Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions and marking scheme Set 1 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 1 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
(i) The question paper comprises four sections A, B, C and D. There are 36 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Section-A – question no. 1 to 20 – all questions and parts there of are of one mark each.
These questions contain multiple choice questions (MCQs), very short answer questions and assertion – reason type questions. Answers to these should be given in one word or one sentence.
(iii) Section-B – question no. 21 to 26 are short answer type questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
(iv) Section-C – question no. 27 to 33 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each.
Answers to these questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words. :
(v) Section—D – question no. – 34 to 36 are long answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
(vi) There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
(vii) Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
Section – A
Question 1.
A women gave birth to a girl. Name the chromosome from sperm responsible for the offspring.
Answer:
Sperm with X chromosome from male is responsible for the birth of female and Y chromosome would be responsible for the male offspring. So for the given case, X chromosome from sperm is responsible for the offspring.
Question 2.
Name the gases which have replaced CFCs.
Answer:
- HFCs (Hydrofluorocarbons)
- Perfluorocarbons (PFCs) have replaced CFCs.
Question 3.
When calcium oxide is added to water, it completely dissolves in water without forming bubbles. What product is formed in this reaction?
Answer:
Ca(OH)2
Question 4.
A plant gets rid of excess water through transpiration. What is the method used by plants to get rid of solid waste products?
Answer:
Shedding of yellow leaves
Question 5.
In peas, a pure tall plant (TT) is crossed with a short plant (tt). What is the ratio of pure tall plants to short plants in F2?
Answer:
3 : 1
Question 6.
State the direction of magnetic field in the following case.
Answer:
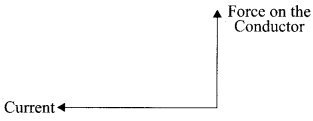
Perpendicular to the plane of paper in the outward direction by using Fleming’s left hand rule.
Question 7.
Why covalent compounds have low melting and boiling points?
OR
What is catenation?
Answer:
As the bond is formed by sharing of electrons between two atoms. Intermolecular forces are small between the covalent compounds. These bonds break easily.
OR
Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with the other atoms of carbon which gives rise to large molecules. This property of self linking is called catenation.
Question 8.
What is the formula of oxide and hydride of Group I elements?
OR
What are isotopes?
Answer:
Oxide formula → R2O; Hydride formula → RH.
‘R’ represents Group I element. F-31
OR
Isotopes are the atoms of same element having same atomic number but different mass number.
![]()
Question 9.
Why are the rings of cartilage present in air tube—Trachea?
OR
In what form is food energy stored in plants and animals?
Answer:
Rings of cartilage prevents the trachea from collapsing.
OR
Plants—Starch; Animals—Glycogen.
Question 10.
List two functions performed by the testis in human beings.
OR
What happens when a mature spirogyra filament attains considerable length?
Answer:
- To produce sperms
- To produce male sex hormone/testosterone
OR
Its filament breaks up into smaller fragments or pieces, and each fragment grows into a new filament/individual.
Question 11.
Name two human traits that show variations.
OR
How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival?
Answer:
Colours of eyes and shape of external ears.
OR
Variations increases the adaptability of an organism to its changing environmental conditions.
Question 12.
What is silvering of mirror?
Answer:
Silvering of mirror means coating the surface of mirror with a thin layer of silver, aluminium or some other shiny, opaque material.
Question 13.
Write the two raw materials for making food, used by living organisms of first tropic level.
Answer:
CO2 and Water
Assertion (A) and Reason (R)
For question numbers 14,15 and 16, two statements are given- one labeled Assertion (A) and the other labeled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) as given below:
(i) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(ii) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(iii) A is true, but R is false.
(iv) A is false, but R is true.
Question 14.
A. Magnetic field lines have both direction and magnitude.
R. The field lines, emerge from the north pole and merge at south pole
OR
A. Compass is a small magnet and gives direction of magnetic field lines.
R. It gets deflected when brought near a bar magnet.
Answer:
(ii) OR (i)
Question 15.
A. Copper does not displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
R. Copper is less reactive than hydrogen.
Answer:
(i)
Question 16.
A. When two resistances of 4 Ω are connected in parallel total resistance is 2 Ω.
R. When two resistances of 4 Ω are connected in series total resistance is 8 Ω.
Answer:
(ii)
Answer Q. No 17 – 20 contain five sub-parts each. You are expected to answer any four subparts in these questions.
Question 17.
Read the following and answer any four questions from 17 (i) to 17 (v) (4 × 1 = 4)
The table below shows the results of different experiment conducted on two acids X and Y of equal concentration:
| X | Y | |
| Conductivity of Solution | 400 S m1 | 7.0 S m1 |
| Temperature change when excess acid reacted with 100 mL of 1.0 M NaOH solution | 6.9°C | 6.7°C |
| Reaction with Mg | Hydrogen gas is produced rapidly with rapid effervescence | Hydrogen gas is produced slowly with gradual effervescence |
(i) Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) X is stronger acid because it has higher conductivity.
(b) Y is stronger acid because hydrogen is produced slowly when reacts with Mg.
(c) X is weaker acid because temperature change is higher when reacts with NaOH.
(d) Y is weaker acid because is has higher conductivity.
Answer:
(a) X is stronger acid because it has higher conductivity.
(ii) Select the correct relation from the following:
(a) (H+) x < (H+)y
(b) (pH) x < (pH)Y
(c) (H+) x = (H+)Y
(d) (PH) y > 7
Answer:
(b) (pH) x < (pH)Y
(iii) What will be colour of universal indicator in ‘X’?
(a) Blue
(b) Orange
(c) Green
(d) Red
Answer:
(d) Red
(iv) How many moles of H2 gas will be liberated by ‘X’ and ‘Y’ during reaction with 1 mole of Mg?
(a) 1/2
(b) 1/4
(c) 2
(d) 1
Answer:
(d) 1
(v) The gas formed when X and Y reacts with a metal carbonate is:
(a) Hydrogen
(b) Hydrogen Sulphide
(c) Oxygen
(d) Carbon dioxide
Answer:
(d) Carbon dioxide
Question 18.
Read the following and answer any four questions from 18 (i) to 18 (v) (4 × 1 = 4)
Answer:
Ohm’s law gives the relationship between current flowing through a conductor with potential difference across it provided the physical conditions and temperature remains constant. The electric current flowing in a circuit can be measured by an ammeter.
Potential difference is measured by voltmeter connected in parallel to the battery or cell. Resistances can reduce current in the circuit. A variable resistor or rheostat is used to vary the current in the circuit.
(i) Graphs between electric current and potential difference across two conductors A and B are shown in the figure. Which of the following conductor has more resistance?
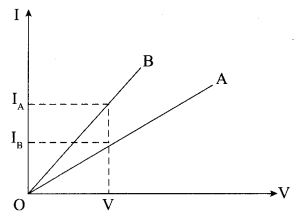
(a) B
(b) A
(c) Both have equal resistance
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) A
(ii) Seven identical lamps of resistance 220 Ω each are connected to a 220 V line as shown in figure. Then reading of the ammeter will be:
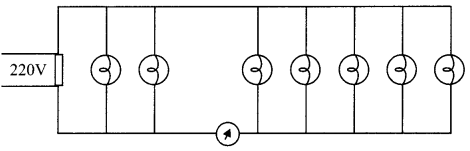
(a) \(\frac{1}{10} \mathrm{~A}\)
(b) \(\frac{2}{5} \mathrm{~A}\)
(c) \(\frac{3}{10} \mathrm{~A}\)
(d) None of there
Answer:
(d) None of there
(iii) For metallic conductor voltage uses current graph is shown at two different temperatures T1 and T2. From the graph it follows:
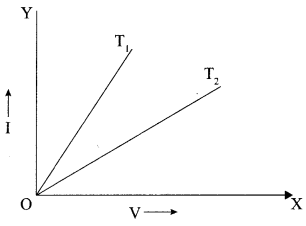
(a) T1 = T2
(b) T1 > T2
(c) T1 < T2
(d) None of above
Answer:
(c) T1 < T2
(iv) If the resistance of wire A is four times resistance of wire B then the ratio of cross sectional areas of wires is
(a) 1:2
(b) 1:4
(c) 1:8
(d) 1:6
Answer:
(b) 1:4
(v) Ohm’s law is valid only when
(a) Temperature increases
(b) Temperature decreases
(c) Graph between V and I is a straight line
(d) Pressure remains constant.
Answer:
(c) Graph between V and I is a straight line
Question 19.
Read the following and answer any four questions from 19 (i) to 19 (v) (4 × 1 = 4)
Answer:
A student took HC1 in a conical flask and was placed on a white tile with cross mark. When seen through the flask the mark was visible. On adding some sodium thiosulphate in the flask the cross marked disappeared when seen through the flask. The student observed some reaction as
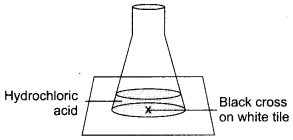
(i) Name the type of reaction seen in the setup.
(a) Redox reaction
(b) Precipitation reaction
(c) Displacement reaction
(d) Double displacement reaction
Answer:
(b) Precipitation reaction
(ii) Why did the cross mark disappear?
(a) The insoluble precipitate that is formed in the flask does not allow the light to pass through it to see the cross mark.
(b) The resultant solution is dark coloured which does not allow the light to pass through it.
(c) The resultant solution has high viscosity due to which it refracts the light to other angle.
(d) The solution so formed has ability to absorb black colour hence black coloured cross is not seen.
Answer:
(a) The insoluble precipitate that is formed in the flask does not allow the light to pass through it to see the cross mark.
(iii) Give the chemical formula of the gas formed in the reaction.
(a) SO2
(b) SO3
(c) O2
(d) Cl2
Answer:
(a) SO2
(iv) Name the resultant insoluble substance formed in the flask.
(a) Sodium sulphide
(b) Sodium sulphate
(c) Sodium sulphite
(d) Sulphur
Answer:
(d) Sulphur
(v) Which of the following reaction is of similar type as observed in the given set up.
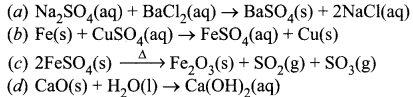
Answer:
(a)
Question 20.
Read the following and answer any four questions from 20 (i) to 20 (v) (4 × 1 = 4)
Answer:
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image distance (v) with object distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow, without doing any calculations:
| S. No. | Object distance u (cm) | Image distance v (cm) |
| 1 | -90 | + 18 |
| 2 | -60 | + 20 |
| 3 | -30 | + 30 |
| 4 | -20 | + 60 |
| 5 | -18 | + 90 |
| 6 | -10 | + 100 |
(i) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason in support of your answer.
(a) -10
(b) +10
(c) -15
(d) +15
(ii) Write the serial number of that observation which is not correct.
(a) S.No. 1
(b) S.No. 4
(c) S.No. 3
(d) S.No. 6
(iii) The approximate value of magnification in case of S.No. 4 is
(a) -2
(b) -3
(c) +3
(d) +2
(iv) The image formed in case of S.No. 2 is
(a) virtual and enlarged
(b) virtual and diminished
(c) real and diminished
(d) real and enlarged
(v) If a convex lens is used to focus sunlight on a paper, where the paper should be placed so that it catches fire.
(a) At centre of curvature
(b) At principal focus.
(c) At optical centre of lens
(d) At 25 cm away from lens
Answer:
(i) (d) From S.No.3 we can say that the radius of curvature of the lens is 30 cm because when an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a convex lens its image is formed on the other side of the lens at the same distance from the lens. And, we also know that focal length is half of the radius of curvature. Thus, focal length of the lens is + 15 cm.
(ii) (d) S.No.6 is not correct as the object distance is between focus and pole, so for such cases the image formed is always virtual but in this case it is written that a real image is formed as the image distance is positive.
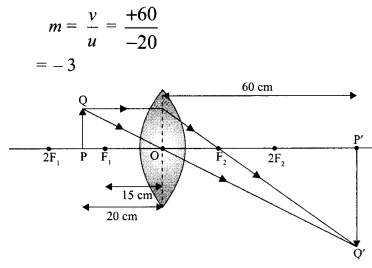
(iii) \(\text { (b) } m=\frac{v}{u}=\frac{+60}{-20}=-3\)
(iv) (c)
(v) (b)
Section-B
Question 21.
A 5 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principal axis of a convex lens of focal length 18 cm at a distance of 12 cm from it. Use lens formula to determine the position, size and nature of image formed.
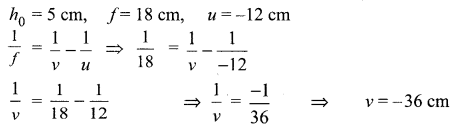
The image formed is on the same side as the object, at a distance of 36 cm from the optical centre. The -ve sign shows that the image is virtual.
\(m=\frac{h_{i}}{h_{o}}=\frac{v}{u}=\frac{-36}{-12}=3\)
h0 – 5 cm, then hi = 3 x 5 = 15 cm The image is three times larger than the size of the object.
Question 22.
How is bleaching powder prepared? Give its chemical equation and write its two uses.
OR
A white coloured powder is used by doctors for supporting fractured bones.
(i) Write chemical name and formula of the powder
(ii) When this white powder is mixed with water a hard solid mass is obtained. Write balanced chemical equation for the change.
Answer:
Preparation: On passing chlorine gas through a test tube containing dry slaked lime Ca(OH)2, bleaching powder is prepared.
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
Uses:
(i) It is used as. bleaching agent in textile industry and paper factories.
(ii) It is used as an oxidising agent in many industries.
OR
(i) Calcium sulphate hemihydrate, \(\mathrm{CaSO}_{4} \cdot \frac{1}{2} \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)
(ii) \(\mathrm{CaSO}_{4} \cdot \frac{1}{2} \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\frac{3}{2} \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{CaSO}_{4} \cdot 2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)
Question 23.
(i) Choose the amphoteric oxides from the following oxides.
Na2O, ZnO, Al2O3, CO2, H2O.
(ii) Why is it that non-metals do not displace hydrogen from dilute acids?
Answer:
(i) Al2O3, H2O and ZnO are amphoteric oxides.
(ii) Non-metals cannot loose electrons so that H+ ions from acids become hydrogen gas and thus, cannot be displaced.
Question 24.
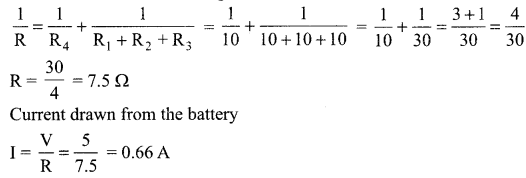
Find the current drawn from the battery by the network of four resistors shown in the figure.
Answer:
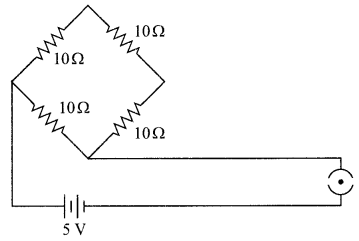
Equivalent resistance of the given network is
Question 25.
An element ‘E’ has following electronic configuration:
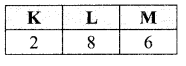
(i) To which group of the periodic table does element ‘E’ belong?
(ii) To which period of the periodic table does element ‘E’ belong?
(iii) State the number of valence electrons present in element ‘E’
(iv) State the valency of the element ‘E’
Answer:
(i) ‘E’ belongs to group 16
(ii) It belongs to 3rd period
(iii) It has 6 valence electrons
(iv) Its valency is equal to 2
Question 26.
Why is respiration considered as exothermic reaction? Explain.
OR
(i) Hydrogen being a highly inflammable gas and oxygen being a supporter of combustion, yet water which is a compound made up of hydrogen and oxygen is used to extinguish fire. Why?
(ii) What change in colour is observed when silver chloride is left exposed to sunlight? What type of chemical reaction is this?
Answer:
In respiration, glucose gets oxidized to form carbon dioxide, water and heat is evolved.
As heat energy is released during respiration it is regarded as an exothermic reaction.
OR
(i) It is because properties of compound (H2O) are different from properties of its constituting elements, i.e., H2 and O2.
(ii) Silver turns black, the reaction is decomposition.
Section – C
Question 27.
Leaves of healthy potted plants were coated with vaseline to block the stomata. Will this plant remain healthy for long? State 3 reasons for your answer.
Answer:
No, this plant will not stay healthy for long. The plant will start dying because:
- Stomata gets blocked and no exchange of gases takes place.
- No intake of CO2 for photosynthesis and O2 for respiration.
- No transpiration and hence water transportation will be affected.
Question 28.
Describe briefly the three ways in which individual with a particular trait may increase in population.
Answer:
- Variation helps in survival of individuals.
- Sexual reproduction results in variation.
- Adaptation and natural selection.
Question 29.
How do Mendel’s experiments show that traits may be dominant or recessive?
Answer:
Mendel conducted a monohybrid cross with pea plants, and he observed that one of the contrasting characters disappears in F1 generation. This character reappears in F2 generation (obtained by selfing F1) in just 25% of the progeny.
Mendel conclude that the character which expresses itself in F1 is the dominant character while the other one which is not able to express in F1 individuals is recessive character. This recessive character is able to express only in its pure form i.e. in 25% of F2 individuals.
Question 30.
Study the given flow chart and answer the below given questions.
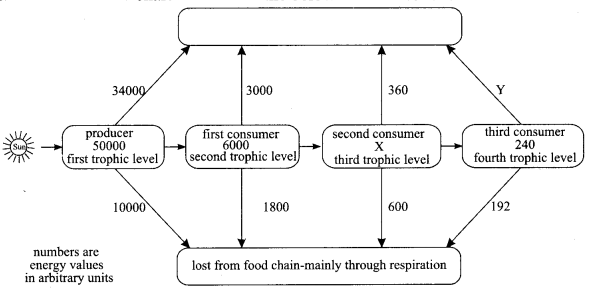
(i)
(a) Which form of the Sun’s energy is trapped by the producer?
(b) Into which energy form is the Sun’s energy converted when it is trapped by the producer?
(ii)
(a) Calculate X in the flow chart.
(b) Calculate Y on the flow chart.
(c) Label the above box on flow chart.
Answer:
(i)
(a) Light (or solar) energy
(b) Chemical energy
(ii)
(a) 1200 units
(b) 48 units
(c) Decomposers like bacteria or fungi.
Question 31.
Samples of four metals A,B, C and D were taken and added to the following solutions one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated as follows.
| Metal | Iron (II) sulphate | Copper (II) sulphate | Zinc sulphate | Silver nitrate |
| A | No reaction | Displacement | — | — |
| B | Displacement | — | No reaction | — |
| C | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | Displacement |
| D | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction |
Use the table above to answer the following questions about metals A, B, C and D.
(i) Which is the most reactive metal?
(ii) What would you observe if B is added to a solution of copper (II) sulphate?
(iii) Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity.
Answer:
(i) B is most reactive.
(ii) Blue colour of copper sulphate solution disappears and reddish brown copper metal is deposited on the metal B.
(iii) B > A > C > D is the order of reactivity.
Question 32.
Foetus derives its nutrition from the mother.
(i) Identify the tissue used for above purpose. Explain its structure.
(ii) Explain how wastes generated by developing embryo are removed.
(iii) How does the birth of child take place?
Answer:
(i) Placenta is a special tissue connection between embryo and uterine wall. It acts as an endocrine gland. It possesses villi that increases the surface area for absorption of nutrients. Facilitates passage of nutrition and oxygen to embryo from mother through blood.
(ii) Waste substances produced by embryo are removed through placenta into mother’s blood.
(iii) Birth of child takes place after the gestation period (9 months inside the womb of mother). When the pain in the uterine walls is at highest then the birth of child takes place by the birth canal.
Question 33.
(i) Show the formation of Na2O by transfer of electrons between the combining atoms.
(ii) Why are ionic compounds usually hard?
(iii) How is it that ionic compounds in the solid state do not conduct electricity, but they do so when in molten state?
OR
(i) Which product is formed in the chemical reaction between a small strip of magnesium and nitric acid?
(ii) What happens when a pellet of sodium is dropped in water?
(iii) Identify the ‘X’ in the given reaction: P4(s) + SO2(g) → X
Answer:
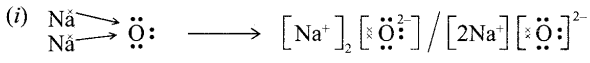
(ii) Ionic compounds are hard due to strong force of attraction between oppositely charged i0ns.
(iii) In solid-state, ions are not free to move, whereas in molten state ions are free to move. Therefore, they conduct electricity in a molten state.
OR
(i) Mg(NO3)2 and 2H2
(ii) It catches fire and forms sodium hydroxide
(iii) P4O10(s)
Section-D
Question 34.
(i) Write the functions of the following parts in human female reproductive system:
(a) Ovary
(b) Oviduct
(c) Uterus
(ii) Describe the structure and function of placenta.
OR
What is binary fission in organisms? With the help of suitable diagrams, describe the mode of reproduction in amoeba.
Answer:
(i) (a) Ovary –
• Production of female hormone
• Production of female gamete
(b) Oviduct –
• Transfer of female gamete from the ovary
• Site of fertilization
(c) Uterus –
• Implantation of the zygote
• Nourishment of the developing embryo/placenta formation.
(ii) Structure of Placenta: It is a disc-like structure embedded in the uterine wall, connected to the embryo. It has villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue and on the mother side it has blood spaces, which surround the villi.
(iii) (a) Circuit diagram
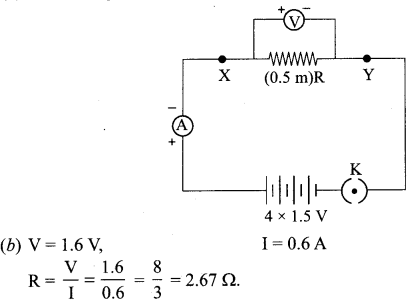
| V | I = V/R | V/I |
| 0.8 V | 0.8/2.67 = 0.30 | 8/3 |
| 1.2 V | 1.2/2.67 = 0.45 | 8/3 |
| 1.6 V | 1.6/2.67 = 0.60 | 8/3 |
Conclusion: ‘R’ is constant at given temperature. VI graph shows straight line.
Question 36.
(i) A thin converging lens forms a
(a) Real magnified image.
(b) Virtual magnified image of an object place in front of it.
Write the positions of the object in each case.
(ii) Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the image formation in each case.
(iii) How will the following be affected on cutting this lens into two halves along the principal axis?
(a) Focal length
(b) Intensity of image formed by half lens.
OR
Analyse the following observation table showing variation of image distance (v) with object distance (u) in case of a convex lens and answer the questions that follow, without doing any calculations:
| S.No. | Object distance u (cm) | Image distance v (cm) |
| 1 | -90 | + 18 |
| 2 | -60 | + 20 |
| 3 | -30 | + 30 |
| 4 | -20 | + 60 |
| 5 | – 18 | + 90 |
| 6 | – 10 | + 100 |
(i) What is the focal length of the convex lens? Give reason in support of your answer.
(ii) Write the serial number of that observation which is not correct. How did you arrive at this conclusion?
(iii) Take an appropriate scale to draw a ray diagram for the observation at S. No. 4 and find the approximate value of magnification.
Answer:
(i) (a) When the object is placed between ‘F’ and ‘2F’
(b) When the object is placed between pole ‘P’ and ‘F’
(ii)
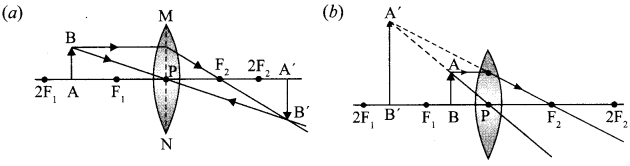
(iii) No, focal length will remain the same because radius of curvature remains the same. Therefore, intensity of the image will decrease.
OR
(i) From S.No.3 we can say that the radius of curvature of the lens is 30 cm because when an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a convex lens its image is formed on the other side of the lens at the same distance from the lens. And, we also know that focal length is half of the radius of curvature. Thus, focal length of the lens is + 15 cm.
(ii) S.No.6 is not correct as the object distance is between focus and pole, so for such cases the image formed is always virtual but in this case it is written that a real image is formed as the image distance is positive which is not possible.
(ii) Approximate value of magnification for object distance – 20 cm and image distance + 60 cm is 3.