Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 12 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Term 2 Set 12 for Practice
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 35
General Instructions:
- There are 12 questions in this question paper with internal choice.
- SECTION A – Q. No. 1 to 3 are very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.
- SECTION B – Q. No. 4 to 11 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.
- SECTION C- Q. No. 12 is case based question carrying 5 marks.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed.
Section – A
(Section A-Question No 1 to 3 are very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.)
Question 1.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated – (Any two) (2)
(A) CH3CHO, C6H5CHO, HCHO (reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reaction).
(B) 2, 4-dinitrobenzoic acid, 4-methoxybenzoic acid, 4 nitrobenzoic acid(acidic character).
(C) CH3CH2CH2CH3, CH3OCH2CH3,
CH3CH2CHO, CH3COCH3, CH3CH2CH22OH
(boiling point)
Question 2.
Why do amines act as nucleophiles? Give example of a reaction in which methylamine acts as a nucleophile. (2)
![]()
Question 3.
(A) In the expression of rate of reaction in terms of reactants, what is the significance of negative sign?
(B) What is the use of integrated rate equation? (2)
Section – B
(Section B-Question No 4 to 11 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.)
Question 4.
(A) What may be the stable oxidation state of the transition element with the following d electron configurations in the ground state of their atoms: 3d3 and 3d4?
(B) What are interstitial compounds? Why are such compounds well known for transition metals? (3)
Question 5.
When Liquid ‘A’ is treated with a freshly prepared ammoniacal silver nitrate solution, it gives bright silver mirror. The liquid forms a white crystalline solid on treatment with sodium hydrogen sulphite. liquid ‘B’ also forms a white crystalline solid with sodium hydrogen sulphite but it does not give test with ammoniacal silver nitrate. Which of the two liquids is aldehyde? Write the chemical equations of these reactions also.
OR
Complete the following equation and write the structures of A, B, C, D, E, and F.
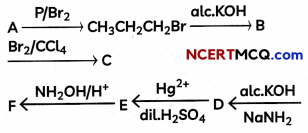
Question 6.
(A) Differentiate between the following with the help of one example of each
(i) Homoleptic and Heterolytic Complexes
(ii) Double salt and a complex
(B) What is the coordination number of Fe in [Fe(EDTA)]3+ ? (3)
Question 7.
(A) How does the precipitation of colloidal smoke takes place in Cottrell precipitator?
(B) Observe the following diagram and answer the questions that follow –
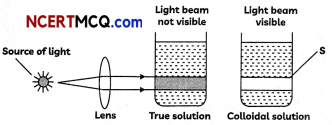
(i) Name the property which is shown by the colloidal solution.
(ii) Explain the reason for the property shown by colloidal solution. (3)
Question 8.
Write the structures of the following compounds.
(A) α-Methoxypropionaldehyde
(B) 3-Hydroxybutanal
(C) 2-Hydroxycyclopentanecarbaldehyde (3)
![]()
Question 9.
(A) Why does acetylation of -NH2 group of aniline reduce its activating effect?
(B) What is the product when C6H5CH2NH2 reacts with HNO2 ?
(C) What is the structure and IUPAC name of the compound, allyl amine?
OR
How will you convert the following:
(A) Nitrobenzene into aniline
(B) Ethanoic acid into methanamine
(C) Aniline into N-phenylethanamide (3)
Question 10.
For the complex [Fe(en)2 Cl2 ], Cl, (en = ethylene diamine), identify:
(A) the oxidation number of iron,
(B) the hybrid orbitals and the shape of the complex,
(C) the magnetic behaviour of the complex,
OR
(A) What type of isomerism is shown by the complex [Co(NH3 )6 ][Cr(CN)6 ]?
(B) Why a solution of [Ni(H2O)6 ]2+ is green while a solution of [Ni(CN)4]2- is colourless? (At. no. of Ni = 28)
(C) Write the IUPAC name of the following complex: [Co(NH3 )5 (CO3 )]Cl. (3)
Question 11.
For the reaction A + B → products, the following initial rates were obtained at various given initial concentrations:
| [A] mol / L | [B] mol / L | Initial rate M/s |
| 1) 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.05 |
| 2) 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.10 |
| 3) 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.05 |
Determine the half-life period.
OR
The following data were obtained during the first order thermal decomposition of
SO2Cl2 at a constant volume:
SO2Cl2(g) → SO2(g) + Cl2(g)
| Experiment | Time/s-1 | Total Pressure/atm |
| 1 | 0 | 0.4 |
| 2 | 100 | 0.7 |
Calculate the rate constant.
(Given: log 4 = 0.6021, log 2 = 0.3010) (3)
![]()
Section – C
(Section C-Question No 12 is case-based question carrying 5 marks.)
Question 12.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
ALl chemical reactions involve interaction of atoms and molecules. A large number of atoms/ molecules are present in a few grams of any chemical compound varying with their atomic/ molecular masses. To handle such large number conveniently, the mole concept was introduced. All electrochemical cell reactions are also based on mole concept. For example, a 4.0 molar aqueous solution of NaCI is prepared and 500 mL of this solution is electrolysed. This leads to the evolution of chlorine gas at one of the electrode. The amount of products formed can be calculated by using mole concept.
(A) How many moles of chlorine gas will be evolved from the reaction given in the above passage? .
(B) In electrolysis of aqueous NaCl solution when Pt electrode is taken, then which will the products formed at cathode and anode?
(C) What will be number of moles of electrons exchanged during electrolysis of aqueous solution of NaCl?
(D) Calculate the time to deposit 1.5 g of silver at cathode when a current of 1.5A was passed through the solution of AgNO3. (Molar mass of Ag = 108 g mol- 1,1 F = 96500 C mol-1). ”
OR
How many electrons flow through a metallic wire if a current of 0.5 A is passed for 2 hours? (Given: IF = 96,500 C mol-1) (5)