Students can access the CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science with Solutions and marking scheme Term 2 Set 8 will help students in understanding the difficulty level of the exam.
CBSE Sample Papers for Class 12 Political Science Term 2 Set 8 with Solutions
Time allowed: 2 Hours
Maximum Marks: 40
General Instructions:
- The question paper has three sections as A,B and C.
- Section A has 8 questions of 2 marks each. Answer to these questions should be completed within 50 words each.
- Section B has 3 questions of 4 marks each. Answer to these questions should be completed within 100 words each. Answer of map question should be attempted accordingly.
- Section C has 2 question of 6 marks each. Answer to these questions should be completed within 170 words each.
Section A
Question 1.
Discuss the importance of SAARC. (2)
Or
What are the significance of SAARC for India?
Answer:
SAARC comprises 3% of the world’s area, 21% of the world’s population and 3.8% of the global economy.
Creating Synergies: It is the world’s most densely populated region and one of the most fertile areas. SAARC countries have common tradition, dress, food and culture and political aspects thereby synergising their actions. SAARC has initiated SAFTA to free trade zones for whole South Asia for collective economic activity.
Common Solutions: All SAARC countries have common problems and issues like poverty, illiteracy, malnutrition, natural disasters, internal conflicts, industrial and technological backwardness, low GDP and poor socio-economic condition.
![]()
These countries uplift their living standards thereby creating common areas of development and progress having common solutions.
Or
The significance of SAARC for India is discussed below
- Economic Integration India’s Look East Policy links South Asian economies with South-East Asia will bring further economic integration and prosperity to India mainly in the Service sector.
- Geostrategic Significance It can counter China through engaging Nepal, Bhutan, the Maldives and Sri Lanka in development process and economic cooperation.
- Regional Stability SAARC can help in creation of mutual trust and peace within the region.
- Global Leadership Role It offers India a platform to showcase its leadership in the region by taking up extra responsibilities.
Question 2.
Discuss the negative impact of globalisation. (2)
Answer:
The negative impacts of globalisation are as follows
- Globalisation has not generated much more employment opportunities because it needs highly skilled people only.
- The foreign companies focus on their profit orientation projects only in place of social welfare.
- It has widened income disparities by making the rich richer and the poor more poorer.
- Gradually, globalisation is also a reason for depletion of flora and fauna in country.
- Even farmers are supposed to be well educated if they want to use modem methods of cultivation.
![]()
Question 3.
What were the two main consequences of Indo-Pak Conflict of 1971? (2)
Answer:
The consequence of Indo-Pakistan conflict of 1971 are:
- Eastern command of Pakistan military collapsed and East Pakistan was recognised as Bangladesh.
- Over 93000 Pakistani Pakistani troops surrendered to the India forces making the largest surrender since second World War.
Question 4.
Give four reasons why globalisation is being resisted. (2)
Answer:
Globalisation means the flows of ideas, capital, commodities and people across different parts of the world. It is a multidimensional concept. It has political, economic and cultural manifestations and these must be adequately distinguished.
The four reasons due to which globalisation is resisted are
- Leftist parties argue that contemporary globalisation represents a global capitalism that makes the rich richer and the poor poorer.
- Weakening of the state leads to a reduction in the capacity of the state to protect the interest of its poor.
- Rightist parties express anxiety over the political economic and cultural effects.
- The cultural globalisation would harm age old values of people while harming their traditional culture.
Question 5.
Describe briefly about Naxalite Movement. (2)
Answer:
In 1967 a peasant uprising took place in the Naxalbari police station area of Darjeeling Hills district in West Bengal under the leadership of the local cadres of the Communist Party of India (Marxist). Beginning from the Naxalbari police station, the peasant movement spread to several states of India and came to be known as the Naxalite Movement.
In 1969, one branch broke off from the CPI (M) and a new party, Communist Party (Marxist-Leninist) (CPI-ML) was formed under the leadership of Charu Majumdar. It argued that democracy in India was pretence and decided to adopt a strategy of protracted guerrilla warfare in order to lead to a revolution.
![]()
Question 6.
What effect did the National Emergency have on India’s political system? (2)
Answer:
Under Article 352 of Indian Constitution upon the advice by Prime Minister Indira Gandhi President Fakhruddin Ali Ahmed declared a state of emergency. Impact of National Emergency on party system in India are as follows –
(i) After the end of National Emergency, the major opposition parties started coming together on the eve of elections and formed a new party known as the Janta Party.
(ii) The people’s verdict of 1977 elections were decisively against the emergency the Congress lost elections and Janta Party came to power. During this period, the Congress(R) also underwent a major split resulting in the formation of Congress (I). Initially, it appeared that Indian political system is heading towards a ‘two party system’ as Janta Party was considered to be an alternative to the Congress.
(iii) Later there was an emergence of multi-party system or coalition government as against one party system or two-party system.
Question 7.
Describe any four consequences of Bangladesh war of 1971. (2)
Answer:
The consequences of Bangladesh war of 1971 are as follow.
- India supported the demand of East Pakistan financially and militarily.
- The war of 1971 made Pakistani forces to surrender in East Pakistan.
- Bangladesh was formed as an independent country.
- Bangladesh drafted its constitution declaring faith in secularism, democracy and socialism.
Question 8.
Issues have become converging point rather than ideologies in the current era of coalition politics. Discuss? (2)
Answer:
Three features of coalition government has been given in which we have to understand the not aligning and re-aligning on the basis of ideologies. These are Unstable Government The coalition government has its own interest and they fight for their own self interest.
Political Opportunism Government formed on the basis of coalition becomes selfish, as opportunist, power hungry and unscrupulous politicians focus on the self-interest only.
Lack of Polarisation The coalition governments afe formed not on the basis of polarisation of political forces, but for the sake of capturing power and vested interest.
![]()
Section B
Question 9.
How are coalition governments more democratic than one-party governments? (4)
Answer:
When two or more parties join hands together to form a government is known as coalition government, e.g UP A, NDA, etc. Benefits of coalition government are as follows
Dominance of one party is minimised, this will lead to more democratic way of functioning. The government cannot just pass a bill without debate as it is happening in the current Lok Sabha.
More than one ideology come together and gives strength to democracy i.e., the government will have to listen to all other parties and try to fulfill their requirement as much as possible so that other section of society does not leave untouched.
Drawbacks of coalition government are as follows
It gives unstable government i.e., the government cannot function smoothly because it has a support of other parties due to this government cannot take bold decision for the welfare of society and nation.
![]()
It slows the process of policy-making. It means it is hard for the government to fulfill everyone wishes which result in delay in the policy making.
Question 10.
There are numerous issues between India and Pakistan. Discuss any three controversies. (4)
Answer:
The three issues of conflict between India and Pakistan are discussed below
(i) There was a dispute over Kashmir immediately after the partition in 1948 between India and Pakistan. Both the governments continue to be suspicious of each other. The Indian Government has blamed the Pakistan Government for using a strategy of low key violence by helping the Kashmiri militants with arms, training, money and protection to carry out terrorist strikes against India.
(ii) India’s conflict with Pakistan is also over the strategic issues like the control of the Siachen Glacier and over acquisition of arms. The arms race between the two countries assumed a new character with both states acquiring nuclear weapons and missiles to deliver such arms against each other in the 1990s.
(iii) India and Pakistan also had problems over the sharing of river water. Until 1960, they were locked in fierce argument over the use of the rivers of the Indus Basin. Eventually, in 1960, with the help of World Bank, India and Pakistan signed the Indus Water Treaty which has survived to this day inspite of various military conflicts in which two countries have been involved. There are still some minor issues about the interpretation of Indus Water Treaty and the use of the river water.
![]()
Question 11.
In the given political outline map of India, four states have been marked as (A), (B),(C) and (D). Identify these states on the basis of the information given below and give their correct names along with their respective serial number of the information used and the concerned alphabets as per the following format. (4)
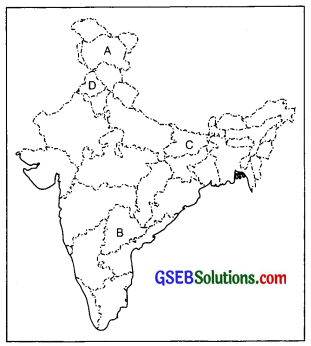
| Sr. No. of the Information Used | Alphabet Concerned | Name of the State |
| (i) | ||
| (ii) | ||
| (iii) | ||
| (iv) | ||
(i) State to which the Nizam belonged to.
(ii) State which is related to article 370 of the Indian constitution.
(iii) State where the operation blue star was launched.
(iv) State from where the J.P. Narayan demanded the dismissal of congress govt.
Answer:
| Sr. Number of the information used | Alphabet concerned | Name of the State |
| (i) | B | Hyderabad |
| (ii) | A | Jammu and Kashmir |
| (iii) | D | Punjab |
| (iv) | E | Bihar |
Section C
Question 12.
Identify four elements that contributed to the Congress Party’s dominance in India from 1947 to 1967. (6)
Or
What is meant by opposition in a democratic system? Describe activities of the opposition during the first two Parliaments of 1952 and 1957.
Answer:
The Congress Party succeed in maintaining its dominance till 1967 due to the following reasons
(i) The Congress Party was supported by elites, educated business classes and middle classes people. It also got support from peasants because of its socialist nature.
(ii) It had many popular faces like Jawaharlal Nehru, C. Rajagopalachari, Vallabhbhai Patel,etc. Moreover, Jawaharlal Nehru was charismatic and a very popular leader.
(iii) Congress worked at upper level as well as at grass root level. Congress was popularised due to the participation in Civil Disobedience Movement.
(iv) During period of Nehru Ji, Congress attained mass popularity, but the powerful narrow elite of Congress continued to benefit from the low level of political consciousness of the electorate.
(v) The traditional loyalities made Congress, a one-party dominance.
Or
At the time of Independence, there were many opposition parties and after independence it increased, but it gained only token representation in the Lok Sabha and also in state assemblies. Yet their presence Played a crucial role in maintaining the democratic character of the system. The four activities of the opposition during the Parliament of 1952 and 1957 are as follows
(i) These opposition parties offered sustained and principled criticism of the policies and practices of the Congress Party. This phenomena indicated the check and balance of power of the Congress.
(ii) In 1957, in Kerala, Congress was defeated by CPI and made government, but after that Congress dismissed the Kerala Government under Article 356. It was criticised by the opposition leaders and said that it was the first instance of the misuse of constitutional emergency powers.
![]()
(iii) In 1950, Bhartiya Jansangh was able to secure 3 seats and in 1957, it secured 4 seats. The party played the role of opposition and started agitation to replace English with Hindi as the official language and also advocated for the development of nuclear weapons.
(iv) The opposition parties prevented the resentment with the system from turning anti-democratic. These parties also groomed the leaders (young citizens) who wanted to shape the India as developed and powerful state.
Question 13.
Explain the factors responsible for the rise of the Chinese economy. (6)
Or
Analyse the basis of projection of China to overtake the US as the world’s largest economy by 2040.
Answer:
China is the third major alternative centre of power. It is the fastest growing economy. China at one time was based on Soviet model and at that time, it broke all the links with capitalist world.
Following are the factors responsible for rise of Chinese economy Use of Soviet Model China accepted the Soviet model aind relied on its resources. China decided to substitute imports by domestic goods and create state owned heavy industries from capital produced by agriculture.
Development of Industrial Economy China used all its resources to develop an industrial economy. All citizens were provided education and health programmes. Relationship With USA China established relation with USA in 1972.
Modernisation Modernisation in field of agriculture, industry, military, science and technology were proposed. Major Policies Announced Open Door Policy was announced by Deng Xiaoping in 1978, which aimed at generation of high productivity by investments in capital and technology from abroad.
![]()
Era of Privatisation Privatisation of agriculture in 1982 and privatisation of industry in 1998 was done. Establishment of SEZ’s Special Economic Zones were set up. State had a centralised role in setting up of China’s economy.
Or
China is viewed to dominate US by the year 2040. The basis of the projection are
(i) China is considered as the driver of East-Asian growth because of the economic integration into regions. China is considered to be very powerful and factors such as population, landmass, resources, regional location and political influence adds to its strength.
(ii) China announced ‘Open Door Policy’ in 1978 which aimed at generation of high productivity by investments in capital and technology from abroad. In economic sector, various steps were taken to encourage investment by Western entrepreneurs for modernisation of industry, science and technology, agriculture and military. In 1980, China became the member of World Bank and International Monetary Fund.
(iii) Privatisation of agriculture and industry helped in growing economy rapidly.
(iv) Foreign trade grew with the creation of SEZs and new trading laws. This resulted in high foreign exchange reserves. In this way, China became most significant for FDI. The above points show China’s ability to overtake US as world’s largest economy by 2040.