Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 2 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Standard Term 2 Set 2 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections and 13 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 6 questions of 2 marks each; Section-B has 6 questions of 3 marks each; and Section-C has a case-based question of 5 marks.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn.
SECTION – A
(Section A has 6 Questions of 2 marks each.)
Question 1.
Give reasons for the following:
(A) An inoculum of curd is added to milk for curdling it.
(B) Dough has a puffed-up appearance.
OR
Why it is considered beneficial to construct a biogas plant in rural areas? (2)
Answer:
(A) The inoculum contains millions of Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) or Lactobacilli which have the ability to convert the lactose sugar present in the milk into lactic acid. This lactic acid results in coagulation and digestion of milk protein casein. Therefore, the milk changes into curd.
(B) The dough has a puffed-up appearance due to the production of CO2 gas which is produced through the process of fermentation by bacteria.
OR
Cattle dung serves as the raw material for the biogas plant and it is available in plenty amount in rural areas. In agriculture, the spent slurry from the biogas plant is used as a manure. Also, the biogas is used for lighting and cooking in rural areas as distribution is only in short distances. Therefore, it is beneficial to construct a biogas plant in rural areas.
![]()
Question 2.
The diagram given below shows the formation of a tumour in between the normal cells. The cancer cells divide uncontrollably. Name the process in which the cells from these tumours migrate through blood or lymph to other parts of the body, and wherever they get lodged in the body, they result in the development of a new tumour. Which kind of tumour is shown this process? (2)
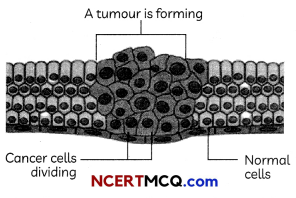
Answer:
The process in which the cells of the tumours migrate through blood or lymph to other parts of the body, and wherever they get lodged in the body, they result in the development of a new tumour is called as Metastasis.
The process of Metastasis is shown by malignant tumours.
Question 3.
In the diagram given below, a bacterial cell is shown. Write the name of the part labeled as part ‘A’ and ‘B’. Also mention the use of part ‘A’ in rDNA technology. (2)
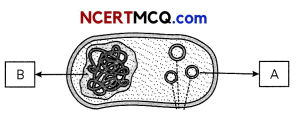
Answer:
The name of the part labeled as part ‘A’ and ‘B’ is:
A – PLasmid,
B – Nucleoid
In rDNA technology, plasmid is used as a cloning vector to transfer the gene of interest into the host cell.
Question 4.
(A) Ramesh explained Riya that ecology is defined as the branch of science that deals with the study of the interactions among organisms. Elaborate the definition to make her understand better.
(B) Due to global warming, Life of many organisms has changed and became difficult. Which among eurythermal or stenothermal organisms can cope up better during global warming? (2)
Answer:
(A) Ecology is the field that deals with the balance between development and maintenance of natural environment and biotic communities, use and conservation of resources, finding solutions of local, regional and global environmental problems.
(B) The organisms that can cope up better during global warming are Eurythermal organisms. These organisms have greater adaptability.
Related Theory
Eurythermal are the organisms that can tolerate and thrive in a wide range of temperatures. Examples: most mammals and birds. Stenothermal are the organisms that can tolerate a narrow range of temperatures. Example: amphibians.
![]()
Question 5.
(A) Roma was wondering about the diverse organisms present around her. She was excited by the fact that so many different types of plants and animals and even microorganisms are present around us. What is the term used for this? Define it.
(B) Within a species, how different sub¬species, variety, breeds and forms are created? illustrate with an example. (2)
Answer:
(A) The variety of life on earth at all its levels, from genes to ecosystems is referred to as biodiversity. Biodiversity can be simply defined as the number and variety of organisms found within a specified geographic region. It refers to the varieties of plants, animals and microorganisms, the genes they contain and the ecosystems they form.
(B) Different sub-species, variety, breeds, forms are formed due to genetic diversity within the species.
Example: The medicinal plant Rauwolfia vomitoria growing in different Himalayan ranges shows genetic variation in terms of the potency and concentration of the active chemical called reserpine that the plant produces.
Related Theory
Genetic diversity is defined as the measure of variety of genetic information contained within the species. Another example is: India has more than 50,000 genetically different strains of rice, and 1,000 varieties of mango.
Question 6.
(A) After the Covid-19 pandemic, government is stressing on vaccination campaign. What is it that prevents a person to suffer from a disease he/she is vaccinated against? Give one reason.
(B) It is advised to avoid crowded and closed places like cinema halls, etc, during What do you mean by withdrawal syndrome changing weather. Why? jn case of drug and alcohol abuse? (2)
Answer:
(A) The vaccine contains the dead pathogen that provokes the active immunity of an individual leading to the formation of antibodies that protect him/her from the disease.
Related Theory
Active Immunity: When an individual (host) is exposed to antigens in the form of living or dead microbes or other proteins. It results in the production of antibodies. This kind of immunity is slow and thus takes time to give its full effective response, but its effect is long lasting. It has no side effects.
An active immunity is induced in our body by deliberately injecting the microbes/antigens either through immunization/vaccination (termed as artificial immunity) or through natural infection by infectious organisms (termed as natural immunity).
(B) During changing weather, the germs or pathogens are more active and prevalent in the atmosphere as the conditions are suitable for their growth and these pathogens are more in crowded and closed places. Therefore, the chances of infection are high in such places.
Related Theory
Infectious agents are more active during changing weather as moist conditions favors the growth of pathogens. Also, at that time the body of the individual is adapting the changing environmental conditions of temperature, humidity, etc., so the person is more vulnerable to diseases and thus can easily get infected by these pathogens.
OR
Withdrawal syndrome is also known as discontinuation syndrome. This occurs in individuals who have developed physiological dependence on drugs or alcohol and who discontinue or reduce their use of it.
Related Theory
The person becomes addicted and dependent on drugs or alcohol in the absence of any guidance or counselling. The tendency of the body to manifest a characteristic and unpleasant withdrawal syndrome if regular dose of drugs/alcohol is abruptly discontinued is called as Dependence. The withdrawal symptoms include anxiety, shakiness, nausea and sweating that are relieved when use is resumed again. The withdrawal symptoms can be severe and even life threatening and the person may require medical supervision. The patient can break all social norms in order to get sufficient funds to satiate his/her needs due to dependence on drugs or alcohol. This can lead to many social adjustment problems.
![]()
SECTION – B
(Section B has 6 Question of 3 marks each.)
Question 7.
(A) Suhani and her friends went for
educating their colony regarding the spread of diseases via mosquitoes. They emptied all the overhead tanks, which were not in use for last few months. What was the purpose of this act? Name the pathogen which is responsible for causing malaria (mosquito borne disease).
(B) The thymus gland of a person is removed. Will the immune system of that person be affected? If yes, how? (3)
Answer:
(A) The purpose behind emptying the overhead tanks was to prevent mosquito borne diseases as the water in the tanks was stagnant and can become a breeding ground for the mosquitoes. The pathogen which is responsible for causing malaria is Plasmodium (a protozoan).
(B) Thymus gLand is a primary lymphoid organ where immature lymphocytes differentiate into antigen-sensitive lymphocytes. Therefore, removal of thymus gland makes the immune system weak and as a result the person’s body becomes more prone to infectious diseases.
Question 8.
The following picture shows the three basic steps of genetic engineering. Write down these steps briefly.
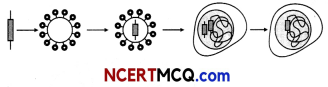
OR
One of the crucial steps of genetic engineering is the identification of recombinant DNA containing the desired gene. This is done by a process called insertional inactivation. Explain this process with the help of an example. (3)
Answer:
The three basic steps of genetic engineering or making a Genetically Modified Organism(GMO) are:
(i) Identification of DNA with desirable genes.
(ii) Introduction of the identified DNA into the suitable host to form recombinant DNA (rDNA).
(iii) Maintenance of introduced DNA in the host and transfer of the DNA to its progeny.
OR
Insertional inactivation refers to the insertion of a certain gene in the host DNA at a particular site. Due to this insertion, the function of the gene at whose site insertion has taken place gets inactivated. This process is used to identify recombinant DNA containing organisms from those who are non-recombinants.
Example: A recombinant DNA is inserted within the coding sequence of an enzyme, (3-galactosidase, that results into inactivation of the gene for synthesis of this enzyme. This is known as insertional inactivation. If the plasmid in the bacteria is devoid of the insert (foreign DNA), it will result in the formation of blue-coloured colonies due to the presence of a chromogenic substrate. Whereas the presence of insert results into insertional inactivation of
the β-galactosidase gene and thus it does not code for the enzyme, hence the chromogenic substrate is not acted upon by the enzyme, thus the colonies do not produce any coLour and are identified as recombinant coLonies.
![]()
Question 9.
(A) A 4-year-old girl undergone the first gene
therapy in 1990 as shown in the picture below. For which disease she was treated and name the scientists responsible for attempting this successful therapy?
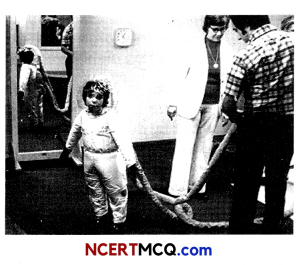
(B) RNA interference is a method of cellular defense in which silencing of a specific mRNA is performed through a complementary RNA molecule that binds to and prevents translation of the mRNA. From where does this complementary RNA come from? (3)
Answer:
(A) In 1990, the first clinical gene therapy was given to a 4-year-old girl suffering from Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) deficiency by Michael Blease and W. French Andreson of National Institute of Health.
Related Theory
The enzyme adenosine deaminase is very important for the immune system to function. The cause of the disorder is deletion of the gene coding for adenosine deaminase.
(B) This complementary RNA can come from:
(i) An infection by viruses having RNA genomes.
(ii) Mobile genetic elements (transposons) that replicate via an RNA intermediate.
Question 10.
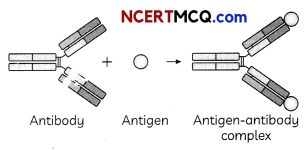
(A) The given picture shows the antigen- antibody reaction. Name a technique based on the principle of antigen- antibody reaction used in the detection of a virus.
(B) It was an amazing discovery in the field of biotechnology that bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis produces a toxin that can kill insects belonging to a particular group. But the bacteria itself do not get killed by the toxin it produces. Explain the major reason behind this? (3)
Answer:
(A) The technique that is based on the principle of antigen-antibody interaction and used in the detection of a virus is Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA).
Related Theory
Antigen-antibody interaction refers to a specific chemical interaction between antibodies produced by B-lymphocytes and antigens from any source during an immune reaction. Antibodies recognize specific proteins present on antigen surface. The reaction between antigen and antibody leads to agglutination. ELISA can be used to detect an antibody to HIV.
(B) Bacillus thuringiensis forms protein crystals during a particular phase of their growth. A toxic insecticidal protein is present in these crystals. But the bacterium itself is not affected or killed by this toxin because the BT toxin protein exist as inactive protoxins, but when an insect feed on such a plant and ingest the inactive toxin, the protoxin gets converted into an active form due to the alkaline pH of the gut, that solubilize the crystals. The activated toxin binds to the surface of midgut epithelial cells and make it porous resulting in cell swelling and lysis and finally cause death of the insect.
![]()
Question 11.
(A) Parasites are well adapted to survive inside the body of their respective hosts. Enlist any two adaptive features evolved in parasites that enable them to survive successfully in or on their hosts.
(B) Among all the abiotic factors that influences life of organisms, why temperature is considered to be the most relevant factor? (3)
Answer:
(A) Parasites have evolved special adaptations that enable them to survive successfully, in or on their hosts they are:
- Loss of unnecessary sense organs.
- Presence of adhesive organs or suckers to cling on to the host.
- Loss of digestive system.
- High reproductive capacity. (Any two)
(B) Temperature is an important ecologically
environmental factor that affects the different aspects of the living organism. Different types of physiological activities such as enzymatic activities as well as geographical distribution of different species depends on the temperature conditions and levels of their thermal tolerance. Therefore, the living organism is required to maintain specific internal temperatures.
Related Theory
Temperature influences the distribution of species as the species are able to grow within a narrow range of temperature which is known as the optimum temperature. The organisms are able to survive by maintaining all biological processes within an optimum temperature. The primary factors that affect the organisms are temperature, water, humidity, pH.
Question 12.
The available species inventories to estimate the global species diversity do not include the diversity of prokaryotic species. The biologists are still unaware of the total prokaryotic diversity. Why? Give reasons. (3)
Answer:
Biologists are still unaware of the total prokaryotic diversity because of the following reasons:
- The conventional taxonomic methods are not suitable for identifying microbial species.
- Many microbial species cannot be cultured under laboratory conditions.
- If biochemical or molecular criteria for delineating microbial species is accepted and followed, then their diversity alone might run into millions.
![]()
SECTION – C
(Section C has a case-based question of 5 marks.)
Question 13.
A school student trip was organized and students were taken to a sewage treatment plant, where the students observed the treatment of sewage before it can be discharged into rivers.
Based on this, answer the following questions:
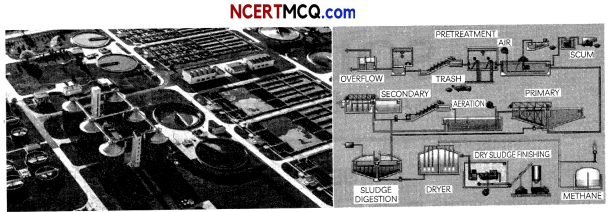
(A) What do you mean by waste water?
(B) Why reduction in BOD is required in the treatment of sewage water?
(C) The process which involves removal of large and small particles through filtration and sedimentation is called as?
(D) State two advantages of sewage treatment plants.
OR
Rekha observed the following pictures of microbes showing virus and bacteria. On seeing these pictures, it reminded her of the beginning of the Covid-19 pandemic. She started cursing microbes as she thought that they are a curse on this earth. But her teacher told her that all the microbes are not harmful for us. Microorganisms are very useful as they provide various medicines, household products, bioactive molecules, etc.
Based on this answer the following questions:
(A) (i) Apart from making curd, what is the function of microbe Lactobacillus1
(ii) Name any two enzymes produced by microbes that are used for clarification of bottled juices.
(B) (i) Name the fungus from which first antibiotic was isolated.
(ii) Write any two roles served by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. (5)
Answer:
(A) Waste water is the water that is produced after the use of fresh water by human beings for variety of applications such as domestic, commercial and industrial use.
(B) The greater the BOD of sewage water, more is its polluting potential. So, the sewage water is treated, till its BOD is reduced to reduce the organic matter present in it.
(C) The process which involves removal of large and small particles through filtration and sedimentation is called as primary treatment of sewage.
(D) The advantages of sewage treatment plants (STPs) are:
(i) STPs preserve natural environment against pollution.
(ii) STPs eliminate disease-causing bacteria and kills harmful organisms from the sewage water before its discharge into the rivers. In this way, STPs reduces risk to public health and the environment.
OR
(A) (i) Lactobacillus increases the nutritional value of the curd by increasing the amount of vitamin B12 in it.
(ii) Two enzymes produced by microbes that are used for clarification of bottled juices are pectinase and protease.
![]()
(B) (i) The fungus/mould from which first antibiotic was isolated was Penicillium notatum.
(ii) Two roles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are:
(i) It is used in bread making.
(ii) It is used in the commercial production ofethanoL
Related Theory
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is also known as baker’s and brewer’s yeast.