Here we are providing Online Education for Reaching the Age of Adolescence Class 8 Extra Questions and Answers Science Chapter 10 was designed by subject expert teachers. https://ncertmcq.com/extra-questions-for-class-8-science/
Online Education for Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Extra Questions and Answers Reaching the Age of Adolescence
Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Class 8 Questions Answers Question 1.
When do human beings and many other kinds of animals become capable of reproduction?
Answer:
They become capable when they get reproductive maturity.
Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Questions And Answers Question 2.
What brings about changes that make a child grow into an adult?
Answer:
Hormones bring about these changes.
Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Question Answer Question 3.
What period covers the “teens”?
Answer:
The years 13 to 18 or 19 covers the ‘teens’.
Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Question And Answer Question 4.
What is the other name of adolescents?
Answer:
It is ‘teenagers’.
![]()
Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Class 8 Questions And Answers Question 5.
What is the conspicuous change during the puberty?
Answer:
The most conspicuous change during puberty is the sudden increase in height.
Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Class 8 Pdf Questions And Answers Question 6.
Up to what age girls grow in height faster than the boys?
Answer:
Girls grow in height faster than boys up to 18 years of age.
Question Answer Of Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Question 7.
Do all parts of the body grow at the same rate?
Answer:
No, all parts of the body do not grow at the same rate.
Question And Answer Of Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Question 8.
What factor does height depend on?
Answer:
Height depends upon the genes inherited from parents.
Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Class 8 Solutions Question 9.
What happens to the quality of voice on puberty?
Answer:
Girl’s voice becomes high-pitched and that of boys becomes deep or hoarse.
Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Class 8 Question 10.
Where do endocrine glands release hormones?
Answer:
Endocrine glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream.
![]()
Extra Questions For Class 8 Science With Answers Question 11.
Name the secretion of ovaries on reaching puberty.
Answer:
Ovaries begin to produce female hormones called estrogen.
Question Answers Of Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Question 12.
What makes ova in ovaries and sperms in testes mature?
Answer:
FSH or Follicle Stimulating Hormone makes ova mature in ovaries and sperms in testes.
Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Question Answers Question 13.
What marks the beginning of reproductive period when one becomes capable of reproduction ?.
Answer:
It is puberty.
Reaching The Age Of Adolescence Class 8 Notes Question 14.
When does menstrual cycle stop?
Answer:
At 45 to 50 years of age, the menstrual cycle stops.
Extra Questions Class 8 Science Question 15.
What do you understand by menopause?
Answer:
The stoppage of menstrual cycle is termed as menopause.
Class 8 Science Extra Questions Question 16.
How many chromosomes do all humans have?
Answer:
All humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes.
Extra Questions Of Science Class 8 Question 17.
What determines the sex of unborn baby?
Answer:
Sex chromosomes of father determine the sex of unborn baby.
![]()
Question 18.
What are sex chromosomes? How many are they?
Answer:
Chromosomes carrying genes for different sexual characters are termed as sex chromosomes. There are two sex chromosomes out of 23 pairs of chromosomes.
Question 19.
What is the hormone produced by pancreas? What is the disease caused due to the non-production of that hormone?
Answer:
Pancreas secretes insulin hormone. Insulin hormone regulates the levels of sugar in the blood. Its deficiency in the blood causes diabetes. In diabetic patients, it is not secreted in required amount, therefore, blood sugar level rises and causes various harmful effects.
Question 20.
How do you calculate the probable full height of a adolescent? Give the formula for this purpose and state an example.
Answer:
The formula for calculation of full height (in cm) is given as follows :
\(\frac{\text { Present height }(\text { in } \mathrm{cm})}{\text { Percentage of full height at this age }} \times 100 \)
Example: A girl is 10 years old and her height is 130 cm. At the end of the growth period, she is likely to be of what height?
Solution:
\(\frac{130 \mathrm{~cm}}{78} \times 100 \mathrm{~cm}\) ≈ 166 cm.
![]()
Question 21.
By seeing the data of activity 10.1, can you read the graph and say at what age girls grow in height faster than the boys?
Answer:
Initially girls grow faster than boys but by about 18 years of age, both reach their maximum height. The rate of growth in height is different in different individuals. Some grow suddenly at puberty and then slow down, while others grow gradually.
Question 22.
What is the proportion of growth of the body parts in adolescence?
Answer:
All the parts of the body do not grow at the same rate. Sometimes the arms and legs of adolescents, look oversized and out of proportion with the body. But, soon the other parts catch up and result into a proportionate body.
Question 23.
How does body get adequate nourishment for growth?
Answer:
It is very important to eat the right kind of food, especially during the growing years. This helps the bones, muscles and other parts of the body get adequate nourishment for growth.
Question 24.
What happens to the sex organs of boys and girls at puberty?
Answer:
At puberty, male sex organs like the testes and penis develop completely. The testes also begin to produce sperms. In girls, the ovaries enlarge and eggs begin to mature. Also, ovaries start releasing mature eggs.
Question 25.
What are psychological changes in adolescence?
Answer:
Adolescence is also a period of change in a person’s way of thinking.
- Adolescents are more independent than before and are also self-conscious.
- Intellectual development takes place and they tend to spend considerable time in thinking.
- It is often the time in one’s life when the brain has the greatest capacity for learning.
- Sometimes, however, an adolescent may feel insecure while trying to adjust to the changes in the body and mind.
Question 26.
Describe menstrual cycle.
Answer:
Menstrual cycle is controlled by hormones. The cycle includes the maturation of the egg, its release, thickening of uterine wall and its breakdown if fertilization does not occur. In case the egg is fertilized, it begins to divide and then gets embedded in the uterus for further development.
![]()
Question 27.
What do you understand by the term ‘chromosomes’? Diseuss.
Answer:
These are the thread-like structures found in the nucleus of a cell. It contains genes. All human beings have 23 pairs of chromosomes in the nuclei of their cells. Two chromosomes out of these are sex chromosomes.
Question 28.
What should one do to keep the body healthy?
Answer:
To keep the body healthy, one needs to:
- have a balanced diet,
- observe personal hygiene and cleanliness regularly, and
- undertake adequate physical exercises.
During adolescence, however, these become even more essential.
Question 29.
What are the required hygienic activities for boys and girls when they become adolescents?
Answer:
Everyday bath is more necessary for teenagers because the increased activities of sweat glands sometimes make the body smelly. If cleanliness is not maintained, there are chances of catching bacterial infection. Girls should keep track of their menstrual cycle and be prepared for the onset of menstruation. Undergarments should be changed every day. Cotton undergarments should be preferred.
Question 30.
How do HIV viruses enter the human bodies?
Answer:
HIV pass on to a normal person from an infected person by :
- sharing the syringes used for injecting drugs.
- from the infected mother to an infant through milk.
- through sexual contact with a person infected with HIV.
Question 31.
What are myths and taboos regarding bodily changes in case of adolescents?
Answer:
There are many myths and taboos regarding bodily changes that adolescents experience. Some of these are given below :
- A girl becomes pregnant if she looks at boys during menstruation.
- The mother is responsible for the sex of the child.
- A girl should not be allowed to work in the kitchen during menstruation.
These should be discarded outrightly.
Question 32.
What are the drawbacks of early marriage and motherhood?
Answer:
The followings are the drawbacks of early marriage and motherhood :
- Teenage girls are not prepared mentally or physically for motherhood.
- Early marriage and motherhood cause health problems in the mother and the child.
- It also curtails employment opportunities for a young woman and causes mental agony as she is not ready for the responsibilities of motherhood.
![]()
Question 33.
Describe the reproductive phase of life in females.
Answer:
Reproductive phase of life in females :
- In females, the reproductive phase of life begins at puberty (10 to 12 years of age) and generally lasts till the age of approximately 45 to 50 years.
- The ova begins to mature with the onset of puberty. One ovum matures and is released by the ovaries once in about 28 to 30 days.
- During this period, the wall of the uterus becomes thick. This is a natural preparation to receive the egg in case it is fertilized and pregnancy occurs.
- If fertilization does not occur, the released egg and the thickened lining of the uterus along with its blood vessels are shed off. This causes bleeding in women which is known as menstruation.
Menstruation occurs once in about 28 to 30 days. Initially, menstrual cycle may be irregular and takes some time to become regular. In case the egg is fertilized, it begins to divide and then gets embedded in the uterus for further development.
Question 34.
What are the changes appears in boys and girls on reaching the adolescence?
Answer:
Changes in boys :
- Muscles of the body grow more prominently.
- Facial hair (beard and moustache) appears.
- Voice becomes hoarse, as voice box enlarges.
- Under shoulder hair and pubic hair appears.
Changes in girls :
- Region below the waist becomes wider.
- Voice pitch increases.
- Breast appears.
- Menstrual cycle begins.
- Under shoulder hair and pubic hair appears.
Question 35.
Name the various secretions (release) of endocrine glands.
Answer:
Endocrine glands release hormones directly into the bloodstream.
| Endocrine glands | Hormones secreted |
| (1) Testes | Testosterone |
| (2) Ovary | Estrogen |
| (3) Adrenal | Adrenalin |
| (4) Thyroid gland | Thyroxin |
| (5) Pituitary glands | Follicle Stimulation Hormone (FSH), Growth hormone |
| (6) Pancreas | Insulin. |
![]()
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
1. What percentage of height does a boy attain at 13 years?
(a) 95%
(b) 88%
(c) 84%
(d) 91%.
Answer:
(b) 88%.
2. At what age does a girl attain 95% height?
(a) 12 years
(b) 15 years
(c) 13 years
(d) 17 years
Answer:
(c) 13 years.
3. At 13 years, a girl is 145 cm tall and a boy is 135 cm tall. Which of the following is likely to happen at 18 years?
(a) The boy will be taller than the girl.
(b) The girl will be taller than the boy.
(c) Both will attain the same height.
(d) The height will depend on the financial status.
Answer:
(a) The boy will be taller than the girl.










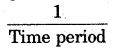 = 5Hz.
= 5Hz.