Practical Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chemistry
Question 1.
Mention the temperature of the following in degree Celsius and Kelvin Scales
- Ice and ice cold water
- Boiling water and steam.
Answer:
- 6°C and 273K
- 100°C and 373K.
Question 2.
Rima took fine chalk powder, egg albumin, starch powder and alum powder in four test tubes. A, B, C and D respectively. After adding water to all the four test tubes, identify the test tubes as true solution, suspension and colloid. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Test tube A : Suspension; Test Tube B : Colloidal solution; Test Tube C : Colloidal solution; Test Tube D : True solution.
Question 3.
A student added water to sand and starch in different test tubes. How will you differentiate between the two on the basis of transparency ? (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
The solution of sand in water is a suspension and is opaque. On the other hand, the solution of starch in water is colloidal and is transleucent. This means that the light can pass partially through the second solution. (CBSE 2013)
Question 4.
List two precautions you must take while finding the melting point of ice.. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
- The bulb of the thermometer must not be dipping in ice. It must touch ice.
- The constant stirring must be done during the process of melting.
Question 5.
Dipti was asked to prepare four separate mixtures in four beakers A, B, C and D by mixing sugar, fine sand, thin paste of starch and chalk powder respectively in water and then categorise each as stable or unstable. What will be correct categorization ?
Answer:
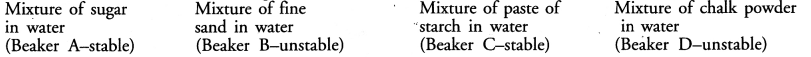
Question 6.
Identify two clear and transparent solutions from the following mixtures :
(a) Milk and water
(b) Sugar and water
(c) Starch powder and water
(d) Glucose and water.
(CBSE 2013)
Answer:
(b) Sugar and water
(d) Glucose and water.
Question 7.
In an experiment to determine the boiling point of water, state the reason for the following precautions :
- The bulb of the thermometer should not touch the sides of the beaker.
- While boiling water, pumice stone should be added. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
- The sides of the glass beaker are at higher temperature than the contents of the beaker. Therefore, the reading given by the thermometer touching the sides of the beaker does not give correct result.
- Pieces of pumice stone are added to boiling water in order to check any bumping.
Question 8.
Four students A, B, C and D were given funnels, filter paper, test tubes, test tube stands, common salt, chalk powder, starch and glucose powder. They prepared the true solution, suspension and colloidal solutions. Test tubes were arranged as shown in the figure. Observe the filtrate obtained in the test tubes and residue on filter paper. Conclude about filtrate residue and type of solution. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
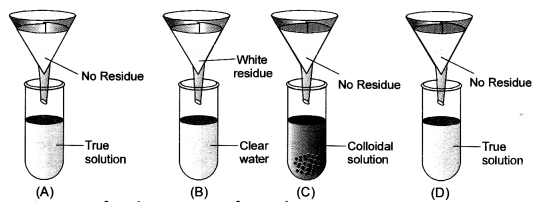
Question 9.
If in the determination of melting point of ice, the ice is contaminated with some non-volatile impurity like common salt, how is the melting point of ice affected ? (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
Melting point of ice gets lowered. Impurities always lower the melting point temperature of solid.
Question 10.
A mixture of sand, powdered glass and common salt is dissolved in water and then filtered. Name the substance left on the filter paper. Name the substance in the filtrate. (CBSE 2013, 2016)
Answer:
Sand and powdered glass are left as residue on the filter paper. Common salt (sodium chloride) solution in water constitutes the filtrate.
Question 11.
In an experiment to determine the boiling point of water, mention two important precautions. (CBSE 2013)
Answer:
- Constant stirring must be done so that heating may be uniform.
- Bulb of the thermometer must not dip in water.
Question 12.
Four students A, B, C and D are asked to prepare colloidal solutions. The following diagrams show the preparation done by them. Name the student who will be able to prepare colloidal solution. Write two properties of colloidal solutions. (CBSE 2014)
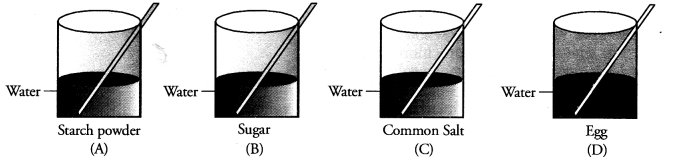
Answer:
Only student A’ has prepared the colloidal solution. Egg as such does not mix with water. Only white of an egg forms colloidal solution on stirring in water. Both sugar and common salt form true solution in water. The two properties of colloidal solution are :
- Colloidal solutions are of heterogeneous nature consisting of dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
- Colloidal solutions show Tyndall effect.
Question 13.
Rima took fine chalk powder, egg albumin, starch powder and alum powder in four test tubes A, B, C and D respectively. After adding water to all the four test tubes, identify the test tubes as true solution, suspension and colloid. (CBSE 2014)
Answer:
Test tube (A) contains a suspension
Test tube (B) contains a colloidal solution
Test tube (C) contains a colloidal solution
Test tube (D) contains a true solution.
Question 14.
What is a suspension ? Give two characteristics of suspension ? (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
A suspension may be defined as a heterogeneous mixture in which the solid particles are spread throughout the liquid without dissolving in it. They settle as precipitate if the suspension is left undisturbed for sometime.
Two characteristics:
- A suspension is of heterogeneous nature. There, are two phases. The solid particles represent one phase while the liquid in which these are suspended or distributed forms the other phase.
- The particle size in a suspension is more than 100 nm .
Question 15.
List two properties of a true solution. How would you prepare a true solution. List two different solutes which will form a true solution. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
- A true solution is always homogeneous in nature.
- A true solution is transparent in nature.
A true solution can be prepared by dissolving water soluble solute such as sugar/sodium chloride in water. Both sugar and sodium chloride form true solution when dissolved separately in water.
Question 16.
While doing an experiment to determine the melting point of ice, state the role of glass stirrer and mention the correct position of bulb of the thermometer. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
Stirring the contents of the beaker with a glass stirrer keeps the heating uniform. The position of the thermometer should be such the bulb is just touching the ice cubes.
Question 17.
Rima took fine chalk powder, egg albuminm starch powder and alum powder in four test tubes A, B, C and D respectively. After adding water to all the four test tubes, identify the test tubes as true solution, suspension and colloid. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
True solution is formed in test tube D. Test tube A contains suspension while colloidal solutions are formed in test tubes B and C.
Question 18.
While determining the melting point of ice, it was observed that even when ice cubes were being moderately heated using the gas burner, the temperature did not rise for sometime till the whole ice melted. Give the possible reason. (CBSE 2015)
Answer:
Once the melting of ice, starts upon heating with the help of a gas burner, the temperature becomes constant till the entire ice melts to form water. In fact the heat energy now absorbed is used up to overcome the intermoleular foces or is used as latent heat of fusion. Therefore, the temperature does not rise.
Question 19.
In an experiment to verify the law of Conservation of Mass in a chemical reaction, four students A, B, C and D noted down the following observations for the difference in the mass of apparatus before and after the chemical reaction;
A – 4 g ; B- 8 g ; C – zero g ; D – 10 g
Which student has made the correct observation and why ?
Answer:
Student C has made the correct observation since according to the law, there is no change in mass of reactants and products taking part in a chemical reaction.
Question 20.
When 15g of copper sulphate react with 15g of sodium hydroxide, 20g of sodium sulphate along with copper hydroxide is formed. What is the mass of copper hydroxide formed ?
Answer:
The chemical reaction taking place is :
![]()
On the basis law of conservation of mass :
Mass of copper hydroxide (x) = (15 g + 15 g) – (20 g) = 10 g
Question 21.
To verify the law of conservation of mass in a chemical reaction, four students A, B, C and D perfomed the following chemical reactions in the school laboratory.
(A) Added zinc granules to dil hydrochloric acid
(B) Heated lead nitrate (solid) in a test tube
(C) Dipped Mg ribbon in copper sulphate solution
(D) Added barium chloride solution to sodium sulphate solution.
Which student according to you is likely to obtain the best results and why ?
Answer:
Student (D) is likely to obtain the best results because the reaction is completed immediately and a white precipitate is formed.
Question 22.
16.8 g of sodium hydrogen carbonate are added to 12.0 g of acetic acid. The residue left weighed 20.0 g. What is the mass of CO2 escaped in the reaction ?
Answer:
The chemical reaction taking place is :
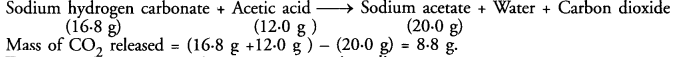
Mass of CO2 released = (16.8 g +12.0 g ) – (20.0 g) = 8.8 g.
Question 23.
While studying the properties of cathode rays in a discharge tube, a student placed a mica wheel mounted on an axle in the path of the rays. What would happen to the. wheel ? What conclusions can be drawn from it ? (CBSE 2016)
Answer:
The mica wheel would start rotating around the axle. This shows that the cathode rays are made of material particles (electrons).