Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions and marking scheme Set 2 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 2 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
(i) The question paper comprises four sections A, B, C and D. There are 36 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Section-A – question no. 1 to 20 – all questions and parts there of are of one mark each.
These questions contain multiple choice questions (MCQs), very short answer questions and assertion – reason type questions. Answers to these should be given in one word or one sentence.
(iii) Section-B – question no. 21 to 26 are short answer type questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
(iv) Section-C – question no. 27 to 33 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each.
Answers to these questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words. :
(v) Section—D – question no. – 34 to 36 are long answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
(vi) There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
(vii) Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
Section-A
Question 1.
List any two observations when ferrous sulphate is heated in a dry test tube?
OR
Identify the products formed when 1 mL of dil. hydrochloric acid is added to 1g of sodium metal?
Answer:
- Initial light green colour changes to reddish-brown colour
- Colourless gas is evolved
- Gas with choking smell is evolved (Any two)
OR - Sodium chloride and hydrogen gas
Question 2.
Write the chemical name and chemical formula of the salt used to remove the permanent hardness of water.
Answer:
Sodium carbonate decahydrate, Na2CO3.10H2O
Question 3.
Which of the following is not observed in a homologous series? Give reason for your choice,
(a) Change in chemical properties
(b) Difference in -CH2 and 14u molecular mass
(c) Gradation in physical properties
(d) Same functional group
Answer:
(a) It does not occur due to the presence of the same functional group.
Question 4.
Why does the sun appear white at noon?
Answer:
The light is least scattered at noon.
Question 5.
Both a spherical mirror and a thin spherical lens have a focal length of (-)15 cm. What type of mirror and lens are these?
Answer:
Both are concave.
Alternative answer that should be given credit: Plano-concave lens.
Question 6.
The image formed by a concave mirror is observed to be real, inverted and larger than the object. Where is the object placed?
OR
Name the part of a lens through which a ray of light passes without suffering any deviation.
Answer:
Between the principal focus and the centre of curvature.
OR
Optical centre.
Question 7.
In the arrangement shown in figure there are two coils wound on a nonconducting cylindrical rod. Initially the key is not inserted in the circuit. Later the key is inserted and then removed shortly after.
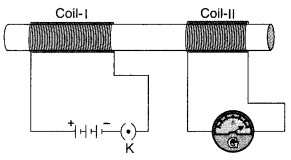
What are the two observations that can be noted from the galvanometer reading?
Answer:
There are momentary galvanometer deflections that die out shortly; the deflections are in opposite directions.
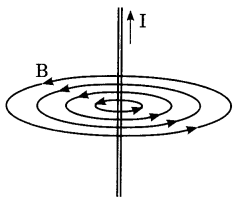
Question 8.
Draw the magnetic field lines around a straight current carrying conductor.
Answer:
The field consists of concentric circles centred on the wire
Question 9.
Two unequal resistances are connected in parallel. If you are not provided with any other parameters (eg. numerical values of I and R), what can be said about the voltage drop across the two resistors?
OR
Some work is done to move a charge Q from infinity to a point A in space. The potential of the point A is given as V. What is the work done to move this charge from infinity in terms of Q and V?
Answer:
Voltage-drop is same across both OR W = QV
Question 10.
Veins are thin walled and have valves. Justify.
Answer:
Veins have thin walls because the blood there is no longer under pressure and they have valves to ensure blood flow in one direction.
Question 11.
How is the wall of small intestine adapted for performing the function of absorption of food?
OR
Out of a goat and a tiger, which one will have a longer small intestine? Justify your answer.
Answer:
The inner lining of the small intestine has numerous finger-like projections called villi which increase the surface area for absorption.
OR
Goat because herbivores eating grass need a longer small intestine to allow the cellulose to be digested.
Question 12.
Explain how ozone being a deadly poison can still perform an essential function for our environment.
OR
Give reason why a food chain cannot have more than four trophic levels.
Answer:
Ozone layer protects us from harmful effects of UV radiation.
OR
The loss of energy at each step is so great that very little usable energy remains after four trophic levels.
Question 13.
State the role of pancreas in digestion of food.
Assertion (A) and Reason (R)
For question numbers 14,15 and 16, two statements are given- one labeled Assertion (A) and the other labeled Reason (R).
Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) as given below:
(i) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(ii) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(iii) A is true, but R is false.
(iv) A is false, but R is true.
Answer:
The pancreas secretes digestive juice which contains enzymes like trypsin for digesting proteins and lipase for breakdown of emulsified fats.
Question 14.
A. After white washing the walls, a shiny white finish on walls is obtained after two to three days. R. Calcium oxide reacts with carbon dioxide to form calcium hydrogen carbonate which gives a shiny white finish.
Answer:
(iii)
Question 15.
A. Food chain is responsible for the entry of harmful chemicals in our bodies. R. The length and complexity of food chains vary greatly.
OR
A. Greater number of individuals are present in lower trophic levels.
R. The flow of energy is unidirectional.
Answer:
(ii) OR (ii)
Question 16.
A. A geneticist crossed a pea plant having violet flowers with a pea plant with white flowers, he got all violet flowers in first generation. R. White colour gene is not passed on to next generation.
Answer:
(i)
Answer Q. No 17 – 20 contain five sub-parts each. You are expected to answer any four sub¬parts in these questions.
Question 17.
Read the following and answer any four questions from 17 (i) to 17 (v) (4 x 1 = 4)
All living cells require energy for various activities. This energy is available by the breakdown of simple carbohydrates either using oxygen or without using oxygen. 4 x 1 = 4
(i) Energy in the case of higher plants and animals is obtained by
(a) Breathing
(b) Tissue respiration
(c) Organ respiration
(d) Digestion of food
Answer:
(b) Tissue respiration
(ii) The graph below represents the blood lactic acid concentration of an athlete during a race of 400 m and shows a peak at point D. Respiration in athletics: The blood of an athlete was tested before, during and after a 400 m race:
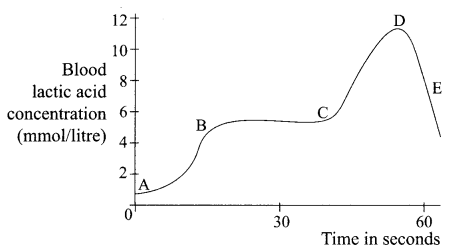
Lactic acid production has occurred in the athlete while running in the 400 m race. Which of the following processes explains this event?
(a) Aerobic respiration
(b) Anaerobic respiration
(c) Fermentation
(d) Breathing
Answer:
(b) Anaerobic respiration
(iii) Study the graph below that represents the amount of energy supplied with respect to the time while an athlete is running at full speed.
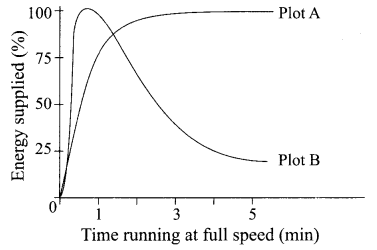
Choose the correct combination of plots and justification provided in the following table.
| Plot A | Plot B | Justification | |
| (a) | Aerobic | Anaerobic | Amount of energy is low and inconsistent in aerobic and high in anaerobic |
| (b) | Aerobic | Anaerobic | Amount of energy is high and consistent in aerobic and low in anaerobic |
| (c) | Anaerobic | Aerobic | Amount of energy is high and consistent in aerobic and low in anaerobic |
| (d) | Anaerobic | Aerobic | Amount of energy is high and inconsistent in anaerobic and low in aerobic |
Answer:
(b)
(iv) The characteristic processes observed in anaerobic respiration are
(1) presence of oxygen
(2) release of carbon dioxide
(3) release of energy
(4) release of lactic acid
(a) (1), (2) only
(b) (1), (2), (3) only
(c) (2), (3), (4) only
(d) (4) only
Answer:
(c) (2), (3), (4) only
(v) Study the table below and select the row that has the incorrect information.
| Aerobic | Anaerobic | ||
| (a) | Location | Cytoplasm | Mitochondria |
| (b) | End Product | CO2 and H2O | Ethanol and CO7 |
| (c) | Amount of ATP | High | Low |
| (d) | Oxygen | Needed | Not needed |
Answer:
(d)
Question 18.
Read the following and answer any four questions from 18 (i) to 18 (v). (4 x 1 = 4)
Answer:
Metallic Character
The ability of an atom to donate electrons and form positive ion (cation) is known as electropositivity or metallic character. Down the group, metallic character increases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to right electropositivity decreases due to decrease in atomic size.
Non-Metallic Character
The ability of an atom to accept electrons to form a negative ion (anion) is called non-metallic character or electronegativity. The elements having high electronegativity have a higher S tendency to gain electrons and form anion. Down the group, electronegativity decreases due to increase in atomic size and across the period, from left to S right electronegativity increases due to decrease in atomic size.
(i) Which of the following correctly represents the decreasing order of metallic character of alkali metals plotted in the graph?
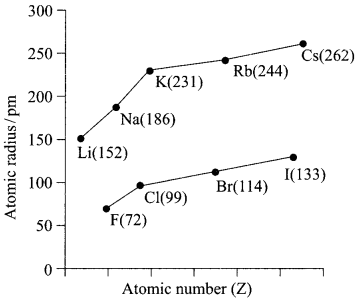
(a) Cs > Rb > Li > Na > K
(b) K > Rb > Li > Na > Cs
(c) Cs > Rb > K > Na > Li
(d) Cs > K > Rb > Na > Li
Answer:
(c) Cs > Rb > K > Na > Li
(ii) Hydrogen is placed along with alkali metals in the modem periodic table though it shows non-metallic character
(a) as hydrogen has one electron & readily loses electron to form negative ion
(b) as hydrogen can easily lose one electron like alkali metals to form positive ion
(c) as hydrogen can gain one electron easily like halogens to form negative ion
(d) as hydrogen shows the properties of non-metals
Answer:
(b) as hydrogen can easily lose one electron like alkali metals to form positive ion
(iii) Which of the following has highest electronegativity?
(a) F
(b) Cl
(c) Br
(d) I
Answer:
(a) F
(iv) Identify the reason for the gradual change in electronegativity in halogens down the group.
(a) Electronegativity increases down the group due to decrease in atomic size
(b) Electronegativity decreases down the group due to decrease in tendency to lose electrons
(c) Electronegativity decreases down the group due to increase in atomic radius/ tendency to gain electron decreases
(d) Electronegativity increases down the group due to increase in forces of attractions between nucleus & valence electrons
Answer:
(c) Electronegativity decreases down the group due to increase in atomic radius/ tendency to gain electron decreases
(v) Which of the following reason correctly justifies that “Fluorine (72pm) has smaller atomic radius than Lithium (152pm)”?
(a) F and Li are in the same group. Atomic size increases down the group
(b) F and Li are in the same period. Atomic size increases across the period due to increase in number of shells
(c) F and Li are in the same group. Atomic size decreases down the group
(d) F and Li are in the same period and across the period atomic size/radius decreases from left to right.
Answer:
(a) F and Li are in the same group. Atomic size increases down the group
Question 19.
Read the following and answer any four questions from 19 (1) to 19 (v). (4 x 1 = 4)
Sumati wanted to see the stars of the night sky. She knows that she needs a telescope to see those distant stars. She finds out that the telescopes, which are made of lenses, are called refracting telescopes and the ones which are made of mirrors are called reflecting telescopes.
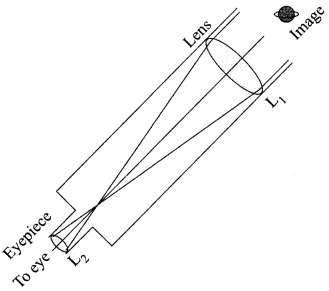
So she decided to make a refracting telescope. She bought two lenses, Lj and L2. out of which Lj was bigger and L2 was smaller. The larger lens gathers and bends the light, while the smaller lens magnifies the image. Big, thick lenses are more powerful. So to see far away, she needed a big powerful lens.
Unfortunately, she realized that a big lens is very heavy. Heavy lenses are hard to make and difficult to hold in the right place. Also since the light is passing through the lens, the surface of the lens has to be extremely smooth. Any flaws in the lens will change the image. It would be like looking through a dirty window.
(i) Based on the diagram shown, what kind of lenses would Sumati need to make the telescope?
(a) Concave lenses
(b) Convex lenses
(c) Bifocal lenses
(d) Flat lenses
(ii) If the powers of the lenses L1 and L2 are in the ratio of 4:1, what would be the ratio of the focal length of L1 and L2?
(a) 4:1
(b) 1:4
(c) 2:1
(d) 1:1
(iii) What is the formula for magnification obtained with a lens?
(a) Ratio of height of image to height of object
(b) Double the focal length.
(c) Inverse of the radius of curvature.
(d) Inverse of the object distance.
(iv) Sumati did some preliminary experiment with the lenses and found out that the magnification of the eyepiece (L2) is 3. If in her experiment with L2 she found an image at 24 cm from the lens, at what distance did she put the object?
(a) 72 cm
(b) 12 cm
(c) 8 cm
(d) 6 cm
(v) Sumati bought not-so-thick lenses for the telescope and polished them. What advantages, if any, would she have with her choice of lenses?
(a) She will not have any advantage as even thicker lenses would give clearer images.
(b) Thicker lenses would have made the telescope easier to handle.
(c) Not-so-thick lenses would not make the telescope very heavy and also allow considerable amount of light to pass.
(d) Not-so-thick lenses will give her more magnification.
Answer:

Question 20.
Read the following and answer any four questions from 20 (i) to 20 (v). (4 x 1 = 4)
A solenoid is a long helical coil of wire through which a current is run in order to create a magnetic field. The magnetic field of the solenoid is the superposition of the fields due to the current through each coil.
It is nearly uniform inside the solenoid and close to zero outside and is similar to the field of a bar magnet having a north pole at one end and a south pole at the other depending upon the direction of current flow. The magnetic field produced in the solenoid is dependent on a few factors such as, the current in the coil, number of turns per unit length etc.
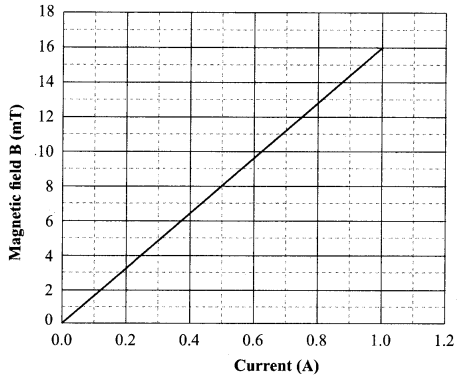
The following graph is obtained by a researcher while doing an experiment to see the variation of the magnetic field with respect to the current in the solenoid.
The unit of magnetic field as given in the graph attached is in milli-Tesla (mT) and the current is given in Ampere.
(i) What type of energy conversion is observed in a linear solenoid?
(a) Mechanical to Magnetic
(b) Electrical to Magnetic
(c) Electrical to Mechanical
(d) Magnetic to Mechanical
Answer:
(c) Electrical to Mechanical
(ii) What will happen if a soft iron bar is placed inside the solenoid?
(a) The bar will be electrocuted resulting in short-circuit.
(b) The bar will be magnetised as long as there is current in the circuit.
(c) The bar will be magnetised permanently.
(d) The bar will not be affected by any means.
Answer:
(b) The bar will be magnetised as long as there is current in the circuit.
(iii) The magnetic field lines produced inside the solenoid are similar to that of…
(a) a bar magnet
(b) a straight current carrying conductor
(c) a circular current carrying loop
(d) electromagnet of any shape
Answer:
(a) a bar magnet
(iv) After analysing the graph a student writes the following statements.
I. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is inversely proportional to the current.
II. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is directly proportional to the current.
III. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is directly proportional to square of the current.
IV. The magnetic field produced by the solenoid is independent of the current.
Choose from the following which of the following would be the correct statement(s).
(a) Only IV
(b) I and III and IV
(c) I and II
(d) Only II
Answer:
(d) Only II
(v) From the graph deduce which of the following statements is correct.
(a) For a current of 0.8 A the magnetic field is 13 mT
(b) For larger currents, the magnetic field increases non-linearly.
(c) For a current of 0.8A the magnetic field is 1.3 mT
(d) There is not enough information to find the magnetic field corresponding to 0.8A current.
Answer:
(a) For a current of 0.8 A the magnetic field is 13 mT
Section-B
Question 21.
Bile juice does not have any digestive enzyme but still plays a significant role in the process of digestion. Justify the statement.
OR
In birds and mammals the left and right side of the heart are separated. Give reasons.
Answer:
Bile juice makes the acidic food coming from the stomach alkaline for the action of pancreatic enzymes. Bile salts break the large globules of fat in the intestine to smaller globules increasing the efficiency of enzyme action. This is similar to the emulsifying action of soaps on dirt.
OR
The separation keeps oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing allowing a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body. This is useful in animals that have high energy needs (birds and mammals) which constantly use energy to maintain their body temperature.
Question 22.
State the events occurring during the process of photosynthesis. Is it essential that these steps take place one after the other immediately?
Answer:
![]()
Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll.
- Conversion of light energy to chemical energy and splitting of water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen.
- Reduction of carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
These steps need not take place one after the other immediately. For example, desert plants take up carbon dioxide at night and prepare an intermediate which is acted upon by the energy absorbed by the chlorophyll during the day
Question 23.
Give a test that can be used to confirm the presence of carbon in a compound. With a valency of 4, how is carbon able to attain noble gas configuration in its compounds?
OR
The number of carbon compounds is more than those formed by all other elements put together. Justify the statement by giving two reasons.
Answer:
A bum compound in air/ oxygen; Gas evolved turns lime water milky
By sharing its four valence electrons with other elements.
OR
- Due to self linking ability of carbon/catenation
- Since carbon has a valency of four it can form bonds with four other atoms of carbon or atoms of some other mono-valent element.
- Due to small size of carbon it forms very strong and (or) stable bonds with other elements
Question 24.
The following observations were made by a student on treating four metals P, Q, R and S with the given salt solutions:
| Sample | MgS04(aq) | Zn(NO3)2(aq) | CaS04(aq) | Na2S04(aq) |
| P | No reaction | Reaction occurs | Reaction occurs | No reaction |
| Q | Reaction occurs | Reaction occurs | Reaction occurs | Reaction occurs |
| R | No Reaction | Reaction occurs | No Reaction | No Reaction |
| S | No Reaction | No Reaction | No Reaction | No Reaction |
Based on the above observations:
(i) Arrange the given samples in the increasing order of reactivity
(ii) Write the chemical formulae of products formed when Q reacts with CuS04 solution.
Answer:
(i) S > R > P > Q
(ii) Cu and QSO4
Question 25.
A student observes the given phenomenon in the lab as a white light passes through a prism. Among many other colours, he observed the position of the two colours red and violet. What is the phenomenon called? What is the reason for the violet light to bend more than the red light?
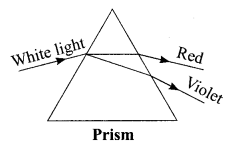
Answer:
- The phenomenon is called dispersion.
- Speed of violet light inside the prism is slowest and that of red is highest. Hence, the deviation of violet light is maximum and that of red is minimum.
Question 26.
A student has two resistors- 2 Q and 3 Q. She has to put one of them in place of R2 as shown in the circuit. The current that she needs in the entire circuit is exactly 9A. Show by calculation which of the two resistors she should choose.
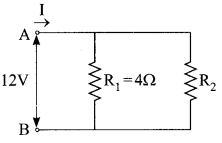
Answer:
The overall current needed = 9A. The voltage is 12V Hence by Ohm’s law V=IR,
R2 = 2Q
The resistance for the entire circuit = \(=\frac{12}{9}=\frac{4}{3} \Omega=\mathrm{R}\)
R1 and R2 are in parallel.
Hence, R = \(R=\frac{\left(R_{1} R_{2}\right)}{\left(R_{1}+R_{2}\right)}=\frac{4 R_{2}}{\left(4+R_{2}\right)}=\frac{4}{3}\)
Section-C
Question 27.
After self-pollination in pea plants with round, yellow seeds, following types of seeds were obtained by Mendel:
| Seeds | Number |
| Round, yellow | 630 |
| Round, green | 216 |
| Wrinkled, yellow | 202 |
| Wrinkled, green | 64 |
Analyse the result and describe the mechanism of inheritance which explains these results.
OR
In humans, there is a 50% probability of the birth of a boy and 50 % probability that a girl will be born. Justify the statement on the basis of the mechanism of sex-determination in human beings.
Answer:
The ratio obtained is 9:3:3:1 in which parental as well as new combinations are observed. This indicates that progeny plants have not inherited a single whole gene set from each parent. Every germ cell takes one chromosome from the pair of maternal and paternal chromosomes. When two germ cells combine, segregation of one pair of characters is independent of other pair of characters.
OR
In human beings, the genes inherited from our parents decide whether we will be boys or girls. Women have a perfect pair of sex chromosomes (XX). But, men have a mismatched pair (XY).
All children will inherit an X chromosome from their mother regardless of whether they are boys or girls. Thus, the sex of the children will be determined by what they inherit from their father. A child who inherits an X chromosome from her father will be a girl, and one who inherits a Y chromosome from him will be a boy.
Question 28.
Plastic cups were used to serve tea in trains in early days- these could be returned to the vendors, cleaned and reused. Later,Kulhads were used instead of plastic cups. Now, paper cups are used for serving tea. What are the reasons for the shift from Plastic to Kulhads and then finally to paper cups?
Answer:
- Use of Plastic cups raised the concern towards hygiene thus they were replaced by disposable plastic cups.
- Plastic cups are non-biodegradable and harm the environment. They were thus replaced by Kulhads.
- Making Kulhad made of clay on a large scale resulted in the loss of top fertile soil.
- Now, disposable paper cups are used because – the paper can be recycled, it is biodegradable and is eco-friendly material which does not cause environmental pollution.
Question 29.
Explain where and how urine is produced?
Answer:
Blood passes through filtration units in the kidney called nephron
- Passes through glomerulus in the Bowman’s capsule – Ultra filtration
- Filtrate initially has glucose, amino acids, water, salts and nitrogenous waste
- Reabsorption – Water (as per the need of the body), Glucose and amino acids are all reabsorbed
- Secretion of excess water, salts and urea (nitrogenous waste) which makes up the urine.
Question 30.
(i) Which of the following reactions is/ are an endothermic reaction(s) where decomposition also happens?
• Respiration
• Heating of lead nitrate
• Decomposition of organic matter
• Electrolysis of acidified water
(ii) Silver chloride when kept in the open turns grey. Illustrate this with a balanced chemical equation.
Answer:
(i) Heating of lead nitrate; and electrolysis of acidified water
(ii) \(2 \mathrm{AgCl}(\mathrm{s}) \stackrel{\text { Sunlight }}{\longrightarrow} 2 \mathrm{Ag}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{Cl}_{2}(\mathrm{~g})\)
(No deduction for not mentioning state of reactants and products.)
Question 31.
The following table shows the position of five elements A, B, C, D and E in the modem periodic table.
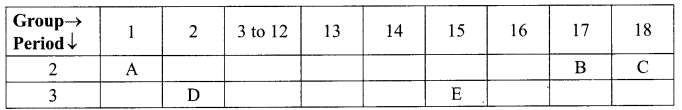
Answer:
(i) D, As it is on the left side of the table in group 2.
(ii) C, as it is in the group 18/ Noble gas.
(iii) E, as we move from left to right across a period, atomic radius decreases.
Question 32.
(i) Explain the formation of calcium chloride with the help of electron dot structure. (At numbers: Ca = 20; Cl = 17)
(ii) Why do ionic compounds not conduct electricity in solid state but conduct electricity in molten and aqueous state?
Answer:
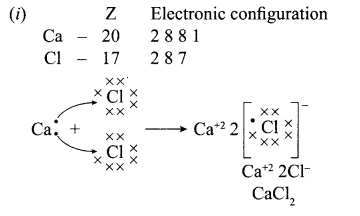
(ii) Ionic compounds do not conduct in solid state due to absence of free ions but they conduct electricity in molten and aqueous state due to presence of free ions.
Question 33.
Refractive index of water with respect to air is 1.33 and that of diamond is 2.42.
(i) In which medium does the light move faster, water or diamond?
(ii) What is the refractive index of diamond with respect to water?
Answer:
Refractive index = speed of light in vacuum / speed of light in medium.
Since the refractive index of diamond is more, hence the speed of light is lesser in diamond.
Let speed of light in water be vw and in diamond be vd.
Refractive index of diamond w.r.t water is say n = speed of light in water / speed of light in diamond
n = vwvd
Dividing both numerator and denominator by speed of light [c] we get
n = (vw/c) (vd/c)
= Inverse ratio of refractive index of water and diamond.
n = 2.42/1.33 = 1.82 (approx.)
Section-D
Question 34.
Match the following pH values 1,7, 10, 13 to the solutions given below:
• Milk of magnesia
• Gastric juices
• Brine
• Aqueous sodium hydroxide
Amit and Rita decided to bake a cake and added baking soda to the cake batter.
Explain with a balanced reaction, the role of the baking soda. Mention any other use of baking soda. 5
OR
(i) Four samples A, B, C and D change the colour of pH paper or solution to green, reddish- pink, blue and orange. Their pH was recorded as 7,2, 10.5 & 6 respectively. Which of the samples has the highest amount of hydrogen ion concentration? Arrange the four samples in the decreasing order of their pH.
(ii) Rahul found that the Plaster of Paris, which he stored in a container, has become very hard and lost its binding nature. What is the reason for this? Also, write a chemical equation to represent the reaction taking place.
(iii) Give any one use of Plaster of Paris other than for plastering or smoothening of walls.
Answer:
- Milk of magnesia – 10
- Gastric juices – 1
- Brine – 7
- Aqueous sodium hydroxide – 13
Baking soda undergoes thermal decomposition to form Na2CO3, CO2 and H2O; CO2 makes the cake fluffy & soft
\(\mathrm{NaHCO}_{3} \stackrel{\text { Heat }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3}+\mathrm{CO}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)
Uses:
Used in fire extinguishers/ antacid to neutralize excess acid in stomach / to neutralize the effect of acid in insect sting.
OR
(i) (a) B
(b) C,A,D,B
(ii) Due to moisture in the atmosphere it converted into gypsum
\(\mathrm{CaSO}_{4} \cdot 1 / 2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+1 / 2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow \mathrm{CaSO}_{4} \cdot 2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\)
(iii) Making toys/dolls or statues /fixing broken limbs/making decorative materials.
Question 35.
Trace the changes that take place in a flower from gamete formation to fruit formation.
Answer:
[Diagram drawn and annotated with the following points will also be considered]
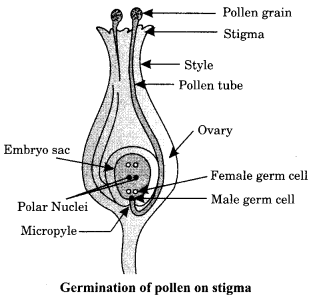
- Stamen is the male reproductive part and it produces pollen grains.
- The ovary contains ovules and each ovule has an egg cell.
- The pollen needs to be transferred from the stamen to the stigma.
- If this transfer of pollen occurs in the same flower, it is referred to as self-pollination.
On the other hand, if the pollen is transferred from one flower to another, it is known as cross-pollination.
After the pollen lands on a suitable stigma, it has to reach the female germ-cells which are in the ovary. For this, a tube grows out of the pollen grain and travels through the style to reach the ovary/Figure
- The male germ-cell produced by pollen grain fuses with the female gamete present in the ovule.
- This fusion of the germ-cells or fertilisation gives the zygote.
- After fertilisation, the zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule.
- The ovule develops a tough coat and is gradually converted into a seed. The ovary grows rapidly and ripens to form a fruit.
- Meanwhile, the petals, sepals, stamens, style and stigma may shrivel and fall off.
Question 36.
In the given circuit, A, B, C and D are four lamps connected with a battery of 60V.
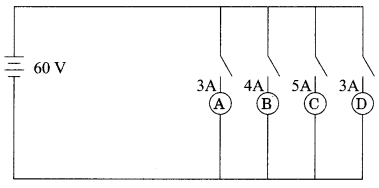
Analyse the circuit to answer the following questions.
(i) What kind of combination are the lamps arranged in (series or parallel)?
(ii) Explain with reference to your above answer, what are the advantages (any two) of this combination of lamps?
(iii) Explain with proper calculations which lamp glows the brightest?
(iv) Find out the total resistance of the circuit.
OR
PQ is a current carrying conductor in the plane of the paper as shown in the figure below.
(i) Find the directions of the magnetic fields produced by it at points R and S?
(ii) Given r1> r2 where will the strength of the magnetic field be larger? Give reasons.
(iii) If the polarity of the battery connected to the wire is reversed, how would the direction of the magnetic field be changed?
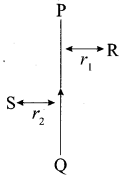
(iv) Explain the rule that is used to find the direction of the magnetic field r2 for a straight current carrying conductor.
Answer:
(i) The lamps are in parallel.
(ii) Advantages:
If one lamp is faulty, it will not affect the working of the other lamps.
They will also be using the full potential of the battery as they are connected in parallel.
(iii) The lamp with the highest power will glow the brightest.
P= VI
In this case, all the bulbs have the same voltage. But lamp C has the highest current. Hence, for lamp C, P = 5 x 60 Watt = 300 W. (the maximum).
(iv) The total current in the circuit = (3 + 4 + 5 + 3) A = 15A
The Voltage = 60V
V = IR and hence R = V/I
R= 60/15 Ω = 4Ω
OR
(i) The magnetic field lines produced is into the plane of the paper at R and out of it at S.
(ii) Field at S > Field at P Magnetic field strength for a straight current carrying conductor is inversely proportional to the distance from the wire.
(iii) The current will be going from top to bottom in the wire shown and the magnetic field lines are now in the clockwise direction on the plane which is perpendicular to the wire carrying current.
(iv) Right hand thumb rule. The thumb is aligned to the direction of the current and the direction in which the fingers are wrapped around the wire will give the direction of the magnetic field.