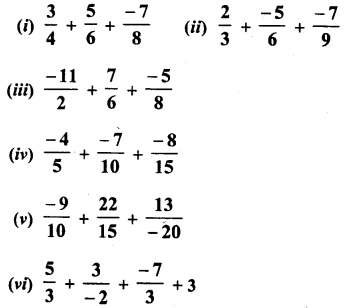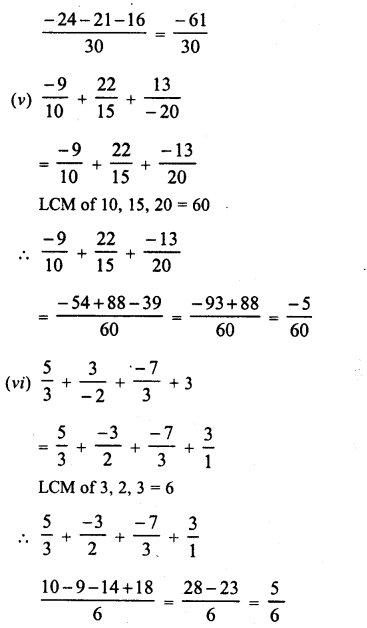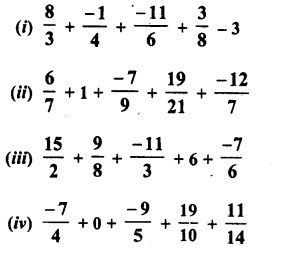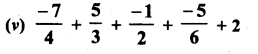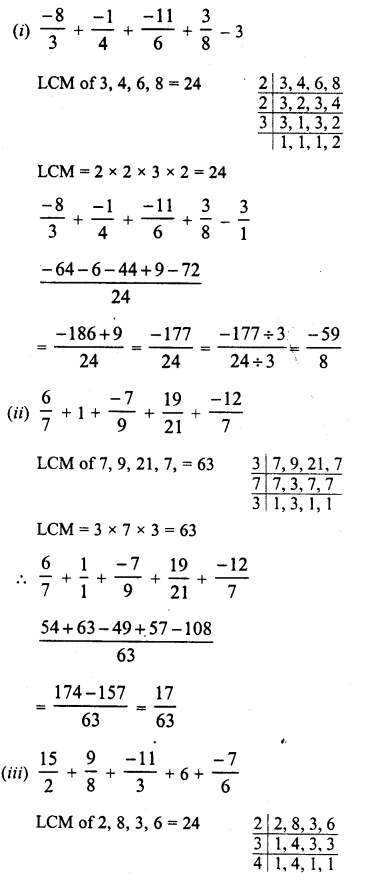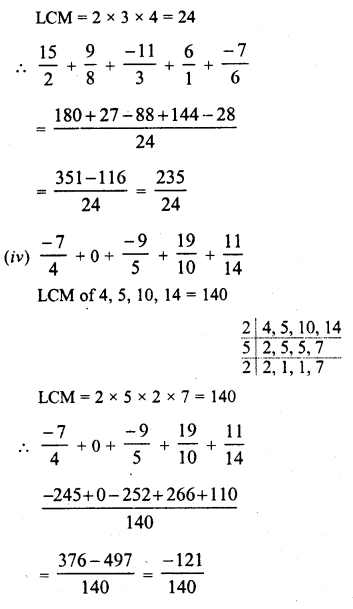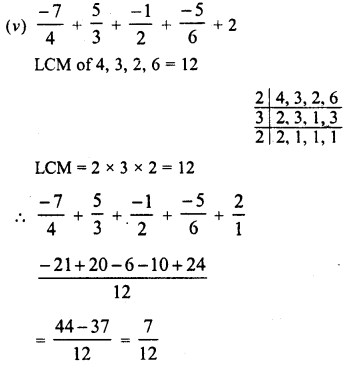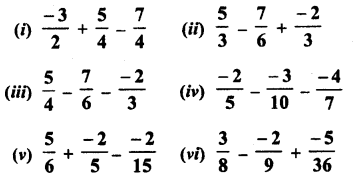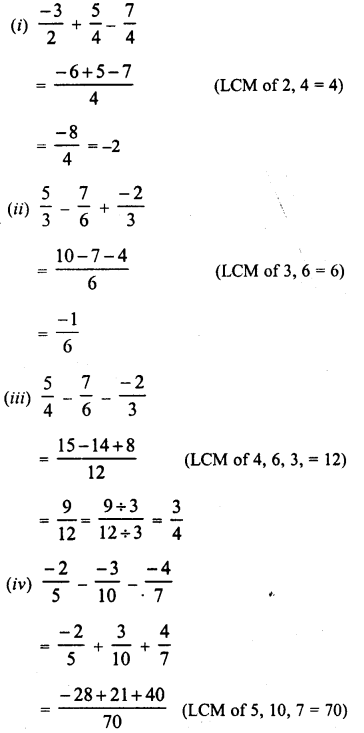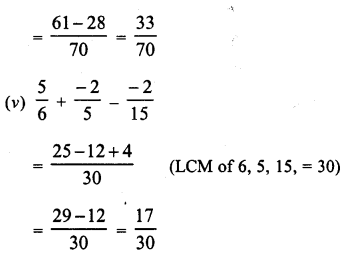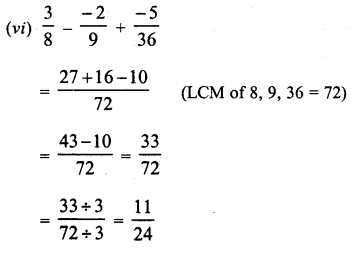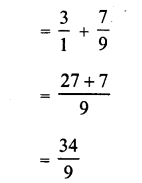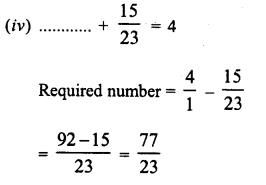RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots Ex 3.1
These Solutions are part of RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions. Here we have given RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots Ex 3.1
Other Exercises
- RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots Ex 3.1
- RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots Ex 3.2
- RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots Ex 3.3
- RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots Ex 3.4
- RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots Ex 3.5
- RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots Ex 3.6
- RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots Ex 3.7
- RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots Ex 3.8
- RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots Ex 3.9
Question 1.
Which of the following numbers are perfect squares ?
(i)484
(ii) 625
(iii) 576
(iv) 941
(v) 961
(vi) 2500
Solution:

Grouping the factors in pairs, we have left no factor unpaired
∴ 484 is a perfect square of 22
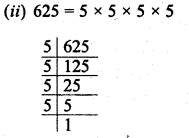
∴ Grouping the factors in pairs, we have left no factor unpaired
∴ 625 is a perfect square of 25.

Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that no factor is left unpaired
∴ 576 is a perfect square of 24
(iv) 941 has no prime factors

∴ 941 is not a perfect square.
(v) 961 =31 x 31
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that no factor is left unpaired
∴ 961 is a perfect square of 31

Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that no factor is left impaired
∴ 2500 is a perfect square of 50 .
Question 2.
Show that each of the following* numbers is a perfect square. Also find the number whose square is the given number in each case :
(i) 1156
(ii) 2025
(iii) 14641
(iv) 4761
Solution:
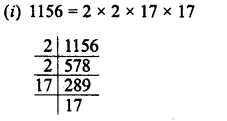
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that no factor is left unpaired
∴ 1156 is a perfect square of 2 x 17 = 34
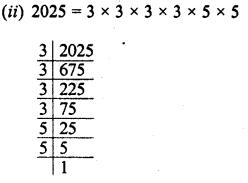
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that no factor is left unpaired
2025 is a perfect square of 3 x 3 x 5 =45

Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that no factor is left unpaired
∴ 14641 is a perfect square of 11×11 = 121
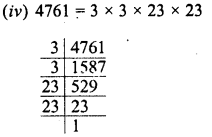
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that no factor is left unpaired
∴ 4761 is a perfect square of 3 x 23 = 69
Question 3.
Find the smallest number by which the given number must be multiplied so that the product is a perfect square.
(i) 23805
(ii) 12150
(iii) 7688
Solution:
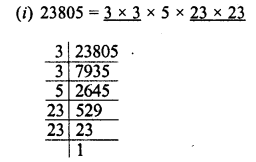
Grouping the factors in pairs of equal factors, we see that 5 is left unpaird
∴ In order to complete the pairs, we have to multiply 23805 by 5, then the product will be the perfect square.
Requid smallest number = 5
(ii) 12150 = 2 x 3 x 3×3 x 3×3 x 5×5

Grouping the factors in pairs of equal factors, we see that factors 2 and 3 are left unpaired
∴ In order to complete the pairs, we have to multiply 12150 by 2 x 3 =6 i.e., then the product will be the complete square.
∴ Required smallest number = 6

Grouping the factors in pairs of equal factors, we see that factor 2 is left unpaired
∴ In order to complete the pairs we have to multiply 7688 by 2, then the product will be the complete square
∴ Required smallest number = 2
Question 4.
Find the smallest number by which the given number must be divided so that the resulting number is a perfect square.
(i) 14283
(ii) 1800
(iii) 2904
Solution:
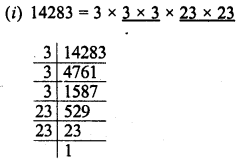
Grouping the factors in pairs of equal factors, we see that factors we see that 3 is left unpaired
Deviding by 3, the quotient will the perfect square.
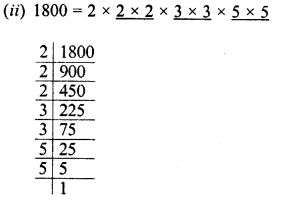
Grouping the factors in pair of equal factors, we see that 2 is left unpaired.
∴ Dividing by 2, the quotient will be the perfect square.
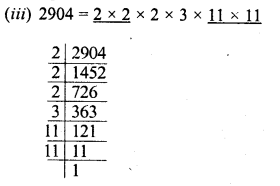
Grouping the factors in pairs of equal factors, we see that 2 x 3 we left unpaired
∴ Dividing by 2 x 3 = 6, the quotient will be the perfect square.
Question 5.
Which of the following numbers are perfect squares ?
11, 12, 16, 32, 36, 50, 64, 79, 81, 111, 121
Solution:
11 is not a perfect square as 11 = 1 x 11
12 is not a perfect square as 12 = 2×2 x 3
16 is a perfect square as 16 = 2×2 x 2×2
32 is not a perfect square as 32 = 2×2 x 2×2 x 2
36 is a perfect square as 36 = 2×2 x 3×3
50 is not a perfect square as 50 = 2 x 5×5
64 is a perfect square as 64 = 2×2 x 2×2 x 2×2
79 is not a perfect square as 79 = 1 x 79
81 is a perfect square as 81 = 3×3 x 3×3
111 is not a perfect square as 111 = 3 x 37
121 is a perfect square as 121 = 11 x 11
Hence 16, 36, 64, 81 and 121 are perfect squares.
Question 6.
Using prime factorization method, find which of the following numbers are perfect squares ?
∴ 189,225,2048,343,441,2916,11025,3549
Solution:
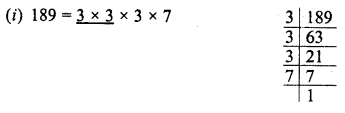
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that are 3 and 7 are left unpaired
∴ 189 is not a perfect square
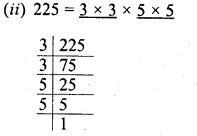
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see no factor left unpaired
∴ 225 is a perfect square

Grouping the factors in pairs, we see no factor left unpaired
∴ 2048 is a perfect square
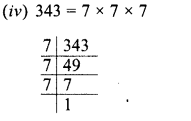
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that one 7 is left unpaired
∴ 343 is not a perfect square.
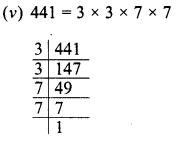
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that no factor is left unpaired
∴ 441 is a perfect square.
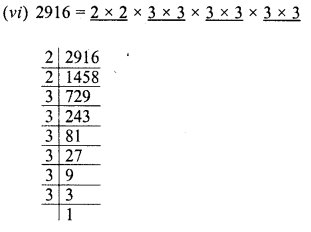
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that no factor is left unpaired
∴ 2916 is a perfect square.
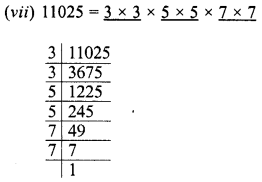
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that no factor is left unpaired
∴ 11025 is a perfect square.
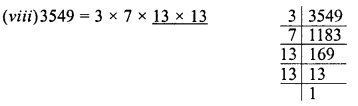
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that 3, no factor 7 are left unpaired
∴ 3549 is a perfect square.
Question 7.
By what number should each of the following numbers be multiplied to get a perfect square in each case ? Also, find the number whose square is the new number.
(i) 8820
(ii) 3675
(iii) 605
(iv) 2880
(v) 4056
(vi) 3468
Solution:
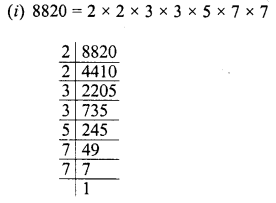
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that 5 is left unpaired
∴ By multiplying 8820 by 5, we get the perfect square and square root of product will be
= 2 x 3 x 5 x 7 = 210
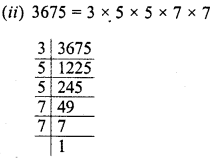
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that 3 is left unpaired
∴ Multiplying 3675 by 3, we get a perfect square and square of the product will be
= 3 x 5 x 7 = 105
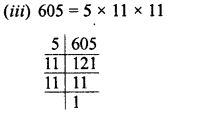
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that 5 is left unpaired
∴ Multiplying 605 by 5, we get a perfect square and square root of the product will be
= 5 x 11 =55

Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that 5 is left unpaired
∴ Multiplying 2880 by 5, we get the perfect square.
Square rooi of product will be = 2 x 2 * 2 – 3 x 5 = 120

Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that 2 and 3 are left unpaired
∴ Multiplying 4056 by 2 x 3 i.e., 6, we get the perfect square.
and square root of the product will be
= 2 x 2 x 3 x 13 = 156
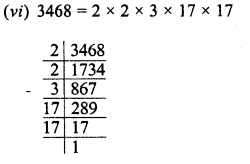
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that 3 is left unpaired
∴ Multiplying 3468 by 3 we get a perfect square, and square root of the product will be 2 x 3 x 17 = 102

Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that 2 and 3 are left unpaired
∴ Multiplying 7776 by 2 x 3 or 6 We get a perfect square and square root of the product will be
= 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 x 3 = 216
Question 8.
By what numbers should each of the following be .divided to get a perfect square in each case ? Also find the number whose square is the new number.
(i) 16562
(ii) 3698
(iii) 5103
(iv) 3174
(v) 1575
Solution:
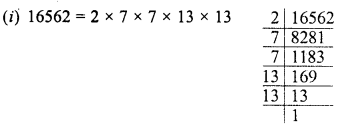
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that 2 is left unpaired
∴ Dividing by 2, we get the perfect square and square root of the quotient will be 7 x 13 = 91
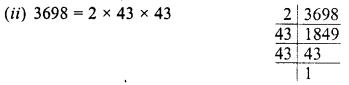
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that 2 is left unpaired,
∴ Dividing 3698 by 2, the quotient is a perfect square
and square of quotient will be = 43
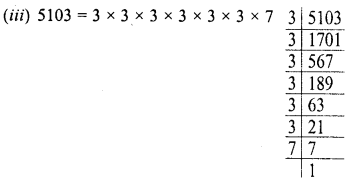
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that 7 is left unpaired
∴ Dividing 5103 by 7, we get the quotient a perfect square.
and square root of the quotient will be 3 x 3 x 3 = 27
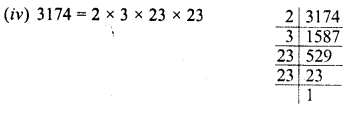
Grouping the factors iq pairs, we see that 2 and 3 are left unpaired
∴ Dividing 3174 by 2 x 3 i.e. 6, the quotient will be a perfect square and square root of the quotient will be = 23
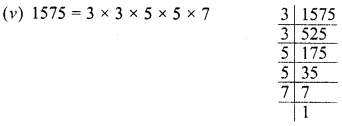
Grouping the factors in pairs, we find that 7 is left unpaired i
∴ Dividing 1575 by 7, the quotient is a perfect square
and square root of the quotient will be = 3 x 5 = 15
Question 9.
Find the greatest number of two digits which is a perfect square.
Solution:
The greatest two digit number = 99 We know, 92 = 81 and 102 = 100 But 99 is in between 81 and 100
∴ 81 is the greatest two digit number which is a perfect square.
Question 10.
Find the least number of three digits which is perfect square.
Solution:
The smallest three digit number =100
We know that 92 = 81, 102 = 100, ll2 = 121
We see that 100 is the least three digit number which is a perfect square.
Question 11.
Find the smallest number by which 4851 must be multiplied so that the product becomes a perfect square.
Solution:
By factorization:
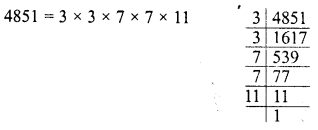
Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that 11 is left unpaired
∴ The least number is 11 by which multiplying 4851, we get a perfect square.
Question 12.
Find the smallest number by which 28812 must be divided so that the quotient becomes a perfect square.
Solution:
By factorization,

Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that 13 is left unpaired
∴ Dividing 28812 by 3, the quotient will be a perfect square.
Question 13.
Find the smallest number by which 1152 must be divided so that it becomes a perfect square. Also find the number whose square is the resulting number.
Solution:
By factorization,

Grouping the factors in pairs, we see that one 2 is left unpaired.
∴ Dividing 1152 by 2, we get the perfect square and square root of the resulting number 576, will be 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 = 24
Hope given RD Sharma Class 8 Solutions Chapter 3 Squares and Square Roots Ex 3.1 are helpful to complete your math homework.
If you have any doubts, please comment below. Learn Insta try to provide online math tutoring for you.