Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 10 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Economics Term 2 Set 10 for Practice
Time allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- This is a Subjective Question Paper containing 13 questions.
- This paper contains 5 questions of 2 marks each, 5 questions of 3 marks each and 3 questions of 5 marks each.
- 2 marks questions are Short Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 30-50 words.
- 3 marks questions are Short Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 50-80 words.
- 5 marks questions are Long Answer Type Questions and are to be answered in 80-120 words.
- This question paper contains Case/Source Based Questions.
![]()
Question 1.
“Full employment implies zero unemployment when nobody is ever unemployed in the economy.” Defend or refute the statement with valid reason.
OR
“APS can be negative whereas MPS can never be negative.” Justify the statement. (2)
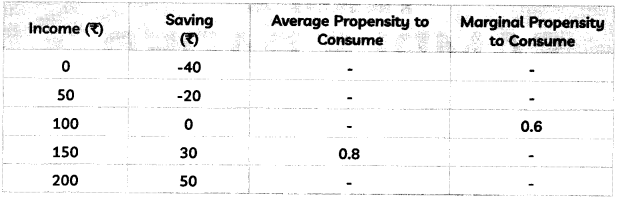
Question 2.
Given marginal propensity to save 0.25, what will be the increase in national income if investment increases by ₹ 125 crores. Calculate.
OR
S = – 100 + 0.2 Y is the saving function in an economy. Investment expenditure is ₹5,000. Calculate the equilibrium level of income. (2)
Question 3.
Nurse in a government hospital comes under the category of‘Regular Salaried Employee’. Justify the statement with valid reason. (3)
Question 4.
“Compared to females, more males are found to be working. The difference in participation rates is very large in urban areas.” Justify the statement with valid reason. (3)
![]()
Question 5.
“Environment and economy are inter¬dependent and need each other.” Justify the given statement with a valid argument.
OR
“The concept of sustainable development relates to development that doesn’t compromise the needs of the future generation.” Explain. (2)
Question 6.
Will the following be included in the domestic product of India? Give reasons for your answer.
(A) Profits earned by foreign companies in India.
(B) Salaries of Indians working in the Russian Embassy in India.
(C) Profits earned by a branch of State Bank of India in Japan.
OR
From the following information, compute GNPMP.
GDPFC = ₹ 2,000
Net factor income to abroad = ₹ 100
Indirect Taxes = ₹ 320
Subsidies = ₹ 100. (3)
![]()
Question 7.
Compare and contrast the development of India, China and Pakistan with respect to some salient human development indicators.
Some Selected Indicators of Human Development, 2017-2019


Note: * for the year 2011: for the year 2015.
Sources: Human Development Report 2019 and 2020 and Word Development Indicators (www.world in. org); Key indicators for Asia and the Pacific 2019. Asian development bank (ADB).
Read the following case carefully and answer question number 8 and 9 given below:
As per the Census 2001, the Indian workforce is over 400 million strong, which constitutes 39.1 % of the total population of the country. The workers comprise 312 million main workers and 88 million marginal workers (i.e., those who did not work for at least 183 days in the preceding 12 months to the census taking). Sex differential among the number of male and female worker in the total workforce is significant. Of the total 402 million workers, 275 million are males and 127 million females. This would mean that 51.7 percent of the total males and 25.6 percent of the total females are workers.
The number of female workers is about less than half the number of male workers. In terms of proportion, 68.4 percent of the workers are males and 31.6 percent females. Among the main workers, female workers, are only 23.3 % and 76.7% are male workers. Majority of female workers (87.3 percent) are from rural areas. This is also twice that of male workers, which may be due to their being employed predominantly in activities like cultivation and agricultural labour. In the urban areas, majority of female workers are engaged in Households industry and other work.
![]()
Question 8.
“If a person had worked as a daily wage labourer for four months, as an agricultural labourer for one month”. Identify the type of worker he will be considered? (3)
Question 9.
“The nature of employment in India is multifaceted.” Justify the statement. (3)
Question 10.
Why did China introduce structural reforms in 1978? (3)
Question 11.
(A) “Circular flow principle is based on the assumption that one’s expenditure will become other’s income.” Explain the given statement.
(B) “Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is not the best indicator of the economic welfare of a country.” Defend or refute the given statement with valid reasons. (5)
Question 12.
(A) Define the problem of double counting in the computation of national income.
(B) Calculate national income from the following data: (₹ in crores)
(i) Private final consumption expenditure 500
(ii) Net domestic fixed capital formation 100
(iii) Net factor income from abroad 30
(iv) Change in stock 20
(v) Net exports 40
(vi) Net indirect taxes 50
(vii) Mixed income 300
(viii) Government final consumption expenditure 200
OR
(A) Explain mixed income of self-employed. (2)
(B) Calculate Gross National Product at market price by expenditure method. (₹ in crores)
(i) Compensation of employees 100
(ii) Private final consumption expenditure 200
(iii) Rent 20
(iv) Government final consumption expenditure 50
(v) Profits 10
(vi) Interest 10
(vii) Gross domestic capital formation 60
(viii) Net imports 10
(ix) Consumption of fixed capital 20
(x) Net Indirect Taxes 30
(xi) Net factor income from abroad(-)20
(xii) Change in stocks 10
(xiii) Mixed income 110 (3)
![]()
13. Complete the following table: