Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science with Solutions and marking scheme Set 3 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 10 Social Science Set 3 with Solutions
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 80
General Instructions:
(i) Question paper comprises five Sections – A, B, C, D and E. There are 32 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
(ii) Section A – Question no. 1 to 16 are Objective Type Questions of 1 mark each.
(iii) Section B – Question no. 17 to 22 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 80 words.
(iv) Section C – Question no. 23 to 26 are source based questions, carrying 4 marks each.
(v) Section D – Question no. 27 to 31 are long answer type questions, carrying 5 marks each. Answer to each question should not exceed 120 words.
(vi) Section E – Question no. 32 is map based, carrying 5 marks with two parts, 32.1 from History (2 marks) and 32.2 from Geography (3 marks).
(vii) There is no overall choice in the question paper. However, an internal choice has been provided in few questions. Only one of the choices in such questions have to be attempted.
(viii) In addition to this, separate instructions are given with each section and question, wherever
Section-A
Question 1.
Why did Gandhiji decide to withdraw the Non-Cooperation Movement in 1922? 1
(a) Because violence occurred in Kheda and Gandhiji did not like it.
(b) Because violence occurred in Chauri Chaura and many other places, and Gandhiji was firm believer of ahimsa.
(c) Because people did not support the movement.
(d) Because violence occurred in Champaran and some other places, and Gandhiji was firm believer of ahimsa.
Answer:
(b) Because violence occurred in Champaran and some other places, and Gandhiji was firm believer of ahimsa.
Question 2.
Lala Lajpat Rai was assaulted by the British police during a peaceful demonstration against the which one of the following?
(a) Simon Commission
(b) Indian Commission
(c) Rowlatt Act
(d) Quit India Movement
Answer:
(a) Simon Commission
Question 3.
Leading the procession, way past the Statue of Liberty, the peoples of Germany were bearing
which of the following flags?
(a) Black
(b) Red
(c) Gold
(d) Black, red and gold
Answer:
(d) Black, red and gold
Question 4.
Fill in the blanks
……………. is the largest producer of raw jute and jute goods and stands at second place as an exporter after Bangladesh.
Or
The deepest, landlocked and well protected sea port is …………………..
Answer:
India
Or
Vishakhapatnam
Question 5.
Choose the correctly matched pair about the crops from the following options:
(a) Golden fibre – Jute
(b) Fibre crop – Rubber
(c) Food crop – Cotton
(d) Non-food crop – Silk
Answer:
(a) Golden fibre – Jute
Question 6.
Fill in the blank:
Biotic and Abiotic resources: on the basis of origin, Renewable and non-renewable resources:on the basis of exhaustibility, …………………… : on basis of the status of development
(a) National and International resources
(b) Potential and Developed resources
(c) Individual and Community owned resources
(d) Human resources
Answer:
(b) Potential and Developed resources
Question 7.
Identify the industry with the help of the following features.
- Manufactures aircrafts, utensils and wires
- Light and a good conductor of heat
- Second most important metallurgical industry in India
Answer:
Aluminium Smelting
Question 8.
Aluminium Smelting
The oldest artificial sea port of India is
(a) Kolkata
(b) Mumbai
(c) Chennai
(d) Kandla
Answer:
(c) Chennai
Question 9.
Modem democracies maintain check and balance system. Identity the correct option based on the horizontal power sharing arrangement.
(a) Central government, state government, local bodies
(b) Legislative, executive, judiciary
(c) Among different social groups
(d) Among different pressure groups
Answer:
(b) Legislative, executive, judiciary
Question 10.
If federalism works only in big country then why did Belgium adopt it?
Or
What is decentralisation?
Answer:
Belgium decided to divide its power between the national government and the constituent states.
Or
When power is taken away from central and state governments and given to local government, it is called decentralisation.
Question 11.
State any one step taken in Belgium to rule out the problem of regional differences and cultural diversities.
Or
Which is a major caste group of Sri Lanka?
Answer:
Step taken by Belgium:
The Constitution prescribes that the number of Dutch and French speaking ministers shall be equal in the Central Government.
Or
Sinhala and Tamil is a major caste group of Sri Lanka.
Question 12.
12. Read the given table and find out in comparison to Kerala, which state has the highest infant mortality rate.
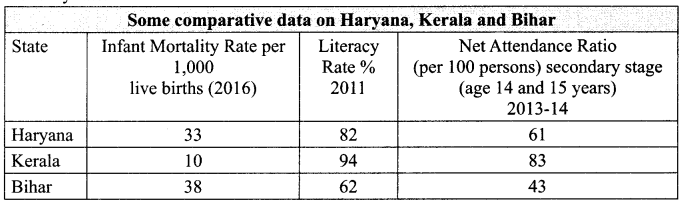
Sources: Economic Survey, 2017-18 Vol. 2, Government of india: National Sample Survey
Organisaiion (Report No. 575)
(a) Haryana
(b) Bihar
(c) Both Haryana and Bihar
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Bihar
Question 13.
Read the information given below and select the correct option.
Until the middle of the twentieth century, production was largely organised within countries. What crosses the boundaries of these countries were raw material, foodstuff and finished products. Colonies such as India exported raw material and foodstuff and imported finished goods. Trade was the main channel connecting distant countries. This w’as before large companies connecting distant countries. This was before large companies called multinational corporations (MNCs) emerged on the scene.
Foreign trade creates an opportunity’ for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets i.e., markets of their own countries. Producers can sell their produce not only in markets located within the country but can also compete in markets located in other countries of the world. Similarly, for the buyers, import of goods produced in another country is one way of expanding the choice of goods beyond what is domestically produced.
MNCs are a major force in connecting the countries of the world because-
(a) they can form and utilize the connections between national economics.
(b) they help in the integration of market and in flow of information.
(c) they may also outsource their production processes, often to lesser developed nations to reduce their costs.
(d) All of the above (d)
Answer:
(d) All of the above (d)
Or
Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets i.e., markets of their own countries. How does foreign trade become a main channel in connecting countries? Choose the correct option.
(a) Foreign trade creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets.
(b) Producers can sell their produce not only in market located within the country but also compete in markets located in other countries of the world.
(c) Impact of the goods produced in another country is also one of the way is expanding the choice of goods.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 14.
How is Public sector different for Private sector? Choose the correct option from the following.
(a) In the public sector government owns most of the assets and provides all the services, whereas in private sector ownership of assets and delivery of services is in the hand of private individual or companies.
(b) In the public sector ownership of assets and delivery of services is in the hand of private individual or companies, whereas in the private sector government owns most of the assets and provides all the services.
(c) In the public sector government owns minimum assets and provides limited sendees, whereas in the private sector assets and delivery of services is the responsibility of private companies only.
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) In the public sector government owns most of the assets and provides all the services, whereas in private sector ownership of assets and delivery of services is in the hand of private individual or companies.
Question 15.
Suggest the way to create employment in rural areas from the options given below:
(a) Launching projects like irrigation facilities
(b) Building dams and developing infrastructural projects
(c) By opening services like cooperatives or banks
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 16.
In the question given below, there are two statements marked as Assertion (A) and Reason
(R). Read the statements and choose the correct option:
Assertion (A): Demand deposits offer an interesting facility of cheque.
Reason (R): Modern forms of money includes gold and silver coins.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is false.
Section-B
Question 17.
Give a brief description of Mahatma Gandhi’s Satyagraha Movements which he organised in various places after arriving in India from South Africa.
Answer:
After arriving in India, Mahatma Gandhi organised several Satyagraha movements in various places:
- Champaran:
In 1917, he travelled to Champaran in Bihar to inspire the peasants to struggle against the exploitative plantation system. - Kheda:
In 1917, he organised a Satyagraha Movement in support of the Kheda peasants in Gujarat. These peasants were very much worried due to crop failure and a plague epidemic. Since they could not pay the revenue, they demanded relaxation in revenue collection. - Ahmedabad:
In 1918, he went to Ahmedabad to organise Satyagraha movement among the workers of cotton mills.
Question 18.
Though conservative forces were able to suppress liberal movements in 1848, they could not restore the old order. How?
Or
“The Congress was reluctant to include the demands of industrial workers in its programme of struggle.” Analyse the reasons.
Answer:
- Monarchs now began to realise that the cycles of revolution and repression would only be ended by granting concessions to the liberal-nationalist revolutionaries.
- Therefore, in the years after 1848, the autocratic monarchies of Central and Eastern Europe began to introduce the changes that had already taken place in Western Europe before 1815.
- Thus, the systems of serfdom and bonded labour were abolished both in the Habsburg dominions and in Russia.
- The Habsburg rulers granted more autonomy to the Hungarians in 1867.
Or
The Congress was reluctant to include the demands of industrial workers in its programme of struggle because:
- The industrial working classes did not participate in the Civil Disobedience Movement in large numbers, except in the Nagpur region.
- As the industrialists came closer to the Congress, workers stayed aloof.
- The Congress felt that by including workers’ demands as part of its programme of struggle it would alienate industrialists and divide the anti-imperial forces.
Question 19.
“Efficient means of transport are pre-requisites for fast development of the country.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer:
- The pace of development of country depends upon the production of goods and services as well as their movement over space. Therefore, efficient means of transport are pre-requisite for national development.
- Today, the world has been converted into a large village with the help of efficient and fast moving transport system.
- The trades from local to international levels have added to the vitality of our economy with the help of dense and efficient network of transport in the country.
- It has enriched our life and added substantially to growing amenities and facilities for the comforts of life.
Question 20.
Describe any three features of ‘federal government’.
Or
Describe any three features of ‘unitary government’.
Answer:
Feature of Federal Government:
- Sharing of powers two or more levels of government
- Each government has its own jurisdiction
- Courts have the power to interpret the Constitution and the powers of different levels of government.
- Sources of revenue for each level of government are clearly specified to ensure its financial autonomy.
- The fundamental provisions of the Constitution can be changed with the consent of both, (vz) It has dual objectives to safeguard and promote unity of the country.
(Any three)
Or
Features of Unitary Government:
- Only one level of Government or the sub-units are subordinate to Central Government.
- The Central Government can pass an order to provincial or the local government
- State government has power of its own for which it is not answerable to the Central government.
- Both these governments are separately answerable to the people.
(Any three)
Question 21.
“Tertiary sector activities help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors.”
Evaluate the statement.
Answer:
The tertiary sector activities help in the development of the primary and secondary sectors because, these activities do not produce goods but they are an aid or a support for the production process. For example, goods that are produced in the primary or secondary sector would need to be transported by trucks or trains and then sold in wholesale and retail shops.
At times, it may be necessary to store these in godowns. We also may need to talk to others over telephone or send letters or borrow money from banks to help production and trade. Transport, storage, communication, banking, trade are some of the examples of tertiary activities.
Question 22.
“Primary sector was the most important sector of economic activity at initial stages of development.” Evaluate the statement.
Answer:
As the methods of farming changed and agriculture sector began to prosper, it produced much more food than before. Many people could now take up other activities. There were increasing number of craftpersons and traders. Buying and selling activities increased many times. Beside, there were also transporters, administrators, army, etc. However, at this stage, most of the goods produced were natural products from the primary sector and most people were also employmed in this sector.
But overtime and especially because new methods of manufacturing were introduced, factories came up and started expanding. In past 100 years, there has been a further shift from secondary to tertiary sector.
Therefore, we can say that primary sector was the most important sector of economic activity at initial stages of development.
Section-C
Question 23.
Read the source given below and answer the questions that follows. (4 × 1 = 4)
The movement started with middle-class participation in the cities. Thousands of students left government-controlled schools and colleges, headmasters and teachers resigned, and lawyers gave up their legal practices. The council elections were boycotted in most provinces except Madras, where the Justice Party, the party of the non-Brahmans. felt that entering the council was one way of gaining some power-something that usually only Brahmans had access to.
The effects of non-cooperation on the economic front were more dramatic. Foreign goods were boycotted, liquor shops picketed, and foreign cloth burnt in huge bonfires. The import of foreign cloth halved between 1921 and 1922, its value dropping from Rs. 102 crore toRs. 57 crore. In many places merchants and traders refused to trade in foreign goods or finance foreign trade. As the boycott movement spread, and people began discarding imported clothes and wearing only Indian ones, production of Indian textile mills and handlooms went up.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Question 23.1.
Which of the following statements correctly explains the role of ‘Justice Party’ in boycotting of council elections?
(a) Justice Party felt that entering the council was one way of gaining some power.
(b) Justice Party of Madras was not boycotted the council elections.
(c) The Party wanted power that usually only Brahmans had access to.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 23.2.
Identify how was the effects of ‘Non-Cooperation on the economic front’ dramatic from the following options:
(a) Foreign goods were boycotted.
(b) Liquor shops were picketed.
(c) Foreign cloths were burnt in huge bonfires
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 23.3.
Which among the following is/are the effect of Boycott movement on foreign textile trade? Select the appropriate option.
(a) The import of foreign cloth halved.
(b) Merchants and traders refused to trade in foreign goods or finance foreign trade.
(c) Indian textile mills and handloom went up.
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 23.4.
Identify the form of demonstration by which people block the entrance to a shop, factory or office from the given options:
(a) Satyagraha
(h) Block Movement
(c) Picket
(d) Guerrilla Movement
Answer:
(c) Picket
Question 24.
Read the text given below and answer the following questions. (4 × 1 = 4)
Different persons can have different developmental goals and what may be development for one may not be development for the other. It may even be destructive for the other. Besides seeking more income, one-way or the other, people also seek, things like equal treatment, freedom, security, and respect of others. They resent discrimination. All these are important goals. In fact, in some cases, these may be more important than more income or more consumption because material goods are not all that you need to live.
Money, or material things one can busy with it, it one factor on which our live depends. But the quality of our life also depends on non-material things mentioned above. If it is not obvious to you, then just think of the role of your friends in your life. You may desire their friendship. Similarly, there are many things that are not easily measured but they mean a lot to our lives. These are often ignored.
However, it will be wrong to conclude that what cannot be measured is not important. Consider another example. If you get a job in a far off place, before accepting it you would try to consider many factors, apart from income, such as facilities for your family, working atmosphere, or opportunity to learn. In another case, a job may give you less pay but may offer regular employment that enhances your sense of security. Another job, however, may offer high pay but no job security and also leave no time for your family. This will reduce your sense of security and freedom.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Question 24.1.
Economic development applies to the ……………… development of a country where the people earn ……………… income and can satisfy all their needs.
(a) social; higher
(b) social; lower
(c) all round; higher
(d) political; average
Answer:
(c) all round; higher
Question 24.2.
Different people have different goals or aspirations. Identify which development goals/ aspirations the following people belong to:
|
Category of person |
Development goals/Aspirations |
| a. Landless rural labourers | 1. More days of work and better wages |
| b. Prosperous farmers from Punjab | 2. Availability of other sources of irrigation |
| c. Farmers who depend only on rain for growing crops | 3. Assured a higher support prices for their crops |
| d. A rural woman from a land owning family | 4. Education of her child in English medium school by more earning from the land by giving it on rent
|
Choose the correct option.
(a) a-1, b-3, c-2, d-4
(b) a-3, b-4, c-1, d-2
(c) a-3, b-1, c-4, d-2
(d) a-4, b-2, c-1, d-3
Answer:
(a) a-1, b-3, c-2, d-4
Question 24.3.
Besides seeking more income what do people want?
(a) Security
(b) Freedom
(c) Equal treatment
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 24.4.
Which of the following is not an important goal of people’s life?
(a) Good education
(b) Blood donation
(c) High salaried job
(d) Facilities for going abroad
Answer:
(b) Blood donation
Question 25.
Read the extract and answer the following questions. (4 × 1 = 4)
Democracies that follow a federal system all over the world tend to have two kinds of political parties: parties that are present in only one of the federal units and parties that are present in several or all units of the federation. This is the case in India as well. There are some countrywide parties, which are called ‘national parties’. These parties have their units in various states. But by and large, all these units follow the same policies, programmes and strategy that is decided at the national level. Every party in the country has to register with the Election Commission.
While the Commission treats all parties equally, it offers some special facilities to large and established parties. These parties are given a unique symbol only the official candidates of that party can use that election symbol. Parties that get this privilege and some other special facilities are ‘recognised’ by the Election Commission for this purpose. That is why these parties are called, ‘recognised political parties’. The Election Commission has laid down detailed criteria of the proportion of votes and seats that a party must get in order to be a recognised party.
A party that secures at least six per cent of the total votes in an election to the Legislative Assembly of a State and wins at least two seats is recognised as a State party. A party that secures at least six per cent of the total votes in Lok Sabha elections or Assembly elections in four States and wins at least four seats in the Lok Sabha is recognised as a national party.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Question 25.1.
The most visible pillar of democracy is
(a) Adult Franchise
(b) Seats reservation
(c) Elections
(d) Political Parties
Answer:
(c) Elections
Question 25.2.
What do you know about Federal System?
(a) It is a system of government under which the power is divided between a central authority and its various constituent units.
(b) The various constituent units and the central authority run their administrative independently.
(c) These units and central authority do not interfere in the affairs of one another unnecessarily.
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 25.3.
The Party that secure at least …………………..percent the total votes in the Lok Sabha elections or Assemly elections in four states and wins at least four seats in the Lok Sabha is recognised as a national party.
(a) Four
(b) Six
(c) Five
(d) Seven
Answer:
(b) Six
Question 25.4.
Who issues a Model Code of Conduct for political parties?
(a) The Judiciary
(b) The Parliament
(c) The Press
(d) The Election Commission
Answer:
(d) The Election Commission
Question 26.
Read the extract given below and answer the following questions. (4 × 1 = 4)
Globalisation and greater competition among producers-both local and foreign producers- has been of advantage to consumers, particularly the well-off sections in the urban areas. There is greater choice before these consumers who now enjoy improved quality and lower prices for several products. As a result, these people today, enjoy much higher standards of living than was possible earlier.
Answer the following MCQs by choosing the most appropriate option.
Question 26.1.
It creates an opportunity for the producers to reach beyond the domestic markets. What does it refer to?
(a) Technology
(b) Investments
(c) Globalisation
(d) Trade Barriers
Answer:
(c) Globalisation
Question 26.2.
How is globalisation beneficial for consumers?
(a) Greater choice before the consumers and improved quality
(b) Lower prices for several products
(c) People enjoying higher standards of living than was possible earlier
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 26.3.
The negative impact of globalisation-
(a) Availability of variety of products led to higher standard of living.
(b) Rising competition has led to shutting down of many units.
(c) It has enabled some large Indian companies to emerge as MNCs.
(d) It increases foreign direct investment.
Answer:
(b) Rising competition has led to shutting down of many units.
Question 26.4.
Factors that helped in the process of globalisation are-
(a) Information and technology
(b) Liberalisation of foreign trade and foreign investment
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Creating barriers and other restrictions
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Section-D
Question 27.
How did ideas of national unity in early nineteenth century Europe allied to the ideology of liberalism? Explain.
Or
How did Greek war of independence moblilise nationalist feelings among the educated elite across Europe? Explain.
Answer:
Ideas of national unity in early nineteenth century Europe were closely allied to the ideology of liberalism. The term ‘liberalism’ derives from the Latin root liber, meaning free. For the new middle classes liberalism stood for freedom for the individual and equality of all before the law.
Politically, it emphasised the concept of government by consent. Since the French Revolution, liberalism had stood for the end of autocracy and clerical privileges, a constitution and representative government through parliament. Nineteenth-century liberals also stressed the inviolability of private property.
Yet, equality before the law did not necessarily stand for universal suffrage. Men without property and all women were excluded from political rights. Only for a brief period under the Jacobins did all adult males enjoy suffrage. However, the Napoleonic Code went back to limited suffrage and reduced women to the status of a minor, subject to the authority of fathers and husbands.
Throughout the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries women and non-propertied men organised opposition movements demanding equal political rights.
In the economic sphere, liberalism stood for the freedom of markets and the abolition of state- imposed restrictions on the movement of goods and capital. During the nineteenth century this was a strong demand of the emerging middle classes.
Such conditions were viewed as obstacles to economic exchange and growth by the new commercial classes, who argued for the creation of a unified economic territory allowing the unhindered movement of goods, people and capital. In 1834, a customs union or zollverein was formed at the initiative of Prussia and joined by most of the German states.
The union abolished tariff barriers and reduced the number of currencies from over thirty to two. The creation of a network of railways further stimulated mobility, harnessing economic interests to national unification. A wave of economic nationalism strengthened the wider nationalist sentiments growing at the time.
Or
Answer:
Greek war of independence mobilised nationalist feelings among the educated elite across Europe through:
- Greece had been part of the Ottoman Empire since the fifteenth century.
- The growth of revolutionary nationalism in Europe sparked off a struggle for independence amongst the Greeks which began in 1821.
- Nationalists in Greece got support from other Greeks living in exile and also from many West Europeans who had sympathies for ancient Greek culture.
- Poets and artists lauded Greece as the cradle of European civilisation and mobilised public opinion to support its struggle against a Muslim empire.
- The English poet Lord Byron organised funds and later went to fight in the war, where he died of fever in 1824.
- Finally, the Treaty of Constantinople of 1832 recognised Greece as an independent nation.
Question 28.
State any five features of plantation farming.
OR
Describe the geographical conditions required for the growth of rice.
Answer:
- It is a type of commercial farming.
- It is single crop farming practised on a large area.
- Crops are mainly grown for the market.
- It is both labour intensive and capital intensive.
- It has an interface of agriculture and industry.
- All the products are used as raw material in respective industries.
- Examples of plantation crops are tea, coffee, rubber, sugarcane and banana.
Or
- Rice is a Kharif crop which requires high temperature above 25°C.
- It requires high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm.
- In the areas of less rainfall, it grows with the help of irrigation.
- It is grown in the plains of north and north-eastern India coastal areas and the deltaic regions where fertile alluvial soil is available.
- Development of dense network of canal irrigation and tubewells have made it possible to grow rice in areas of less rainfall in Punjab and Haryana.
Question 29.
Describe the role of political parties in modem democracy.
Answer:
In a modem democracy political parties performed the following major functions:
(i) In most democracies, elections are fought mainly among the candidates put up by political parties. Parties select their candidates in different ways. In India top party leaders choose candidates for contesting elections.
(ii) Parties put forward different policies and programmes and the voters choose from them. In a democracy, a large number of similar opinions have to be grouped together to provide a direction in which policies can be formulated by the governments. A government is expected to base its policies on the line taken by the ruling party.
(iii) Parties play a decisive role in making laws for a country. Formally laws are debated and passed in the legislature. But since most of the members belong to a party, they go by the direction of the party leadership, irrespective of their personal opinions.
(iv) Parties form and run governments. Parties recruit leaders, train them and then make them ministers to run the government in the way they want.
(v) Those parties that lose in the elections play the role of opposition to the parties in power by voicing different views and criticising government for its failure or wrong policies.
(vi) Parties shape public opinion. They raise and highlight issues. Parties sometimes also launch movements for the resolution of problems faced by people. Often opinions in the society crystallise on the lines parties take.
(vii) Parties provide people access to government machinery and welfare schemes implemented by governments.
Question 30.
“Democracy plays an important role to accommodate social diversity.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer:
(i) No society can fully or permanently resolve conflicts among different groups. But we can certainly learn to respect these differences and we can also evolve mechanisms to negotiate the differences. Democracy is best suited to produce this outcome. Non-democratic regimes often turn a blind eye to or suppress internal social differences. Ability to handle social differences, divisions and conflicts is thus a definite plus point of democratic regimes.
(ii) Democracy continues to be democracy as long as all citizens have a chance to be part of majority at any point of time. If someone is debarred from being part of majority on the basis of birth then democracy is said to be concentrated in the hands of a few people.
(iii) It is necessary to understand that democracy is not simply a rule by majority opinion. The majority always needs to work with the minority so that government can function to represent the opinion of common people.
(iv) The rule of majority should not be ruled by majority on the basis of religion or race or linguistic group, etc. Rule by majority means that in case of every decision or in case of very election, different persons and groups may form a majority.
Thus, through the above points, can say that the democracy plays an important role to accommodate social diversity.
Question 31.
“Bank plays an important role in the economic development of the country.” Support the statement with examples.
Oo
“Credit sometimes pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very painful.” Support the statement with examples.
Answer:
Banks play an important role in developing the economy of India:
- They keep money of the people in its safe custody.
- They give interest on the deposited money to the people.
- They mediate between those who have surplus money and those who are in need of money.
- They provide loan to large number of people at low interest rate.
- They promote agricultural and industrial sector by providing loans.
- They also provide funds to different organisations.
Or
In rural areas, the main demand for credit is for crop production. Crop production involves considerable costs on seeds, fertilisers, pesticides, water, electricity, repair of equipment, etc. There is a minimum stretch of three to four months between the time when the farmers buy these inputs and when they sell the crop. Farmers usually take crop loans at the beginning of the season and repay the loan after harvest. Repayment of the loan is crucialy dependent on the income from farming.
If the failure of the crop made loan repayment impossible, then farmers had to sell part of the land to repay the loan. Credit, instead of helping those farmers to improve their earnings, left them worse off and they came into the debt trap. In this case, credit pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very painful.
In one situation credit helps to increase earnings and, therefore, the person/farmer is better off than before. In another situation, because of the crop failture, credit pushes the person into debt trap. To repay the loan farmers have to sell a portion of their land. They are now clearly much worse off than before. Whether credit would be useful or not, therefore, depends on the risks in the situation and whether there is some support in case of loss.
Thus, through the above situation or example, we can easily say that credit sometimes pushes the borrower into a situation from which recovery is very painful.
Section-E
Map Skill Based Question
Question 32.1
Two places A and B have been marked on the given outline map of India. Identify them and
write their correct names on the lines drawn near them.
(A) The place where the Indian National Congress Session was held.
(B) The place where the movement of Indigo planters was started.
Question 32.2
On the same outline map of India locate and label any THREE of the following with suitable symbols.
(a) Sardar Sarovar Dam
(b) Bhilai Iron and Steel Plant
(c) Pune Software Technology Park
(d) Kochi Sea Port
(e) Indore Cotton Textile Industry
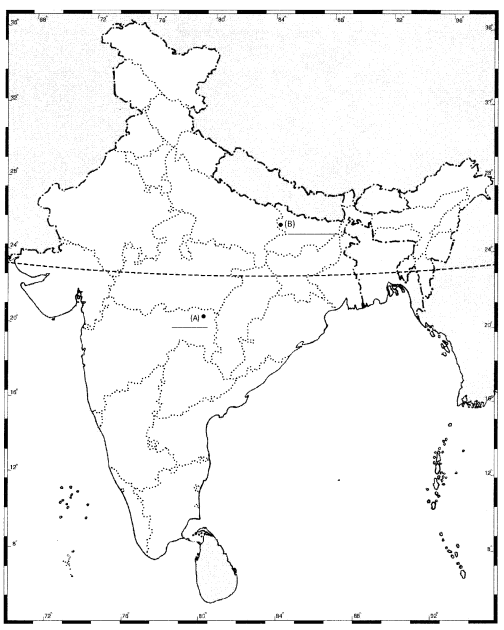
Answer: