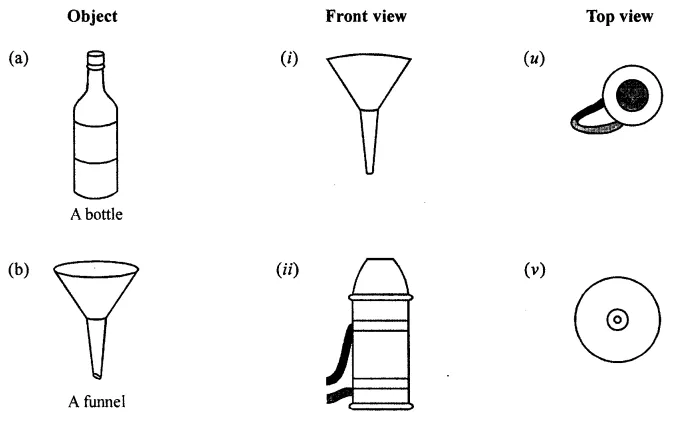
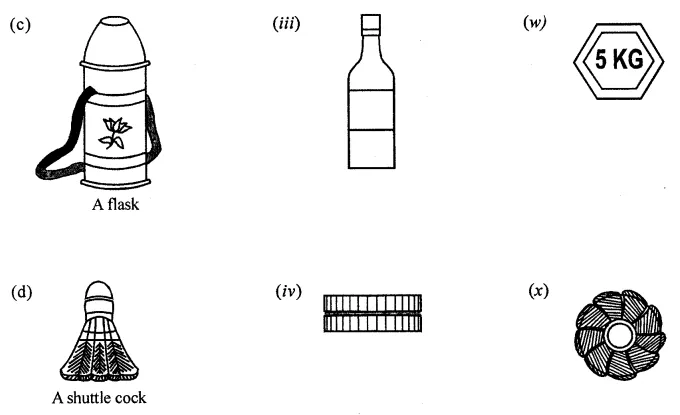
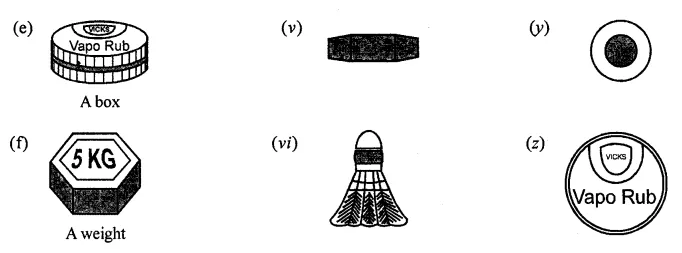
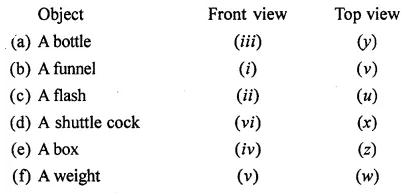
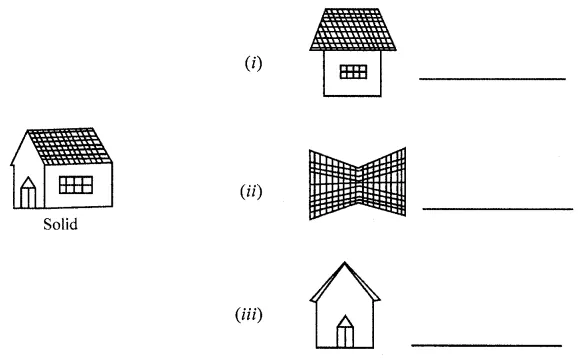
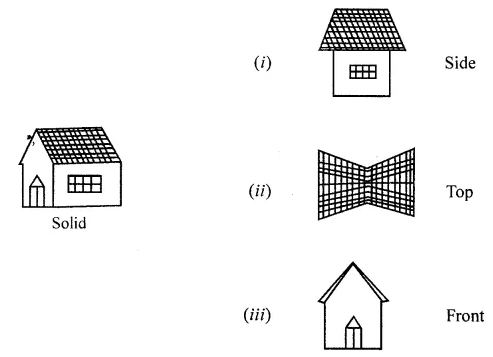
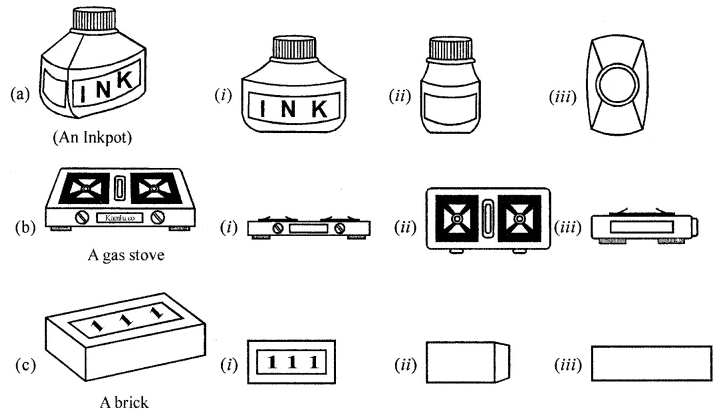
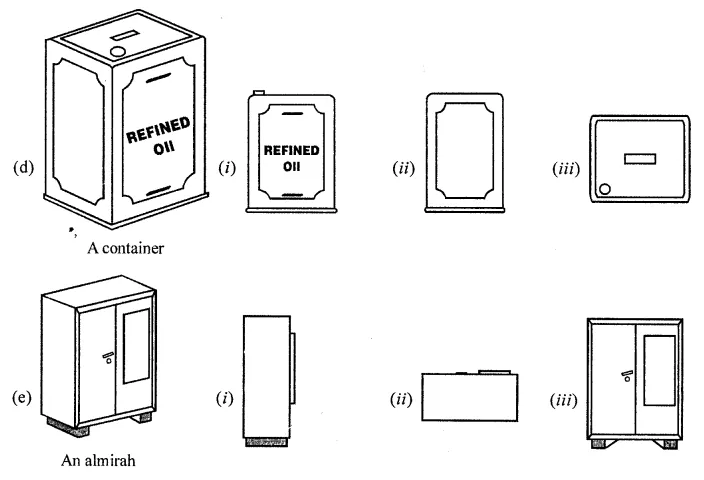
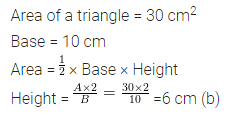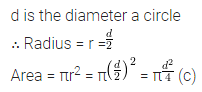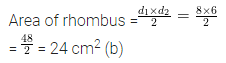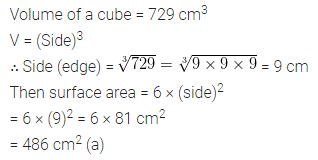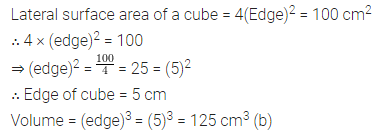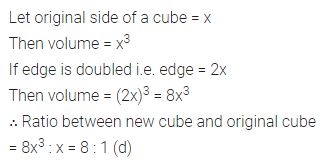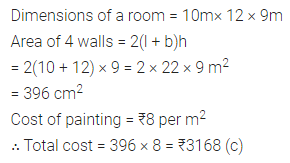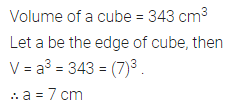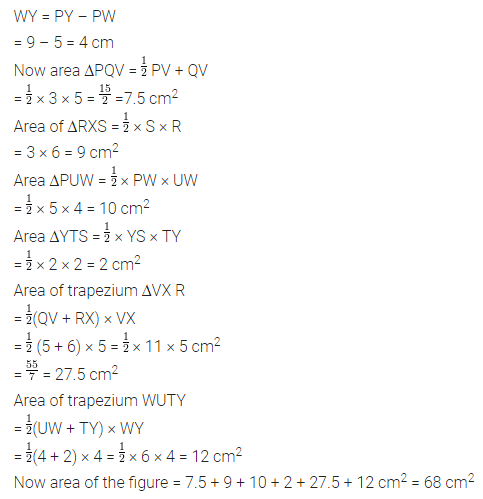ML Aggarwal Class 8 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 18 Mensuration Check Your Progress
Question 1.
A square field of side 65 m and rectangular field of length 75 m have the same perimeter. Which field has a larger area and by how much?
Solution:

Question 2.
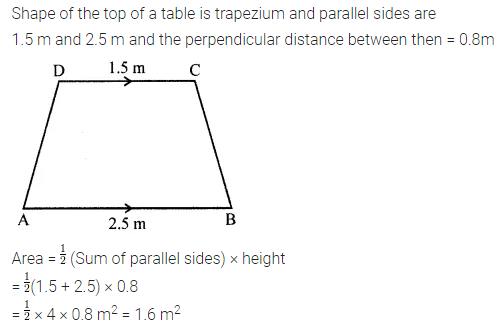
The shape of a top surface of the table is a trapezium. Find the area if its parallel sides are 1.5 m and 2.5 m and the perpendicular distance between them is 0.8 m.
Solution:
Question 3.
The length and breadth of a hall of a school are 26 m and 22 m respectively. If one student requires 1.1 sq. m area, then find the maximum number of students to be seated in this hall.
Solution:
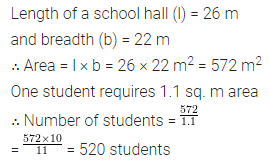
Question 4.
It costs ₹936 to fence a square field at ₹7·80 per metre. Find the cost of levelling the field at ₹2.50 per square metre.
Solution:

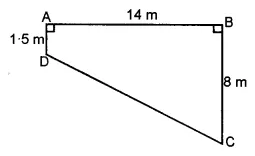
Question 5.
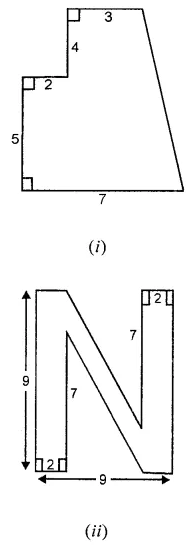
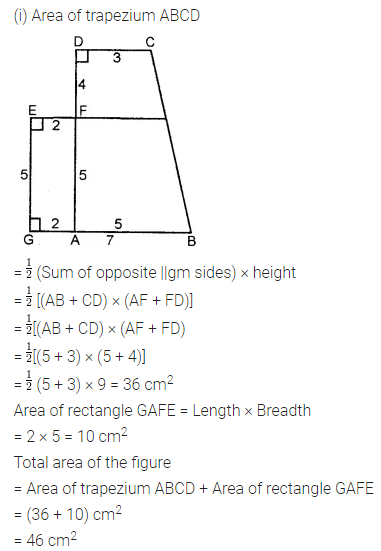
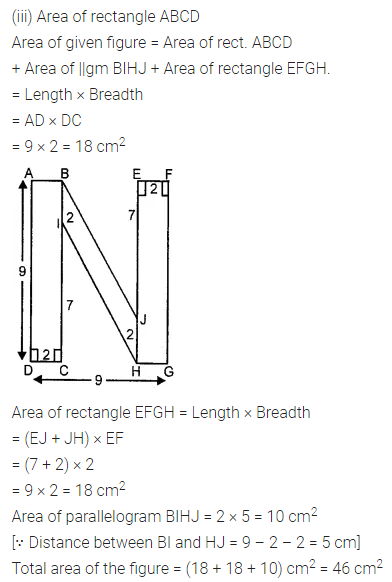
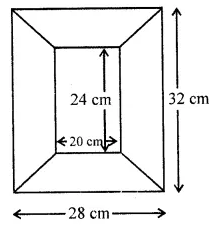
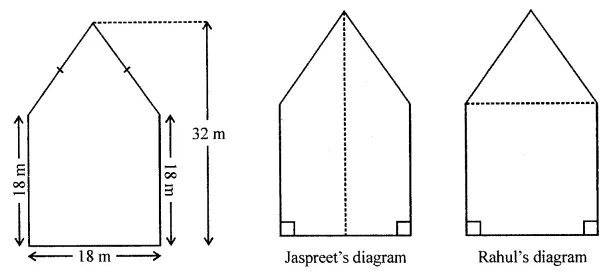
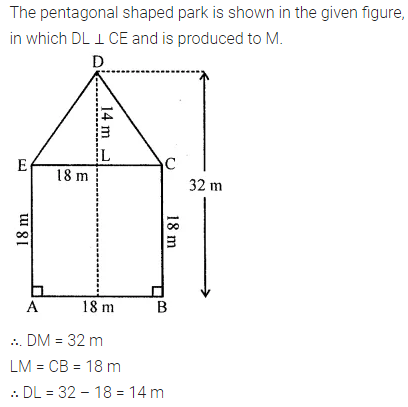
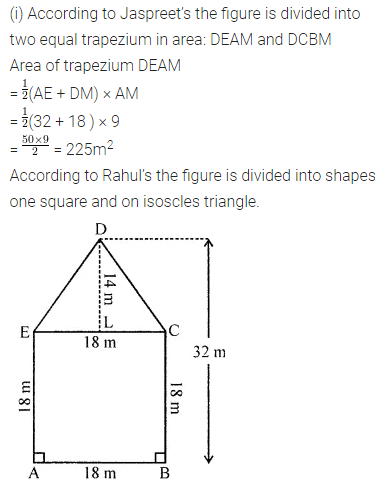
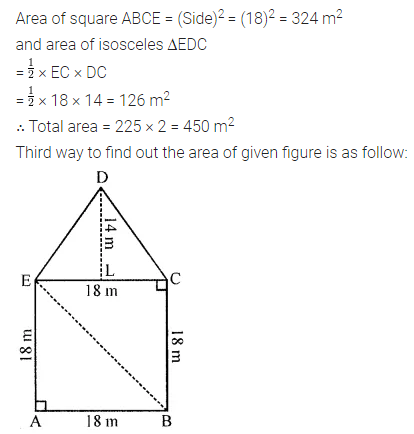
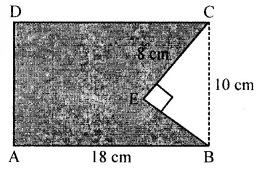
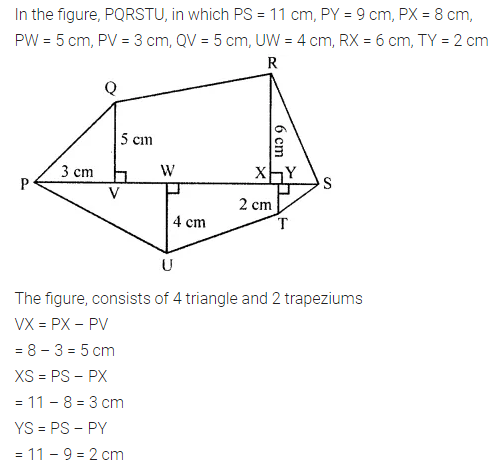
Find the area of the shaded portion in the following figures all measurements are given in cm.
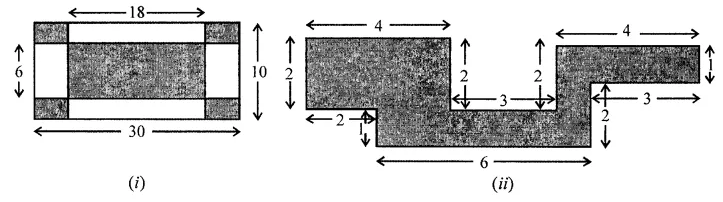
Solution:
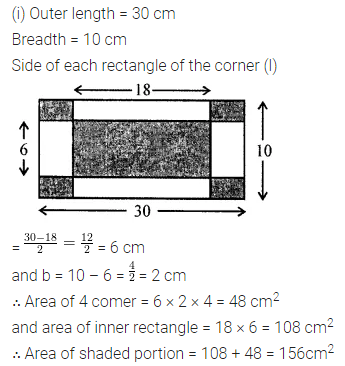
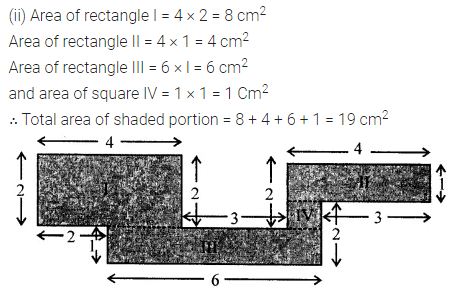
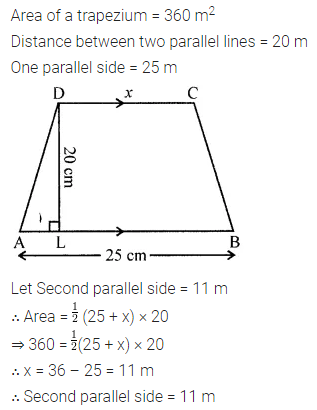
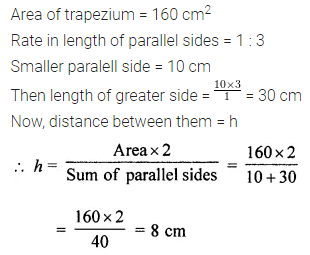
Question 6.
Area of a trapezium is 160 sq. cm. Lengths of parallel sides are in the ratio 1:3. If smaller of the parallel sides is 10 cm in length, then find the perpendicular distance between them.
Solution:
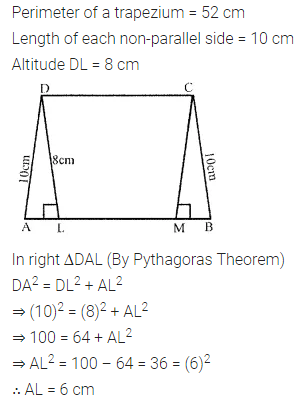
Question 7.
The area of a trapezium is 729 cm2 and the distance between two parallel sides is 18 cm. If one of its parallel sides is 3 cm shorter than the other parallel side, find the lengths of its parallel sides.
Solution:

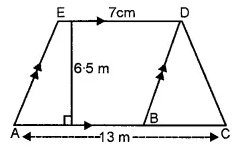
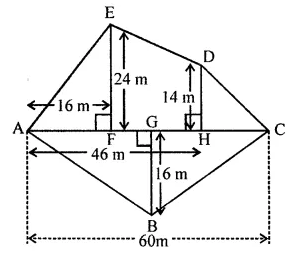
Question 8.
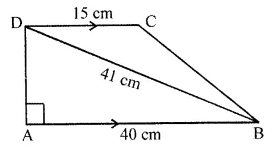
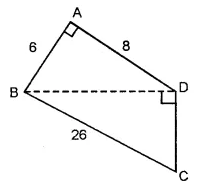
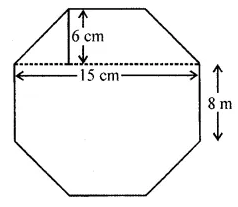
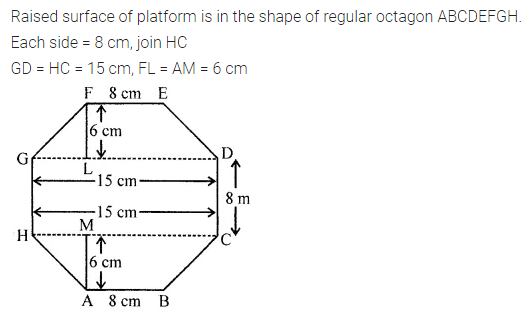
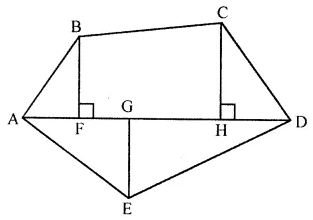
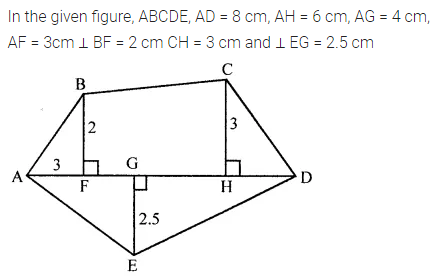
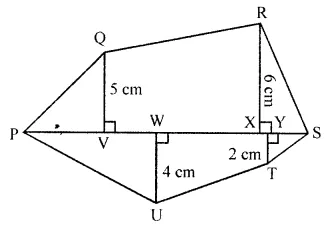
Find the area of the polygon given in the figure:
Solution:


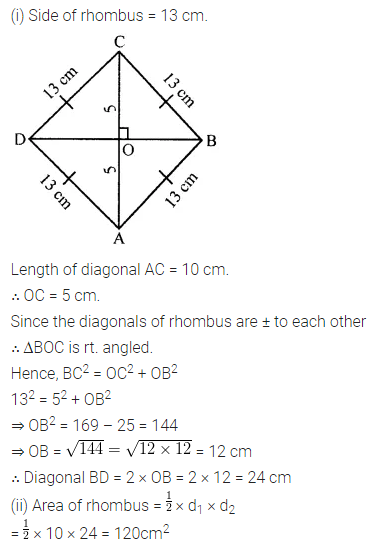
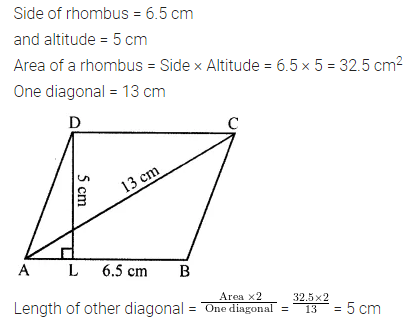
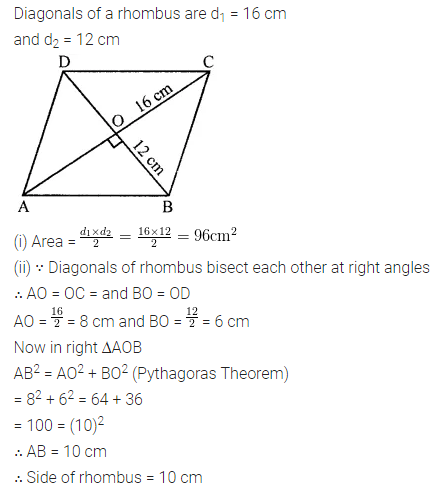
Question 9.
The diagonals of a rhombus are 16 m and 12 m, find:
(i) it’s area
(ii) length of a side
(iii) perimeter.
Solution:
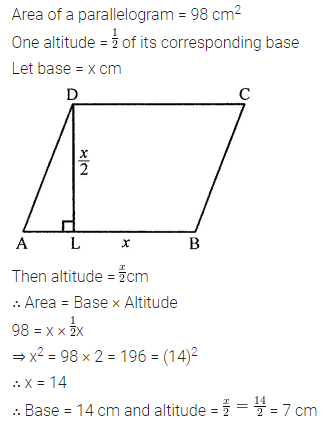
Question 10.
The area of a parallelogram is 98 cm2. If one altitude is half the corresponding base, determine the base and the altitude of the parallelogram.
Solution:
Question 11.
Preeti is painting the walls and ceiling of a hall whose dimensions are 18 m × 15 m × 5 m. From each can of paint 120 m2 of area is painted. How many cans of paint does she need to paint the hall?
Solution:

Question 12.
A rectangular paper is size 22 cm × 14 cm is rolled to form a cylinder of height 14 cm, find the volume of the cylinder. (Take π = \(\frac{22}{7}\))
Solution:

Question 13.
A closed rectangular wooden box has inner dimensions 90 cm by 80 cm by 70 cm. Compute its capacity and the area of the tin foil needed to line its inner surface.
Solution:

Question 14.
The lateral surface area of a cuboid is 224 cm2. Its height is 7 cm and the base is a square. Find
(i) side of the square base
(ii) the volume of the cuboid.
Solution:

Question 15.
The inner dimensions of a closed wooden box are 2 m by 1.2 m by 0.75 m. The thickness of the wood is 2.5 cm. Find the cost of wood required to make the box if 1 m3 of wood costs ₹5400.
Solution:

Question 16.
A car has a petrol tank 40 cm long, 28 cm wide and 25 cm deep. If the ful consumption of the car averages 13.5 km per litre, how far can the car travel with a full tank of petrol?
Solution:

Question 17.
The diameter of a garden roller is 1.4 m and it is 2 m long. How much area it will cover in 5 revolutions?
Solution:

Question 18.
The capacity of an open cylindrical tank is 2079 m3 and the diameter of its base is 21m. Find the cost of plastering its inner surface at ₹40 per square metre.
Solution:
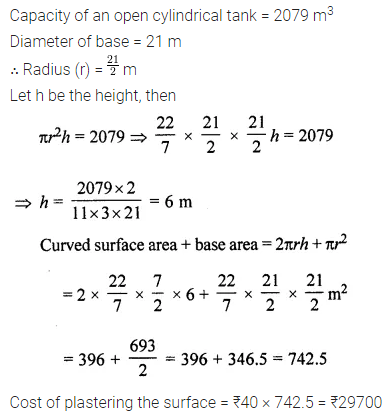
Question 19.
A solid right circular cylinder of height 1.21 m and diameter 28 cm is melted and recast into 7 equal solid cubes. Find the edge of each cube.
Solution:

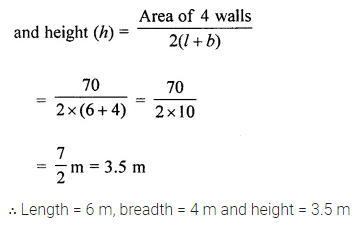
Question 20.
(i) How many cubic metres of soil must be dug out to make a well 20 m deep and 2 m in diameter?
(ii) If the inner curved surface of the well in part (i) above is to be plastered at the rate of ₹50 per m2, find the cost of plastering.
Solution: