Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Accountancy with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 3 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Accountancy Term 2 Set 3 for Practice
Time : 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- The Question Paper consists of two Parts – A and B. There are total 12 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Part – A consists of Accounting Process.
- Part – B consists of Financial Accounting and Computers in Accounts.
- Question Nos. 1 to 2 and 5 to 6 are short answer type questions – I carrying 2 Marks each.
- Question Nos. 3 and 7 to 9 are short answer type questions – II carrying 3 Marks each.
- Questions Nos. 4 and 10 to 12 are long answer type questions carrying 5 marks each.
- There is no overall choice. However, an internal choice has been provided in 3 questions of three marks and 1 question of five marks.
Part-A (12 marks)
Accounting Process
Question 1.
Calculate the due dates of the following bills:
| Date of Bill | Period |
| (a) 28th January 2018 | 1 month |
| (b) 1st December 2017 | 60 days |
| (c) 30th April 2018 | 2 months |
| (d) 23rd November 2017 | 2 months |
![]()
Question 2.
Rectify the following errors :
(a) Goods withdrawn by proprietor for personal use 2,000 were debited to trade expenses account.
(b) Sales return book overcast by ₹ 400.
(c) Credit sales to Mohan ₹ 11,000 were recorded in purchase book.
(d) Credit purchases from Rohan ₹ 6,500 were not posted to his account. [2]
Question 3.
A bill for ₹ 1,000 is drawn by P on Q and accepted by the latter payable at the New Bank of India. Show what entries should be passed in the books of P under each of the following circumstances:
(i) If P retained the bill till due date and then realised it on maturity.
(ii) If he discounted it with his bankers for ₹ 950.
(iii) If he endorsed it to his creditor R in full settlement of his debt.
(iv) If he sent it to his bankers for collection.
Also give necessary entries in each of the cases if the bill is dishonoured.
OR
On 1st January, 2014, A and B drew on each other a bill for ₹ 20,000, payable three months after date for their mutual benefit. On 4th January, they discounted with their bank each other’s bill at 18% per annum. On the due date, each met their own acceptance. Record transactions in the Journal of A and B. [3]
Question 4.
From the following Ledger Balance, draw up the Trial Balance: [5]
| Particulars | Balance |
| Capital | 2,00,000 |
| Purchases | 2,00,000 |
| Stock | 70,000 |
| Sales | 3,00,000 |
| Returns Inward | 1,50,000 |
| Sundry Debtors | 3,00,000 |
| Cash | 1,80,000 |
| Creditors | 1,00,000 |
![]()
Part-B (28 marks)
(Financial Accounting and Computer in Accounts)
Question 5.
Find out the Gross Profit from the following information: [2]
| ₹ | |
| Closing stock | 70,000 |
| Salaries | 30,000 |
| Wages | 40,000 |
| Sales | 6,88,000 |
| Adjusted purchase | 5,50,000 |
Question 6.
From the following figures calculate the operating profit: [2]
| ₹ | |
| Net Profit | 1,00,000 |
| Rent Received | 10,000 |
| Gain on sale of machine | 15,000 |
| Interest on loans | 20,000 |
| Donation | 2,000 |
Question 7.
What are the main disadvantages of computerized accounting ?
OR
(a) What is the difference between RAM and ROM?
(b) Explain the structure and working of CPU.
Question 8.
Arshi does not keep proper records of his business. She provided the following information. You are required to prepare a statement showing profit and loss for the year. [3]
| Particular | Amount ₹ |
| Owner’s Equity at the beginning of the year | 15,00,000 |
| Bills receivable | 60,000 |
| Cash in hand | 80,000 |
| Furniture | 9,00,000 |
| Building | 10,00,000 |
| Creditors | 6,00,000 |
| Stock in trade | 2,00,000 |
| Further capital introduced | 3,20,000 |
| Drawings made during the period | 80,000 |
OR
Gopal does not keep proper books of account. Following information is given below:
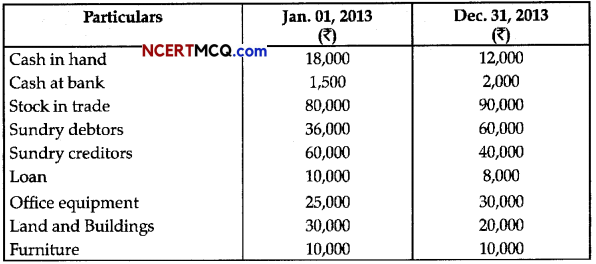
During the year, he introduced an additional capital of ₹ 20,000 and withdrew ₹ 12,000 from the business. Prepare the statement of profit or loss on the basis of the given information. [3]
![]()
Question 9.
Cash Sales ₹ 29,000, Credit Sales ₹ 31,000, Cost of Goods Sold ₹ 52,000, Expenses on Purchases ₹ 3,000,Expenses on Sales ₹ 6,700. Find out Gross Profit and Net Profit. [3]
Question 10.
Following are balances from the trial balance of Mukesh Traders on 31st March, 2016:
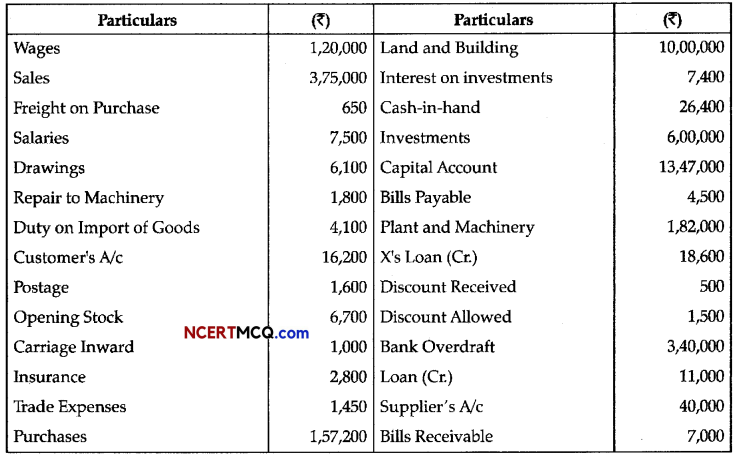
Prepare Trading and Profit & Loss Account for the year ended 31st March, 2016 and Balance Sheet as at that date after taking into account the following adjustments:
(i) Closing Stock was valued at ₹ 20,000.
(ii) Insurance was prepaid ₹
(iii) Write off ₹ 2,000 as Bad debt.
(iv) Depredation to be provided on Land and Building @ 5% p.a. and on Plant and Machinery® 10% p.a.
(v) Create provision for doubtful debts @ 5% on debtors.
(vi) Wages include ₹ 4,800 for installation of a new machinery.
OR
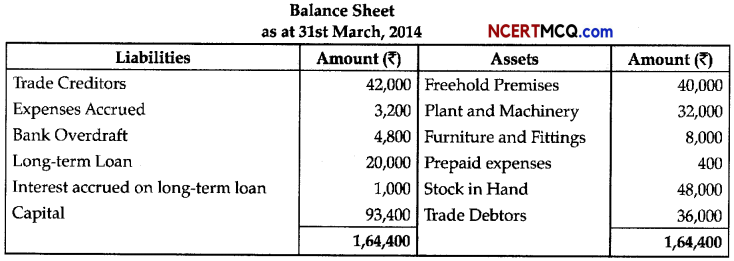
From the Balance Sheet given below, calculate the following:
(i) Fixed Assets
(ii) Current Assets
(iii) Current Liabilities
(iv) Working Capital
(v) Capital Employed
Question 11.
Prepare a Trading Account of M/s Prashant Products from the following particulars pertaining to the year 2013-14 :
| ₹ | |
| Opening stock | 1,50,000 |
| Purchases | 2,10,000 |
| Returns inward | 15,000 |
| Sales | 5,00,000 |
| Returns outward | 17,000 |
| Factory rent | 60,000 |
| Wages | 70,000 |
![]()
Question 12.
“All aspects have different elements which are required to complete it.” In the light of this statement explain the various elements that form a computer. [5]