Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 11 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Term 2 Set 11 for Practice
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 35
General Instructions:
- There are 12 questions in this question paper with internal choice.
- SECTION A – Q. No. 1 to 3 are very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.
- SECTION B – Q. No. 4 to 11 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.
- SECTION C- Q. No. 12 is case based question carrying 5 marks.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed.
Section – A
(Section A-Question No 1 to 3 are very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.)
Question 1.
Define the following terms – (Any two):
(A) Molar conductivity
(B) Inert electrolyte in salt bridge
(C) Cell constant (2)
Question 2.
Aldol condensation of a ketone in the presence of a dilute alkali gives 4-Hydroxy – 4 – methyl pentan – 2 – one. Write the structure of the ketone and its IUPAC name. (2)
Question 3.
Give reasons for the following:
(A) Iodoform is obtained when methyl ketones react with hypoiodite but not with iodide.
(B) Hydrazones of aldehydes and ketones are not prepared in highly acidic medium. (2)
![]()
Section – B
(Section B-Question No 4 to 11 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.)
Question 4.
Write the products formed when ethanal reacts with the following reagents:
(i) CH3MgBr and then H3O+
(ii) Zn-Hg/conc. HCl
(iii) C6H5CHO in the presence of dilute NaOH
OR
Write the chemical equations to illustrate each of the following name reactions:
(i) Rosenmund reduction
(ii) Cannizzaro reaction
(iii) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction (3)
Question 5.
Answer the following questions –
(A) Why is the third ionisation energy of Manganese (Z = 25) is unexpectedly high?
(B) Silver (Ag) has completely filled d-orbitals (4d10) in its ground state. How can you say that it is a transition element?
(C) Mention the name of the element among lanthanoids known to exhibit a +4 oxidation state. (3)
Question 6.
For the first-row transition metals the enthalpy of atomisation values are:
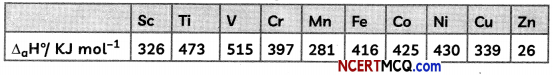
Assign reason for the following:
(A) Transition elements have higher values of enthalpies of atomisation.
(B) The enthalpy of atomisation of zinc is the lowest in 3d – series.
(C) Transition metals have high melting points.
OR
Answer the following questions:
(A) Explain briefly how +2 state becomes more and more stable in the first half of the first row transition elements with increasing atomic number?
(B) In what way is the electronic
configuration of the transition elements different from that of the non-transition elements? 3
(a) A chelating agent has two or more than two donor atoms to bind to a single metal ion. Give one example of such type of ligand. Write its structure also.
(B) What kind of isomerism exists between [Cr(H2O)6]Cl3 (violet) and [Cr(H2O)5Cl)Cl2. H2O (greyish- green)?
(C) Why are low spin tetrahedral complexes not formed? (3)
![]()
Question 8.
Consider the following figure and answer the following questions.
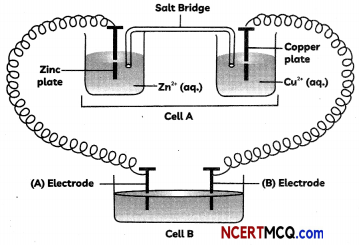
(A) Cell ‘A’ has Ecell = 2 V and cell ‘B’ has Ecell= 1.1 V which of the two cells ‘A’ or ‘B’ will act as an electrolytic cell. Which electrode reactions will occur in this cell?
(B) If cell ‘A’ has Ecell = 0.5 V and cell ‘B’ has Ecell = 1.1 V, what will be the reactions at anode and cathode?
OR
Calculate E°cell and ∆rG° for the following reaction at 25 °C:
A2+(aq) + B+(aq) → A5+(aq) + B(s)
Given Kc = 1010, 1F = 96500 C mol-1 (3)
(A) Why is Fe(OH)3 colloid positively charged, when prepared by adding FeCl3 to hot water?
(B) On the basis of Hardy-Schulze rule, explain why the coagulating power of phosphate is higher than chloride?
(C) Why does leather get hardened after tanning? (3)
Question 10.
Identify the missing reagent/product in the following reactions:
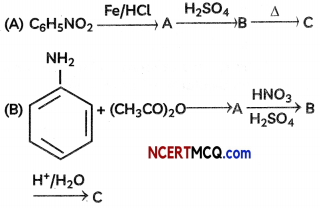
OR
An organic compound A (C2H3N) is used as a solvent of choice for many organic reactions because it is not reactive in mild acidic and basic conditions. Compound A on treatment with Ni/H2 forms B. When B is treated with nitrous acid at 273 K, ethanol is obtained. When B is warmed with chloroform and NaOH, a foul-smelling compound C formed. Identify A, B and C. Write all the chemical reactions involved. (3)
Question 11.
Account for the following:
(A) Aniline cannot be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis,
(B) The C-N-C bond angle in trimethyl amine is 108°.
(C) The pKb value of benzeneamine is 9.33 while that of ammonia is 4.75. (3)
![]()
Section – C
(Section C-Question No 12 is case-based question carrying 5 marks.)
Question 12.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Number of molecules which must collide simultaneously to give product is called molecularity. It is equal to sum of coefficient of reactants present in stoichiometic chemical equation.
For reaction, m1A + m2B → product
Molecularity = [m1 + m2]
In complex reaction each step has it own molecuiarity which is equal to the sum of coefficients of reactants present in a particular step. Molecuiarity is a theoretical property. Its value is any whole number. Number of concentration terms on which rate of reaction depends is called order of reaction or sum of powers of concentration terms present in the rate equation is called order of reaction.
If rate equation of reation is:
Rate = k × CAm1. CBm2
Then order of reaction = m1 + m2
In simple reaction, order and molecuiarity are same.
In complex reaction, order of slowest step is the order of over all reaction. This step is known as rate determining step. Order is an experimental property. Its value may be zero, fractional or negative.
(A) Write two differences between order and molecuiarity of a reaction?
(B) What will be the molecuiarity of the following reaction?
6FeSO4 + 3H2S04 + KClO3 → KCl + 3Fe2(S03)2 + 3H2O
(C) The rate of reaction, A + 2B -> products, is given by – d[A] / dt = k[A] [B]2. If B is present in large excess, what will be the order the reaction?
(D) The rate of a certain reaction is given by , rate = k [H+]n. The rate increases 100 times when the pH changes from 3 to 1. What will be the order (n) of the reaction?
OR
In a chemical reaction A + 2B → products, when concentration of A is doubled, rate of the reaction becomes 4 times and concentration of B alone is doubled rate continues to be the same. What will be the order of the reaction? (5)