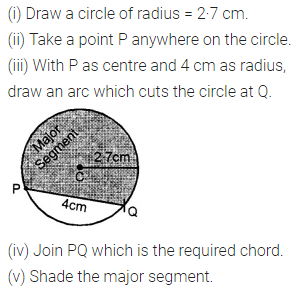
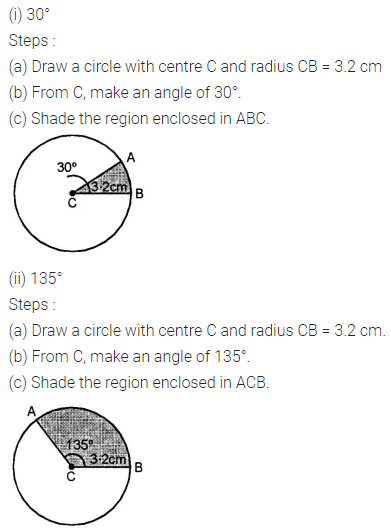
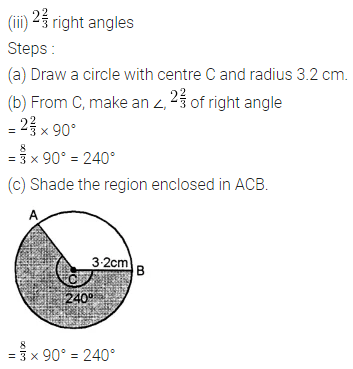
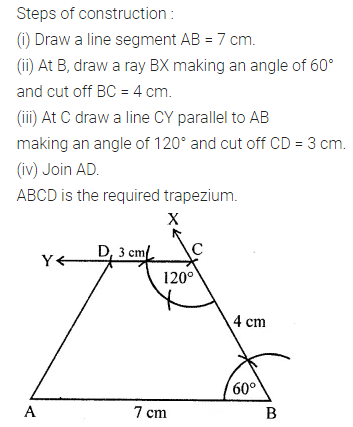
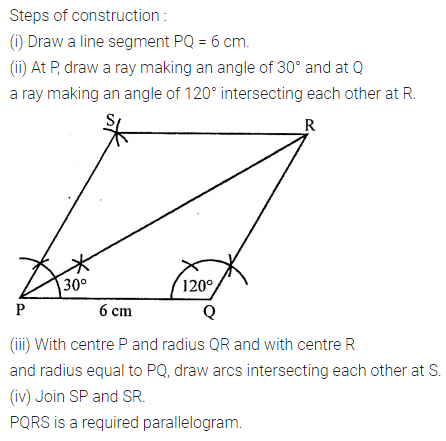
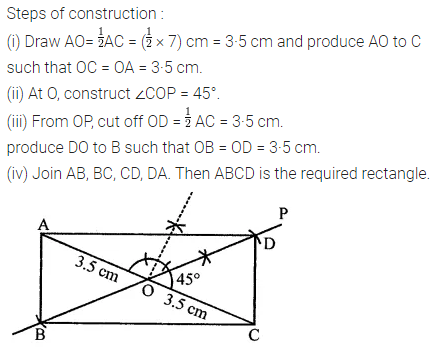
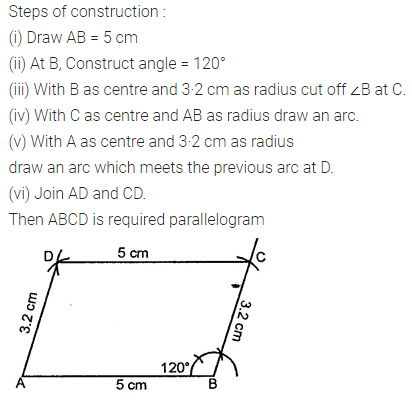
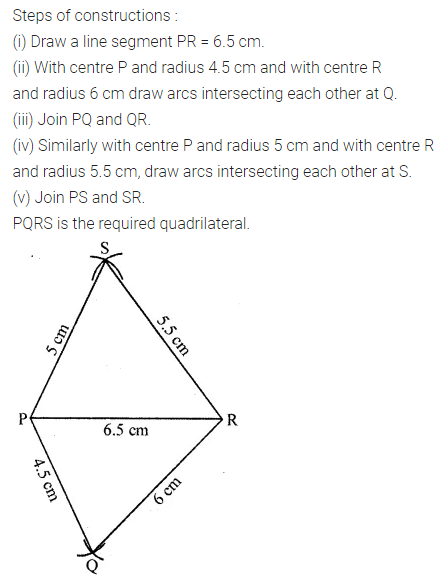
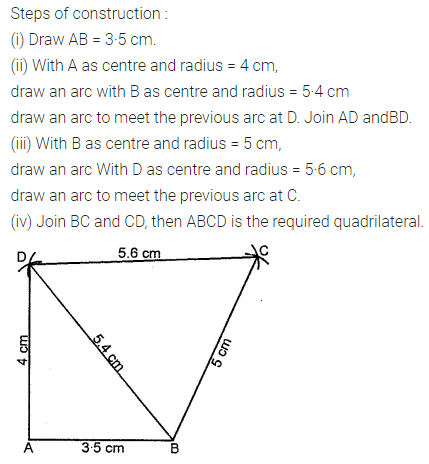
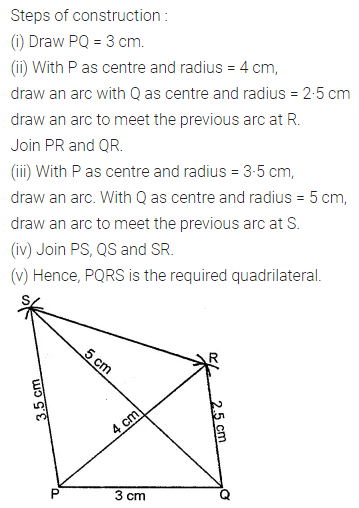
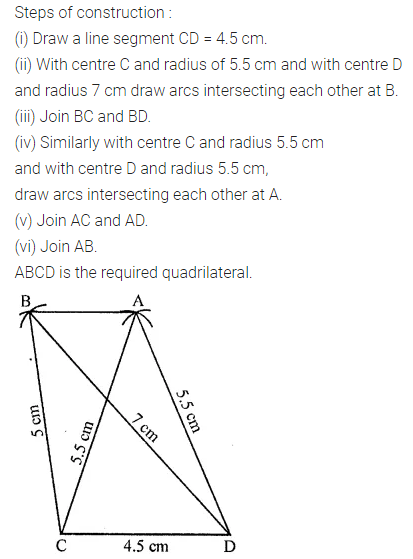
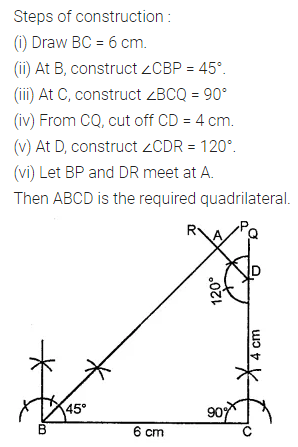
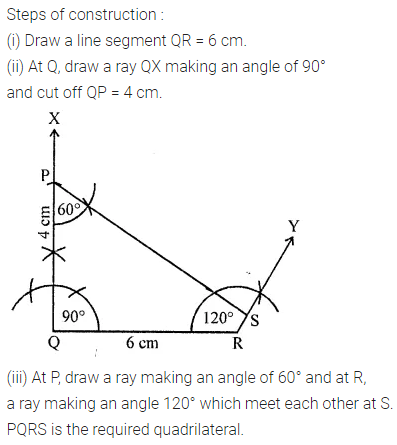
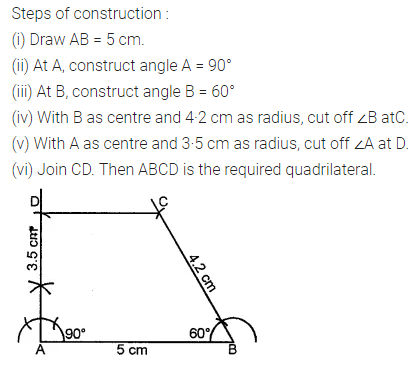
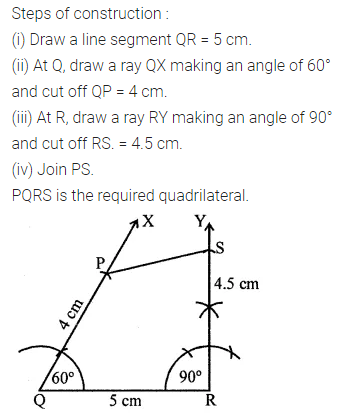
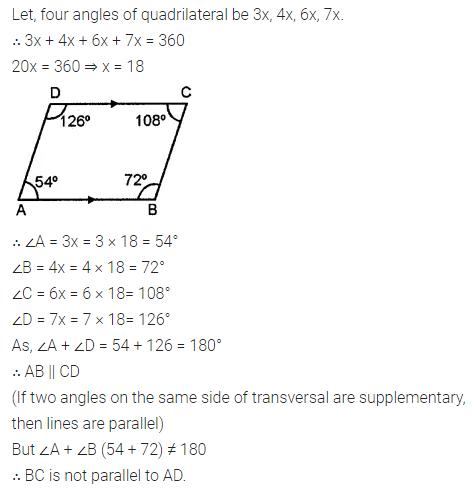
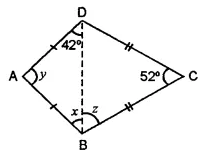
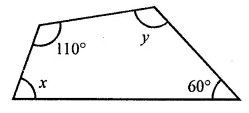
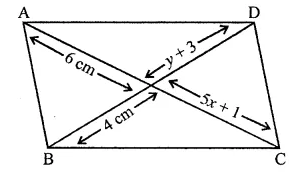
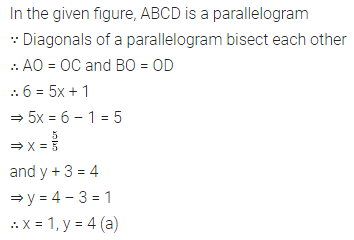
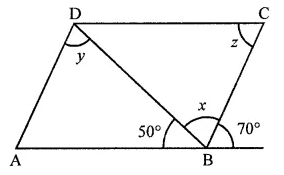
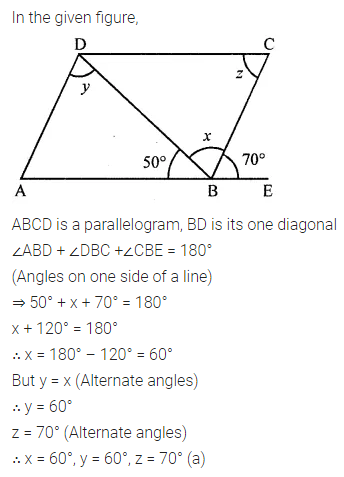
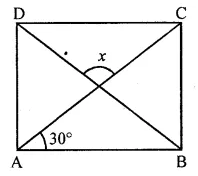
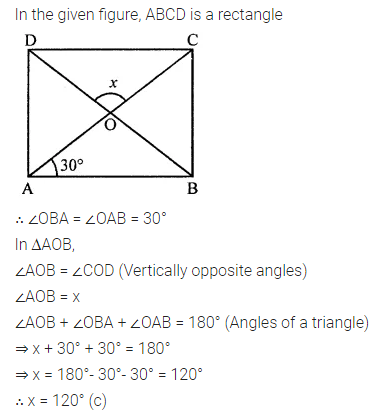
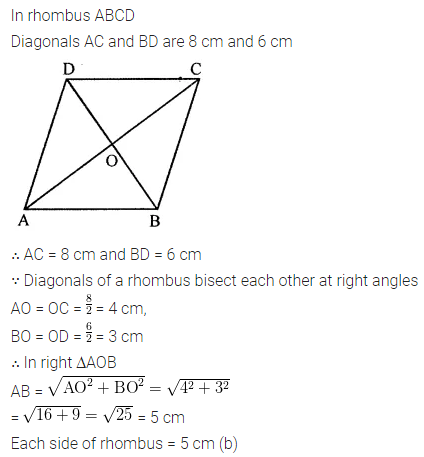
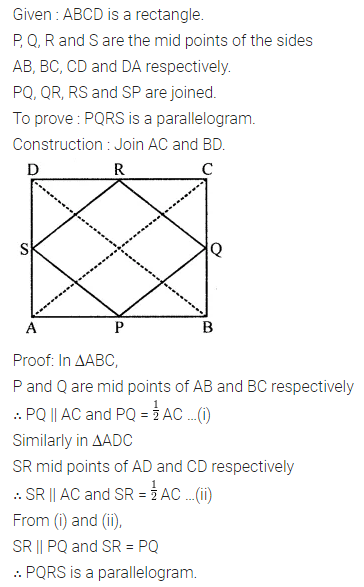
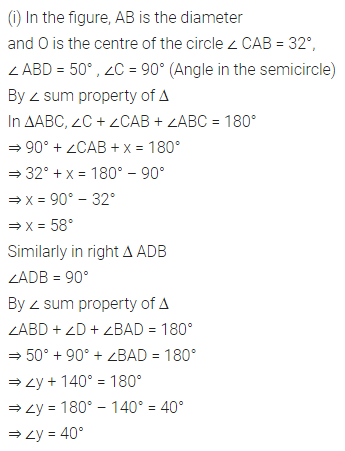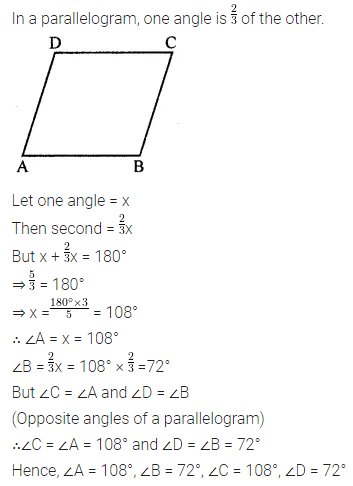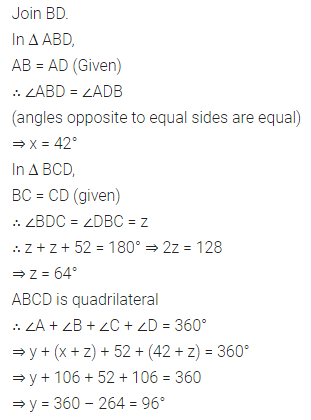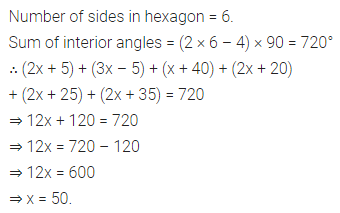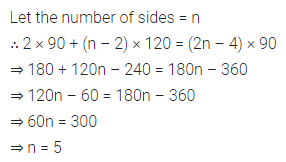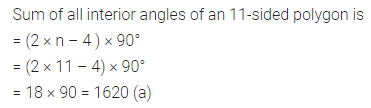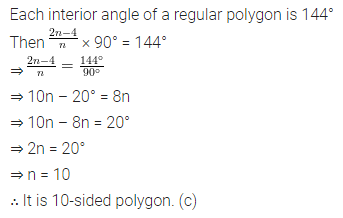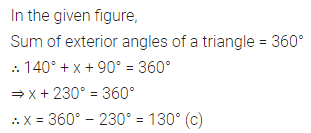ML Aggarwal Class 8 Solutions for ICSE Maths Chapter 16 Symmetry Reflection and Rotation
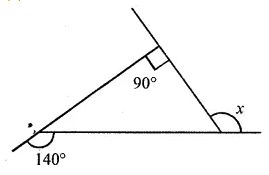
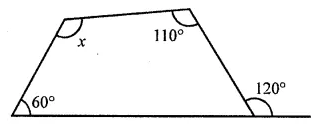
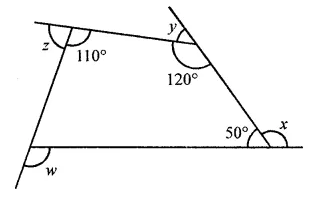
Question 1.
Draw the line or lines of symmetry, if any, of the following shapes and count their number:
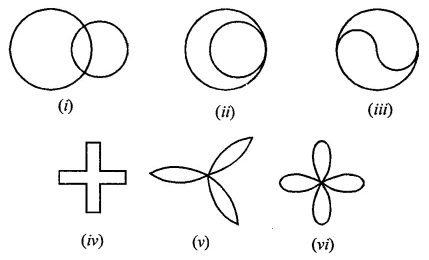
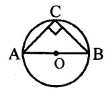
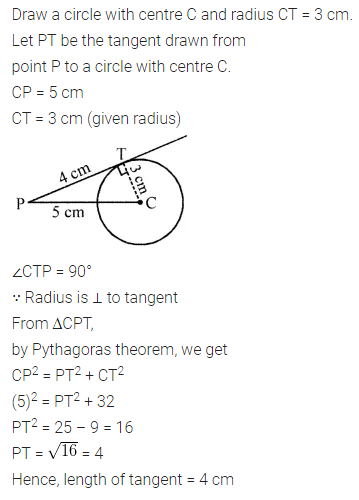
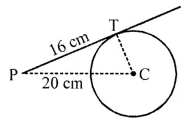
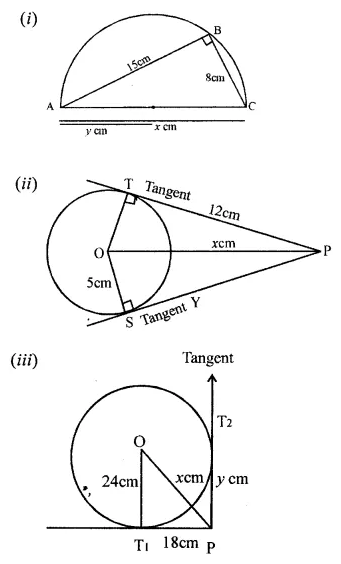
Solution:
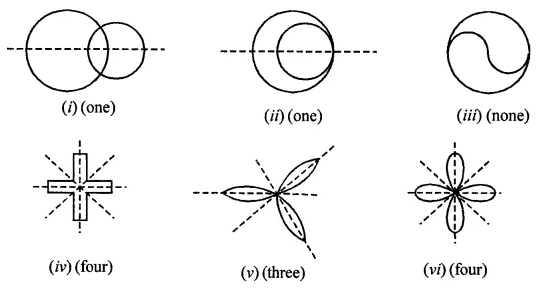
Question 2.
For each of the given shape in question 1, find the order of the rotational symmetry (if any).
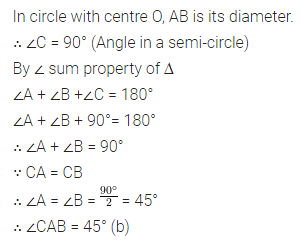
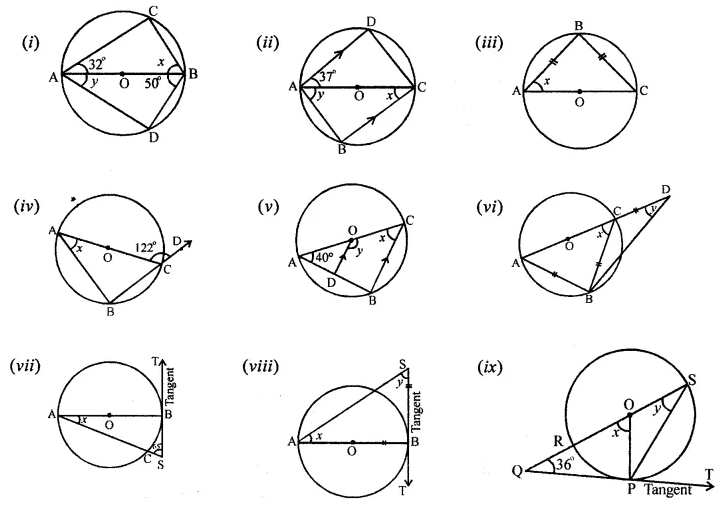
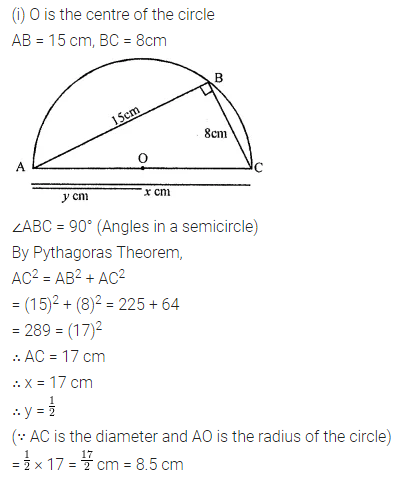
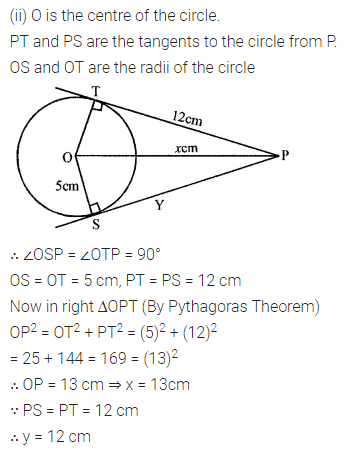
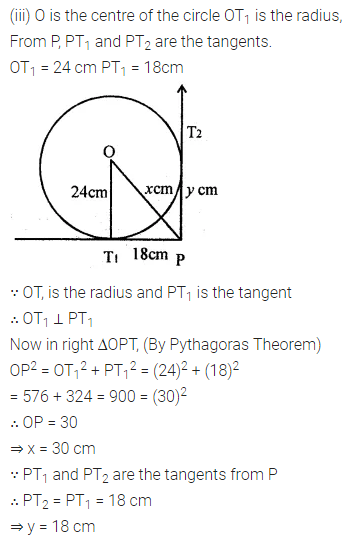
Solution:

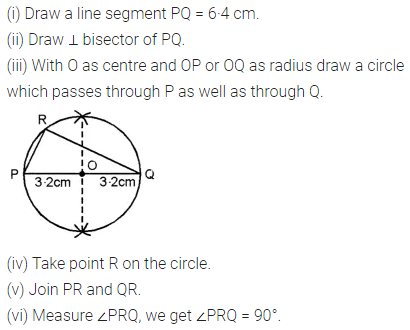
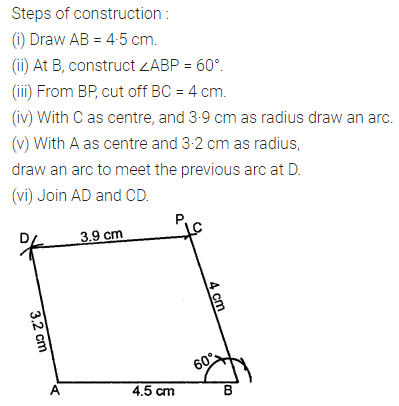
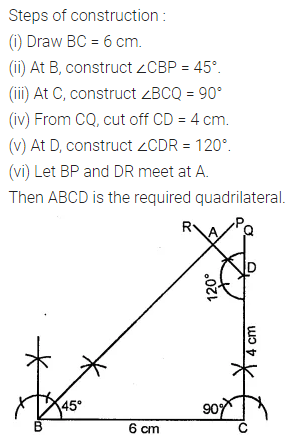
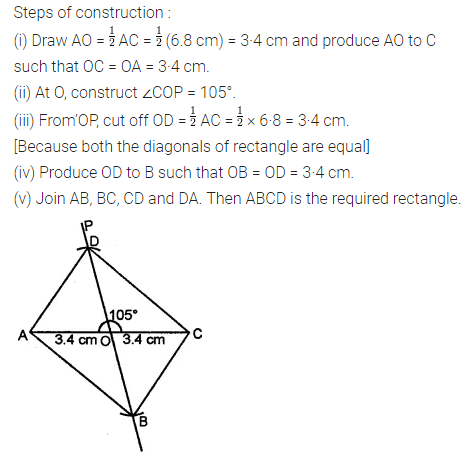
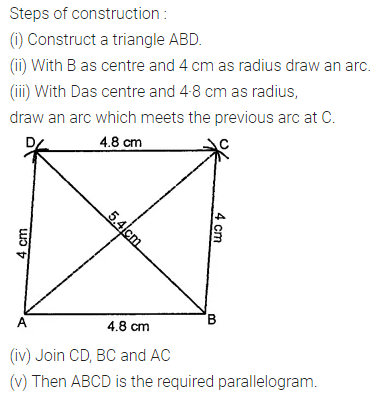
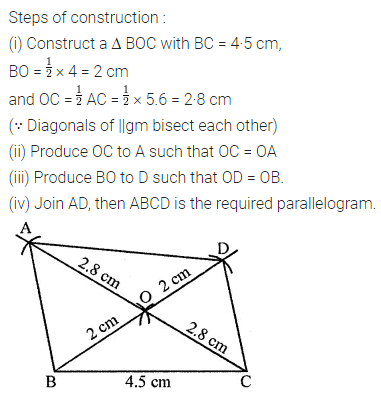
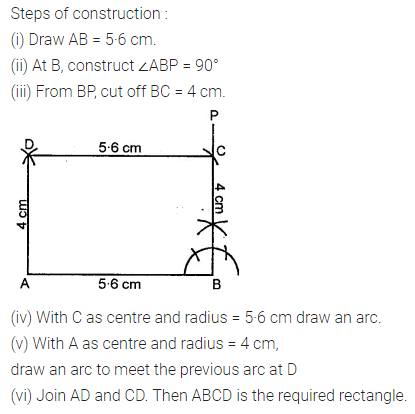
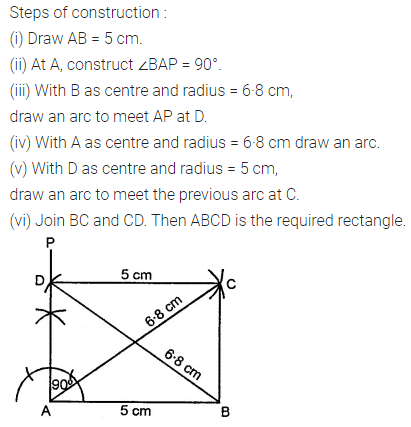
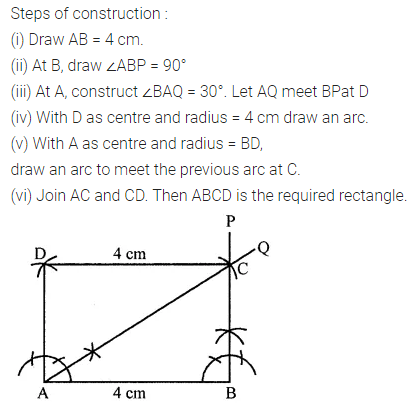
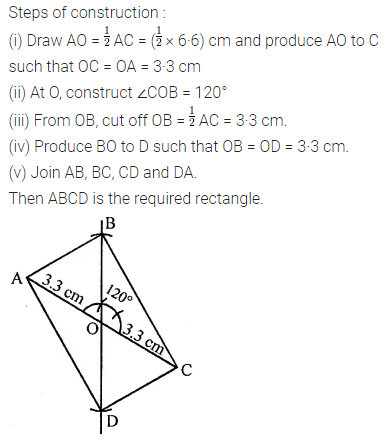
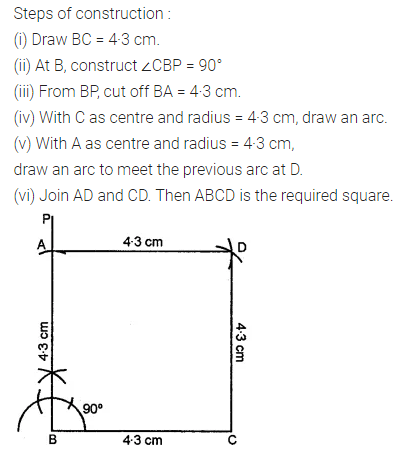
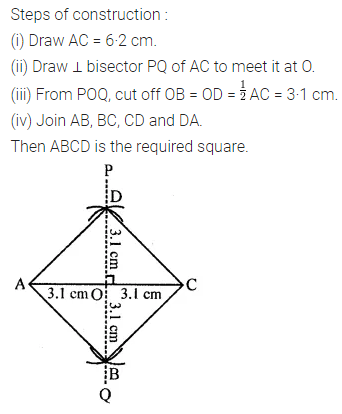
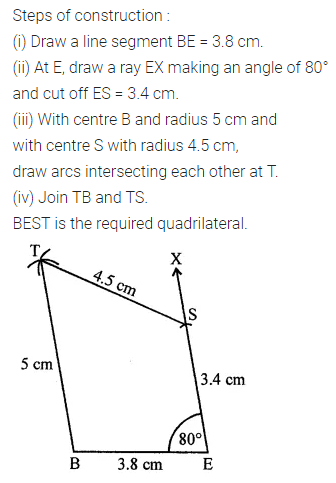
Question 3.
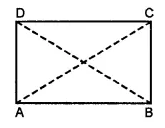
Construct a rectangle ABCD such that AB = 4.5 cm and BC = 3 cm. Draw its line (or lines) of symmetry.
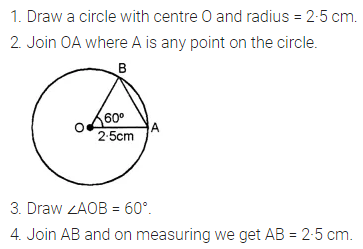
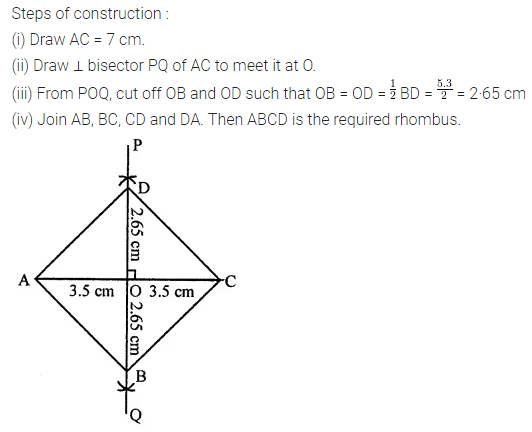
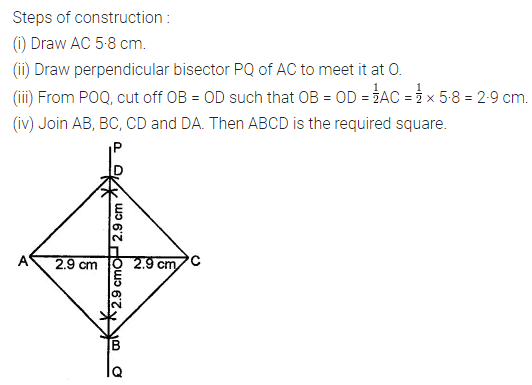
Solution:
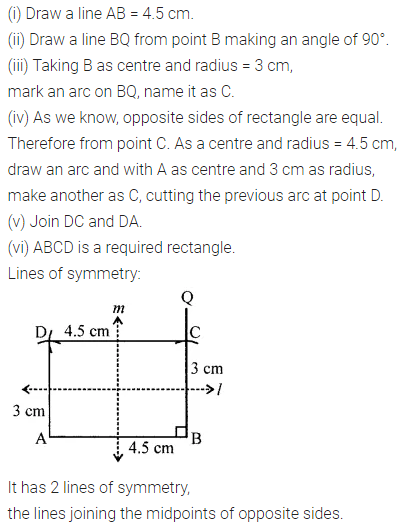
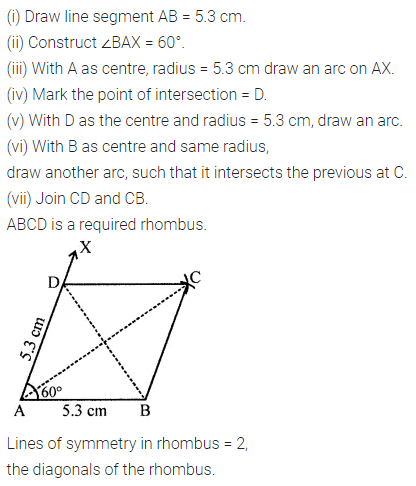
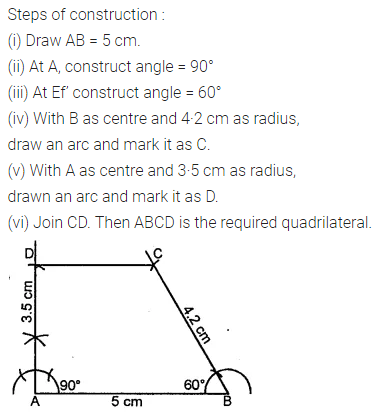
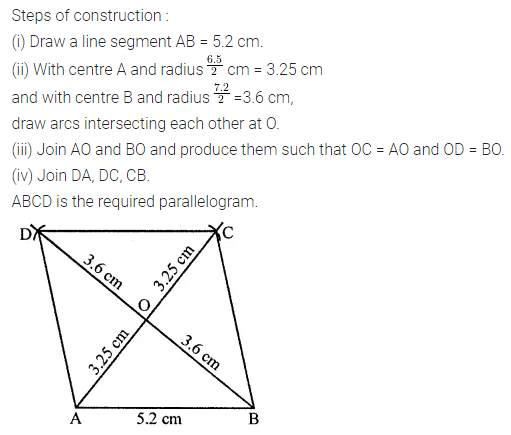
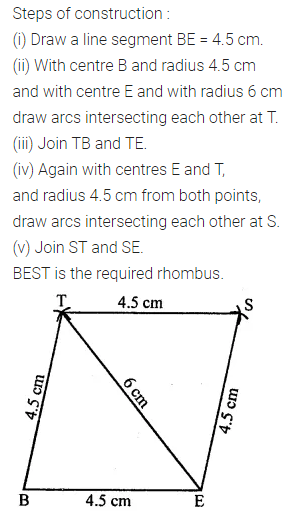
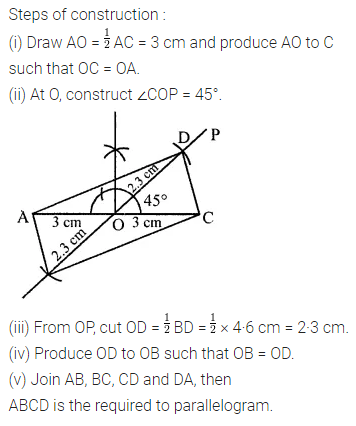
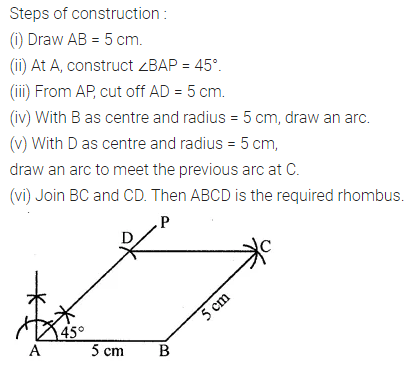
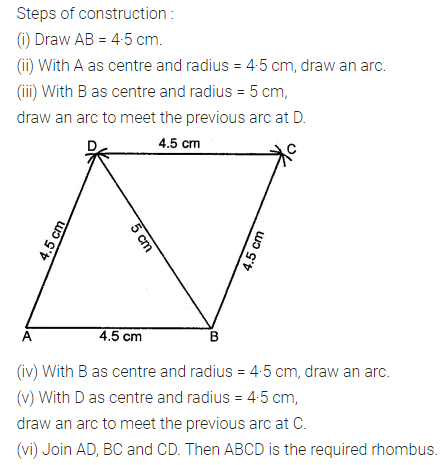
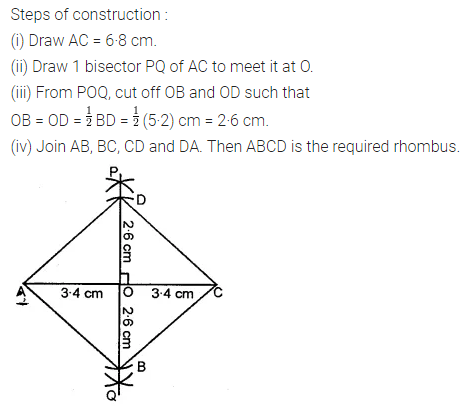
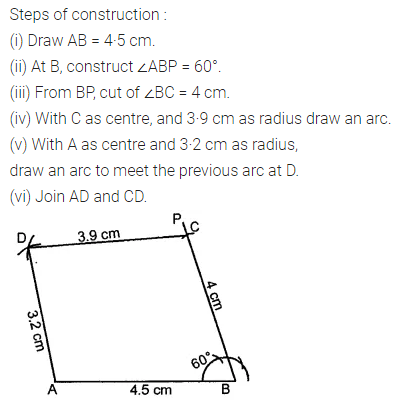
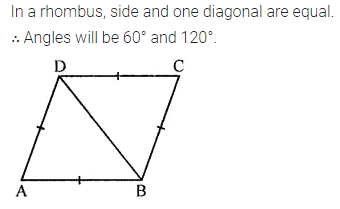
Question 4.
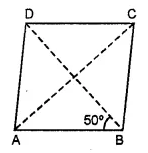
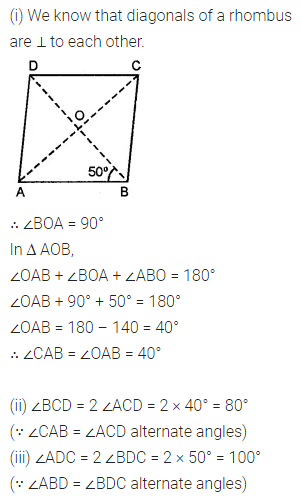
Construct a rhombus ABCD with AB = 5.3 cm and ∠A = 60°. Draw its line (or lines) of symmetry.
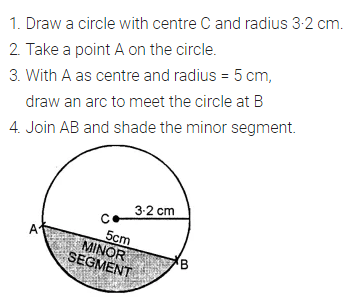
Solution: