Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 11 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Geography Term 2 Set 11 with Solutions
Time Allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 35
Roll No. ___________
General Instructions:
- Question paper is divided into 5 sections A, B, C, D & E
- In section A, question number 1 to 3 are Very Short Answer type questions. Attempt any 3 questions.
- In section B, question number 4 is Source based question.
- In section C, question number 5 & 6 are Short Answer type questions.
- In section D, question number 7 to 9 are Long Answer type questions.
- In section E, question number 10 is a Map based question.
Section – A
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Define cyberspace. (2)
Or
Write a short note each on the Danube waterway and Volga waterway.
Answer:
Cyberspace is the world of electronic computerised space. It is encompassed by the Internet such as the World Wide Web (www). In simple words, it is the electronic digital world for communicating or accessing information over computer networks without physical movement of the sender and the receiver. It is also referred to as the Internet. Cyberspace exists everywhere.
Or
The Danube Waterway It is an important inland waterway that serves Eastern Europe. The Danube river rises in the Black Forest and flows Eastwards through many countries. It is navigable up to Taurna Severin. Volga Waterway Russia has a large number of developed waterways, of which the Volga is one of the most important. It provides a navigable waterway of 11,200 km and drains into the Caspian Sea.
![]()
Question 2.
Mention about solar energy. (2)
Answer:
Sun rays which tapped in photovoltaic cells can be converted into energy, known as solar energy. The two effective processes considered to be very effective to tap solar energy are photovoltaics and solar thermal technology. Solar energy is generally used more in appliances like heaters, crop dryers, cookers, etc.
Question 3.
State any two measures which aimed at promoting sustainable development in the Indira Gandhi Canal project area. (2)
Answer:
The measures which aimed at promoting sustainable development in the Indira Gandhi Canal project area are
- The first requirement is strict implementation of water management policy. The canal project envisages protective irrigation in Stage-I and extensive irrigation of crops and pasture development in Stage-II.
- In general, the cropping pattern shall not include water intensive crops. It shall be adhered to and people shall be encouraged to grow plantation crops such as citrus fruits.
Section – B
Source Based Question
Question 4.
Read the source given below and answer the following questions by choosing the correct option.
Jhabua district is located in the westernmost agro-climatic zone in Madhya Pradesh. It is, in fact, one of the five most backward districts of the country. It is characterised by high concentration of tribal population (mostly Bhils). The people suffer due to poverty which has been accentuated by the high rate of resource degradation, both forest and land.
The watershed management programmes funded by both the ministries of “Rural Development” and “Agriculture”, Government of India, have been successfully implemented in Jhabua district which has gone a long way in preventing land degradation and improving soil quality. Watershed Management Programmes acknowledge the linkage between land, water and vegetation and attempts to improve livelihoods of people through natural resource management and community participation.
In the past five years, the programmes funded by the Ministry of Rural Development alone (implemented by Rajiv Gandhi Mission for Watershed Management) has treated 20 per cent of the total area under Jhabua district. The Petlawad block of Jhabua is located in the Northernmost part of the district and represents an interesting and successful case of Government-NGO partnership and community participation in managing watershed programmes.
The Bhils in Petlawad block, for example, (Sat Rundi hamlet of Karravat village) through their own efforts, have revitalised large parts of common property resources. Each household planted and maintained one tree on the common property. They also have planted fodder grass on the pasture land and adopted social-fencing of these lands for at least two years.
Even after that, they say, there would be no open grazing on these lands, but stall feeding of cattle, and they are thus confident that the pastures they have developed would sustain their cattle in future. An interesting aspect of this experience is that before the community embarked upon the process of management of the pasture, there was encroachment on this land by a villager from an adjoining village.
The villagers called the tehsildar to ascertain the rights of the common land. The ensuing conflict was tackled by the villagers by offering to make the defaulter encroaching on the CPR a member of their user group and sharing the benefits of greening the common lands/pastures.
(i) The Jhabua district of Madhya Pradesh is a poor and backward region. What is the reason due to which economic condition of its people is further worsening? (1)
Answer:
The Jhabua district of Madhya Pradesh is a poor and backward region where the economic condition of people is further worsening due to forest and land degradation.
![]()
(ii) Soil quality and recovery from land degradation can be achieved by which measure? (1)
Answer:
The soil quality and recovery from land degradation can be achieved by watershed management.
(iii) The Ministry of Rural Development funded the restoration of degraded land in Jhabua under which management scheme? (1)
Answer:
The Ministry of Rural Development funded the restoration of degraded land in Jhabua under Rajiv Gandhi Mission for Watershed Management Scheme.
Section – C
Short Answer Questions
Question 5.
Discuss quaternary activities and how have they replaced primary and secondary employment as basis for economic growth. (3)
Answer:
Quaternary activities involve the collection, production and dissemination of information or even the production of information. Quaternary activities centre around research, development and may be seen as an advanced form of services involving specialised knowledge and technical skills. The quaternary sector along with the tertiary sector has replaced most of the primary and secondary employment as the basis for economic growth.
Over half of all workers, in developed economies are in the Knowledge Sector’ and there has been a very high growth in demand for and consumption of information based services from mutual fund managers to tax consultants, software developers and statisticians. Personnel working in office buildings, elementary schools and university classrooms, hospitals and doctors’ offices, theatres, accounting and brokerage firms all belong to this category of services.
![]()
Question 6.
Outline the distribution of inter-continental air routes across the world. (3)
Or
Discuss the emergence of satellite communication. Also, comment on the status of India’s satellite development.
Answer:
The distribution of inter-continental air routes
- In the Northern Hemisphere, there is a distinct East-West belt of inter-continental air routes. Dense network exists in Eastern USA, Western Europe and South-East Asia.
- USA alone accounts for 60 per cent of the airways of the world.
- New York, London, Paris, Amsterdam, Frankfurt, Rome, Moscow, Karachi, New Delhi, Mumbai, Bangkok, Singapore, Tokyo, San Francisco, Los Angeles and Chicago are the nodal points where air routes converge or radiate to all continents.
- Africa, Asiatic part of Russia and South America lack air services.
- There are limited air services between 10-35 latitudes in the Southern hemisphere due to sparser population, limited landmass and economic development.
Or
Communication through satellites emerged as a new area in communication technology since the 1970s after USA and former USSR pioneered space research. Artificial satellites, now, are successfully deployed in the earth’s orbit to connect even the remote corners of the globe with limited onsite verification. These have rendered the unit cost and time of communication invariant in terms of distance.
This means it costs the same to communicate over 500 km as it does over 5,000 km via satellite. India has also made great strides in satellite development. Aryabhatt was launched on 19 April 1979, Bhaskar-I in 1979 and Rohini in 1980. On 18 June 1981, APPLE (Arian Passenger Payload Experiment) was launched through Arian rocket. Bhaskar, Challenger and INSAT 1-B have made long distance communication, television and radio very effective.
Section – D
Long Answer Questions
Question 7.
What role does ‘outsourcing plays in quaternary activities? (5)
Or
What is meant by digital divide and how does it affect a country?
Answer:
Outsourcing is contracting out or giving work to an outside agency to improve efficiency and to reduce costs. Outsourcing plays a key role in the quatemary sector in the following ways
Business activities are outsourced which includes Information Technology (IT), human resources, customer support and call centre services and at times also manufacturing and engineering Data processing is an IT related service which can easily be carried out in Asian, East European and African countries.
In these countries IT skilled staff with good English language skills are available at lower wages than those in the developed countries. It helps reduce the overall cost of the service
Overhead costs are also much lower making it profitable to get job-work carried out overseas, whether it is in India, China or even a less populous country like Botswana in Africa.
Outsourcing generates employment and has resulted in the opening up of a large number of call centres in India, China, Eastern Europe, Israel, Philippines and Costa Rica. It has created new jobs in these countries. Outsourcing is coming to those countries where cheap and skilled workers are available. These are also out-migrating countries.
With the work available through outsourcing the migration in these countries may come down. The several key advantage are the main reason for continuing outsourcing. New trends in quinary services include Knowledge Processing Outsourcing (KPO) and ‘home shoring, the latter as an alternative to outsourcing
Or
Digital divide refers to the gap or deficit of affordable and efficient internet services, between people. This divide can be between two countries, e.g. between a developed and developing country, or between different regions within a country due to lack of access and infrastructure.
Digital divide has an impact in the following ways
Opportunities emerging from the Information and Communication Technology based development is unevenly distributed across the globe. There are wide ranging economic, political and social differences among countries. How quickly countries can provide information and communication technology access and benefits to its citizens is the deciding factor.
Developed countries in general have surged forward, the developing countries have lagged behind which has created a digital divide between the two. Within a country, low literacy and income levels, geographical inaccessibility (eg, mountainous terrain), lack of physical access to technology due to poor infrastructure, and digital illiteracy due to poor standard of education and training can contribute towards a digital divide. Digital divide can be reduced by initiating digital literacy programs by governments and NGOs for the digital illiterate group of people. A global mutual program for public access to updated information should be formed.
![]()
Question 8.
Discuss the importance of National highways and role of NHAI in India. (5)
Answer:
The main roads in India which are constructed and maintained by the Central Government are known as the National Highways. These roads are of very high importance as these connect the state capitals, major cities, important ports, railway junctions, etc. in the country. The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) is entrusted with the responsibility of development, maintenance and operation of National Highways.
This is also the apex body to improve the quality of the roads designated as National Highways. NHAI was operationalised in 1995 and is an autonomous body under the Ministry of Surface Transport. NHAI has taken up some major projects in the country under different phases which are
Golden Quadrilateral It comprises construction of 5,846-km long 4/6 lane, high density traffic corridor, to connect India’s four big metro cities of Delhi-MumbaiChennai-Kolkata. With the construction of Golden Quadrilateral, the time, distance and cost of movement among the mega cities of India will be considerably minimised.
North-South and East-West Corridors North-South corridor aims at connecting Srinagar in Jammu and Kashmir with Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu (including Kochchi-Salem Spur) with 4,076-km long road. The East-West Corridor has been planned to connect Silchar in Assam with the port town of Porbandar in Gujarat with 3,640-km of road length.
Question 9.
Mass communications networks are essential for dissipating important information to large number of people in shortest time. Briefly discuss various forms of mass communication systems. (5)
Answer:
There are three main forms of Mass Communication
(i) Radio Radio broadcasting started in India in 1923 by the Radio Club of Bombay. Since then, it gained immense popularity and changed the socio-cultural life of people. Government brough radio under its control in 1930 under the Indian Broadcasting System. It was changed to All India Radio in 1936 and to Akashwani in 1957. All India Radio broadcasts a variety of programmes related to information, education and entertainment.
(ii) Television (TV) Television broadcasting has emerged as the most effective audio-visual medium for disseminating information and educating masses. Initially, the TV services were limited only to the National Capital where it began in 1959. After 1972, several other centres became operational. In 1976, TV was delinked from All India Radio (AIR) and got a separate identity as Doordarshan (DD). After INSAT-IA (National Television-DD1) became operational, Common National Programmes (CNP) were started for the entire network.
(iii) Satellite Communication Satellites are mode of communication in themselves as well as they regulate the use of other means of communication. Satellite images can be used for the weather forecast, monitoring of natural calamities, surveillance of border areas, etc. On the basis of configuration and purposes, satellite system in India can be grouped into two; Indian National Satellite System (INSAT) and Indian Remote Sensing Satellite System (IRS).
![]()
Section – E
Map Based Question
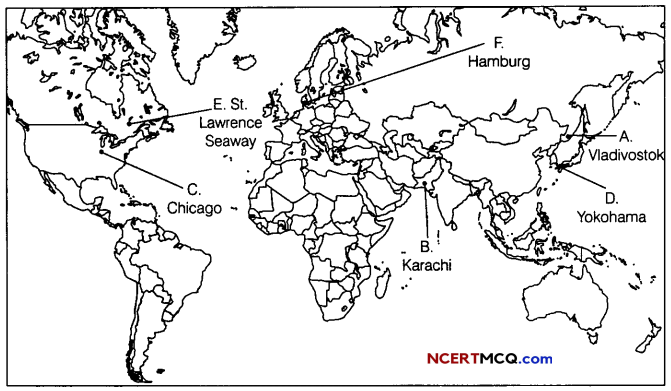
Question 10.
On the political map of the world, identify the following features (Attempt any 5). (1 × 5 = 5)
A. Eastern Terminal station of Trans-Siberian Railway
B. A major seaport
C. A major airport is USA
D. A major seaport in Asia
E. An Inland waterway
F. An important seaport
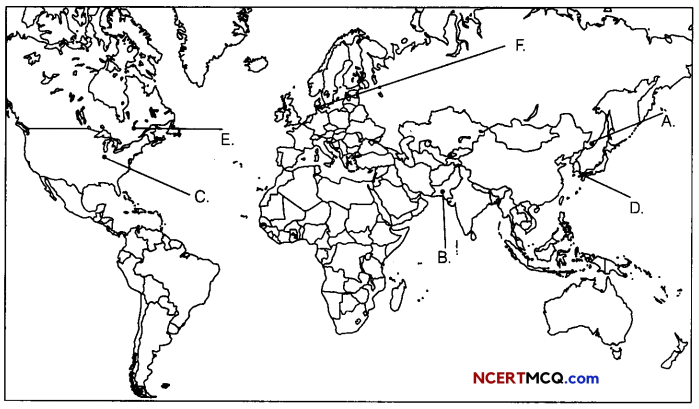
Answer: