Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Chemistry with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 4 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 11 Chemistry Standard Term 2 Set 4 for Practice
Max. Marks: 40
Time: 2 Hours
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions carefully.
- There are 12 questions in this question paper with internal choice.
- SECTION A-Q. No. 1 to 3 are very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.
- SECTION B-Q. No. 4 to 11 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.
- SECTION C-Q. No. 12 is case based question carrying 5 marks.
- Alt questions are compulsory.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed.
Section – A (2 Marks each)
Question 1.
Arrange the following in the increasing order of their property indicated (any 2):
(j) BaCl2, MgCl2, BeCl2, CaCl2 (ionic character)
(ii) Mg(OH)2, Sr(OH)2, Ba(OH)2, Ca(OH)2 (Increasing solubility in water)
(iii) MgCO3,CaCO3, SrCO3 and BaCO3 (thermal stability)
Question 2.
In one litre saturated solution of AgCl [Ksp = 1.6 × 10-10 0.1 mol of CuCl [Ksp = 1.0 × 106] is added. Find out the resultant concentration of Ag+ in the solution.
![]()
Question 3.
Give reasons to support your answer:
(i) Although heat is a path function but heat absorbed by the system under certain specific conditions
is independent of path.
(ii) Density, pressure and temperature are intensive properties.
Section – B (3 Marks each)
Question 4.
Account for the following:
(i) The boiling point of pentane is higher than 2,2-dimethylpropane.
(ii) Acetylene is acidic but it does not react with NaOH or KOH.
(iii) AIkynes do not show geometrical isomerism.
OR
Convert the following:
(i) Ethyne into but-2-yne
(ii) Acetic acid into methane,
(iv) Bromoethane into ethane.
Question 5.
Answer the following questions:
(i) Silicon forms \(\mathrm{SiF}_{6}^{2-}\) ion whereas corresponding fluoro compound of carbon is not known. Explain to support your answer.
(ii) What is the state of hybridisation of carbon in (a) \(\mathrm{CO}_{3}^{2}\), (b) Diamond
OR
(i) Why CCl4 is immiscible in water whereas SiCl4 is easily hydrolysed?
(ii) Write balanced equations for:
(a) BF3 + LiH →
(b) A1 + NaOH →
![]()
Question 6.
Account for the following:
(i) Down the group, stability of peroxide and superoxide of alkali metals increases.
(ii) LiF is almost insoluble in water whereas LiCl is soluble not only in water but also in acetone.
(iii) Alkali metals are prepared by electrolysis of their fused chlorides.
Question 7.
An alkene A’ contains three C – C, eight C – H σ bonds and one C – C π bond. ‘A’ on ozonolysis gives two moles of an aldehyde of molar mass 44 u. Write IUPAC name of A.
Question 8.
Observe the figure given below and answer the questions that follow:
The variation of pressure with volume of the gas at different temperatures can be graphically represented as shown in figure.
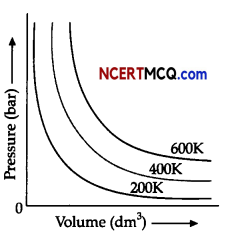
(i) An increase in pressure of a gas at constant temperature, how does the volume of gas vary?
(ii) What will be the change in volume of gas observed if the temperature is increased from 200K to
400K at a constant pressure?
(iil)Calculate the volume occupied by 8.8 g of carbon dioxide at 31.1°C and I bar pressure. (R = 0.083
bar L K-1 mol-1]
![]()
Question 9.
What happens when the following chemical reactions occur:
(i) Beniene is treated with acetyl chloride in presence of anhydrous AlCl3
(ii) Sodium acetate solution is electrolysed.
(ili)Hexane on heating with vanadium oxide over alumina at 10-20 atm pressure.
OR
(i) Write IUPAC names of the following organic compound:
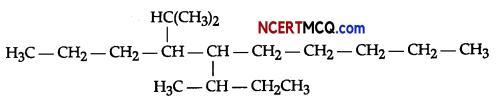
(ii) Complete the following chemical reaction:
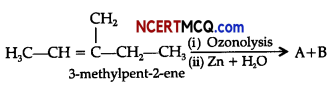
Question 10.
What will be the pressure of the gas mixture when 0.5L of H2 at 0.8 bar and 2.0L of oxygen at 0.7 bar
are introduced in a 1L vessel at 27°C?
Question 11.
(i) Why BCl3 molecule has zero dipole moment, while B-Cl bond has a dipole moment?
(ii) Why pπ – pπ bonding occur in halides of boron and not in those of aluminium?
(iii) What is the resonance structures of CO32- and HCO3–.
OR
On the basis of the figure given below, answer the following questions:
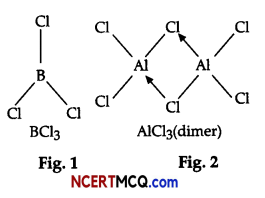
(i) Why do BCl3 and AlCl3 behave as Lewis acids?
(ii) BCl3 exists as monomer whereas AlCl3 is dimerised. Why?
(iii) When BCl3 is treated with water, it hydrolysis and forms [B(OH)4]– only whereas, AlCl3 in acidified
aqueous solution forms [Al(H2O)6]3+ Explain what is the hybridisation of boron and aluminium in
these species?
![]()
Section – C (5 Marks )
Question 12.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow.
The theory of thermodynamics can be summarised in its three main laws. The zeroth law introduces the notion of thermal equilibrium as an equivalence relation of states, where temperature is the parameter that labels the different equivalence classes. In particular, the transitive property of the equivalence relation implies that if a body A is in equilibrium with a body B, and B is with a third body C, then A and C are also in equilibrium. The first law assures energy conservation. It states that in a thermodynamic process not all of energy changes are of the same nature and distinguishes between work, the type of energy that allows for “useful” operations as raising a weight, and its complement heat, any energy change which is not work.
Finally, the second law establishes an arrow of time. It has several formulations and perhaps the most common one is the Clausius statement, which states that no process is possible whose sole result is the transfer of heat from a cooler to a hotter body. Such a restriction not only introduces the fundamental limit on how and to what extent various forms of energy can be converted to accessible mechanical work, but also implies the existence of an additional state function, the entropy, which has to increase.
(i) Name the system which can neither exchange matter nor energy with the surroundings.
(ii) What is the significance of Zeroth Law?
(iii) What Will be the sign of AS for the following reaction? Why is it so?
N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g)
(iv) The enthalpy of combustion of methane, graphite and dihydrogen at 298 K are – 890.3 kj mol-1, -393.5 kj mol-1 and -285.8 kj mol-1 respectively. What is the enthalpy of formation of CH4?
OR
1 g of graphite is burnt in a bomb calorimeter in excess of oxygen at 298 K and 1 atmospheric pressure according to the equation:
C (graphite) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
During the reaction, temperature rises from 298K to 299K. If the heat capacity of the bomb calorimeter is 20.7 kJ/K. What is the enthalpy change for the above reaction at 298K and 1 atm?