Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 7 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Chemistry Term 2 Set 7 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 35
General Instructions:
- There are 12 questions in this question paper with internal choice.
- SECTION A – Q. No. 1 to 3 are very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.
- SECTION B – Q. No. 4 to 11 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.
- SECTION C- Q. No. 12 is case based question carrying 5 marks.
- All questions are compulsory.
- Use of log tables and calculators is not allowed.
Section – A
(Section A-Question No 1 to 3 are very short answer questions carrying 2 marks each.)
Question 1.
Study the change of concentration of reactant with respect to time as depicted in the graphical representation below: (2)
(A) Predict the order of the reaction
Answer:
The variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot shown here represents a zero order reaction, for which the rate of the reaction is proportional to zero power of the concentration of the reactants.
(B) What does the slope represent?
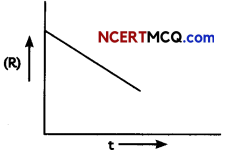
Answer:
For a zero order reaction, rate constant is given as [R] = [R]0 – kt
So, the slope of the curve for the variation in the concentration (R) vs. time (t) plot is equal to the negative of the rate constant for the reaction.
![]()
Question 2.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of their property as indicated. to-carbon bond of alkenes? (Any two)
(A) CH3COCH3, C6H5—CO—C6H5, CH3CHO (Reactivity towards nucleophilic addition reactions)
Answer:
C6H5—CO—C6H5, < CH3COCH3 < CH3CHO
Explanation: Ketones are less reactive towards nucleophilic addition reactions due to more steric hinderance.
(B)
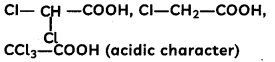
Answer:
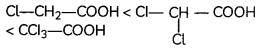
Explanation: More the number of electron withdrawing groups (-Cl), more the acidic character.
(C) C2H5OH, CH3CHO, CH3COOH (Boiling points) (2)
Answer:
CH3—CHO < C2H5OH, < CH3COOH
Explanation: Carboxylic acids have higher boiling points then alcohols due to more extensive association of carboxylic acid molecules through intermolecular hydrogen bonding. The hydrogen bonds are not broken completely even in the vapour phase.
Question 3.
Answer the following questions.
(A) What feature of their structure makes aldehydes easier to oxidize than Ketones?
Answer:
The H on the carbonyl carbon atom of aldehyde makes it easier to oxidize.
(B) How does the carbon-to-oxygen bond of aldehydes and ketones differ from the carbon-to-carbon bond of alkenes? (2)
Answer:
The carbon-to-oxygen double bond is polar due resonance; the carbon-to-carbon double bond is non-polar.
Related Theory:
There is a significant contribution from the resonance structure which puts a formal negative charge on the oxygen atom and a formal positive charge on the carbon atom and there by increases the polarity of the bond.

![]()
SECTION – B
(Section B-Question No 4 to 11 are short answer questions carrying 3 marks each.)
Question 4.
Draw diagram to show splitting of d – orbital in octahedral crystal field. Explain the two patterns of filling d4 in octahedral crystal FIeld. (3)
Answer:
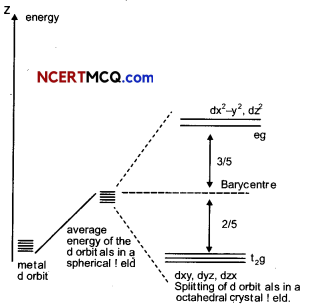
The splitting of the d orbitals in an octahedral field takes place in such a way that dx2 – y2, dz2 experience a rise in energy and form the eg level, while dxy, dyz and dzx experience a fall in energy and form the t2g level.
For electric configuration of d4
(i) When Δ0 > P Electronic configuration is t42g eg0
![]()
When Δ0 < P
Electronic configuration is t32g eg1

![]()
Question 5.
A colloidal solution of Agl is prepared by two methods. (3)
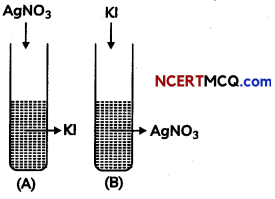
(A) What is the charge on Agl colloidal method.
Answer:
Test tube (A) has negative charge whereas test tube (B) has positive on the colloidal particles.
(B) Give the reason for origin of change.
Answer:
According to preferential adsorption theory, test tube (A) I– is absorbed on precipitate Agl [or Agl / I– is formed] and in test tube (B). Ag+ is absorbed on precipitate Agl [or Agl/Ag+ is formed].
Related Theory:
The electric double layer theory describes the interaction between surface of colloidal particles and ions that are present in the fluid in which the colloidal particles are dispersed.
(C) What ¡s zeta potential?
Answer:
Zeta potential is the potential difference between fixed layer (primary layer) and diffused layer (secondary layer) of colloidal particle. It is also called as electrokinetic potential.
![]()
Question 6.
A first order reaction takes 10 minutes for 25% decomposition. Calculate t1/2 for the reaction. (Given: log 2 = 0.3010, log 3 = 0.4771, log 4 = 0.6021).
OR
Consider the reaction
2A + B → C + D
Following results were obtained in experiments designed to study the rate of reaction:
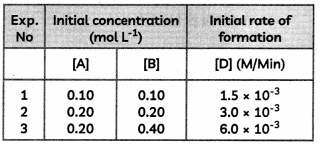
(A) Write the rate law for the reaction.
(B) Calculate the value of rate constant for the reaction. (3)
Answer:
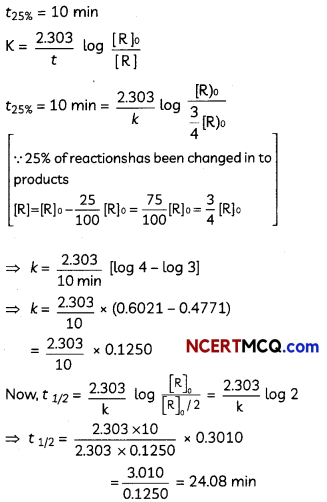
OR

![]()
Question 7.
(A) Describe the mechanism of the addition of Grignard reagent to the carbonyl group of compound to form an adduct which on hydrolysis yields an alcohol.
(B) Write the IUPAC name of the compound.
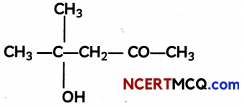
OR
(A) Illustrate the following name reactions:
(i) Hell-Vothard-Zelinsky reaction.
(ii) Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction
(B) Write the structural formula of 1-phenylpentan-l-one. (3)
Answer:
(A) a. Mechanism:
(i) Nucleophilic addition of Grignard reagent to carbonyl group to form an adduct.
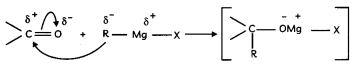
(ii) Hydrolysis of the adduct to alcohol.
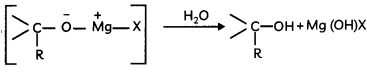
Caution:
Students should draw the curved arrows in proper directions and proper charges on the atoms in the mechanism.
(B) 4-Hydroxy-4-methyl pentan-2-one.
OR
(A) (i) Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction – Carboxylic acids having an α-hydrogen are halogenated at the α-position on treatment with chlorine or bromine in the presence of small amount of red phosphorus to give αx-halocarboxylic acids. The reaction is known as Hell-Volhard- Zelinsky reaction.
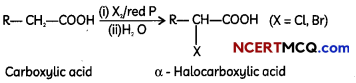
(ii) Wolff-Kishner reduction reaction – The carbonyl group of aldehydes and ketones is reduced to CH2 group on treatment with hydrazine followed by heating with potassium hydroxide in a high boiling solvent such as ethylene glycol.
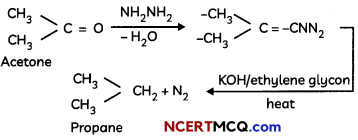
Caution:
Students should write the chemical reaction also otherwise marks would be deducted during evaluation.
(B)
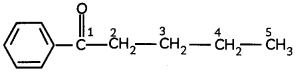
![]()
Question 8.
State Reasons:
(A) Aniline is a weaker base than cyclohexylamine. (3)
Answer:
Aniline is a weaker base than cyclohexylamine because the lone pair of electrons on the N-atom is delocalised over the benzene ring in aniline which results in the decrease in electron density on Nitrogen. In cyclohexylamine, the lone pair of the electrons on N-atom is readily available due to absence of π-electrons.
Caution:
Basicity of the amino group means it is unsuitable for reactions with acids (e.g. H2SO4 or AlCl3) such as nitration, sulfonation and Friedel-Crafts alkylation or acylation.
(B) It is difficult to prepare pure amines by ammonolysis of alkyl halides.
Answer:
It is difficult to prepare pure amines by ammonolysis of alkyl halides as the primary amine formed by ammonolysis acts as a nucleophile. It further produces 2° and 3° alkyl amine.
(C) Etectrophilic substitution in aromatic amines takes place more readily than benzene.
Answer:
Arylamines are potentially very reactive towards electrophilic aromatic substitution. This is because -NH2, -NHR2 and -NR2 are very strong activators and are ortho, para-directing.
Question 9.
Observe the graph and answer the questions that follow:
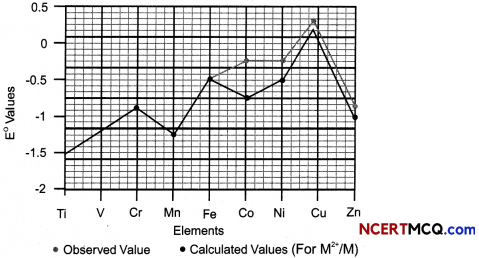
(A) Which transition metaL of 3d series has positive E°(M2+/M) value and why?
Answer:
The E°(M2+/M) for copper is positive. This is because high energy is required to transform Cu to Cu2+ which is not balanced by its hydration enthalpy.
(B) E° value for the Mn+3/Mn+2 couple is positive (+1.5 V) whereas that of Cr+3/Cr+2 is negative (-0.4 V). Why?
Answer:
The E° value for the Mn3+/Mn2+ couple is much more positive than that for Cr3+/ Cr2+ couple. This is because Mn2+ ion is particularly stable due to extra stability of its half filled valence electronic configuration (d5). Thus Mn3+ ion has a very high tendency to gain an electron and form the much more stable Mn2+ ion.
(C) E° values are not regular for first row transition elements? (3)
Answer:
The (M2+/M) values are not regular which can be explained from the irregular variation of ionisation enthalpies (ΔiH1 + ΔiH2) and also the sublimation enthalpies which are relatively much less for manganese and vanadium.
![]()
Question 10.
What is the lanthanoid contraction? What are its causes and consequences? (3)
OR
Explain the following:
(A) Copper (I) ion is not stable in an aqueous solution.
(B) Generally there is an increase in density of elements from titanium (Z = 22) to copper (Z = 29) in the first series of transition elements.
(C) Transition metals in general act as good catalysts.
Answer:
Lanthanoid contractions – The cumulative effect of the regular decrease in size or radii of Lanthanoid with increase in atomic number is called Lanthanoid contraction.
Causes: With an increase in the atomic number, the positive charge on nucleus increases by one unit and one more electron enters same 4f subshell.
The electrons in 4f subshell imperfectly shield each other. Shielding in a 4f subshell is lesser than in d subshell.
With the increase in nuclear charge, the valence shell is pulled slightly towards the nucleus. This causes lanthanide contraction.
Consequences: Due to Lanthanoid contraction.
1. Radii of the members of the third transition series is similar to those of second transition series.
2. It becomes difficult to separate Lanthanoids.
OR
(A) In an aqueous medium, Cu2+ is more stable than Cu+. This is because although energy is required to remove one electron from Cu+ to Cu2+, high hydration energy of Cu2+ compensates for it. Therefore, Cu+ ion in an aqueous solution is unstable. It disproportionates to give Cu2+ and Cu.
(B) The density of elements from titanium to copper increase in the first series of transition elements. This is due to decrease in metallic radius coupled with increase in atomic mass results in a general increase in the density.
Explanation: As the atomic radii decreases moving across from titanium to Cu, So its volume will decrease and density is expected to increase.
(C) They have variable valencies and show multiple oxidation states and transition metals sometime form unstable intermediate compounds and provide a new path with lower activation energy for the reaction. In some cases transition elements provide a suitable surface for the reaction to take place.
Question 11.
An aromatic compound ‘A’ of moLucutar formula C7H5O2 undergoes a series of reactions an shown below. Write the structures of A, B, C, D and E in the following reactions.
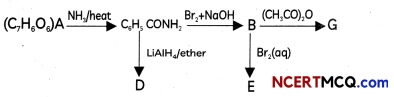
OR
How will you convert the following –
(A) Aniline to chtorobenzene
(B) Ethanoic acid to methanamine
(C) Methyl chloride to ethanamine (3)
Answer:
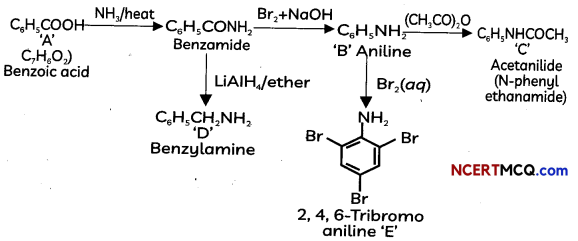
OR
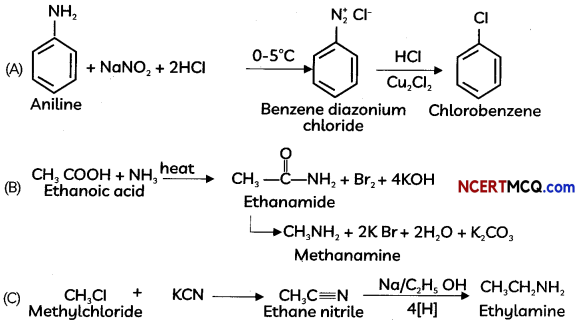
![]()
Section – C
(Section C-Question No 12 is case-based question carrying 5 marks.)
Question 12.
Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow:
The potential of each electrode is known as electrode potential. Standard electrode potential is the potential when concentration of each species taking part in electrocde reaction is unity and the reaction is taking place at 298 K. By convention, the standard electrode potential of hydrogen (SHE) is 0.0 V. The electrode potential value for each electrode process is a measure of relative tendency of the active species in the process to remain in the oxidised/reduced form. The negative electrode potential means that the redox couple is stronger reducing agent than H+/H2 couple. A positive electrode potential means that the redox couple is a weaker reducing agent than the H+/H2 couple. Metals which have higher positive value of standard reduction potential form the oxides of greater thermal stability.
(A) What is meant by reference electrode?
(B) Platinum is used in the standard hydrogen electrode. Give reason.
(C) Explain the term Standard electrode potential.
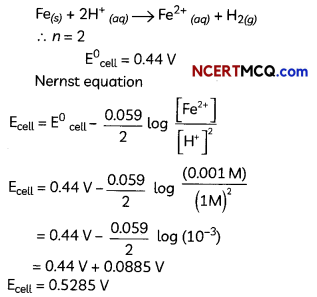
(D) Calculate the emf of the following cell at 298 K: Fe(s) | Fe2+ (0.001 M) || H+ (1M) | H2(g)(1 bar), Pt(s) (Given E°cell = +0.44V)
OR
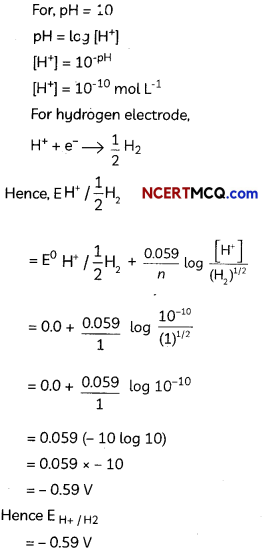
Calculate the potential of hydrogen electrode in contact with a solution whose pH is 10. (5)
Answer:
(A) Standard Hydrogen electrode: It is a reference electrode against which the electrode potentials of all electrodes are measured.
Explanation: The Standard electrode potential of SHE is zero volt. This SHE can act as anode or cathode, depending upon the half cell that is attached to it.
(B) Platinum is a less reactive metal. So, it doesn’t easily react with other metals. As a result, it provides the surface for the redox reaction.
(C) The potential difference developed between metal electrode and solution of ions of unit molarity (1M) at 1 atm pressure and 25°C (298 K) is called standard electrode potential. It is denoted by E°.
(D) The cell reaction: