Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 2 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Science Term 2 Set 2 with Solutions
Time allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections and 15 questions. ALL questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 7 questions of 2 marks each; Section-B has 6 questions of 3 marks each, and Section-C has 2 case based questions of 4 marks each.
- Internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
Section – A
Question 1.
The following table lists the boiling points of some alkanes having the general formula CnH2n + 2, where n = number of carbon atoms:
Boiling Points of Alkanes
| Name | B.P., °C (760 mm) |
| Methane | -1615 |
| Ethane | -88.6 |
| Propane | -42.1 |
| Butane | -0.5 |
| Pentane | 36.1 |
| Hexane | 68.7 |
| Heptane | 98.4 |
| Octane | 125.7 |
| Nonane | 150.8 |
| Decane | 174.1 |
Can we say that they belong to the same homologous series? List any two characteristics of homologous series. (2)
Answer:
Yes, the given compounds belong to the same homologous series as they have the same formula CnH2n + 2.
Characteristics of homologous series are:
- All members of a homolgous series can be represented by the same general formula. For example the general formula for alkanes is CnH2n + 2, where n is the number of carbon atoms.
- They have similar chemical properties.
- Any two adjacent homologues differ by – CH2 in their molecular formula.
- The difference in the molecular masses of any two adjacent homolgues is 14 u.
- All the compounds belonging to the same homolgous series have similar chemical properties.
- The members of a homolgous series show a gradual change in their physical properties with increase in molecular mass.
![]()
Question 2.
A letter ‘A’ consists of a uniform wire of resistance 1 ohm cm”1. The side of the letter are each 20 cm long and the cross-piece in the middle is 10 cm long while apex angle is 60°. Find the resistance of the letter between the two ends of the legs.
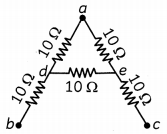
Answer:
Let us look at the given circuit.
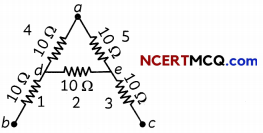
The net resistance can be found as folLows.
R45 = 10 + 10 = 20 Ω
R452 = \(\left(\frac{1}{20}+\frac{1}{10}\right)^{-1}\) = \(\frac{20}{3}\)Ω
Rnet = R452 + R1 + R3 = \(\frac{20}{3}\) + 10 + 10
= \(\frac{80}{3}\) = 26.67Ω
Hence, the net resistance of the circuit is 26.67 Ohms.
Question 3.
The variation of electronegativity values for the first 20 elements is shown in the graph below that demonstrates the trend in etectronegativity of elements in the periodic table. The X-axis depicts the period and the Y-axis depicts etectronegotivity.
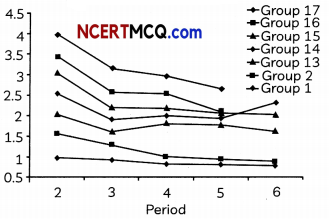
(A) With the help of the given graph, identify the trend of electronegativity for elements in the period. (1)
(B) Why do you think all the periods do not show the normal gradation in electronegativity? (1)
OR
(A) From the given graph, which period demonstrates maximum electronegativity. (1)
(B) Arrange the following on the basis of increase in electronegativity: C, N, O, F and Cl. (1)
Answer:
(A) Electronegativity increases as we move in a period and decreases as we move in a group as is evident from the graph.
(B) All periods do not show normal gradation in properties due to half filled and fully filled stability that few elements attain that lead to abnormal gradation in properties.
OR
(A) According to the graph, period 2 shows maximum electronegativity.
(B) Let us arrange the elements according to their position.
| 1 | ||
| 2 | ||
| 13 | ||
| 14 | C | |
| 15 | N | |
| 16 | 0 | |
| 17 | F | Cl |
| 18 |
The increasing order of electronegativity is: C < N < O < Cl < F
Electronegativity increases in a period whereas it decreases in a group.
![]()
Question 4.
(A) How will you infer with the help of an experiment that the same current flows through every part of the circuit containing three resistors R1, R2 and R3 in series connected to a battery of V volts? (1)
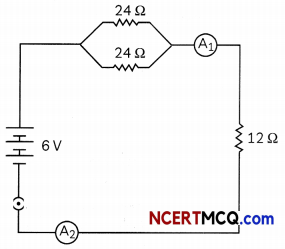
(B) Study the following circuit and find out:
(i) Current in 12 Ω resistor. (½)
(ii) Difference in the readings of A1 and A2, if any. (½)
OR
Answer the following questions:
(A) What is solenoid? Draw field lines of the magnetic field through a current carrying solenoid. (1)
(B) If field lines of a magnetic field are crossed at a point, what does it indicate? (1)
Answer:
(A) (i) Take three resistors Rlt R2 and R3 of different values and connect them in series with the help of a battery, ammeter and plug key as shown in the circuit diagram.
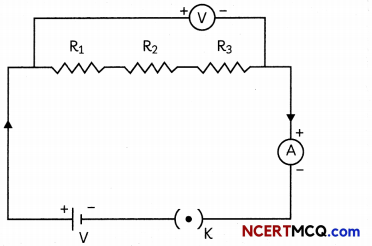
(ii) Plug in the key K and note the reading of the ammeter.
(iii) Change the position of the ammeter in between any of the resistors, say between R1 and R2, as shown after taking out the key.
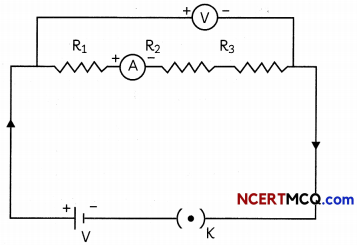
(iv) Plug in the key again and note the ammeter reading.
(v) Repeat steps (iii) and (iv) for different positions of the ammeter.
Observation: We will observe that the ammeter reading remains same no matter where we connect the ammeter.
Conclusion: This shows that same current flows through every part of a circuit having resistances in series connected to a battery.
(B) (i) In the circuit the two resistors of 24Ω each are connected in parallel to each other. The equivalent resistance of the two resistances in parallel is given, by \(\frac{1}{R_{p}}\) = \(\frac{1}{R_{1}}+\frac{1}{R}\) R1 and R2 are the two resistances in parallel.
\(\frac{1}{R_{p}}\) = \(\frac{1}{24}+\frac{1}{24}\) = \(\frac{2}{24}\) = \(\frac{1}{12}\)
As this combination is in series with the 12Ω resistance, the total resistance in the circuit is given by R = Rp + 12 = 12 = 24Ω
Current is given bu I = \(\frac{V}{R}\) = \(\frac{6}{24}\) A = 0.25A
The current flowing through the 12 Ohm resistance = 0.25A
(ii) Since the same current flows through every part of a circuit having resistances connected in series, both A1 and A2 will give the same reading 0.25 A.
OR
(A) A coil of many circular turns of insulated copper wire wrapped closely in the shape of a cylinder is called a solenoid Magnetic field around a current carrying solenoid is shown in the figure.
Magnetic
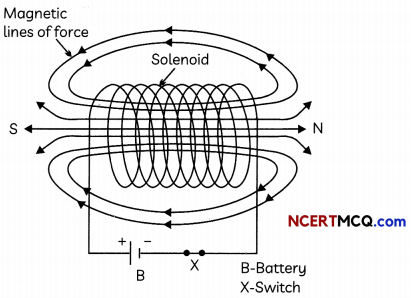
These appear to be similar to that of a bar magnet. One end of the solenoid behaves like North pole and the other end behaves like the South pole. Magnetic field lines inside the solenoid are in the from of parallel straight lines. This means that the field is same at all the points inside the solenoid.
(B) No two field-lines are found to cross each other. If they did, it would mean that at the point at intersection the compass needle would point towards two directions, which is not possible.
![]()
Question 5.
(A) What is meant by the series combination and parallel combination resistances ? (1)
Answer:
Resistors connected in series: In a series combination of resistors the current is the same in every part of the circuit. So same current flows through each resistor, i.e., there is only one path for the flow of current.
When several resistors are joined in series, the resultant resistance of the combination Rs equals the sum of their individual resistances, R1, R2, R3.
Rs = R1 + R2 + R3
Parallel combination of resistors: In a parallel circuit each resistor is placed in its own separate branch. A parallel circuit provides multiple paths for the current to flow.
The reciprocal of the equivalent resistance of a group of resistances joined in parallel is equal to the sum of the reciprocals of the individual resistances.
\(\frac{1}{\mathrm{R}_{p}}\) = \(\frac{1}{R_{1}}\) + \(\frac{1}{R_{2}}\) + \(\frac{1}{R_{3}}\)
(B) In the circuit diagram given below five resistances of 5Ω, 20Ω, 15Ω, 20Ω and connected as given in figure to a 6V battery.
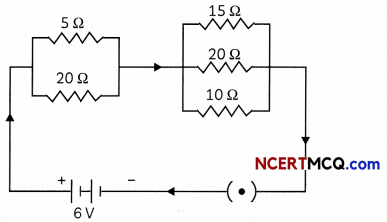
Calculate total resistance in the circuit. (1)
Answer:
To find total resistance in the circuit.
Let RA be the value of total resistance in first combination i.e. 5Ω and 20Ω.

Let RB be the value of resistance in this combination. Then,
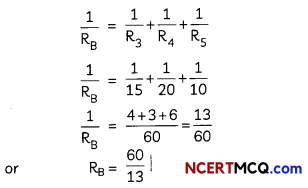
Total resistance across the circuit will be:
RA + RB = 4Ω + \(\frac{60}{13}\) | = 8.6Ω
![]()
Question 6.
Explain and justify the following statements.
(A) The existence of decomposers is essential in a biosphere. (1)
Answer:
The existence of decomposers is essential in a biosphere because they break down complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances that can be absorbed by the plant. Thus, decomposers:
- replaced the soil naturally.
- helps in removing the biodegrade waste.
(B) Flow of energy in a food chain is unidirectional. (1)
Answer:
In a food chain the energy moves progressively through the various trophic levels, it is no longer available to the previous level (i.e. autotrophs) and the energy captured by the autotrophs does not go back to the solar inputs. Hence the flow of energy is unidirectional.
Question 7.
Why is current induced in the secondary coil when current is changed in the primary coil? (2)
OR
What is the role of split ring in an electric motor? (2)
Answer:
Galvanometer is an electromechanical instrument used to detect or indicate the presence of current by deflection in a circuit. It consists of a pointer which can move along a scale with zero marked at its centre and is attached to a moving coil.
Related Theory:
Depending on the direction of induced current given by Fleming’s Right Hand Rule, the pointer of galvanometer can deflect to the right or left of the zero mark of the scale.
If no current is induced the pointer remains at the centre of the scale, which reads zero.
OR
Split ring acts as a commutator. Its function is to reverse the direction of current in the loop after every half a rotation so that the coil rotates continuously in the same direction.
Section – B
Question 8.
(A) What is a gene? How is it important in the living species? (1)
Answer:
Gene is the unit of inheritance. It is a . part of the chromosome which controls the appearance of a set of hereditary characteristics.
(B) How is inheritance different in sexual and asexual mode of reproduction? (1)
Answer:
In case of a sexual mode of reproduction, when two germ cells combine, they will restore the normal number of chromosomes in the progeny, ensuring the stability of the DNA of the species. But in case of asexual mode, genes are obtained form only one parent.
(C) Seema has 2 daughters. Can you analyze the situation genetically and provide a suitable explanation? (1)
Answer:
The woman has an ova having X chromosome. The male has a sperm with X as well as Y chromosomes. In this case, the male gamete with X chromosome fuses with the ova having X chromosome. This results in a zygote.
![]()
Question 9.
Observe the given figure of a leaf.
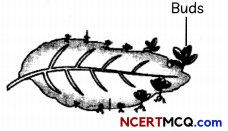
(A) What happens when the leaf shown in the figure falls with buds on it? (1½)
(B) What are the advantages of the type of reproduction shown in figure? Give an example of such a reproduction. (1½)
OR
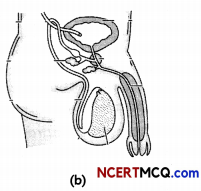
The given figure respresent (a) flower and (b) male reproductive system
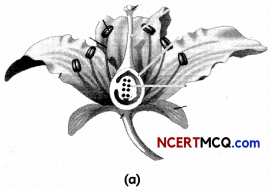
(A) Write the names of those parts of flower which serve the same function as the following do in animals (1½)
(i) Testis
(ii) Sperm
(B) Among testis, scrotum, vas deferens, fallopian tube, prostate gland, which of the following is not a part of fig(b)? (1½)
Answer:
(A) The leaf shown in the figure is of plant Bryophyllum. BryophylLum can be reproduced by vegetative propagation by using a piece of its stem or leaves. The Leaves of a Bryophyllum plant have special buds present in their margins which can get detached from the leaves, fall to the ground. Once the freshly produced plants touch the earth, they can separate from the Leaves and grow into adult plants.
(B) Vegetative reproduction has several benefits, mainly because the developed offspring represents copies of their parent plants. If a plant has positives features, the genetic information can be passed on to the next generation and the commercial growers may profit by cloning such plants in order to ensure their crops remain compatible financially. Budding in Hydra is also an example of vegetative propagation.
OR
(A) (i) Testis : Anther
In animals testes produces pserms whereas in plants anther produces pollen grains.
(ii) Sperm : Pollen grain
Sperm is the male gamete in animals whereas pollen grain is the male gamete in plants.
(B) Fallopian tubes are not a part of Fig (b), it represents the male reproductive system. The fallopian tube, also known as the oviduct, is one of two long, narrow ducts in the female abdominal cavity that transfer male sperm cells to the egg, provide a proper environment for fertilisation and transport the egg from the ovary to the uterus.
![]()
Question 10.
(A) Define the term ‘isomers’. (1)
Answer:
Isomers are the compound with same molecular formula but different structural formula.
(B) Draw two possible isomers of the compound with molecular formula C3H6O and write their names. (1)
Answer:
Isomers of C3H6O:
CH3-CH2-CHO — Propanal
CH3COCH3 — Propanone or acetone.
(C) Give the electron dot structures of the above two compounds. (1)
Answer:
Propanal:
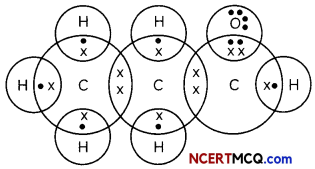
Propanone
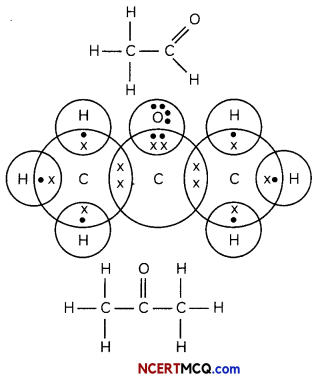
Caution:
Students need to draw alt the possible isomers.
Question 11.
(A) In a food chain 10,000 J of energy is available to the producer. How much energy would be available to the secondary consumers to transfer it to the tertiary consumers? (1)
Answer:
10 J of energy will be available to the secondary consumer to transfer to the tertiary consumers.
Related Theory:
Producer will trap only 1% of energy available to them. Now 1% of 10000 J is 100 J available to producer.
(B) What is the role of decomposers in the ecosystem? (1)
Answer:
The decomposers break down complex organic substances into simpler inorganic substances that go into the soil and are used again by the plants called nutrients cycle.
Related Theory:
There will be no recycling of matter between biotic and abiotic components of an ecosystem, because all the matter will remain locked upon in the dead bodies. Thus, the existence of life on this earth will become impossible.
(C) Why is improper disposal of waste a curse to the environment? (1)
Answer:
Wastes pollute our environment, air, soil and water, and cause harmful effects on all living organisms.
![]()
Question 12.
(A) Name two organisms which can reproduce asexually by regeneration. (1)
(B) How is regeneration carried out in these organisms? (1)
(C) Draw a diagram showing regeneration in any one organism. (1)
OR
List three techniques that have been developed to prevent pregnancy. Which one the techniques is not meant for males? Suggest one contraceptive technique which help to prevent transmission of sexually transmitted diseases. (3)
Answer:
(A) Hydra and Planaria reproduce asexually by regeneration.
(B) Regeneration is carried out by specialized cells. These cells, proliferate and make large number of cells. These large number of cells undergo changes to become various cell types and tissues. These changes take place in a systematic manner called development.
(C) Diagram showing regeneration in Planaria.
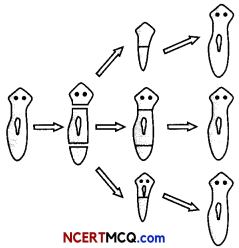
The techniques developed to prevent pregnancy are:
- use of mechanical barners
- oral contraceptives
- surgical methods
Out of the above techniques, oral contraceptives are not meant for males. Using a condom for the penis during sex helps to prevent transmission of sexually transmitted diseases.
![]()
Question 13.
From the part of a periodic table, answer the following questions:
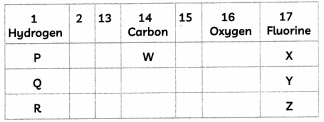
(A) Which of the elements will form covalent compounds? Give reasons. (1)
Answer:
Covalent compounds are formed by sharing of electrons. This property is exhibited by group 14 elements. From the given table, W ‘ will form covalent compounds as it belongs to group 14.
(B) What is the number of valence electrons present in P, Q and R? Identify the trend in ionic radii for group I elements. (1)
Answer:
Elements P, Q and R belong to group 1 and thus all of them have one valence electrons. Group 1 elements are usually termed as alkali metals. The ionic radii also follows the same trend as atomic radii. These metals have a single electron in its outermost shell so that they can easily lose this electron and form uni-positive ions. The ionic radii will increase as we move down in a group thereby P will have the smallest ionic radii and R will have the maximum ionic radii.
(C) Predict the formula of the oxide of W and Q (1)
Answer:
W belongs to group 14 and thus has 4 valence electrons making its valency equal to 4. Q belongs to group 1 and thus has one valence electron making its valency equal to 1. The oxides of these elements will be:
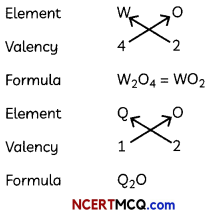
![]()
Section – C
This section has 02 case-based questions (14 and 15). Each case is followed by 03 sub-questions (A, B and C). Parts A and B are compulsory. However, an internal choice has been provided in part C.
Question 14.
A magnetic field will exert a force on a single moving charge, so that it will also exert a force on a current, which is a collection of moving charges. The force experienced by a wire of length L carrying a current I in a magnetic field B is given by force on a current-carrying wire: F = BIL sin θ.
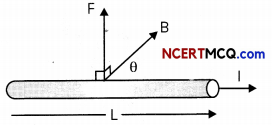
(A) What will be the magnitude of the force on the current carrying conductor if the flow of electric current is parallel to the magnetic field? (1)
Answer:
The force acting an the current carrying conductor will be zero if the current and the magnetic field are parallel to each other.
(B) What do the forefinger, middle finger and thumb indicate as per Michael Faraday. (1)
Answer:
The direction of force experienced by a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is given by Fleming’s left hand rule which states that stretch the forefinger, the central finger and the thumb of your left hand mutually perpendicular to each other. If the forefinger shows direction of the field and the central finger that of the current, then the thumb will point towards the direction of motion ofthe conductor, i.e. force.
(C) (i) The graph below shows the variation of force acting on a conductor with current:
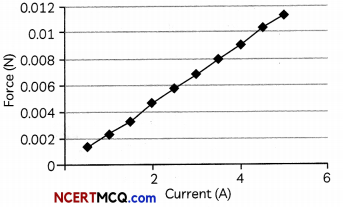
What do you interpret from the graph? (1)
Answer:
The force acting on a conductor increases linearly with increase in current. The graph between the force and current is a straight line which shows that force varies linearly with current.
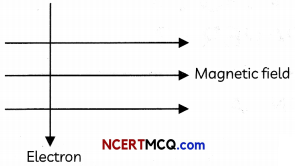
(ii) An electron enters a magnetic field at right angles to it as shown in fig. (1)
OR
Imagine that you are sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving horizontally from back wall towards the front wall, is deflected by strong magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of magnetic field? (2)
Answer:
The direction of force acting on the electron is into the page. The direction of force is perpendicular to the direction ofthe magnetic field and the current as given by Fleming’s left hand rule.
OR
Movement of an electron beam from back wall to front wall is equivalent to the flow of electric current from front wall to the back wall. Now the deflection of the beam towards right means direction of force is towards the right side. According to Fleming’s left hand rule, the magnetic field inside the chamber is in downward direction i.e. perpendicular to the plane of the paper and directed inwards.
![]()
Question 15.
Inheritance from the previous generation provides both a common basic body design, and subtle changes in it, for the next generation. The original organism at the top will give rise to two indiviuals, similar in body design, but with subtle differences. Each of them, in turn, will give rise to two individuals in the next generation. Each of the four individuals in the bottom row will be differnt from each other.
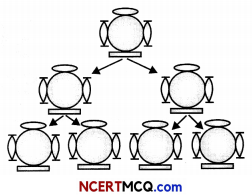
(A) If a trait A exists in 10% of a population of an asexually reproducing species and B exists in 60% of the same population, which trait is likely to have arisen earlier? (1)
Answer:
Trait B is likely to have arisen earlier because in asexual reproduction traits are carried from parents to offspring with least variations so since trait B has higher percentage it is likely to have arisen earlier.
(B) How does the creation of variations in a species promote survival? (1)
Answer:
The variations provide stability to the population of various species by preventing them from getting wiped out during adverse conditions. The natural environment also changes, and variations in species which become suited to the environment help it to survive.
(C) (i) Which of the processes, sexual reproduction or asexual reproduction, brings maxumum variations in the offspring? (1)
(ii) Give the pair of contrasting traits of the following characters in pea plant and mention which is dominant and recessive: Yellow seed and Round seed (1)
OR
Give any two examples of human traits that shows variations. (2)
Answer:
(i) Sexual Reproduction
(ii)
| Character | Contrasting traits | |
| Dominant | Recessive | |
| Seed Colour | Yellow | Green |
| Seed Shape | Round | Wrinkled |
OR
As skin colour and eye colour are polygenic features, they are the two human qualities that display variation. Polygenic traits are traits that are governed by two or more than two genes. Polygenic or quantitative inheritance refers to the inheritance or transmission of polygenic features.