Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 7 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Biology Standard Term 2 Set 7 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- All questions are compulsory.
- The question paper has three sections and 13 questions. All questions are compulsory.
- Section-A has 6 questions of 2 marks each; Section-B has 6 questions of 3 marks each; and Section-C has a case-based question of 5 marks.
- There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
- Wherever necessary, neat and properly labeled diagrams should be drawn.
SECTION – A
(Section A has 6 Questions of 2 marks each.)
Question 1.
(A) Why does a person shivers considerably while suffering from malaria?
(B) Who established that the malarial parasite is transmitted by the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito?
OR
Why intake of cannabinoids is banned in sports and games? (2)
Answer:
(A) The parasites (sporozoites) infect RBCs and rupture them which results in the release of a toxic substance called as haemozoin. This toxin is responsible for the chill (shivering) and high fever recurring every three to four days in malaria.
(B) Sir Ronald Ross.
Related Theory
Sir Ronald Ross of the Indian Medical Service, established on 29th August, 1897 that malarial parasite is transmitted by the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito.
OR
The intake of cannabinoids is banned in sports and games because sportspersons misuse these drugs to enhance their performance. In order to increase muscle strength and bulk and to promote aggressiveness, the sportspersons misuse narcotic analgesics, anabolic steroids, diuretics and certain hormones in sports, that leads to an increase in their athletic performance. This can negatively affect their general health and in long run can hamper the normal functioning of organ systems.
![]()
Question 2.
Write any two benefits that Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) provides. (2)
Answer:
The two benefits of Lactic Acid Bacteria (LAB) are:
- LAB increases the nutritional quality of curd by increasing the amount of Vitamin B12
- It checks the growth of disease-causing organisms in the gut.
Question 3.
Roma was confused after hearing about
red data book which is shown in the picture below. She thinks it to be a storybook. To clear her confusion, explain briefly what do we mean by red data book. When and who initiated the red data book? (2)

Answer:
A Red Data Book is a document that keeps a record of all the rare and endangered species of animals, plants and fungi. IUCN red list of threatened species is an inventory of global conservation status of biological species, which is compiled in Red Data Book.
IUCN established the Red Data Book to safeguard the rare species of flora and fauna on Earth, so as to prevent their extinction and it was initiated in 1964.
Related Theory
Red Data Book has its origins from Russia. But at the present time, the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) maintains the Red Data Book. The IUCN was founded in 1948 with an aim to maintain a complete record of every species that ever lived and it works in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources.
![]()
Question 4.
During sewage treatment, list the events that Lead to a significant reduction in Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) of a primary effluent. (2)
Answer:
The primary effluent produced during primary treatment is passed into large aeration tanks, where it is constantly agitated mechanically and air is pumped into it. This leads to vigorous growth of useful aerobic microbes into floes. The organic matter in the effluent is consumed by these microbes, thereby, decreasing BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) of the effluent.
Related Theory
Floes are masses of bacteria associated with fungal filaments to form mesh like structures. During their growth, the major part of the organic matter in the effluent is consumed by these microbes and converted into microbial biomass. As a result, the BOD (Biochemical Oxygen Demand) of the effluent is significantly reduced.
Question 5.
How the technique of PCR serves as an important tool for early diagnosis of an infectious disease? (2)
Answer:
The technique of PCR, i.e., Polymerase chain reaction is very effective and thus it enables the specific amplification of the desired DNA from a limited amount of DNA template. Therefore, it can detect the presence of an infectious organism in the infected patient at an early stage of infection, even before the infectious organism has multiplied to a large number.
Related Theory
Technique of PCR is routinely used to detect HIV in suspected AIDS patients and also used to detect mutations in genes in suspected cancer patients.
![]()
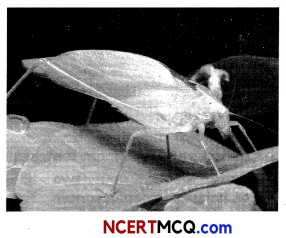
Question 6.
The following picture depicts an insect that closely resembles a leaf. What is this phenomenon called as? How does this phenomenon help an insect?
OR
Give the difference between the two main branches of ecology. (2)
This phenomenon is called as camouflage. Camouflage or cryptic colouration is a type of defense mechanism that gives the organisms like insect, the ability to blend or merge with the surroundings or background. This helps them to conceal their presence or identity in order to avoid being detected easily by the predator or to deceive their prey.
OR
The two main branches of ecology are autecology and synecology and the difference between them are:
| Autecology | Synecology |
| It is the study of individual organism or individual species. It is also known as population ecology. | It is the study of group of organisms of different species in a community. It is also known as community ecology. |
SECTION – B
(Section B has 6 Questions of 3 marks each.)
Question 7.
(A) The following microbes share a common characteristic. List that characteristic. Aspergillus niger, Clostridium butylicum and Lactobacillus.
(B) Why in the treatment of waste water rich in organic matter, aerobic degradation is more important than anaerobic degradation? (3)
Answer:
(A) The common characteristic of the microbes Aspergillus niger, Clostridium butylicum and Lactobacillus is that they all produce organic acids as a part of their metabolism and thus are useful for commercial and industrial production.
Related Theory
Aspergillus niger (a fungus) produces citric acid, Clostridium butylicum (a bacterium) produces butyric acid and Lactobacillus (a bacterium) produces lactic acid.
(B) The aerobic heterotrophic bacteria bring aerobic degradation of sewage. During their vigorous growth, the aerobic microbes consume a major part of the organic matter and thus reduce the BOD significantly. Therefore, aerobic degradation is more important.
Whereas anaerobic degradation is done after the aerobic degradation (where the BOD is already pulled down below a threshold level). In anaerobic degradation, only the bacteria and fungi (present in the floes) in the activated sludge are digested and anaerobic bacteria produce a mixture of gases such as methane, hydrogen sulphide and carbon dioxide. Therefore, it is less important.
![]()
Question 8.
(A) It is very essential to make host cells competent so that they can take up the desired DNA. Describe the two physical methods of making the cells competent for transformation with recombinant DNA.
(B) Expand – cDNA and Bt. (3)
Answer:
(A) The two different physical methods for
making the cells competent are:
- Micro-injection: In this method the recombinant DNA is directly injected into the nucleus of an animal cell.
- Biolistics or gene gun: This method includes physical introduction of foreign DNA in cells and is suitable for plants.
In this method the cells are bombarded with high velocity micro-particles of gold or tungsten coated with DNA.
(B) cDNA – Complementary DNA, Bt – Bacillus thuringiensis.
Question 9.
The introduction of genetically engineered lymphocytes into an ADA deficiency patient served as a cure but it was not a permanent cure. Why? Suggest a possible permanent cure. ?(3)
Answer:
Genetically engineered lymphocytes are created by taking lymphocytes from the blood of ADA deficient patients and grown in a culture. With the help of a retroviral vector, a functional ADA cDNA is then introduced into the lymphocytes. Then these lymphocytes are returned to the patients. Most of the lymphocytes are short lived having an average lifespan of a week to a few months. Since lymphocytes are not immortal, therefore, the patients require periodic infusion of such genetically engineered lymphocytes.
A permanent cure of ADA deficiency is to isolate a normal functioning gene producing ADA from the marrow cells and to introduce them into the cells at early embryonic stages. The lymphocytes of bone marrow then contain the functional ADA gene and reactivate the patient’s immune system.
Related Theory
Adenosine deaminase deficiency is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that causes immuno deficiency.
![]()
Question 10.
Water is used by every cell of our body and thus it is very essential for life. List any three features of plants that help them to survive in water scarce environment. (3)
Answer:
The features of plants that help them to survive in water scarce environment are:
- They have a thick cuticle on their leaf surfaces and have sunken stomata (arranged in deep pits) to minimize water loss through transpiration.
- They follow a special photosynthetic pathway known as Crassulacean Acid Metabolism (CAM) that enables their stomata to remain closed during day time. This also minimize water loss through transpiration.
- Absence of leaves in some desert plants like Opuntia in which the leaves are reduced to spines to reduce water loss and the photosynthetic function is taken over by the flattened stems. The stem is green, succulent and fleshy.
- The roots of these plants grow very deep in search of available underground water.
(Any three)
Question 11.
It is observed that tropical regions have greater biodiversity as compared to temperate regions. Briefly explain the reasons responsible for it.
OR
How does the loss of biodiversity in a particular region affect that region? (3)
Answer:
The tropical regions have greater biodiversity as compared to temperate regions because of the following reasons:
- Speciation is generally a function of time. The temperate regions were subjected to frequent glaciations in the past whereas the tropical latitudes remained relatively undisturbed for millions of years and therefore the tropics got a long evolutionary time for species diversification.
- The Tropical environments are less seasonal as compared to temperate environments and are relatively more constant and predictable. Therefore, niche specialization is promoted in such constant environments which lead to a greater species diversity.
- More amount of solar energy is available in the tropics which contributes to higher productivity and thus lead to greater diversity.
- The resource availability is higher and rate of extinction is low in tropics.
OR
Loss of biodiversity in a region may lead to:
- Decline in plant production.
- Lowered resistance to environmental disturbances; like drought.
- Increased variability in certain ecosystem processes, example – plant productivity, water use, etc.
![]()
Question 12.
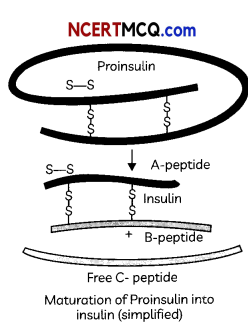
Describe the structure and the process of activation of human insulin with the help of a well labelled diagram. (3)
Answer:
Insulin consists of two short polypeptide chains, i.e., chain A and chain B, which are Linked together by disulfide bridges.
Insulin is synthesized as a pro-hormone in mammals including humans. It contains an extra stretch called the C peptide. The C peptide is absent in mature insulin and therefore it is removed during maturation into insulin.
Related Theory
Pro-hormone is the form of hormone which needs to be processed before it becomes a fully mature and functional hormone.
SECTION – C
(Section C has a case-based question of 5 marks.)
Question 13.
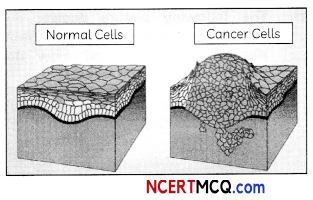
Any individual can suffer from cancer, although the risk goes up with age. But the risk depends on factors such as smoke, Lifestyle choices such as eating habits, frequency of exercise, family history of cancer, etc. Given below is a picture showing a comparison between a normal cell and a cancerous cell.
(A) Define cancer.
(B) Give the difference between benign tumours and malignant tumours.
(C) Write about any two diagnostic techniques to detect cancer.
OR
A 34-year-old woman showed the symptoms of sudden onset of fever, crippling joint pains, lymphadenopathy. The following picture shows one of the symptoms of the disease.
Based on the following picture and description answer the following questions:
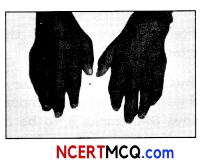
(A) Based on the above mentioned symptoms, name the disease. How can this disease be prevented?
(B) List two ways by which vector-borne diseases can be prevented.
(C) What are pathogens? How do they enter our body? (5)
Answer:
(A) Cancer is a disease that is characterised by uncontrolled division of cells in a part of body that spreads to other parts of the body through blood and lymph.
(B) Benign tumours: These kinds of tumours remain confined to their original Location and thus, do not spread to the other parts of the body. Such tumours cause Little damage.
Malignant tumours: These tumours are a mass of proliferating cells called as neoplastic or tumour cells. These cells invade and damage the surrounding normal tissues/cells .by growing very rapidly.
![]()
(C) Cancer can be detected by the following methods:
- Biopsy: In this method a piece of the suspected tissue is cut into thin sections and then it is stained and examined under microscope by a pathologist. Such a study is termed as histopathological study.
- Radiography involves the use of X-rays to detect cancer of the internal organs.
- Computed – tomography (CT) uses X-rays to generate a three-dimensional image of the internal tissue.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses strong magnetic fields and non-ionising radiations to accurately detect pathological and physiological changes in the living tissue.
- Monoclonal antibodies are the antibodies against cancer-specific antigens that are used to detect certain cancers. (Any two)
OR
(A) Based on the mentioned symptoms, the disease’s name is chikungunya. This disease can be prevented by elimination of mosquitoes and their eggs.
(B) Vector-borne diseases can be prevented by:
- avoiding stagnation of water in and around residential areas.
- regular cleaning of household coolers.
- use of mosquito nets.
- introducing fishes like Gambusia in ponds that feed on mosquito larvae
- spraying of insecticides in ditches, drainage areas and swamps, etc.
- doors and windows should be provided with wire mesh to prevent the entry of mosquitoes.
(Any two)
(C) Pathogens are defined as the disease- causing organisms. These include bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoans, helminths, etc. The pathogens enter our body through different means such as air, water, soil, food, etc., and start multiplying and interfering with our normal vital activities.