Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions and marking scheme Set 5 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Set 5 for Practice
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
(i) The question paper comprises four sections A, B, C and D. There are 36 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Section-A – question no. 1 to 20 – all questions and parts there of are of one mark each.
These questions contain multiple choice questions (MCQs), very short answer questions and assertion – reason type questions. Answers to these should be given in one word or one sentence.
(iii) Section-B – question no. 21 to 26 are short answer type questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should in the range of 30 to 50 words.
(iv) Section-C – question no. 27 to 33 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each.
Answers to these questions should in the range of 50 to 80 words. :
(v) Section—D – question no. – 34 to 36 are long answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
(vi) There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
(vii) Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
Section – A
1. If an element X is placed in group 14, what will be the formula and the nature of bonding of its chloride?
2. Where should an object be placed from a converging lens of focal length 15 cm, so as to obtain the image of same size and real.
3. A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used in white washing.
(i) Name the substance ‘X’ and write its formula.
(ii) Write the reaction of the substance ‘X’ named in (i) above with water.
OR
What happens chemically, when quicklime is added to water filled in a bucket?
4. Three acidic solutions A, B and C have pH = 0, 3 and 5 respectively:
(i) Which solution has the highest concentration of H+ ions?
(ii) Which solution has the lowest concentration of H+ ions?
5. Generally, when metals are treated with mineral acids, hydrogen gas is liberated, but when metals (except Mn and Mg) are treated with HNO3, hydrogen is not liberated, why?
6. The volume of glomerular filtrate produced is 18 L but the volume of urine excreted is just 1 – 2 L. Give a suitable reason for this statement.
7. Ozone is deadly poisonous, still it performs an essential function. How?
OR
Write the appropriate names of trophic level ‘Z’ and ‘X’ in the figure given below.
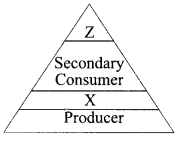
8. Covalent compounds have low melting and boiling point. Why?
9. Give an example of a flower which contains both stamens and carpels.
OR
What are sexually transmitted diseases? Name a STDs which damages the immune system of human body.
10. What is the nature of the image formed by a concave mirror, if the magnification produced by the mirror is +4? OR
The outer surface of a hollow sphere of aluminium of radius 50 cm is to be used as a mirror. What will be the focal length of this mirror? What type of spherical mirror will it provide?
Answer:
OR 25
11. Let the resistance of an electrical component remain constant, while the potential difference across the two ends of the component decreases to half of its former value. What change will occur in the current through it?
OR
If the charge on an electron is 1.602 x 10-19 C, find the approximate number of electrons in 1C.
Answer:
OR 6.25 × 1018
12. Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from the back wall towards the front wall, is deflected by a strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of the magnetic field?
13. What will be the amount of energy available to the organisms of secondary consumer trophic level of food chain, if the energy available to producer level is 10000 Joules.
Assertion (A) and Reason (R)
For question numbers 14,15 and 16, two statements are given- one labeled Assertion (A) and the other labeled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (i), (ii), (iii) and (iv) as given below:
(i) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(ii) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(iii) A is true, but R is false.
(iv) A is false, but R is true.
Answer:
100 J
14. A. The extent of refraction is different for different medium.
R. Different medium have different refractive index.
Answer:
(i)
15. ![]()
R. It is a combination reaction because CO combines with H2 to form CH3OH i.e., two substances combine to form a single compound.
Answer:
(i)
16. A. The sex of a child in human beings will be determined by the type of chromosome he/she inherits from the father.
R. A child who inherits ‘X’ chromosome from his father would be a girl (XX), while a child who inherits a ‘Y’ chromosome from the father would be a boy (XY).
OR
A. Two pink coloured flowers on crossing resulted in 1 red, 2 pink and 1 white flower progeny. R. It is due to double fertilisation.
Answer:
(i) OR (iii)
Answer Q. No 17 – 20 contain five sub-parts each. You are expected to answer any four sub¬parts in these questions.
17. Read the following and answer any four questions from 17 (i) to 17 (v) (4 x 1 = 4)
The splitting of a beam of white light into its seven constituent colours, when it passes through a glass prism, is called the dispersion of light.
When a beam of white light enters a prism, it gets refracted and splits into its seven constituent colours, viz. violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange, and red. This splitting of the light ray occurs because of the different angles of bending for each colour. Hence, each colour while passing through the prism bends at different angles with respect to the incident beam. This gives rise to the formation of the coloured spectrum.
(i) What is the cause of dispersion of light by prism?
I. Different colours move with different speed in the prism.
II. Emergent ray bent to different extent towards the base of prism.
III. Different colours move with same speed in the prism but cover different distance.
IV. Emergent ray bent to different extent away from the base of prism.
(a) I only
(b) I and II
(c) III and IV
(d) II and III
Answer:
(b) I and II
(ii) Which colour of white light suffers least deviation when a beam of white light is passed through the prism?
(a) Blue
(b) Red
(c) Violet
(d) Green
Answer:
(b) Red
(iii) Which of the following colours viz., A, B, C and D has more speed in the prism?
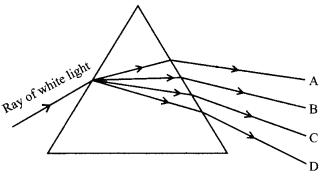
(a) A
(b) B
(c) C
(d) D
Answer:
(d) D
(iv) How will you use two identical prisms P1 and P2 so that a narrow beam of white light incident on one prism emerges out of the second prism as white light?
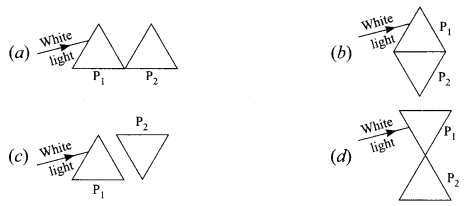
Answer:
(c)
(v) Among the seven colours visible due to splitting of white light through prism which colour has shortest wavelength?
(a) Red
(b) Blue
(c) Violet
(d) Yellow
Answer:
(c) Violet
18. Read the following and answer any four questions from 18 (i) to 18 (v) (4 x 1 = 4)
More than a million Americans die of cardiac diseases each year. One of the major causes is high cholesterol levels in the blood. The National Cholesterol Education Program suggests that total blood cholesterol level should be:
| Blood Cholesterol Level Chart | |||
| Desirable | Borderline (high) | High Risk | |
| Total Cholesterol | <200 | 200-240 | >240 |
| Triglycerides | < 150 | 150-500 | >500 |
| Low Density Cholesterol | < 130 | 130-160 | >160 |
| High Density Cholesterol | >50 | 50-35 | <35 |
Given below are blood report of two persons
| Total Cholesterol | Triglycerides | Low density cholesterol | ||
| Patient A | 356 | 180 | 150 | |
| Patient B | 180 | 100 | 90 |
(i) Which of the organ can be affected in patient A?
(a) Heart
(b) Kidney
(c) Lungs
(d) Brain
Answer:
(a) Heart
(ii) What information is left out for the blank column?
(a) Total cholesterol
(b) Triglycerides
(c) Low density cholesterol
(d) High density cholesterol
Answer:
(d) High density cholesterol
(iii) A person with high risk category have to be suggested a suitable diet? Which of the following are correct guidelines for the patient
(a) High sugar and starch
(b) Low salt and fats
(c) High proteins
(d) Low sugar and proteins
Answer:
(b) Low salt and fats
(iv) Apart from following a prescribed diet, some other changes should be brought in the lifestyle to avoid aggravation of symptoms in a patient who is already suffering from high blood cholesterol-
A. Yoga and exercise
B. Quitting smoking and alcohol
C. Walking and doing small chores on your own
D. Enjoying loud music
Which of the following is the correct option
(a) A ,C
(b) B,C,D
(c) A,B,C
(d) A, D
Answer:
(c) A,B,C
(v) Which of the following is correct for patient B?
(a) High total cholesterol but triglycerides in normal range
(b) Total cholesterol in normal range but triglycerides are high
(c) Total cholesterol in normal range but low density cholesterol are high
(d) Total cholesterol, triglycerides and low density cholesterol are in normal range
Answer:
(d) Total cholesterol, triglycerides and low density cholesterol are in normal range
19. Read the following and answer any four questions from 19 (i) to 19 (v) (4 x 1 = 4)
Most of the characters or traits of an organism are controlled by the genes. Genes are actually segments of DNA guiding the formation of proteins by the cellular organelles. These proteins may be enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and structural components of different types of tissues. In other words, DNA/ genes are responsible for structure and functions of a living body. Genotype of an individual controls its phenotype.
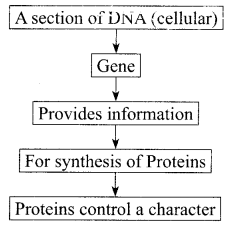

(i) Select the statements that describe characteristics of genes
I. Genes are specific sequence of bases in a DNA molecule
II. A gene does not code for proteins
III. In individuals of a given species, a specific gene is located on a particular chromosome
IV. Each chromosome has only one gene
(a) I and II
(b) I and III
(c) I and IV
(d) III and IV
Answer:
(b) I and III
(ii) A Mendelian experiment consisted of breeding tall pea plants bearing violet flowers with short pea plants bearing white flowers. In the progeny, all bore violet flowers, but almost half of them were short. This suggests that the genetic makeup of tall plant can be depicted as
(a) TTWW
(b) TTww
(c) TtWW
(d) TtWw
Answer:
(c) TtWW
(iii) Two pea plants one with round green seeds (RRyy) and another with wrinkled yellow (rrYY) seeds produce Fj progeny that have round, yellow (RrYy) seeds. When F1 plants are selfed, the F2 progeny will have new combination of characters. Choose the new combination from the following.
I. Round, yellow
II. Round, green
Wrinkled, yellow IV. Wrinkled, green
(a) I and II
(b) I and IV
(c) II and III
(d) I and III
Answer:
(b) I and IV
(iv) A section of DNA providing information for one protein is called—
(a) Nucleus
(b) Chromosomes
(c) Trait
(d) Gene
Answer:
(d) Gene
(v) Which one of the following is present in the nucleus?
(a) Gene
(b) DNA
(c) Chromosomes
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
20. Read the following and answer any four questions from 20 (i) to 20 (v) (4 x 1 = 4)
Answer the question numbers 3(a) to 3(d) on the basis of your understanding of the following paragraph and the related studied concepts.
Atomic size refers to radius of atom. The atomic size may be visualised as the distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell of an atom.
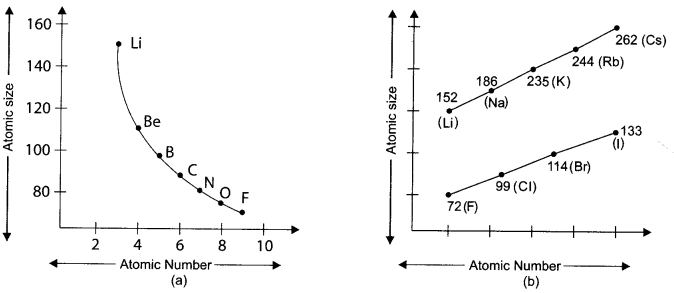
(i) How does atomic size vary along period 2 from left to right and why?
(a) Atomic size increases as atomic number increases
(b) Atomic size increases as number of protons increases
(c) Atomic size decreases as electrons added to same shell and with increase in number of protons, nuclei attracts electrons more
(d) Atomic size decreases as proton has higher positive charge than negative charge on electron and thus protons pulls electrons towards nucleus.
Answer:
(c) Atomic size decreases as electrons added to same shell and with increase in number of protons, nuclei attracts electrons more
(ii) How does atomic size vary in group 1 and group 17 and why?
(a) Atomic size increases because electrons added to the penultimate shell
(b) Atomic size increases because electrons added to next higher energy shell
(c) Atomic size decreases because electrons added to penultimate shell
(d) Atomic size decreases because electrons added to same shell
Answer:
(b) Atomic size increases because electrons added to next higher energy shell
(iii) Which group elements have largest size in periodic table?
(a) Group 1
(b) Group 2
(c) Group 17
(d) Group 18
Answer:
(d) Group 18
(iv) Which element of group 17 is most reactive?
(a) F
(b) Cl
(c) Br
(d) I
Answer:
(a) F
(v) Which of the following has higher distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell of an atom?
(a) Li
(b) C
(c) Be
(d) I
Answer:
(a) Li
Section-B
21. The resistance of a wire of 0.01 cm radius is 10Ω. If the resistivity of the material of the wire is 50 x 10-8 Ωm, find the length of the wire.
Answer:
62.8cm
22. Foetus derives its nutrition from the mother.
(i) Identify the tissue used for above purpose. Explain its structure.
(ii) Explain how wastes generated by developing embryo are removed.
OR
Why do we need to adopt contraceptive measures?
23. A coil of insulated copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is
(i) pushed into the coil
(ii) held stationary inside the coil?
24. Give reason for the following:
(i) Element carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bonding.
(ii) Kerosene does not decolourise bromine water while cooking oils do.
25. An alpha particle (positively charged) enters a magnetic field at right angle to it as shown in figure. Explain with the help of relevant rule, the direction of force acting on the alpha particle.
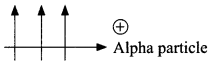
OR
Identify the poles of the magnet in the given figure (i) and (ii).
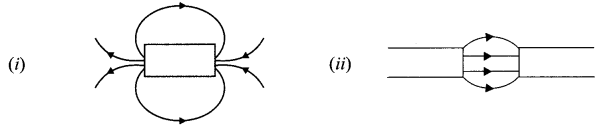
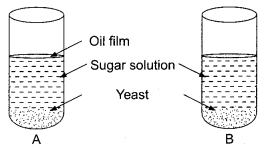
26. In a test tube A and B shown below, yeast was kept in sugar solution. What products of respiration would you expect in tubes A and B?
Section-C
27. Draw a circuit diagram of an electric circuit containing a cell, a key, an ammeter, a resistor of 4D. in series with a combination of two resistors (80 each) in parallel and a voltmeter across parallel combination. Each of them dissipates maximum energy and can withstand a maximum power of 16W without melting. Find the maximum current that can flow through the three resistors.
Answer:
1 A
28. Find the current drawn from the battery by the network of four resistors shown in the diagram.
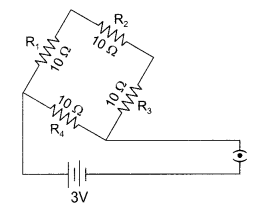
Answer:
0.4A
29. In the electrolysis of water,
(i) Name the gas collected at anode and cathode
(ii) Why is the volume of gas collected at one electrode double than the other?
(iii) What would happen if dil H2S04 is not added to water?
30. A student records the observation to study the rate of respiration in three different people. Study the data collected and answer the questions given below:
| Activity | Person 1 (breathing in one minute) | Person 2 (breathing in one minute) | Person 3 (breathing in one minute) |
| (i) Walking | 20 times | 24 times | 26 times |
| (ii) Running | 35 times | 37 times | 34 times |
| (iii) Climbing 20 stairs by running | 40 times | 30 times | 45 times |
(i) Which variable is kept constant?
(ii) Which reading is anomalous?
(iii) Suggest one improvement in this experiment.
31. The electrons in the atoms of four elements A, B, C and D are distributed in three shells having 1, 3, 5 and 7 electrons in outermost shell respectively. State the period in which these elements can be placed in the modem periodic table. Write the electronic configuration of the atoms A and D and the molecular formula of compound formed when A and D will combine.
32. (i) Construct a terrestrial food chain comprising four trophic levels.
(ii) What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
(iii) Calculate the amount of energy available to the organisms at the fourth trophic level if the energy available to the organisms at the second trophic level is 2000 J.
Answer:
(iii) 2 J
33. “pH has a great importance in our daily life” explain by giving three examples.
OR
A compound which is prepared from gypsum has the property of hardening when mixed with a proper quantity of water. Identify the compound and write its chemical formula. Write the chemical equation for its preparation. Mention any one use of the compound.
Section – D
34. You are given balls and stick model of six carbon atoms and fourteen hydrogen atoms and sufficient number of sticks. In how many ways one can join the models of six carbon atoms and fourteen hydrogen atoms to form different molecules of C6H
OR
(i) Give a chemical test to distinguish between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons.
(ii) What is meant by a functional group in an organic compound? Name the functional group present in
(a) CH3CH2OH
(b) CH3COOH
(iii) What is the difference in the molecular formula of any two consecutive members of a homologous series of organic compounds?
35. A student wants to project the image of candle flame on the wall of school laboratory by using a lens:
(i) which type of lens should be used and why?
(ii) at which distance in term of focal length F of the lens should be placed the candle flame so as to get
(a) a magnified and
(b) a diminished image respectively on the wall?
OR
(i) Complete the following ray diagrams:
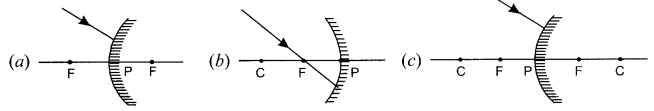
(ii) A ray of light travelling in air enters obliquely into water. Does the light ray bend towards or away from the normal? Why? Draw a ray diagram to show the refraction of light in this situation.
36. (i) To study the respiration of germinating seeds:
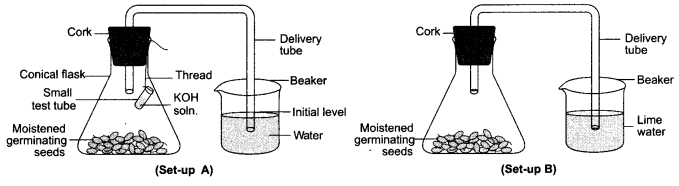
(a) Name two chemicals that are kept in the test tube to absorb carbon dioxide gas released in the conical flask.
(b) Explain why the level of water in the bent tube rises in the set up A
(c) State the observation in set up B:
(ii) What do the following transport:
(a) Xylem
(b) Pulmonary artery
(c) Pulmonary vein
(d) Vena cava