Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 6 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Standard Term 2 Set 6 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections and 13 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 6 questions of 2 marks each; Section-B has 6 questions of 3 marks each; and Section-C has a case-based question of 5 marks.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn.
SECTION – A
(Section A has 6 Questions of 2 marks each.)
Question 1.
Given below is the picture of a transgenic crop – Bt cotton. It is an insect resistant variety. In these plants, a gene is incorporated which produces a toxic protein that kills the insects. Name the toxic protein and source organism. What type of changes occur in the gut of insects on consuming this protein? (2)

Answer:
The bacterium Bacillus thuringiensis produces the toxic protein called as ‘cry protein’ which is lethal to certain insects. This protein is formed in an inactive form called as protoxin. Prototoxin becomes active toxin inside the gut of the insects due to its alkaline pH. Activated toxin bind to surface of midgut epithelial cells and cause perforation, swelling, lysis of cells which ultimately leading to death of the insect.
![]()
Question 2.
The following picture shows the apparatus involved in the process of gel electrophoresis. In the technique of gel electrophoresis, which material is used as matrix? Also mention its role.

OR
How the limitation of traditional hybridisation process was overcome by the use of technique of genetic engineering? (2)
Answer:
Agarose is the most commonly used matrix. The basis of gel electrophoresis is that the DNA fragments separate (resolve) according to their size through sieving effect provided by the agarose gel. Therefore, the smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves.
Related Theory
Agarose is a natural polymer extracted from sea weeds.
OR
The limitation of traditional hybridisation process was overcome by the use of techniques of genetic engineering, including:
- Creation of recombinant DNA.
- Use of gene cloning and gene transfer.
This allows isolation and introduction of only one or a set of desirable genes without introducing undesirable genes into the target organism.
Question 3.
Why did the Indian Parliament clear the second amendment of the Indian patents bill ?
OR
List any two advantages of using a biopesticide. (2)
Answer:
The Indian Parliament cleared the second ‘ amendment of the Indian Patents Bill which takes some issues into consideration, including biopiracy, patent terms, emergency provisions and research and development initiative. The amendment of this bill has empowered India to prevent unauthorized exploitation of their bio-resources and traditional knowledge by other countries.
OR
The advantages of using a biopesticide are:
- With the use of biopesticide, there is great reduction in the use of agrochemicals which are responsible for pollution, thus biopesticides are eco-friendly.
- They serve as a permanent control of pests by having a long persisting effect. Also, they leave no toxic residue.
![]()
Question 4.
Calculate the death rate for the week, in which 5 individuals died in a week in the laboratory population of 100 individuals. (2)
Answer:
Death rate is the number of deaths in a particular area in a particular time period per 1000 individuals.
It is calculated by:
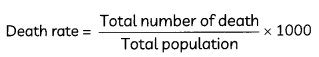
= \(\frac{5}{100}\) x 1000
= 50 individuals per 1000 individuals per week.
Therefore, the death rate is 5% per week.
Related Theory
Death rate can be defined as the number of individuals that are lost per unit of population per unit time due to different reasons like death, certain environmental changes such as competition, predation.
Question 5.
(A) What is the application of genetically engineered bacterium Pseudomonas Putida?
(B) What is the role of C-peptide in human insulin? (2)
Answer:
(A) Pseudomonas putida is capable of digesting hydrocarbons of crude oil, thus are used for scavenging oil spills.
(B) C-peptide is present in immature form of insulin (pro-hormone/pro-insulin). It serves as a linker between the A- and the B- chains of insulin and facilitates the efficient assembly, and folding of insulin in the endoplasmic reticulum of beta cells of the pancreas. But, this C-peptide gets removed during maturation of insulin.
![]()
Question 6.
(A) What is the ill-effect of excessive use of antibiotics?
(B) Who coined the term “Antibiotics”? (2)
Answer:
(A) Excessive use of antibiotics can lead to infection or colonization with resistant pathogens, consuming antibiotics unnecessarily for viral infection is common and thus lead to increasing rates of antibiotic resistance among Streptococcus pneumoniae and other commonly infecting pathogens.
Related Theory
The factors that cause overuse of antibiotics are past experience, patient’s expectations, lack of education and economic incentives.
(B) The term ‘antibiotics’ was given by Selman Waksman (1942).
SECTION – B
(Section B has 6 Questions of 3 marks each.)
Question 7.
A lab technician runs a PCR machine for years by simply making use of the samples and components available to him. But he is not having knowledge of all the components. Enlist the basic components of a Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) to make him understand the process in a better way? (3)
Answer:
Basic components of PCR are as follows:
- DNA template – It is the double-stranded DNA that needs to be amplified.
- Primers – These are chemically synthesised oligonucleotides (short segment of DNA) that are complementary to the regions of DNA template.
- Taq Polymerase – This enzyme is isolated from a thermophilic bacterium – Thermus aquaticus, having the property of remaining active even at high temperature during the denaturation of double stranded DNA. It is a DNA polymerase that helps in the amplification of a segment of DNA.
- Nucleotide bases – These are utilized or added by DNA polymerase to the growing chain.
![]()
Question 8.
(A) A famous example of mutualism is between pollinating species of wasps with specific fig plants. What are the benefits that the female wasps derive from the fig trees from such an interaction?
(B) Why predators are termed as ‘prudent’ in nature? (3)
Answer:
(A) The female wasp is benefited by using the fruit as an oviposition (egg-laying) site and also uses some of its developing seeds within the fruit for nourishing its larvae. In return, the wasp pollinates the fig inflorescence while searching for suitable egg-laying sites.
(B) There is a possibility of prey becoming extinct, if a predator is too efficient and over exploits its prey and as a consequence the predator will also become extinct due to lack of food. This is why the predators eat the prey population in a manner that the prey conlinus to survive and is not over exploited. Just because of this reason, predators eat the prey population in a manner that the prey continues to survive and is not over exploited. Just because of this reason predators are ‘prudent’ in nature.
Question 9.
(A) What do you mean by BOD Test? When is this test performed during sewage treatment?
(B) Three samples of water are taken, their BOD was measured and found to be 40 mg/L, 10 mg/L and 600 mg/L. Which sample of water is most polluted? (3)
Answer:
(A) Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) test refers to a bioassay procedure that measures the oxygen consumed by bacteria from the decomposition of organic matter over a period of five days at an incubation temperature of 20°C. BOD is expressed in milligrams per litre of sample water. Biochemical Oxygen Demand is used in secondary sewage treatment or biological sewage treatment.
(B) The BOD level and oxygen content are inversely related to each other, thus when BOD levels are high, dissolved oxygen levels decrease because the oxygen present in the water is consumed by the bacteria. Therefore, higher the BOD higher the water is polluted.
As a result, the sample with BOD value of 600 mg/L is highly polluted water.
Related Theory
Measuring of Biochemical Oxygen Demand test was given by Sawyer and McCarty in the year 1978.
Caution
Many students get confused with the term BOD, and think it as the amount of oxygen required by organisms. It actually refers to the amount of oxygen consumed by bacteria during oxidation of organic matter in 1 liter of water.
![]()
Question 10.
Name the following:
(A) A drug used for helping patients cope with mental illness like depression but often misuse.
(B) Plant source of the drug popularly called “smack.”
(C) Protozoan parasite that causes amoebic dysentery in humans. (3)
Answer:
(A) Heroin
(B) Papaver somniferum
(C) Entamoeba histolytica
Question 11.
Enlist the benefits that are demonstrated by plants with mycorrhizal association.
OR
How biofertilisers are responsible for increasing the fertility of soil? (3)
Answer:
Plants with mycorrhizal association demonstrate benefits such as:
- Resistance to root-borne pathogens.
- Tolerance to salinity and drought.
- Overall increase in plant growth and development.
OR
A biofertilizer can be defined as a fertiliser that is made up of living microorganisms.
It promotes plant growth when applied to the field, by increasing the supply or availability of primary nutrients to the host plant. Therefore, this helps in increasing the fertility of the soil. The main sources of biofertilisers are several species of bacteria and cyanobacteria which have the ability to fix free atmospheric nitrogen into organic compounds and making it available to plants to be used as a nutrient.
Another is one fungi which form symbiotic associations with plants, known as mycorrhiza. In such associations, the fungal symbiont absorbs phosphorus from soil and transfers it to the plant. This promotes plant growth.
One of the major advantages of biofertilizers is that they are eco-friendly and cost-effective.
![]()
Question 12.
A doctor always advice his/her patients to
maintain good health by practicing certain good habits. List any three of them. (3)
Answer:
Good health can be achieved and maintained by:
- Intake of balanced diet, keeping personal hygiene and doing regular exercise.
- Performing regular yoga to achieve physical and mental health.
- Being aware about diseases and their effect on different bodily functions.
- Getting vaccination or immunization against infectious diseases.
- Disposing of wastes properly, controlling vectors and maintaining hygiene in food and water resources.
(Any three of the above)
SECTION – C
(Section C has a case-based question of 5 marks.)
Question 13.
The teacher showed a picture depicting a wildlife sanctuary and explained that a sanctuary is a place where wild animal and plants are protected in their natural surroundings. The activities such as collection of forest products, harvesting of timber, private ownership of land is allowed here.
Based on this answer the following questions:

(A) There is a region in Biosphere Reserve which is legally protected and where no human activity is allowed. What is that region called as?
(B) Which is the first wildlife Sanctuary in India?
(C) In which year the Indian Board for Wildlife constituted?
(D) Define the following with respect to Biosphere reserve:
(i) Buffer zone
(ii) Transition zone
OR
Alien species or non-native species are often introduced deliberately into a habitat for their economic and other uses. They often become invasive and drive away local species. Exotic
species have proved harmful for both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystem. The following picture shows an invasive plant – water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) that was introduced in India because of its beautiful flowers and shapes of leaves. But it clogged many waterbodies resulting in death of aquatic plants and animals.
Based on this answer the following questions:

(A) (i) Define invasive species.
(ii) Name one invasive species introduced in India apart from water hyacinth.
(iii) What do you mean by an endemic species?
(B) Mention any two ways in which an invasive species affects an ecosystem. (5)
Answer:
(A) The region in Biosphere Reserve which is legally protected and where no human activity is allowedis called a Core zone.
(B) The first Wildlife Sanctuary in India is Manas National Park or Manas Wildlife Sanctuary.
(C) Indian Board for Wildlife was constituted in 1952.
Explanation: The main purpose of the board was to advise the Government on the means of conservation and protection of wildlife, construction of national parks, sanctuaries and zoological gardens as well as promoting public awareness regarding conservation of wildlife.
(D) (i) Buffer zone may accommodate education, training, tourism and recreation, an area with limited human interference.
(ii) Transition zone is the large outer area of a reserve where people live and work, using the natural resources of the area in a sustainable manner.
![]()
OR
(A)
(i) The alien species that is unintentionally or deliberately introduced for different purposes, turn invasive, and cause decline or extinction of indigenous species.
(ii) The invasive weed species carrot grass (Parthenium) or Lantana camara was introduced in India that led to the environmental damage and posed a threat to our native species.
(iii) An endemic species refers to a species that is native to where it is found.
(B) Invasive species can be a major cause of biodiversity loss in an ecosystem. Invasive species competes with the native species for resources and therefore lead to extinction of native species. They can reduce biodiversity and alter the food web and habitats.