Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 2 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Biology Term 2 Set 2 with Solutions
Time : 2 Hours
Maximum Marks : 35
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections of 23 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 6 questions of 2 marks each; Sedion-B has 6 questions of 3 marks each, and Section-C has a case-based question of 5 marks.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn.
![]()
Section – A
(2 Marks each)
Question 1.
RuBisCO is an enzyme that acts both as a carboxylase and oxygenase.
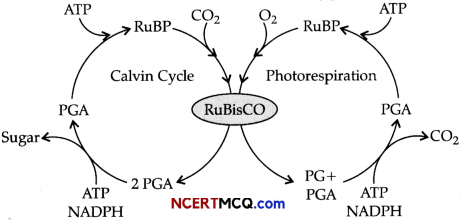
Study the above diagram carefully and explain why RuBisCO carries out more carboxylation in C4 plants?
Answer:
RuBisCO carries out more carboxylation in C4 plants because these plants have mechanism that increases the concentration of CO2 at the enzymatic site. During the C4 pathway, when the C4 acid from the mesophyll cells is broken down in the bundle sheath cells, it releases CO2. This results in the increased intracellular concentration of CO2. So, RuBisCO functions as the carboxylase and binds with plants and carry out more carboxylation.
![]()
Question 2.
What is glycolysis? Where does it occur?
OR
Anaerobic respiration works in contrast to the highly efficient process of aerobic respiration, which relies on oxygen to produce energy. Anaerobic respiration cannot continue for a long in higher organisms. Why? Give any two reasons.
Answer:
Glycolysis is also called as EMP (Embden Meyerhof Parnas) pathway. Glycolysis is the process of breakdown of glucose or similar hexose sugar to two molecules of Pyruvic acid through a series of enzyme-mediated reactions releasing some energy (ATP) and reducing power (NADH). It occurs is cytosol or cytoplasm.
OR
Anaerobic respiration cannot continue for a long in higher organisms because of:
- Low yield of energy.
- Decomposition of large amount of substrates, so that little is left for growth and repairs.
- Toxic effect of end products in higher concentration.
- Inhibition of a number of physiological processes linked with aerobic respiration. (Any two)
Question 3.
A plant hormone is a chemical substance produced naturally in plants which is translocated to another region for regulating one or more physiological reactions, when present in low concentrations.
In how many groups does plant growth regulators are classified?
Answer:
Based on functions, plant growth regulators are broadly classified into two groups:
- Growth promoters: Such plant growth regulators are involved in growth-promoting activities such as cell division, cell enlargement, pattern formation, etc. These include auxins, gibberellins and cytokinins.
- Growth inhibitors: Such PGRs are involved in various growth-inhibiting activities such as promotion of dormancy and abscission. These include abscisic acid and ethylene.
Commonly Made Error
- Some students interchange the names of growth inhibitors and growth promoters.
Answering Tip
- Students should remember that all the plant hormones axe not growth promoters but some are growth inhibitors. Students should understand and learn the function of such phytohormones.
![]()
Question 4.
Neurons are classified into two categories based upon the presence or absence of myelin sheath:
Myelinated neurons and non-myelinated neurons.
(a) Why is the mode of conduction of electrical impulse along the myelinated neurons advantageous to a non-myelinated neuron? (1)
(b) What is this type of conduction called? (1)
Answer:
(a) This is so because the ionic changes and consequent depolarization takes place only at the nodes of Ranvier, which is free from myelin sheath leading to the jumping of action potential from one node to the next.
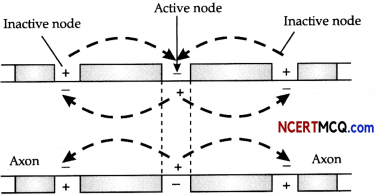
(b) This type of conduction of impulse along a myelinated nerve fibre, is called saltatory conduction.
Commonly Made Error
- Students often get confused between the conduction of impulse in myelinated and non-myelinated nerve fiber.
Answering Tip
- Students should focus on the saltatory conduction and understand the topic thoroughly.
![]()
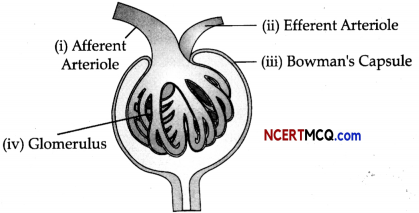
Question 5.
Label the parts in the following diagram using the terms given below: 1/2 × 4
(i) Afferent arteriole
(ii) Efferent arteriole
(iii) Bowman’s capsule
(iv) Glomerulus
Answer:
Question 6.
George comes on a vacation to India from US. The long journey disturbs his biological system and he suffers from jet lag. What is the cause of his discomfort?
OR
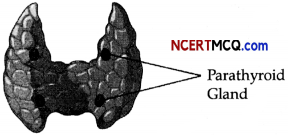
The given gland consists of four separate glands located on the posterior surface of the lobes of the thyroid gland, one pair each in the two lobes.
(a) Name its secretion. How is its secretion regulated? (1)
(b) Mention one parathyroid disorder. (1)
Answer:
It is due to the disturbance in diurnal rhythm. Melatonin plays a very important role in the regulation of a 24-hour (diurnal) rhythm of our body. For example, it helps in maintaining the normal rhythms of the sleep-wake cycle, body temperature and disturbance in this cycle cause discomfort.
OR
(a) The parathyroid glands secrete parathyroid hormone or parathormone, the secretion of which is regulated by the circulating calcium ion.
![]()
(b) Hypoparathyroidism causes the lowering of blood calcium level thereby leading to parathyroid tetany.
Section – B
(3 Marks)
Question 7.
Auxins are the growth hormones capable of promoting cell elongation. They have been used in horticulture to promote growth, flowering and rooting. Write a line to explain the meaning of the following terms related to auxins.
(a) Auxins precursors (1)
(b) Anti-auxins (1)
(c) Synthetic auxins (1)
OR
By looking at which internal structure of a plant you can tell whether a plant is C3 or C4? Explain.
Answer:
(a) Auxin precursors: These are the raw materials used in synthesis of auxins. For example, tryptophan is an Indole-3- acetic acid.
(b) Anti-auxins: These are the compounds which inhibit the action of auxin. For example, TIBA acts as anti-auxins by blocking transport of auxin.
(c) Synthetic auxin: Auxins which are manufactured synthetically and do not grow naturally in plants. E.g. 2,4-D, NAA, etc.
OR
By seeing the V. S. of leaves, one of C3 plant and the other of a C4 plant.
- The C4 plant leaves have Kranz anatomy. The chloroplasts in C4 leaves are dimorphic.
- The bundle sheath cells in C4 make several layers around the vascular bundles. The C3 plants do not have bundle sheath.
- C4 leaves possess large number of chloroplasts, thick cell wall impervious to gaseous exchange and there are no intercellular spaces e.g., maize and Sorghum leaves. The C3 plants possess one type of chloroplasts.
![]()
Question 8.
Respiration is an energy-releasing and enzymatically controlled catabolic process which involves a step-wise oxidative breakdown of organic substances inside living cells. With the help of this statement about respiration, explain the meaning of: O2
(a) Step-wise oxidative breakdown 1 + 1/2
(b) Organic substances (used as substrates). 1 + 1/2
Answer:
(a) Step wise oxidative breakdown means release of small amount of energy, so that same can be trapped and stored for later use. Respiration is a step-wise oxidation of organic molecules in a cell, which involves three main steps: Glycolysis, Krebs cycle and Electron Transport Chain.
(b) Organic substrates are respiratory substrates which are oxidized during respiration to liberate energy inside the living cells. The common respiratory substrates are carbohydrates, proteins, fats and organic acids.
Question 9.
The diagram given below represents a nephron and its blood supply.
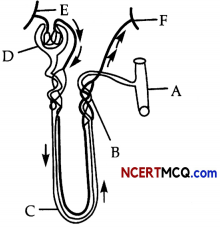
(a) Label parts A, B, C and D.
(b) State the reason for the high hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus.
Answer:
(a) Different parts in the diagram are labelled as:
- A – Collecting duct.
- B – Distal convoluted tubule (DCT).
- C – Loop of Henle.
- D – Bowman’s capsule.
![]()
(b) As the afferent arteriole splits into many fine branches due to which the volume of capillaries reduce, thus raising the hydrostatic pressure in the glomerulus.
Question 10.
The following diagram represents the human heart in one phase of its activity.
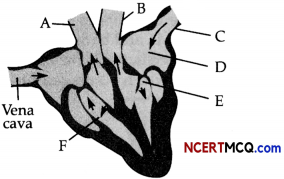
(a) Name the phase. (1)
(b) Which parts of the heart are contracting in this phase? (1)
(c) How many valves are closed in this phase? (1)
Answer:
(a) The phase shown in the figure is ventricular systole.
(b) The lower part consisting of the right and left ventricles are contracting in this phase as the blood seems to be flowing into the pulmonary artery and main aorta, while the bicuspid and tricuspid valves are closed.
(c) Two valves i.e., the bicuspid and tricuspid valves leading from the atria to the ventricles are closed during systole to prevent the back-flow of blood into the atria.
![]()
Commonly Made Error
- Students are not able to identify the blood vessels correctly.
Answering Tip
- Lay emphasis on differences between pulmonary artery and vein.
Question 11.
During muscle contraction, a neural signal, released by central nervous system, when reaches the neuromuscular junction, it releases a neurotransmitter (Acetylcholine) which generates an action potential in the sarcolemma. This action potential along the length spreads through the muscle fibre and causes the release of calcium ions into the sarcoplasm.
(a) Describe the significance of Ca2+ ions in the contraction of muscles. (2)
(b) Which neurotransmitter is responsible for contraction of muscle? (1)
Answer:
(a) Calcium plays a key role in the muscle contraction process. During contraction of muscles, from the motor end plate, an action potential passes over the sarcolemma and further into the T-tubules and sarcoplasmic reticulum and triggers it to produce Ca2+ ions into the sarcoplasm. The binding of calcium ions to the troponin causes its shape and position to change which in turn modifies the position and shape of tropomyosin that binds the troponin. This shift presents the active sites on the molecule, F-actin which prompts the myosin cross-bridges to bind to these active sites.
(b) Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter that is responsible for contraction of muscle.
Question 12.
The given diagram represents the human respiratory system. (2)
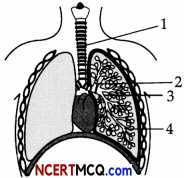
a. Identify the labels 1,2,3 and 4 marked in the diagram.
b. Name the structure which prevents the collapsing of trachea.
c. Why gaseous exchange continues in the lungs even after expiration?
Answer:
(a) In the given diagram, label 1, 2, 3 and 4 represents trachea, bronchi, bronchioles and alveoli respectively.
(b) Cartilaginous rings are the C-shaped structure which prevents the collapsing of trachea.
(c) Gaseous exchange continues in the lungs even after expiration because of the presence of residual volume.
![]()
Section – C
(5 Marks)
Question 13.
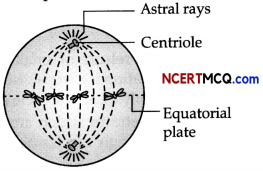
Cell division is the process in which division of nucleus and cytoplasms, occurs. The diagram below represents a stage during the cell division. Study the same and then answer the questions than follow:
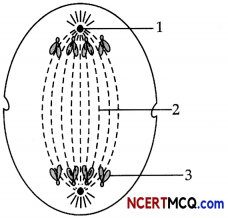
(a) Name the parts labelled 1, 2 and 3.
(b) Identify the above stage and give a reason to support your answer.
(c) Mention where in the body this type of cell division occurs.
(d) Name the stage prior to this stage and draw a diagram to represent the same.
OR
Meiosis is the process in which a single cell divides twice to form four haploid daughter cells. The process is split into meiosis I and meiosis II, and both meiotic divisions have multiple phases. Meiosis I is a type of cell division unique to germ cells, while meiosis II is similar to mitosis. The diagram given below represents a certain phenomenon which occurs during meiosis.
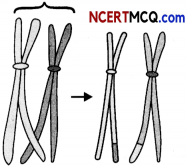
(a) Name the above phenomenon. (1)
(b) Explain it with reference to homologous chromosomes, chromatids, and crossing-over. (4)
Answer:
(a)
- 1 – Centrioles.
- 2 – Spindle fibres
- 3 – Chromatids
(b) The stage described in the diagram is the late anaphase of mitosis in an animal cell. The stage can be identified by the presence of separated chromatids which are found at the two poles of the cell. The appearance of the furrow in the cell membrane classifies the stage as the late anaphase.
![]()
(c) The division shown in the diagram is mitotic division and this kind of cell division occurs in all the cells of the body except for the reproductive cells.
(d) The stage before anaphase is metaphase.
Commonly Made Error
- Students usually find it difficult to identify the correct stage in the process of cell division.
Answering Tip
- Lay emphasis on the diagrams and different stages of cell division. Understand the various changes that a cell undergoes before dividing.
OR
(a) The given phenomenon is the exchange of chromatids between homologous chromosomes called crossing-over. This is the process by which the two chromosomes of a homologous pair exchange equal segments with each other.
(b) Crossing over occurs in the first division of meiosis. At that stage, each chromosome has replicated into two strands called sister chromatids. The two homologous chromosomes of a pair, synapse or come together. While the chromosomes have synapsed, breaks occur at corresponding points in two of the non-sister chromatids, i.e., in one chromatid of each chromosome.
![]()
Since the chromosomes are homologous, breaks at corresponding points, means that the segments that are broken off contain corresponding genes, i.e., alleles. The broken sections are then exchanged between the chromosomes to form complete new units, and each new recombined chromosome of the pair can go to a different daughter sex cell.
It results in recombination of genes found on the same chromosome, called linked genes that would otherwise always be transmitted together.