Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 10 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Term 2 Set 10 for Practice
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 35
General Instructions:
- There are 12 questions in this question paper with internal choice.
- SECTION A – Q. No. 1 to 3 are very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.
- SECTION B – Q. No. 4 to 11 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.
- SECTION C- Q. No. 12 is case based question carrying 5 marks.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed.
Section – A
(Section A-Question No 1 to 3 are very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.)
Question 1.
Calculate ∧0m for acetic acid –
Given that ∧° (HCl) = 426 S cm2 mol-1
∧° (NaCl) = 126 S cm2 mol-1
∧° (CH3COONa) = 91 S cm2 mol-1 (2)
Question 2.
Define the following terms – (Any two)
(A) Order of a reaction
(B) Rate law
(C) Elementary reaction (2)
Question 3.
What products will be formed on reaction of propanal with 2-methyl propanal in the presence of NaOH? Write the name of the reaction also. (2)
![]()
Section – B
(Section B-Question No 4 to 11 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.)
Question 4.
Complete the following reaction sequence:
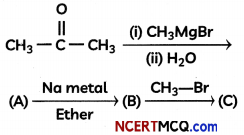
OR
Compound ‘A’ was prepared by oxidation of compound ‘B’ with alkaline KMnO4. Compound ‘A’ on reduction with lithium aluminium hydride gets converted back to compound ‘B’. When compound ‘A’ is heated with compound ‘B’ in the presence of H2S04 it produces fruity smell of compound ‘C to which family the compounds ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ belong to? (3)
(A) Redraw the diagram to show the direction of flow of current.
(B) Write the reactions taking place at anode and cathode.
(C) Construct the Nernst equation for the given Electro chemical cell. (3)
Question 5.
Observe the diagram given below and answer the questions that follow:
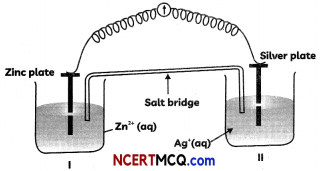
(A) Redraw the diagram to show the direction of flow of current.
(B) Write the reactions taking place at anode and cathode.
(C) Construct the Nernst equation for the given Electrochemical cell. (3)
Question 6.
For the reaction: 2A + B → A2B the rate = klA] [B]2 with k = 2.0 x 10-6 mol L-1 s. Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when [A] = 0.1 mol L-1, [B] = 0.2 mol L-1. CalcuLate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 0.06 mol L-1.
OR
The decomposition of NH3 on platinum surface is zero order. What are the rates of production of N2 and H2 If k = 2.5 × 103 mol L-1 s-1? (3)
Question 7.
What happens when:
(A) A colloidal solution undergoes persistent dialysis.
(B) River water meets sea water.
(c) Alum is applied on cuts during bleeding
OR
Answer the folLowing questions:
(A) Why is it important to have clean surface in surface studies?
(B) Why is chemisorption referred to as activated adsorption?
(C) What type of solutions are formed on dissolving different concentrations of soap in water? (3)
![]()
Question 8.
(A) Out of the following elements, identify the element which does not exhibit a variable oxidation state?
Chromium (Cr), Cobalt (Co), Zinc (Zn)
(B) Calculate the magnetic moment of Cu2+ (Z = 29 ) on the basis of “spin-only” formula.
(C) Out of Fe and Cu, which one would exhibit higher melting point? (3)
Question 9.
(A) Arrange the following complexes in the increasing order of conductivity of their solution:
[Co(NH3)3Cl3], [CO(NH3)4Cl2]Cl,
[CO(NH3)6]Cl3, [CO(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
(B) On the basis of crystal field theory explain why Co (III) forms paramagnetic octahedral complex with weak field ligands whereas it forms diamagnetic octahedral complex with strong field ligands. (3)
Question 10.
Using crystal field theory, draw energy level diagram and write electronic configuration of the central metal ion of [Co(H20)]2+.
OR
Using valence bond theory, explain the following in relation to the complex [Mn(CN)6]3-:
(i) Type of hybridisation.
(ii) Inner or outer orbital complex.
(iii) Magnetic behaviour. (3)
Question 11.
(A) Alkenes (>C = <) and carbonyl compounds (>C = O), both contain a π bond but alkenes show electrophilic addition reactions whereas carbonyl compounds show nucleophilic addition reactions. Explain.
(B) Why is there a large difference in the boiling points of butanal and butan-1 -ol? (3)
![]()
Section – C
(Section C-Question No 12 is case-based question carrying 5 marks.)
Question 12.
Read the following passage and answer the questions that follow: (5)
Amines are classified as primary, secondary and tertiary amines. Primary amines cannot be obtained by ammonolysis of alkyl halide because we will get mixture of 1° 2° and 3° amines. Cyanides, on reduction give primary amines where as isocyanides on reduction give seconday amines. Nitro compounds, on reduction also give primary, amines. Primary amines react with CHCl3 and KOH to form foul smelling isocyanide. They react with HNO2 and liberate N2 gas. They react with Hinsberg’s reagent to form salt soluble in KOH.
Secondary amine form yellow oily compounds with HN02 and salt formed with C6H5SO2Cl is insoluble in KOH. 3° amines form salt soluble in water with HNO2 but does not react with C6H5SO2Cl.
(A) Name two reducing agents which can be used to prepare primary amines from nitro compounds.
(B) Write the isomer of C3H9N which does not react with Hinsberg’s reagent.
(C) Primary amines cannot be prepared by ammonolysis of alkyl halides. Give reason.
(D) Write structures along with the IUPAC names:
(i) the amide which gives propanamine by Hoffmann bromamide reaction.
(ii) the amine produced by the Hoffmann degradation of benzamide.
OR
(i) What is the product when C6H5CH2NH2 reacts with HNO2?
(ii) Why does ethanol have higher boiling point than ethanamine?